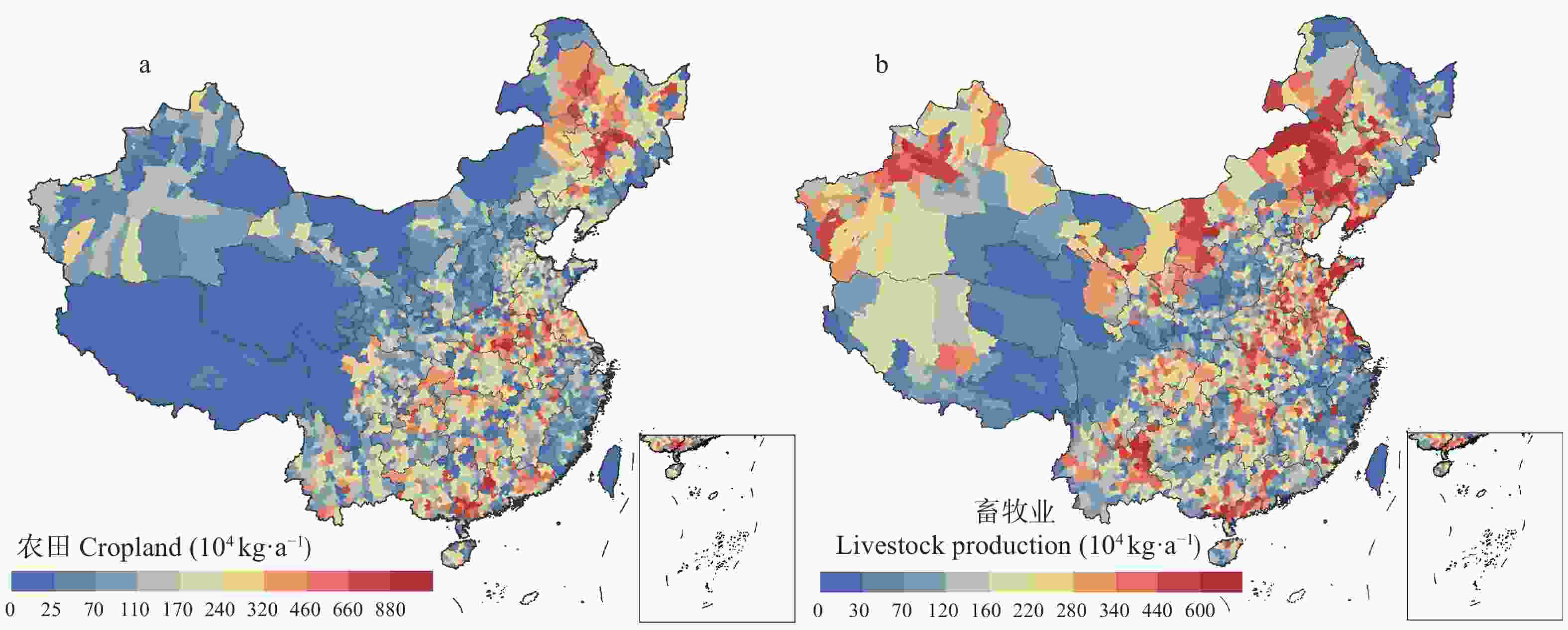
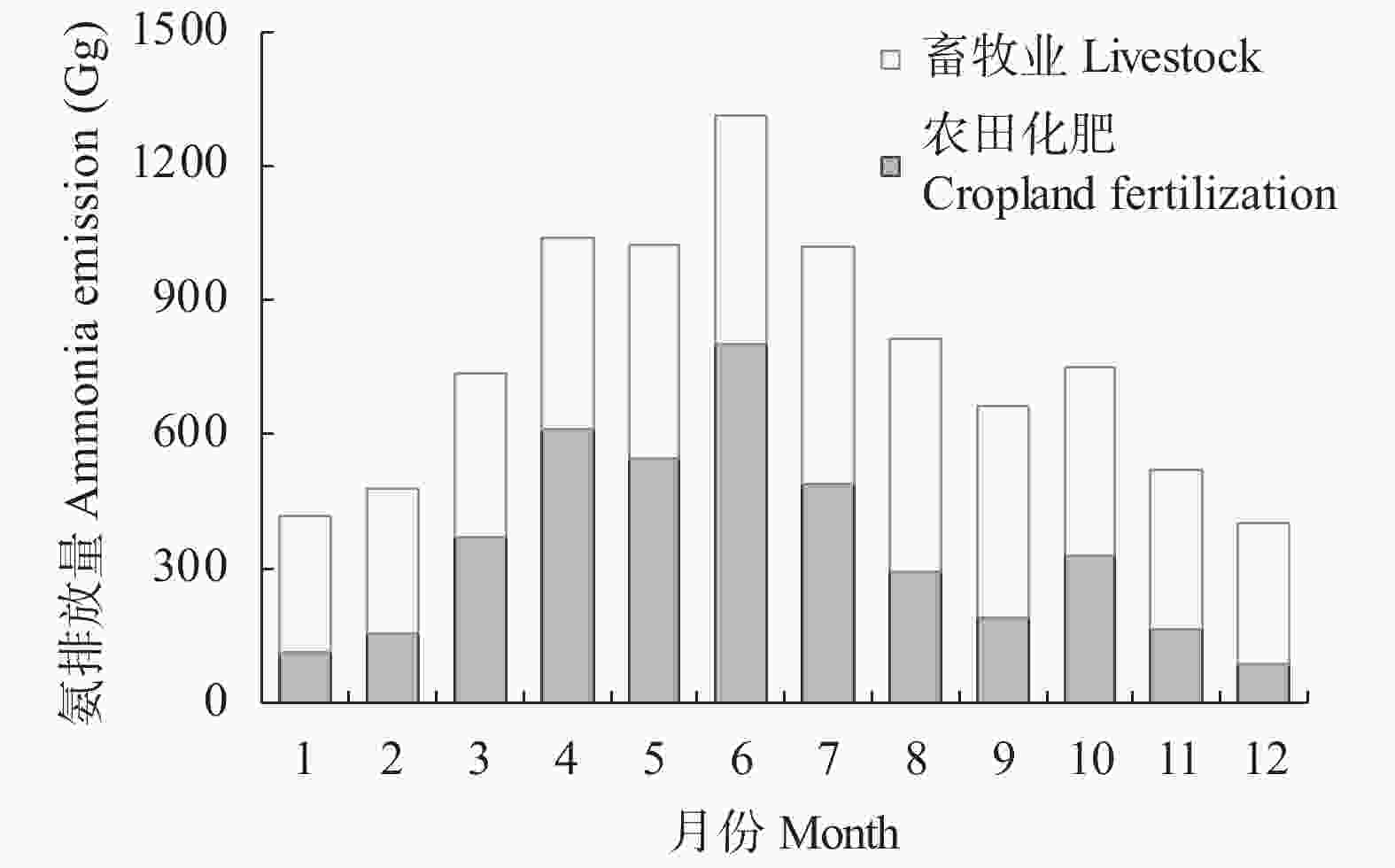
| [1] |
GALLOWAY J N, TOWNSEND A R, ERISMAN J W, et al. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5878): 889−892 doi: 10.1126/science.1136674
|
| [2] |
GU B J, JU X T, CHANG J, et al. Integrated reactive nitrogen budgets and future trends in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(28): 8792−8797 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1510211112
|
| [3] |
HUANG X, SONG Y, LI M M, et al. A high-resolution ammonia emission inventory in China[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2012, DOI: 10.1029/2011gb004161
|
| [4] |
ZHANG L, CHEN Y F, ZHAO Y H, et al. Agricultural ammonia emissions in China: reconciling bottom-up and top-down estimates[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(1): 339−355 doi: 10.5194/acp-18-339-2018
|
| [5] |
KANG Y N, LIU M X, SONG Y, et al. High-resolution ammonia emissions inventories in China from 1980 to 2012[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16(4): 2043−2058 doi: 10.5194/acp-16-2043-2016
|
| [6] |
XU P, KOLOUTSOU-VAKAKIS S, ROOD M J, et al. Projections of NH3 emissions from manure generated by livestock production in China to 2030 under six mitigation scenarios[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 607/608: 78−86 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.258
|
| [7] |
ZHANG X M, GU B J, VAN GRINSVEN H, et al. Societal benefits of halving agricultural ammonia emissions in China far exceed the abatement costs[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4357 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18196-z
|
| [8] |
LI S Q, ZHENG X H, ZHANG W, et al. Modeling ammonia volatilization following the application of synthetic fertilizers to cultivated uplands with calcareous soils using an improved DNDC biogeochemistry model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 660: 931−946 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.379
|
| [9] |
XU R T, TIAN H Q, PAN S F, et al. Global ammonia emissions from synthetic nitrogen fertilizer applications in agricultural systems: Empirical and process-based estimates and uncertainty[J]. Global Change Biology, 2019, 25(1): 314−326 doi: 10.1111/gcb.14499
|
| [10] |
FU X, WANG S X, RAN L M, et al. Estimating NH3 emissions from agricultural fertilizer application in China using the bi-directional CMAQ model coupled to an agro-ecosystem model[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(12): 6637−6649 doi: 10.5194/acp-15-6637-2015
|
| [11] |
ZHAN X Y, CHEN C, WANG Q H, et al. Improved Jayaweera-Mikkelsen model to quantify ammonia volatilization from rice paddy fields in China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(8): 8136−8147 doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04275-2
|
| [12] |
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories: Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/2019-refinement-to-the-2006-ipcc-guidelines-for-national-greenhouse-gas-inventories/
|
| [13] |
ZHAN X Y, ADALIBIEKE W, CUI X Q, et al. Improved estimates of ammonia emissions from global croplands[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(2): 1329−1338
|
| [14] |
TI C P, XIA L L, CHANG S X, et al. Potential for mitigating global agricultural ammonia emission: a meta-analysis[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 245: 141−148 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.124
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Y S, LUAN S J, CHEN L L, et al. Estimating the volatilization of ammonia from synthetic nitrogenous fertilizers used in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 480−493 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.09.018
|
| [16] |
XU P, LIAO Y J, LIN Y H, et al. High-resolution inventory of ammonia emissions from agricultural fertilizer in China from 1978 to 2008[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16(3): 1207−1218 doi: 10.5194/acp-16-1207-2016
|
| [17] |
XU P, ZHANG Y S, GONG W W, et al. An inventory of the emission of ammonia from agricultural fertilizer application in China for 2010 and its high-resolution spatial distribution[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 115: 141−148 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.05.020
|
| [18] |
董艳强, 陈长虹, 黄成, 等. 长江三角洲地区人为源氨排放清单及分布特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(8): 1611−1617 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.08.005DONG Y Q, CHEN C H, HUANG C, et al. Anthropogenic emissions and distribution of ammonia over the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(8): 1611−1617 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.08.005
|
| [19] |
ZHENG J Y, YIN S S, KANG D W, et al. Development and uncertainty analysis of a high-resolution NH3 emissions inventory and its implications with precipitation over the Pearl River Delta region, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(15): 7041−7058 doi: 10.5194/acp-12-7041-2012
|
| [20] |
ZHOU Y, CHENG S Y, LANG J L, et al. A comprehensive ammonia emission inventory with high-resolution and its evaluation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 106: 305−317 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.069
|
| [21] |
WANG C, YIN S S, BAI L, et al. High-resolution ammonia emission inventories with comprehensive analysis and evaluation in Henan, China, 2006−2016[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 193: 11−23 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.08.063
|
| [22] |
WU S P, ZHANG Y J, SCHWAB J J, et al. High-resolution ammonia emissions inventories in Fujian, China, 2009−2015[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2017, 162: 100−114 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.04.027
|
| [23] |
冯小琼, 陈军辉, 姜涛, 等. 四川省2005—2014年农业源氨排放清单及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(7): 2728−2737FENG X Q, CHEN J H, JIANG T, et al. Agricultural ammonia emission inventory and its spatial distribution in Sichuan Province from 2005 to 2014[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(7): 2728−2737
|
| [24] |
杨志鹏. 基于物质流方法的中国畜牧业氨排放估算及区域比较研究[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2008YANG Z P. Estimation of ammonia emission from livestock in China based on mass-flow method and regional comparison[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2008
|
| [25] |
刘东. 中国猪和奶牛粪尿氨(NH3)挥发的评价研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2007LIU D. Evaluation of NH3 emission from pig and dairy cow manure in China[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2007
|
| [26] |
MA L, MA W Q, VELTHOF G L, et al. Modeling nutrient flows in the food chain of China[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2010, 39(4): 1279−1289 doi: 10.2134/jeq2009.0403
|
| [27] |
廖仁郡, 陈玉成. 重庆市规模化畜禽养殖氨排放特征及减排策略研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(5): 769−777LIAO R J, CHEN Y C. Characteristics of ammonia emission from large-scale livestock/poultry breeding and its mitigation countermeasures in Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(5): 769−777
|
| [28] |
刘波, 童仪, 李安, 等. 长江三角洲地区畜禽养殖业氨排放清单研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(11): 1042−1049 doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.11.012LIU B, TONG Y, LI A, et al. Study on ammonia emission inventory of livestock over Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2018, 34(11): 1042−1049 doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.11.012
|
| [29] |
朱志平, 董红敏, 魏莎, 等. 中国畜禽粪便管理变化对温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 743−748 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0095ZHU Z P, DONG H M, WEI S, et al. Impact of changes in livestock manure management on greenhouse gas emissions in China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 743−748 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0095
|
| [30] |
WU H, LI Y P, XIE Z H, et al. Estimating ammonia emissions from cropland in China based on the establishment of agro-region-specific models[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2021, 303: 108373 doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108373
|
| [31] |
WANG C, CHENG K, REN C C, et al. An empirical model to estimate ammonia emission from cropland fertilization in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021: 117982
|
| [32] |
ZHANG X M, REN C C, GU B J, et al. Uncertainty of nitrogen budget in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 286: 117216 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117216
|





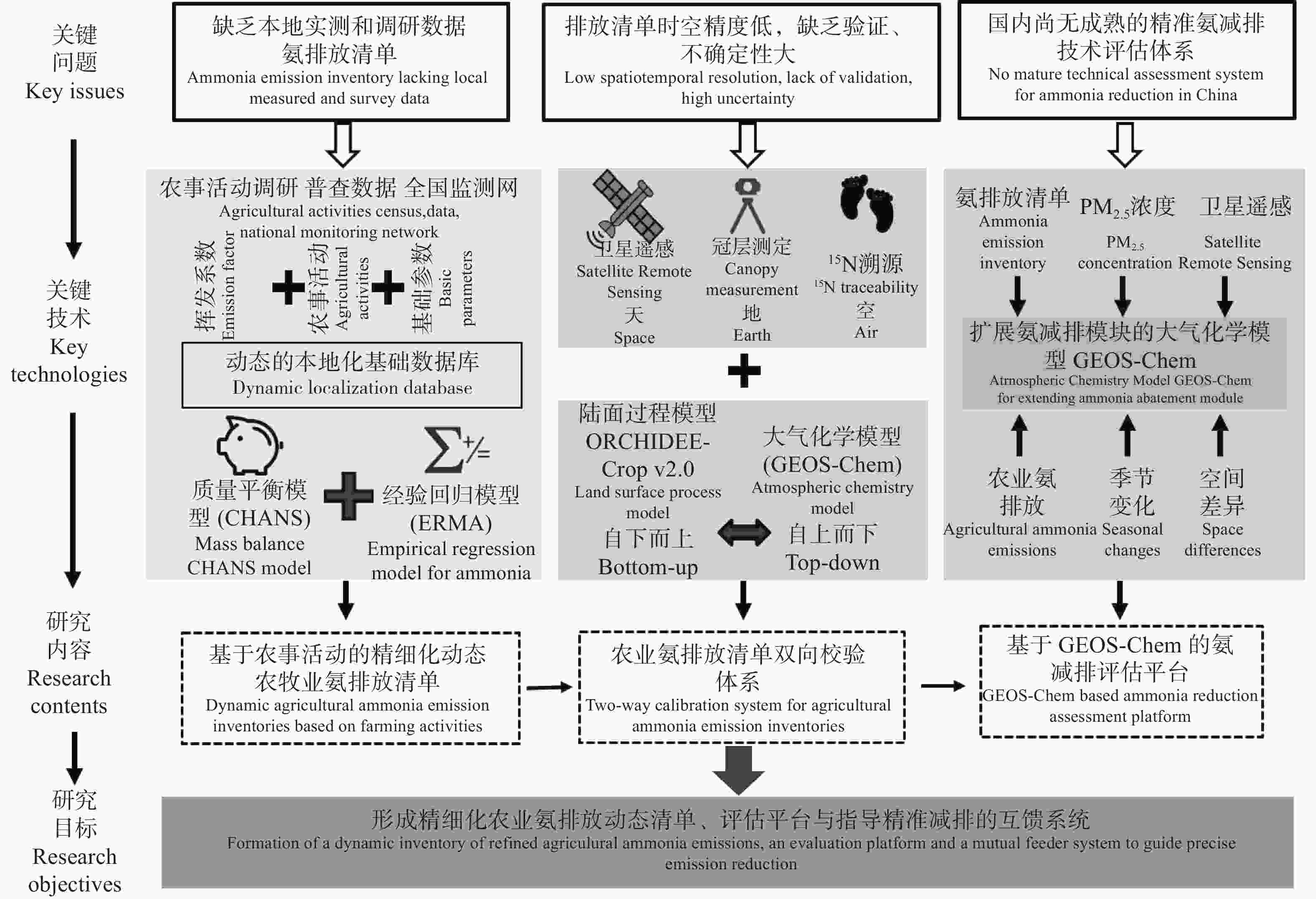
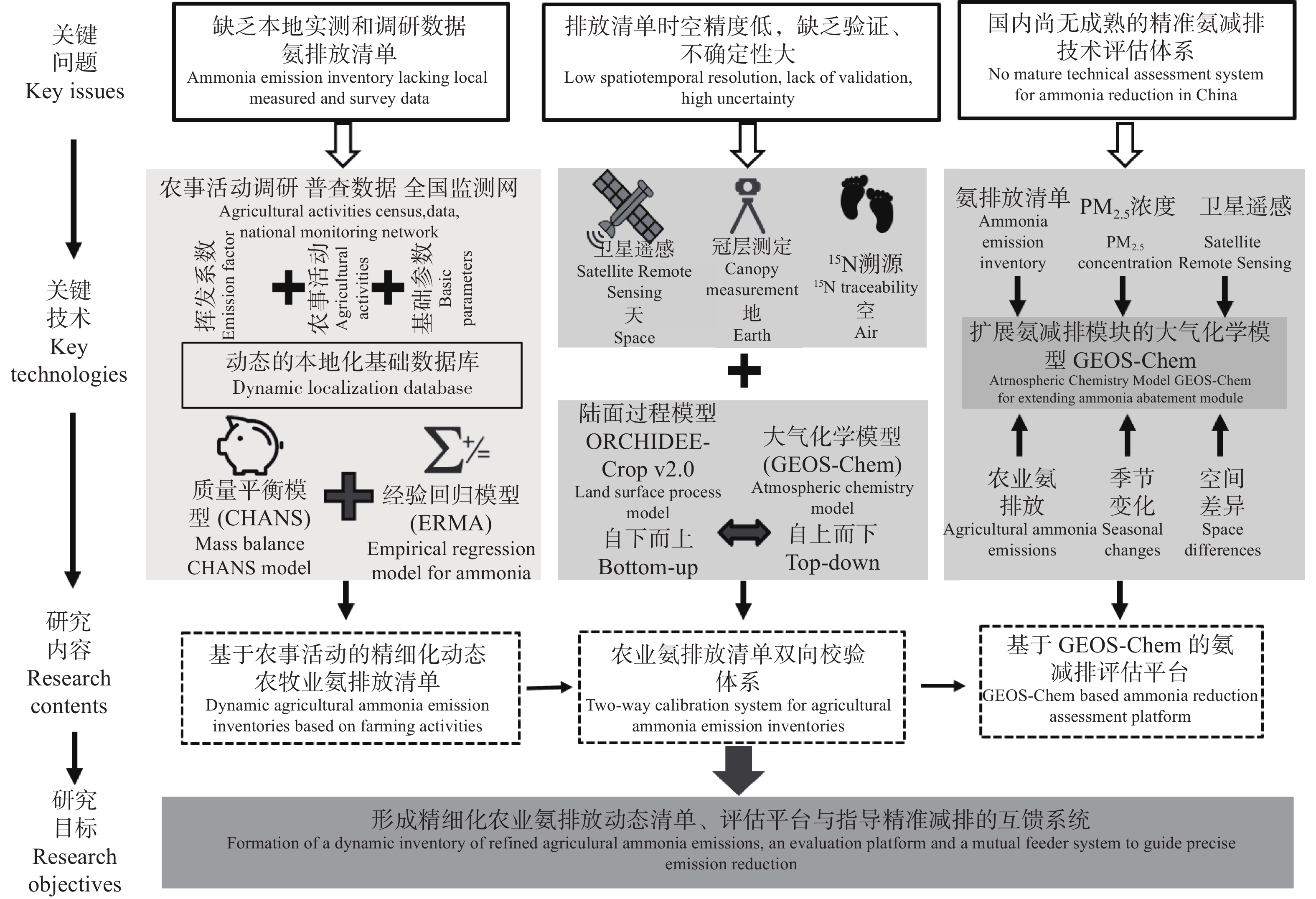
 下载:
下载: