Effects of interspecific maize and soybean interactions on the community structure and diversity of rhizospheric bacteria
-
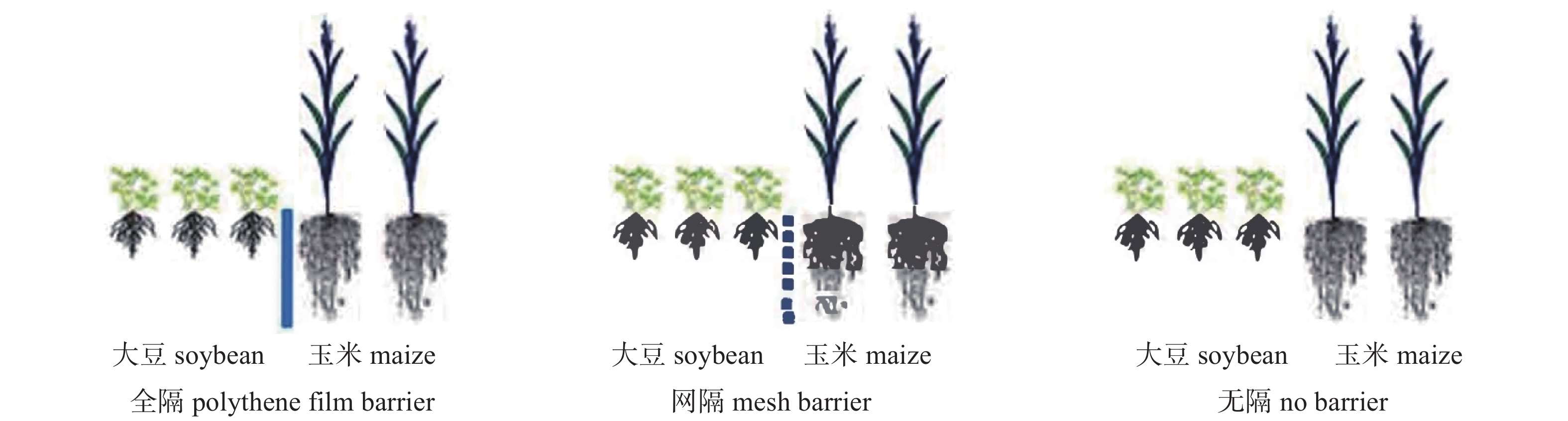
摘要: 研究玉米||大豆种间互作对根际微生物群落结构的影响及其与产量的关系, 对于深入理解特定作物间套作模式的产量效应有重要理论与实际意义。本研究应用随机区组试验设计方法, 在玉米与大豆以最佳间作比例(2∶3)条件下, 采用无隔(无隔离)、网隔(尼龙网分隔)、全隔(塑料薄膜分隔) 3种种间根系间隔处理, 并以两作物的单作为对照, 借助BIOLOG和T-RFLP技术对不同处理下间作玉米与大豆的根际微生物多样性进行分析, 探究不同种间互作对微生物结构和功能的影响及其与复合作物群体产量的关系。结果表明, 玉米||大豆间作下, 无隔、网隔和全隔的根际土壤阻断处理的土地当量比分别为1.39、1.13和0.98, 同一间作模式下种间根系互作加强, 土地当量比随之提高。进一步分析表明, 无论是间作玉米还是间作大豆, 其根际土壤微生物多样性和均匀度指数均随根系互作加强而明显提高。AWCD分析根际微生物生理种群差异的结果显示, 在玉米与大豆间作体系中, 无隔和网隔处理的根际微生物对底物碳源利用能力分别占据第1和第2位; 全隔和单作下, 根际微生物对底物的利用能力相应降低; 而加强种间根系互作(即从网隔到无隔), 大豆根际微生物对6大类碳源底物中酚类碳源和羧酸类碳源利用能力有所下降, 对胺类碳源、聚合物类碳源、氨基酸类碳源和碳水化合物底物的利用能力分别提高181.01%、32.6%、37.84%和78.28%; 而玉米根际微生物对酚类碳源、聚合物类碳源和氨基酸类利用能力有所下降外, 对羧酸类碳源、碳水化合物类碳源和胺类碳源等底物利用能力分别提高46.26%、6.54%和15.84%。T-RFLP分析结果发现, 与全隔处理比较, 无隔处理的大豆根际红球菌属和喜盐芽孢杆菌属等优势菌群丰度明显增多。而玉米根际微生物中也发现相似生理功能红球菌属和芽孢杆菌属等有益优势菌群的丰度增多现象, 最终导致间作作物地上部产量和土地当量比提高。Abstract: Studies on the effects of the interspecific interactions of maize||soybean intercropping on the rhizosphere microbial community structure and their relationship with crop yield are of theoretical and practical significance for elucidating the yield effects of interspecific crops in intercropping systems. The aim of this study was to explore the changes in microbial community structure in the rhizospheres of soybean and maize planted under an intercropping system (soybean||maize) with a 2∶3 line ratio and a randomized design pattern with three types of partitions between two crop roots. The intercropping partitions were a mesh barrier (MB, with exchange of root extudates without roots interaction) or a polythene film barrier (PB, without exchange of root extudates and roots interaction) to separate the maize roots from soybean roots or no barriers (NB) between the roots. An independent monoculture (M) was set up as a control. BIOLOG and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) assays were used to investigate the microbial community diversity in the maize||soybean rhizospheres. The results showed that the land equivalent ratios (LERs) under NB, MB, and PB conditions were 1.39, 1.13, and 0.98, respectively, at a plant row ratio of maize||soybean of 2∶3. These findings suggest that the LER increases with increased interspecific root interactions from PB to NB under the same intercropping pattern. Further analysis revealed that the microbial diversity and evenness indexes in the rhizosphere of both intercropped maize and soybean similarly increased with the increase in interspecific root interactions from PB to NB. Average well color development (AWCD) analysis showed that the rhizospheric microbial communities under NB and MB conditions had the strongest overall ability to utilize carbon sources as substrates, whereas those under PB and M conditions had a lower ability in this regard. The enhancement of interspecific root interactions increased the ability of rhizospheric microbes of intercropped soybean to utilize amines, polymers, amino acids, and carbohydrates (four types of carbon-source substrates) by 181.01%, 32.6%, 37.84%, and 78.28%, respectively. However, the capability of microbes in the intercropped soybean rhizosphere for utilizing two other carbon sources (phenols and carboxylic acids) decreased. Moreover, the ability of the microorganisms in the intercropped maize rhizosphere to utilize carboxylic acids, carbohydrates, and amines increased by 46.26%, 6.54%, and 15.84%, respectively, whereas their ability to utilize phenols, polymers, and amino acids decreased. T-RFLP analysis revealed a significant increase in the abundance of dominant bacteria, such as Rhodococcus (Actinomycetes) and Halobacillus (Firmicutes), in the rhizosphere of intercropped soybean under NB compared with that under PB; whereas the abundance of beneficial dominant bacteria, such as Rhodococcus (Actinomycetes) and Bacillus (Spirochetes), markedly increased in the rhizosphere of intercropped maize under NB conditions compared with that under PB conditions. As a result, the crop yield and LER increased under intercropping conditions.
-
图 2 不同种间根系分隔处理下间作大豆(a)和玉米(b)根际土壤微生物平均颜色变化率(AWCD)随培养时间的变化
NBS: 无隔大豆; MBS: 网隔大豆; PBS: 全隔大豆; MS: 单作大豆; NBM: 无隔玉米; MBM: 网隔玉米; PBM: 全隔玉米; MM: 单作玉米。NBS: no barrier for intercropped soybean; MBS: mesh barrier for intercropped soybean; PBS: polythene film barrier for intercropped soybean; MS: monoculture soybean; NBM: no barrier for intercropped maize; MBM: mesh barrier for intercropped maize; PBM: polythene film for intercropped maize; MM: monoculture maize
Figure 2. Changes of average well color development (AWCD) of microorganisms in rhizosphere soil of soybean (a) and maize (b) with incubation time under different partition patterns of interspecific roots of intercropped maize and soybean
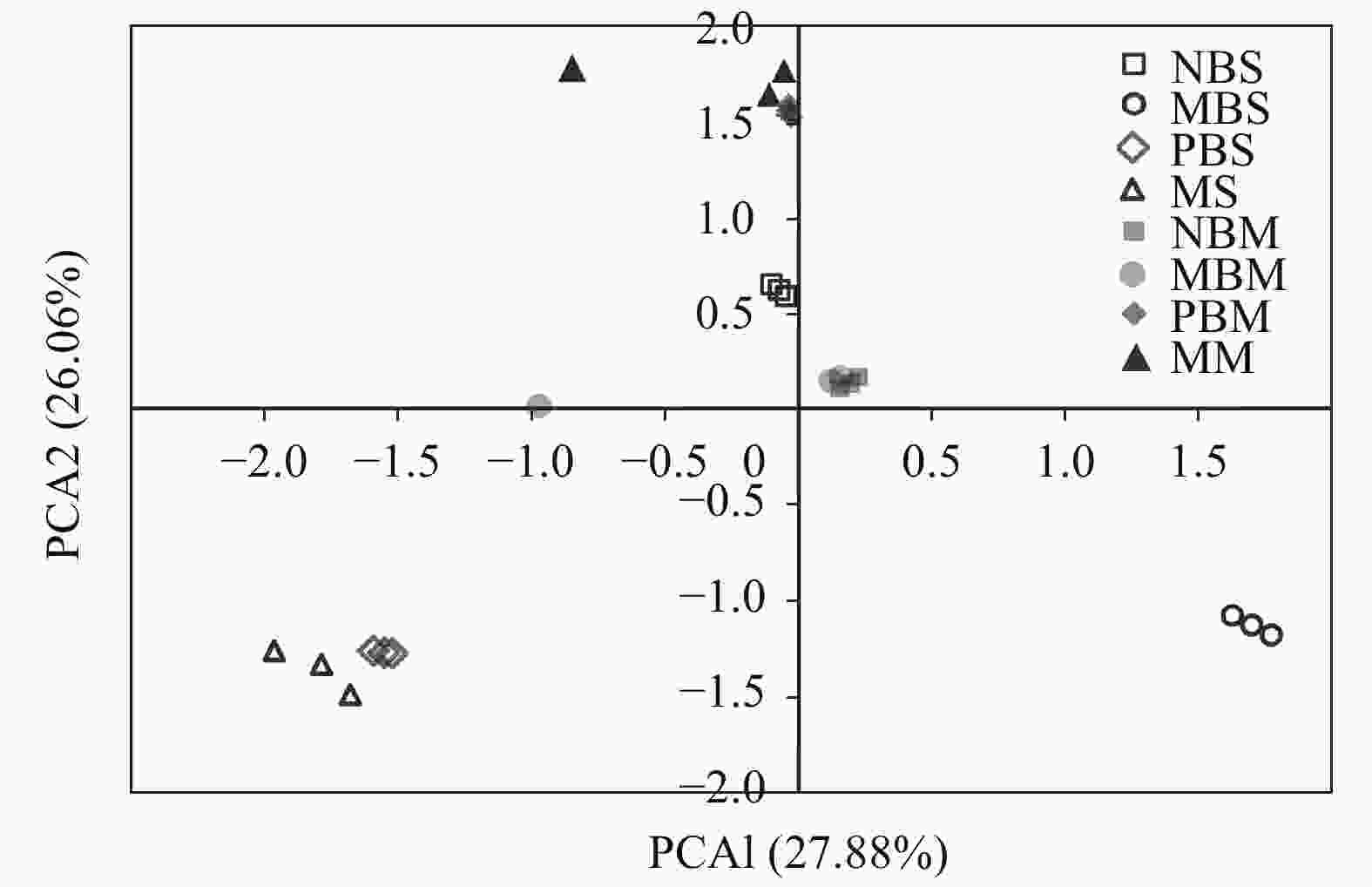
图 3 不同种间根系分隔处理下间作大豆和玉米根际微生物碳源利用特征的主成分分析
NBS: 无隔大豆; MBS: 网隔大豆; PBS: 全隔大豆; MS: 单作大豆; NBM: 无隔玉米; MBM: 网隔玉米; PBM: 全隔玉米; MM: 单作玉米。NBS: no barrier for intercropped soybean; MBS: mesh barrier for intercropped soybean; PBS: polythene film barrier for intercropped soybean; MS: monoculture soybean; NBM: no barrier for intercropped maize; MBM: mesh barrier for intercropped maize; PBM: polythene film barrier for intercropped maize; MM: monoculture maize.
Figure 3. Principal component analysis of carbon utilization profiles of microbes in rhizosphere soil under different partition patterns of interspecific roots of intercropped maize and soybean
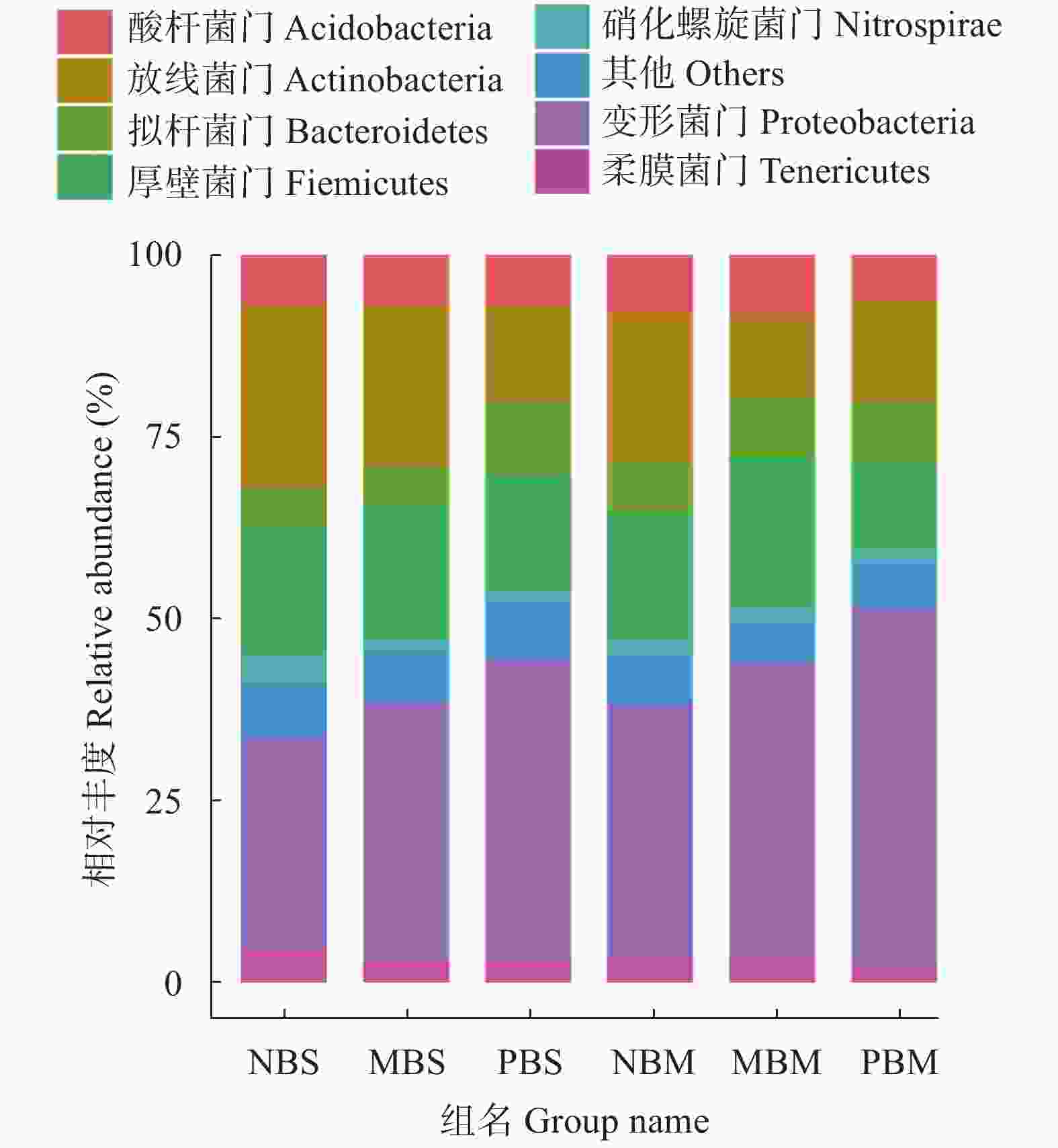
图 4 种间相互作用对间作大豆与玉米根际土壤微生物群落结构的影响
NBS: 无隔大豆; MBS: 网隔大豆; PBS: 全隔大豆; NBM: 无隔玉米; MBM: 网隔玉米; PBM: 全隔玉米。NBS: no barrier for intercropped soybean; MBS: mesh barrier for intercropped soybean; PBS: polythene film barrier for intercropped soybean; NBM: no barrier for intercropped maize; MBM: mesh barrier for intercropped maize; PBM: polythene film barrier for intercropped maize.
Figure 4. Effect of interspecific interaction on microbial community structure in of rhizosphere soil of intercropped soybean and maize
表 1 种间根系分隔处理对间作玉米和大豆籽粒产量、百粒重和土地当量比的影响
Table 1. Effects of partition patterns of interspecific roots on grain yield, hundred-grain weight and land equivalent ratio of intercropped soybean and maize
处理 Treatment 籽粒产量 Grain yield (kg∙hm−2) 百粒重 Hundred-grain weight (g) 土地当量比
Land equivalent ratio (LER)玉米 Maize 大豆 Soybean 玉米 Maize 大豆 Soybean 无隔 No barrier 3231.29±168.71a 887.62±60.97ab 32.98±1.32a 16.67±0.45ab 1.39±0.16a 网隔 Mesh barrier 2324.26±123.76ab 932.91±92.48a 32.33±1.88a 17.34±0.73a 1.13±0.11b 全隔 Polythene film barrier 2021.92±114.62b 717.04±81.27bc 28.73±1.34b 16.46±0.90b 0.98±0.03c 单作 Monoculture 2006.80±325.26b 637.88±22.90c 27.06±0.39b 15.79±0.69b 同列不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。The values within the same column followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 level. 表 2 不同种间根系分隔处理下间作玉米与大豆的根际微生物对碳源底物的利用能力
Table 2. Utilization ability to carbon substrates of rhizosphere microbes under different partition patterns of interspecific roots of intercropped maize and soybean
作物
Crop处理
Treatment羧酸类
Carboxylic acids多聚物类
Polymers糖类
Carbohydrates酚酸类
Phenolics氨基酸类
Amino acids胺类
Amines大豆
Soybean无隔
No barrier0.957±0.017a 0.675±0.018b 0.517±0.011a 1.027±0.017a 0.652±0.021a 0.933±0.006a 网隔
Mesh barrier0.825±0.007b 0.745±0.016a 0.514±0.015a 0.784±0.003b 0.687±0.003a 0.558±0.008b 全隔
Polythene film barrier0.969±0.017a 0.509±0.013c 0.290±0.009b 1.074±0.003a 0.473±0.026b 0.332±0.010c 单作
Monoculture0.915±0.027a 0.489±0.010c 0.234±0.012c 1.037±0.025ab 0.512±0.000b 0.346±0.008c 玉米
Maize无隔
No barrier0.939±0.006a 0.741±0.002c 0.505±0.002a 0.994±0.005b 0.650±0.011a 0.563±0.006b 网隔
Mesh barrier0.841±0.001b 0.773±0.006a 0.469±0.004b 0.829±0.013c 0.472±0.006b 0.820±0.005a 全隔
Polythene film barrier0.642±0.006c 0.752±0.001bc 0.474±0.004b 1.091±0.052ab 0.649±0.018a 0.486±0.021c 单作
Monoculture0.658±0.006c 0.764±0.006ab 0.431±0.002c 1.126±0.059a 0.497±0.011b 0.511±0.006c 同列同一作物不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。The values within the same column of the same crop followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 level. 表 3 不同种间根系互作对间作作物根际土壤微生物多样性指数的影响
Table 3. Effects of different partition patterns of interspecific roots on soil microbial diversity indexes of intercropped maize and soybean
作物
Crop处理
TreatmentShannon-Wiener指数
Shannon-Wiener indexSimpson指数
Simpson indexMcIntosh指数
McIntosh index大豆
Soybean无隔
No barrier3.09±0.01a 0.95±0.01a 5.12±0.02a 网隔
Mesh barrier3.07±0.01a 0.95±0.00a 4.83±0.03b 全隔
Polythene film
barrier3.02±0.01b 0.94±0.00b 4.26±0.05c 单作
Monoculture3.02±0.01b 0.94±0.00b 4.35±0.00c 玉米
Maize无隔
No barrier3.12±0.01a 0.95±0.00a 4.89±0.01a 网隔
Mesh barrier3.10±0.04a 0.95±0.01a 4.63±0.00c 全隔
Polythene film
barrier3.00±0.06b 0.94±0.00b 4.67±0.00b 单作
Monoculture2.99±0.01b 0.94±0.00b 4.61±0.02c 同列同一作物不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。The values within the same column of the same crop followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 level. 表 4 不同种间根系互作对间作玉米与大豆根际土壤细菌微生物多样性和均匀度指数的影响
Table 4. Effect of different partition patterns of interspecific roots on diversity indexes of soil bacteria community of intercropped system of maize and soybean
作物
Crop处理
TreatmentShannon-Wiener指数
Shannon-Wiener indexSimpson指数
Simpson indexMcIntosh指数
McIntosh index大豆
Soybean无隔
No barrier2.24±0.075a 0.99±0.01a 0.65±0.01a 网隔
Mesh barrier2.22±0.041a 0.98±0.05a 0.62±0.01a 全隔
Polythene film barrier1.78±0.14b 0.98±0.01a 0.61±0.01b 玉米
Maize无隔
No barrier1.96±0.02a 0.98±0.07a 0.60±0.01a 网隔
Mesh barrier1.86±0.06ab 0.98±0.01a 0.58±0.01ab 全隔
Polythene film barrier1.76±0.02b 0.97±0.02a 0.54±0.01b 同列同一作物不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。The values within the same column of the same crop followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 level. 表 5 不同种间根系互作对间作大豆和玉米根际土壤细菌群落的影响
Table 5. Effect of interspecific interaction on bacterial community in rhizopshere soil of soybean and maize
作物 Crop 相对丰度 Relative abundance (%) 片段大小 Fragment size (bp) 门 Phylum 属 Genus NB MB PB MspⅠ HaeⅢ AfaⅠ AluⅠ 大豆
Soybean0.92a 0.77b 1.01a 489 199 119 225 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 伯克氏菌属 Burkholderia 1.12c 1.40b 1.63a 164 205 243 218 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 脱硫杆菌属 Desulfobacter 3.19b 4.40a 4.48a 88 206 126 240 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 奈瑟菌属 Neisseria 2.67a 2.35a 1.73b 163 67 80 223 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 棒状杆菌属 Corynebacterium 5.48a 4.84b 3.87c 139 67 78 232 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 红球菌属 Rhodococcus 5.61a 4.84b 4.82b 141 208 453 234 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 动孢囊菌属 Kineosporia 2.46a 2.37a 2.01b 148 246 471 92 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes 喜盐芽孢杆菌属 Halobacillus 1.96a 1.83a 0.91b 91 284 140 239 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes 噬细胞菌属 Cytophaga 玉米
Maize0.55b 0.65ab 0.68a 487 197 562 152 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 无色菌属 Achromobacter 2.46b 2.46b 3.26a 488 198 427 153 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 伯克氏菌 Burkholderia 3.42b 3.22b 7.96a 492 39 72 236 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas 2.37b 2.92ab 3.40a 89 207 127 241 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 艾肯氏菌属 Eikenella 6.56a 7.56a 4.58b 164 207 246 221 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 脱硫杆菌属 Desulfobacter 0.71a 0.59ab 0.46b 162 228 455 71 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 红球菌属 Rhodococcus 1.78a 1.48ab 1.24b 159 224 449 217 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 动孢囊菌属 Kineosporia 2.48a 1.45b 1.11b 122 152 467 229 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes 杆菌属 Bacilli 1.37a 1.42a 0.85b 161 248 503 230 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus 2.11a 1.70ab 1.53b 87 207 177 169 螺旋体门 Spirochaetes 螺旋体属 Spirnrhaetales 1.82a 2.00a 0.91b 91 284 140 239 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes 噬细胞菌属 Cytophagaceae NB: 无隔; MB: 网隔; PB: 全隔。同行不同字母表示P<0.05水平差异显著。NB: no barrier; MB: mesh barrier; PB: polythene film barrier. The values in the same row followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 level. -
[1] 林文雄, 陈婷. 中国农业的生态化转型与发展生态农业新视野[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(2): 169−176LIN W X, CHEN T. Transition of agricultural systems to ecologicalizaton and new vision of modern eco-agriculture development in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(2): 169−176 [2] LI C J, HOFFLAND E, KUYPER T W, et al. Syndromes of production in intercropping impact yield gains[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 653−660 doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0680-9 [3] 姜圆圆, 郑毅, 汤利, 等. 豆科禾本科作物间作的根际生物过程研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2016, 33(5): 407−415JIANG Y Y, ZHENG Y, TANG L, et al. Rhizosphere biological processes of legume//cereal intercropping systems: a review[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2016, 33(5): 407−415 [4] ZHNG F S, LI L. Using competitive and facilitative interactions in intercropping systems enhances crop productivity and nutrient-use efficiency[J]. Plant & Soil, 2003, 248(1/2): 305−312 [5] PARK S E, BENJAMIN L R, WATKINSON A R. Comparing biological productivity in cropping systems: a competition approach[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 39(3): 416−426 doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2664.2002.00732.x [6] HAUGGAARD-NIELSEN H, GOODING M, AMBUS P, et al. Pea-barley intercropping for efficient symbiotic N2-fixation, soil N acquisition and use of other nutrients in European organic cropping systems[J]. Field Crops Research, 2009, 113(1): 64−71 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2009.04.009 [7] LI C J, LI Y Y, YU C B, et al. Crop nitrogen use and soil mineral nitrogen accumulation under different crop combinations and patterns of strip intercropping in northwest China[J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 342(1/2): 221−231 [8] 肖靖秀, 汤利, 郑毅, 等. 大麦/蚕豆间作条件下供氮水平对作物产量和大麦氮吸收累积的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2011, 31(3): 499−503 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2011.03.020XIAO J X, TANG L, ZHENG Y, et al. Effects of N level on yield of crops, N absorption and accumulation of barley in barley and Faba bean intercropping system[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2011, 31(3): 499−503 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2011.03.020 [9] 王恭祎, 段碧华, 石书兵. 作物间作[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2013WANG G Y, DUAN B H, SHI S B. Crops Intercropping[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2013 [10] 李玉英, 胡汉升, 程序, 等. 种间互作和施氮对蚕豆/玉米间作生态系统地上部和地下部生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(6): 1617−1630LI Y Y, HU H S, CHENG X, et al. Effects of interspecific interactions and nitrogen fertilization rates on above- and below-growth in Faba bean/mazie intercropping system[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(6): 1617−1630 [11] LI L, LI S M, SUN J H, et al. Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus-deficient soils[J]. PNAS, 2007, 104(27): 11192− 11196 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704591104 [12] LI L, SUN J H, ZHANG F S, et al. Root distribution and interactions between intercropped species[J]. Oecologia, 2006, 147(2): 280−290 doi: 10.1007/s00442-005-0256-4 [13] LI X F, WANG C B, ZHANG W P, et al. The role of complementarity and selection effects in P acquisition of intercropping systems[J]. Plant and Soil, 2018, 422(1/2): 479−493 [14] 沈雪峰, 方越, 董朝霞, 等. 甘蔗/花生间作对土壤微生物和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2014(5): 55–58SHEN X F, FANG Y, DONG Z X, et al. Effects of sugarcane /peanut intercropping on soil microbes and soil enzyme activities[J]. Crops, 2014(5): 55–58 [15] 章家恩, 高爱霞, 徐华勤, 等. 玉米/花生间作对土壤微生物和土壤养分状况的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(7): 1597−1602ZHANG J E, GAO A X, XU H Q, et al. Effects of maize/peanut intercropping on rhizosphere soil microbes and nutrient contents[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(7): 1597−1602 [16] 宋亚娜, MARSCHNER Petra, 张福锁, 等. 小麦/蚕豆, 玉米/蚕豆和小麦/玉米间作对根际细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(7): 2268−2274 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.07.028SONG Y N, MARSCHNER P, ZHANG F S, et al. Effect of intercropping on bacterial community composition in rhizoshpere of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), maize (Zea mays L.) and faba bean (Vicia faba L.)[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(7): 2268−2274 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.07.028 [17] 陈平, 杜青, 庞婷, 等. 根系互作强度对玉米/大豆套作系统下作物根系分布及地上部生长的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2018, 36(1): 28−37CHEN P, DU Q, PANG T, et al. Effects of root interaction intensity on crop roots distribution above-ground growth in a maize/soybean relay intercropping system[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018, 36(1): 28−37 [18] WANG J Y, WU L K, TANTAI H P, et al. Properties of bacterial community in the rhizosphere soils of Achyranthes bidentata tolerant to consecutive monoculture[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2019, 89(2): 167−178 doi: 10.1007/s10725-019-00523-0 [19] WU L K, YANG B, LI M L, et al. Modification of rhizosphere bacterial community structure and functional potentials to control Pseudostellaria heterophylla replant disease[J]. Plant Disease, 2020, 104(1): 25−34 doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-19-0833-RE [20] 吴林坤, 陈军, 杨波, 等. 地黄连作对叶际细菌群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10): 3509−3517WU L K, CHEN J, YANG B, et al. Effects of Rehmannia glutinosa consecutive monoculture on the community structure and diversity of phyllosphere bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10): 3509−3517 [21] LI Q S, WU L K, CHEN J, et al. Biochemical and microbial properties of rhizospheres under maize/peanut intercropping[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(1): 101−110 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61089-9 [22] 刘朝茂, 李成云. 玉米与大豆、马铃薯间作对玉米叶片衰老、产量及病害控制的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(6): 75−78LIU C M, LI C Y. Effects of maize intercropping with soybean or potato on leaf senescence, yield and disease control[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(6): 75−78 [23] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1989GUAN S Y. Soil Enzyme and its Research Method[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1989 [24] 刘广才, 李隆, 黄高宝, 等. 大麦/玉米间作优势及地上部和地下部因素的相对贡献研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(9): 1787−1795 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.09.011LIU G C, LI L, HUANG G B, et al. Intercropping advantage and contribution of above-ground and below-ground interactions in the barley-maize intercropping[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(9): 1787−1795 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.09.011 [25] 陈胜男, 谷洁, 付青霞, 等. 接种自生固氮菌对玉米根际土壤酶活性和细菌群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(2): 444−450 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11325CHEN S N, GU J, FU Q X, et al. Effects of inoculating Azotobacter on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community functional diversity in the rhizosphere of maize (Zea mays L.)[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(2): 444−450 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11325 [26] 高阳, 段爱旺, 刘祖贵, 等. 玉米和大豆条带间作模式下的光环境特性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(6): 1248−1254GAO Y, DUAN A W, LIU Z G, et al. Light environment characteristics in maize-soybean strip intercropping system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(6): 1248−1254 [27] 冷志杰, 贝丽霞, 徐中儒, 等. 不同熟期大豆、玉米间作的产量产值数学模型的建立[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 1998, 20(1): 16−19LENG Z J, BEI L X, XU Z R, et al. The mathematical models of yield and output value of intercrop corn and soybean[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 1998, 20(1): 16−19 [28] 宋日, 牟瑛, 王玉兰, 等. 玉米、大豆间作对两种作物根系形态特征的影响[J]. 东北师大学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 34(3): 83−86SONG R, MU Y, WANG Y L, et al. Effects of intercropping of maize and soybean on the morphological character of roots[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2002, 34(3): 83−86 [29] 李鑫, 张会慧, 岳冰冰, 等. 桑树-大豆间作对盐碱土碳代谢微生物多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(7): 1825−1831LI X, ZHANG H H, YUE B B, et al. Effects of mulberry-soybean intercropping on carbon-metabolic microbial diversity in saline-alkaline soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(7): 1825−1831 [30] GAO X, WU M, XU R N, et al. Root interactions in a maize/soybean intercropping system control soybean soil-borne disease, red crown rot[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e95031 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095031 [31] LI L, TANG C X, RENGEL Z, et al. Chickpea facilitates phosphorus uptake by intercropped wheat from an organic phosphorus source[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 248(1/2): 297−303 doi: 10.1023/A:1022389707051 [32] EL DESSOUGI H, ZU DREELE A, CLAASSEN N. Growth and phosphorus uptake of maize cultivated alone, in mixed culture with other crops or after incorporation of their residues[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2003, 166(2): 254−261 doi: 10.1002/jpln.200390037 [33] 王建花, 陈婷, 林文雄. 植物化感作用类型及其在农业中的应用[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(10): 1173−1183 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01173WANG J H, CHEN T, LIN W X. Plant allelopathy types and their application in agriculture[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(10): 1173−1183 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01173 [34] CHEN J, WU L K, XIAO Z G, et al. Assessment of the diversity of Pseudomonas spp. and Fusarium spp. in Radix pseudostellariae rhizosphere under monoculture by combining DGGE and quantitative PCR[J]. Front in Microbiol, 2017, 8: 1748 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01748 [35] 马瑞霞, 冯怡, 李萱. 化感物质对枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)在厌氧条件下的生长及反硝化作用的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(3): 452−457 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.03.019MA R X, FENG Y, LI X. Effects of allelochemicals on growth of Bacillus subtilis and its denitrification under anaerobic condition[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000, 20(3): 452−457 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.03.019 [36] LI Y Z, XU L N, LETUMA P, et al. Metabolite profiling of rhizosphere soil of different allelopathic potential rice accessions[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 265 doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02465-6 -





 下载:
下载: