Characteristics of NO3- absorption and utilization in Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings under different phosphorus levels
-
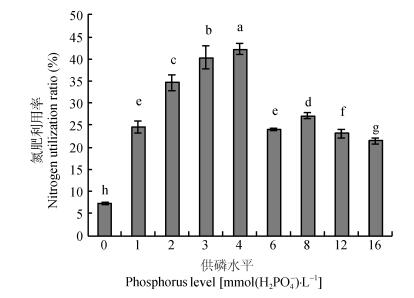
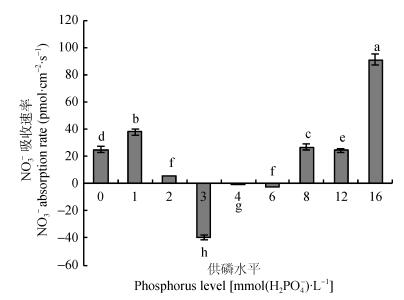
摘要: 运用15N示踪及非损伤微测技术,研究了不同供磷水平(0 mmol·L-1、1.0 mmol·L-1、2.0 mmol·L-1、3.0 mmol·L-1、4.0 mmol·L-1、6.0 mmol·L-1、8.0 mmol·L-1、12.0 mmol·L-1和16.0 mmol·L-1 H2PO4-)对平邑甜茶幼苗NO3--N吸收及利用特性的影响,为提高果园氮肥利用效率提供理论依据。结果表明,在低磷水平(0~1.0 mmol·L-1)时,平邑甜茶根系长度、根系总表面积较小,且根尖数较少。随着供磷水平的增加,在2.0~4.0 mmol·L-1磷浓度处理时,平邑甜茶幼苗生物量、根系长度、根系总表面积及根尖数显著高于其他处理。而在6.0~16.0 mmol·L-1时,过量供磷抑制了根系的生长,使平邑甜茶幼苗根系长度、表面积均大幅降低,根尖数量骤降。非损伤扫描离子选择电极测试表明,当生长介质磷浓度在3.0~6.0 mmol·L-1时,平邑甜茶对NO3-有吸收作用,并在3.0 mmol·L-1磷浓度时其吸收速率最高。而在0~2 mmol·L-1及8.0~16.0 mmol·L-1磷浓度处理下,平邑甜茶对NO3-有外排作用。随供磷水平的增加,各器官从肥料中吸收分配到的15N量对该器官全氮量的贡献率(Ndff)及植株氮素利用率呈现先升高后降低的趋势,4.0 mmol·L-1磷浓度时植株氮素利用率最大,为42.24%,超过4.0 mmol·L-1植株氮素利用率显著降低。适当充足的供磷刺激了幼苗根系生长,从而促进平邑甜茶对氮素的获取,过量的NO3-抑制了平邑甜茶根系的生长,同时叶片硝酸还原酶的活性受到抑制,因此其氮素吸收和利用效率较低。因此,磷浓度在3.0~4.0 mmol·L-1时最有利于平邑甜茶幼苗的生长及氮素的吸收利用。Abstract: In recent years, excessive application of nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers has not only wasted fertilizer, but also brought a high potential risk of environmental pollution. In addition, an unreasonable fertilization over the long-term has damaged the physical and chemical properties of soil, including soil porosity and nutrients contents. Therefore, it is crucial for sustainable fruit tree production to promote scientific utilization of nutrient, increase fertilizer utilization rate, reduce eluviation, volatilization and loss of nitrogen. In order to determine the key factors influencing nitrogen utilization ratio under different phosphorus levels, 15N-labeled tracer and non-invasive micro-test techniques were used to investigate NO3- absorption and utilization in Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings under different phosphorus levels (0 mmol·L-1, 1.0 mmol·L-1, 2.0 mmol·L-1, 3.0 mmol·L-1, 4.0 mmol·L-1, 6.0 mmol·L-1, 8.0 mmol·L-1, 12.0 mmol·L-1, 16.0 mmol·L-1 H2PO4-). The study aimed to increase nitrogen fertilizer utilization and reduce nitrogen fertilizer loss, which could provide theoretical basis for scientific and efficient utilization of phosphate fertilizer in apple orchard. The results showed that root length, root surface area and root tip quantity were lower in seedlings under phosphorus deficiency (0-1.0 mmol·L-1). With the addition of 2.0-4.0 mmol·L-1 of phosphorus, the biomass of single plant, root length, root surface area and root tip quantity increased over seedlings under other treatments. Also root growth was restrained in seedlings under excess phosphorus (6.0-16.0 mmol·L-1). The absorption of NO3- in M. hupehensis seedlings was significantly different under different phosphorus levels. The non-invasive micro-test technique showed significant absorption of NO3- by M. hupehensis seedlings under 3.0-6.0 mmol·L-1 phosphorus with the highest rate of absorption under 3.0 mmol·L-1 treatment. While 0-2 mmol·L-1 and 8.0-16.0 mmol·L-1 phosphorus applications showed efflux effect of NO3-by M. hupehensis seedlings. With the addition of phosphorus, Ndff (percent of nitrogen derived from fertilizer) and nitrogen utilization efficiency initially increased and then decreased. The highest nitrogen use efficiency (42.24%) was observed under the phosphorus treatment of 4.0 mmol·L-1. Then there was a significant reduction under phosphorus application in excess of 4.0 mmol·L-1 treatments. Leaf nitrate reductase activity was very low under phosphorus deficiency, but it had significantly higher levels under 1.0-3.0 mmol·L-1 phosphorus application. There was a marked decrease in leaf nitrate reductase activity when the phosphorus concentration exceeded 4.0 mmol·L-1. In conclusion, phosphorus level had significant effect on NO3- absorption and utilization by M. hupehensis seedlings. Root growth and nitrogen absorption increased with appropriate phosphorus application. With phosphorus overdose, root growth and nitrate reductase activity decreased significantly. This resulted in a decrease in the absorption and utilization of nitrogen. The analysis showed that 3.0-4.0 mmol·L-1 of phosphorus was beneficial to the efficient growth of M. hupehensis seedlings, nitrogen absorption and utilization.
-
表 1 不同供磷水平下平邑甜茶的单株生物量
Table 1 Biomass per plant of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings on different phosphorus levels
供磷水平
Phosphorus level
[mmol(H2PO4-)∙L-1]根生物量
Biomass of root (g)茎生物量
Biomass of stem (g)叶生物量
Biomass of leaf (g)总生物量
Total biomass (g)0 0.17±0.02g 0.12±0.03f 0.28±0.02h 0.57±0.03g 1 0.64±0.01de 0.32±0.02d 0.71±0.02g 1.66±0.02f 2 0.90±0.03ab 0.55±0.04b 1.17±0.02c 2.63±0.06b 3 0.93±0.04a 0.60±0.03a 1.47±0.01a 3.00±0.02a 4 0.88±0.01b 0.52±0.02b 1.28±0.02b 2.68±0.01b 6 0.66±0.02d 0.34±0.01d 0.85±0.03ef 1.86±0.04d 8 0.74±0.04c 0.42±0.02c 0.99±0.03d 2.15±0.04c 12 0.56±0.03f 0.25±0.01e 0.83±0.05f 1.64±0.08f 16 0.59±0.03ef 0.26±0.02e 0.89±0.03e 1.74±0.05e 同列数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Values followed by different lowercase letters in the same column are significantly different at 0.05 level. 表 2 不同供磷水平下单株平邑甜茶的根系形态指标
Table 2 Root architecture parameters of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings on different phosphorus levels
供磷水平
Phosphorus level
[mmol(H2PO4-)∙L-1]根系长度
Root length (cm)根系总表面积
Root surface area (cm2)根尖数
Quantity of tips0 368.63±8.74d 63.73±2.67g 2 390.33±144.46e 1 512.41±9.31c 64.10±2.47g 3 073.67±291.75e 2 1 074.41±130.92a 182.83±7.51a 7 243.33±472.23ab 3 998.68±18.10a 154.25±4.48c 7 879.33±759.36a 4 1 061.85±37.89a 173.13±3.80b 6 920.67±890.22abc 6 776.17±14.36b 120.70±1.42ef 4 798.33±504.80d 8 849.25±26.49b 131.40±4.21d 6 116.00±202.72c 12 807.01±5.47b 125.34±3.27de 6 319.67±592.11bc 16 838.48±6.93b 115.67±7.17f 4 305.33±685.83d 同列数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Values followed by different lowercase letters in the same column are significantly different at 0.05 level. 表 3 不同供磷水平下平邑甜茶叶片硝酸还原酶(NR)活性
Table 3 Nitrate reductase activities in leaves of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings on different phosphorus levels
供磷水平
Phosphorus level
[mmol(H2PO4-)∙L-1]硝酸还原酶活性
Nitrate reductase activity
(μg·g-1·h-1)0 13.98±0.92c 1 34.06±1.33a 2 34.76±0.95a 3 35.46±0.82a 4 16.38±0.54b 6 7.83±0.91d 8 16.87±0.43b 12 18.48±0.73b 16 11.97±3.05c 同列数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Values followed by different lowercase letters in the same column are significantly different at 0.05 level. 表 4 不同供磷水平下平邑甜茶的各器官Ndff值
Table 4 Ndff values of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings on different phosphorus levels
供磷水平
Phosphorus level
[mmol(H2PO4-)∙L-1]Ndff (%) 根Root 茎Stem 叶Leaf 0 3.39±0.04i 4.09±0.07g 3.37±0.05g 1 4.99±0.08f 5.17±0.01d 4.92±0.02a 2 6.54±0.07b 6.24±0.02a 4.57±0.03c 3 6.92±0.01a 6.30±0.02a 4.68±0.06b 4 5.95±0.01c 5.88±0.02b 4.99±0.08a 6 4.56±0.02h 4.71±0.03f 4.21±0.04d 8 5.55±0.04d 5.35±0.09c 3.77±0.07f 12 5.25±0.07e 5.24±0.03d 4.04±0.01e 16 4.70±0.02g 4.82±0.05e 3.81±0.00f Ndff:来自肥料的氮的百分比。同列数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Ndff: percent of nitrogen derived from fertilizer. Values followed by different lowercase letters in the same column are significantly different at 0.05 level. -
[1] 张福锁.测土配方施肥技术[M].北京:中国农业大学出版社, 2011: 7-9. Zhang F S. Soil Testing and Fertilization Recomm endation[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2011: 7-9
[2] 李庆军, 田利光, 刘庆花, 等.山东省果园土壤酸化状况及酸化原因分析[J].山东农业科学, 2011, 10: 57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2011.02.017 Li Q J, Tian L G, Liu Q H, et al. Soil acidification condition and cause analysis of Shandong orchard[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 10: 57-59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2011.02.017
[3] 丁宁, 姜远茂, 陈倩, 等.不同供磷水平对平邑甜茶生长及15N-尿素吸收和利用的影响[J].山东农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 43(2): 223-226. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=scho201202014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Ding N, Jiang Y M, Chen Q, et al. Effect of phosphorus on growth and 15N absorption and utilization of Malus hupenhensis[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University: Natural Science, 2012, 43(2): 223-226 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=scho201202014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[4] 何鹏, 吴敏, 韦家少, 等.不同磷水平对橡胶树幼苗氮钾吸收、分配与利用的影响[J].中国农学通报, 2011, 27(16): 1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201116002.htm He P, Wu M, Wei J S, et al. Influence of different phosphorus levels on absorption, utilization and partition of N, K on Hevea brasiliensis seedlings[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(16): 1-6 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201116002.htm
[5] 袁新民, 同延安, 杨学云, 等.施用磷肥对土壤NO3--N累积的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2000, 6(4): 397-403. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2000.0406 Yuan X M, Tong Y A, Yang X Y, et al. Effect of phosphate application on soil nitrate nitrogen accumulation[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2000, 6(4): 397-403 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2000.0406
[6] Graciano C, Goya J F, Frangi J L, et al. Fertilization with phosphorus increases soil nitrogen absorption in young plants of Eucalyptus grandis[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2006, 236(2/3): 202-210 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378112706008929
[7] Campbell W H, Redinbaugh M G. Ferric-citrate reductase activity of nitrate reductase and it's role in iron assimilation by plants[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 1984, 7(1/5): 799-806 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233120782_Ferric-citrate_reductase_activity_of_nitrate_reductase_and_its_role_in_iron_assimilation_by_plants
[8] 刘丽, 甘志军, 王宪泽.植物氮代谢硝酸还原酶水平调控机制的研究进展[J].西北植物学报, 2004, 24(7): 1355-1361. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNYX200407038.htm Liu L, Gan Z J, Wang X Z. Advances of studies on the regulation of nitrate metabolism of plants at nitrate reductase level[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2004, 24(7): 1355-1361 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNYX200407038.htm
[9] 吕杰, 苗璐, 蔡蕊, 等.非损伤微测技术在植物根系生长发育研究中的应用[J].生物技术, 2013, 23(1): 89-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJS201301026.htm Lü J, Miao L, Cai R, et al. Application of non-invasive micro-test technique in study of plant roots growth and development[J]. Biotechnology, 2013, 23(1): 89-93 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJS201301026.htm
[10] 尹晓明, 贾莉君, 范晓荣, 等.离子选择微电极技术及其在植物营养学研究中的应用[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(3): 744-754. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2011.0053 Yin X M, Jia L J, Fan X R, et al. The application of ion selective microelectrode in the study of plant nutrition[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(3): 744-754 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2011.0053
[11] 骆翔, 朱艳霞, 杜友, 等.柽柳根不同区域吸氮特性研究[J].中国农学通报, 2011, 27(22): 66-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201122013.htm Luo X, Zhu Y X, Du Y, et al. Study on the nitrogen-absorbing characters in different root parts of Tamarix chinensis Lour[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(22): 66-69 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201122013.htm
[12] 李绍长, 胡昌浩, 龚江, 等.供磷水平对不同磷效率玉米氮、钾素吸收和分配的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2004, 10(3): 237-240. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2004.0303 Li S C, Hu C H, Gong J, et al. Effects of phosphorus supply on nitrogen and potassium absorption and distribution of maize with different phosphorus efficiency[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2004, 10(3): 237-240 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2004.0303
[13] 赵秀兰, 李文雄.氮磷水平与气象条件对春小麦籽粒蛋白质含量形成动态的影响[J].生态学报, 2005, 25(8): 1914-1920. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB200508011.htm Zhao X L, Li W X. Effect of the nitrogen and phosphorus levels and meteorological conditions on formation dynamics of grain protein content in spring wheat[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(8): 1914-1920 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB200508011.htm
[14] 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2000: 123-128. Li H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 123-128
[15] 顾曼如. 15N在苹果氮素营养研究中的应用[J].中国果树, 1990, (2): 46-48. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zggs199002020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Gu M R. The application of 15N in the research of nitrogen nutrition on apples[J]. China Fruits, 1990, (2): 46-48 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zggs199002020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[16] 霍常富, 孙海龙, 范志强, 等.根系氮吸收过程及其主要调节因子[J].应用生态学报, 2007, 18(6): 1356-1364. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200706031.htm Huo C F, Sun H L, Fan Z Q, et al. Physiological processes and major regulating factors of nitrogen uptake by plant roots[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(6): 1356-1364 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200706031.htm
[17] Scheible W R, Lauerer M, Schulze E D, et al. Accumulation of nitrate in the shoot acts as a signal to regulate shoot-root allocation in tobacco[J]. The Plant Journal, 1997, 11(4): 671-691 doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11040671.x
[18] Forde B, Lorenzo H. The nutritional control of root development[J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 232(1/2): 51-68 doi: 10.1023/A:1010329902165
[19] Miller A J, Smith S J. Cytosolic nitrate ion homeostasis: Could it have a role in sensing nitrogen status?[J]. Annals of Botany, 2008, 101(4): 485-489 doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm313
[20] Datta R, Sharma R. Temporal and spatial regulation of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase in greening maize leaves[J]. Plant Science, 1999, 144(2): 77-83 doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00057-6
[21] 廖红, 严小龙.高级植物营养学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2003: 149-152. Liao H, Yan X L. Advanced Plant Nutrition[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 149-152




 下载:
下载: