-
摘要: 本试验以‘意大利耐抽薹’生菜为试材, 采用水培法, 设置12 h/12 h (对照)、16 h/8 h、20 h/4 h 3个光周期和叶面喷施0 µmol∙L−1、24 µmol∙L−1和48 µmol∙L−1纳米硒, 两者完全随机组合, 共9个处理, 以此探究两者对生菜生长和品质提升的交互作用, 并筛选出适宜生菜生长的最适处理, 为植物工厂在光环境下施加纳米硒提供理论依据和技术参考。结果表明: 1) 16 h/8 h光周期叶面喷施48 µmol∙L−1纳米硒处理对生菜株高、地上部鲜重、地下部鲜重和根系活力的促进效果较佳。2) 20 h/4 h光周期叶面喷施48 µmol∙L−1纳米硒处理对生菜光合色素含量的促进效果最佳。3) 16 h/8 h光周期处理生菜中可溶性糖、K、Na、Fe含量显著增加, 硝酸盐含量显著下降(P<0.05)。20 h/4 h光周期处理有利于提升可溶性蛋白质、还原糖含量, 但较长的光照处理不利于生菜中氨基酸、Ca、Mg、Zn、Fe、Mn含量提高, 甚至出现抑制效果。与对照(12 h/12 h光周期)相比, 16 h/8 h、20 h/4 h光周期处理均有利于生菜品质的提升, 而且叶面喷施纳米硒后进一步提升了生菜品质。此外, 本试验通过对生菜生长指标和部分品质指标采用主成分分析, 并对其综合排序, 结果表明16 h/8 h光周期下叶面喷施48 µmol∙L−1纳米硒对生菜生长和品质的提质效果最佳。Abstract: Nano-Se (nano-selenium) and illumination length are two important factors those are used for improving vegetable nutritional quality and yield. Although the effects of exogenous Se and photoperiod on the growth and quality of lettuce are well-studied separately, there are few studies reporting on the combination effect of these two factors. As such, in this study, we assessed the interaction of nano-Se and photoperiod on the growth and quality of lettuce; in addition, we derived the optimal combination of photoperiod and nano-Se concentration for the growth of lettuce, with the aim of providing a theoretical basis and technical starting point for plant factories to apply nano-Se under lighting systems. To accomplish this, we used ‘Italian Bolting-resistant’ lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in a hydroponics system with three photoperiods (light/dark: 12 h/12 h, P1; 16 h/8 h, P2; or 20 h/4 h, P3). In addition, the lettuce leaf surfaces were treated with a spray containing 0 μmol∙L−1 (N1), 24 μmol∙L−1 (N2), or 48 μmol∙L−1 (N3) of nano-Se. The two factors were randomly combined, resulting in a total of nine photoperiod and nano-Se treatment combinations. The results revealed that first, the P2N3 treatment had a positive effect on plant height, aboveground fresh weight, underground fresh weight, and root activity. The P2N2 treatment resulted in plant height to increase significantly (P<0.05) by 13.16% and 21.74% when compared to the P1N2 and P3N2 treatments, respectively; and the P2N3 treatment resulted in the lettuce fresh weight to increase by 56.13% and 15.14% when compared to the P1N3 and P3N3 treatments, respectively, but the difference was not significant. Second, prolonging the light period increased the chlorophyll content of the lettuce, with the highest chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents being found in the P3N3 treatment, whereas the highest carotenoid content was found in the P3N2 treatment. Third, the soluble sugar, K, Na, and Fe contents in the lettuce increased significantly under P2 treatment, whereas the nitrate content decreased significantly (P<0.05). The P3 treatment increased the soluble protein content and reduced the sugar content. But the longer illumination period was not conducive to an accumulation of amino acids, Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, nor Mn in the lettuce, instead, inhibitory effects were displayed. The P2N3 treatment resulted in an increased content of various amino acids in the lettuce. Interestingly, the P3 treatment in combination with nano-Se foliar spraying resulted in an increase in the amino acid content of the lettuce, however, the amino acid content decreased with an increasing nano-Se concentration. Compared with P1, the P2 and P3 treatments improved the lettuce quality, which was further improved by nano-Se leaf spraying. Finally, the principal component analysis on the growth and quality indices of the lettuce showed that 48 µmol∙L−1 of nano-Se foliar spraying (i.e., the N3 treatment) under a 16 h/8 h (i.e., the P2 treatment) photoperiod resulted in the greatest improvement to lettuce growth and quality.
-
Key words:
- Nano-Se /
- Photoperiod /
- Lettuce /
- Growth /
- Quality
-
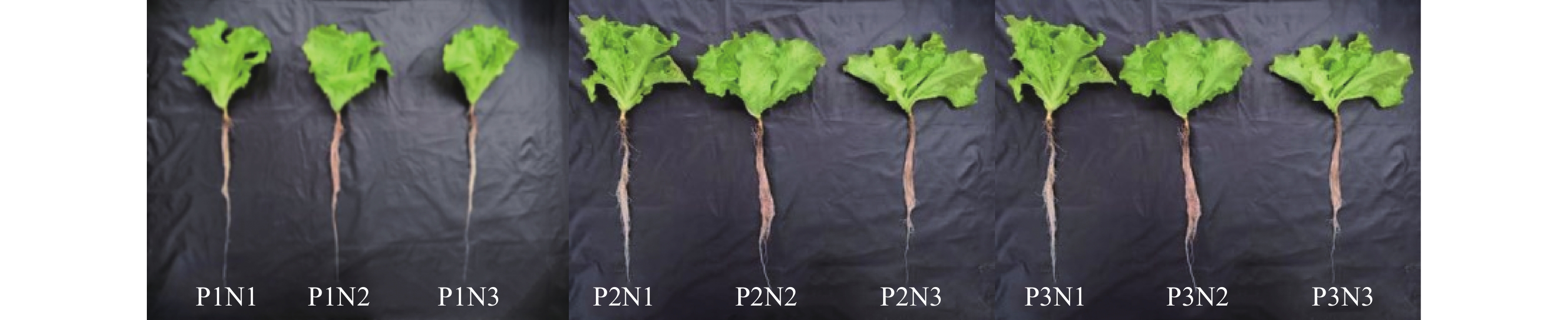
图 1 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜生长的影响
处理具体说明见表1。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1.
Figure 1. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on growth of lettuce under different photoperiods
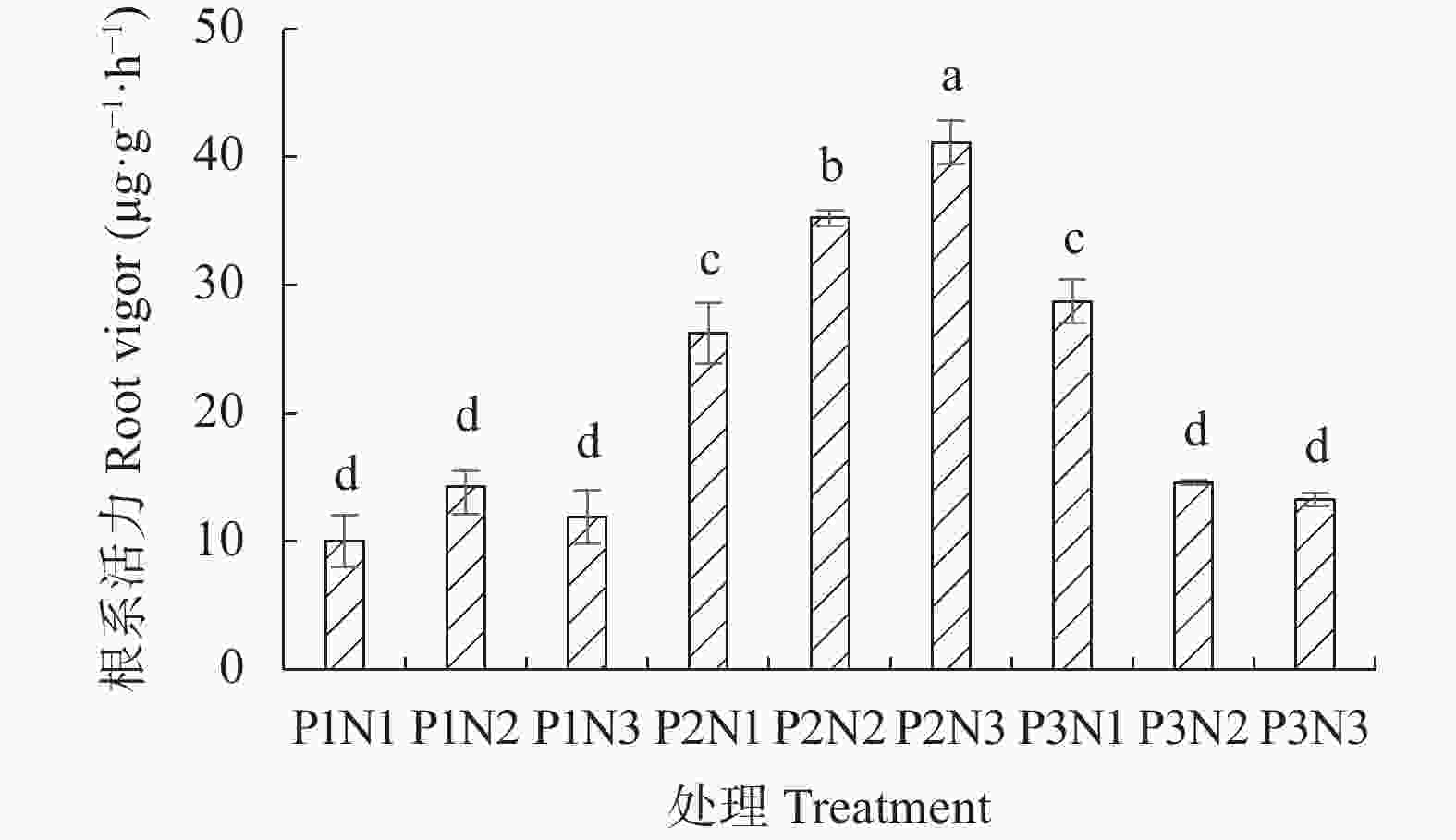
图 2 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜根系活力的影响
处理具体说明见表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Figure 2. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on root activity of lettuce under different photoperiods
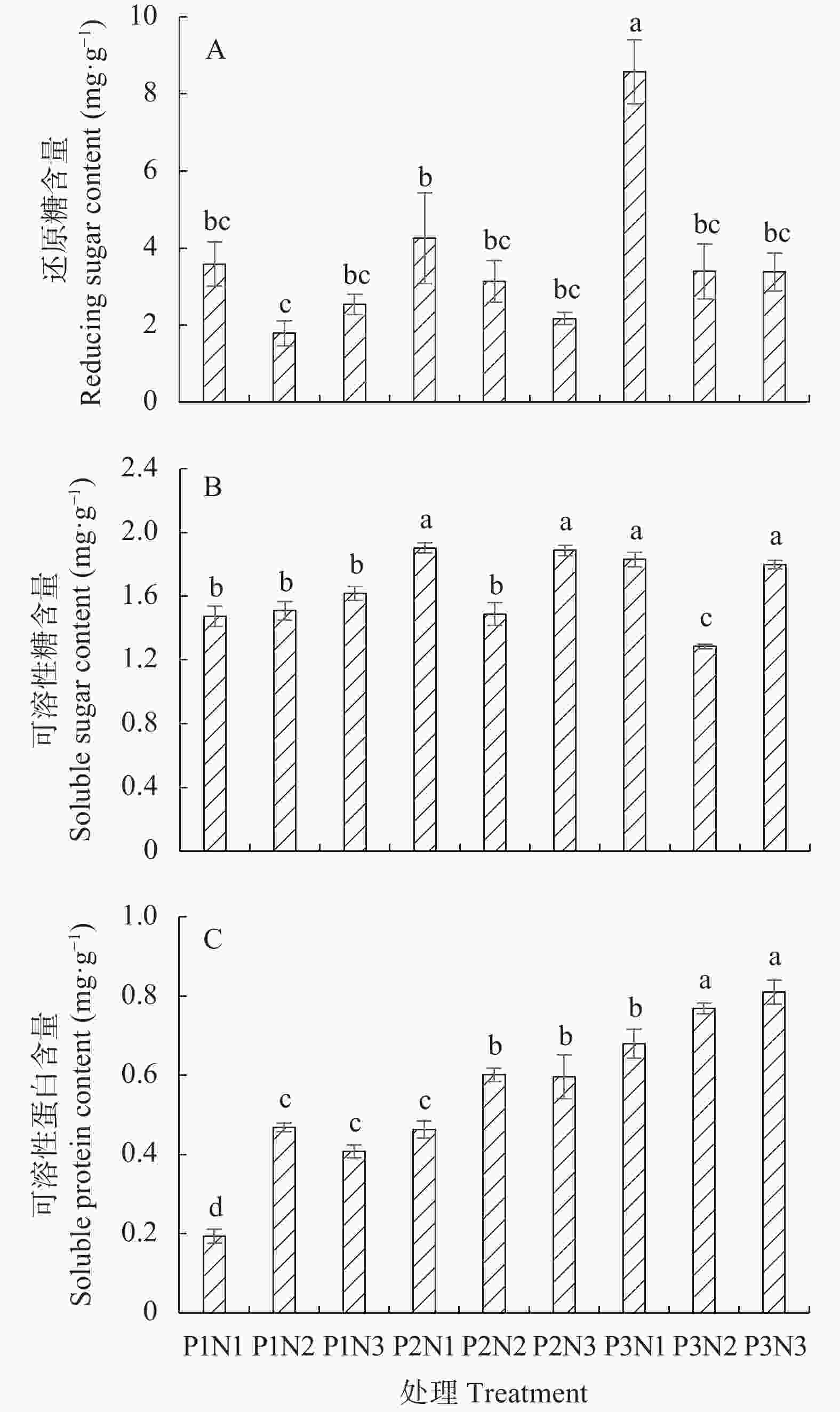
图 3 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜还原糖(A)、可溶性糖(B)和可溶性蛋白质(C)含量的影响
处理具体说明见表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Figure 3. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on contents of reducing sugar (A), soluble sugar (B) and soluble protein (C) of lettuce under different photoperiods
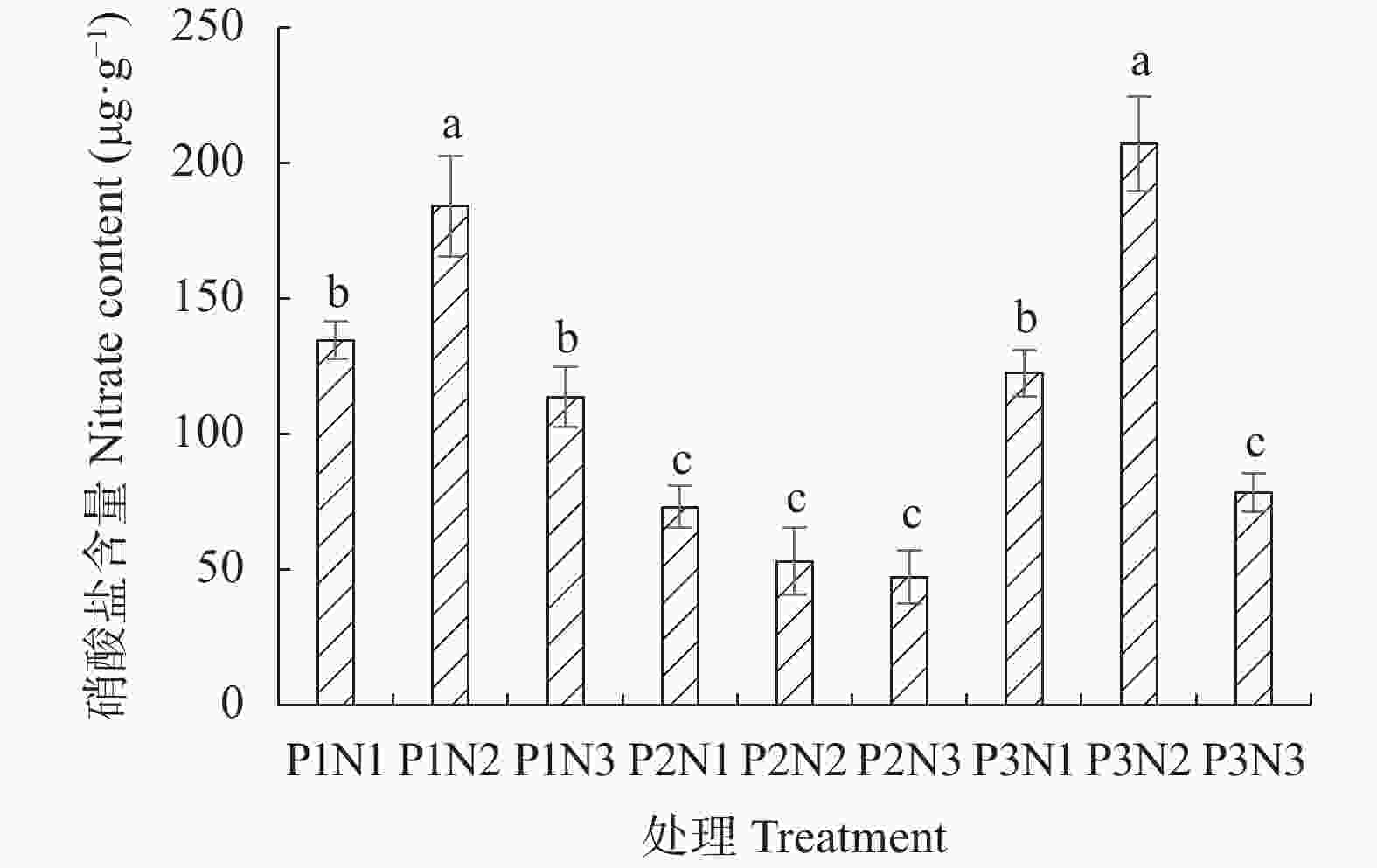
图 4 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜硝酸盐含量的影响
处理具体说明见表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Figure 4. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on nitrate content of lettuce under different photoperiods
表 1 试验处理名称及措施
Table 1. Names and measures of different experiment treatments
处理
Treatment光周期(光/暗)
Photoperiod (light/dark)叶面喷施纳米硒
Foliar spraying nano-Se (μmol∙L−1)P1N1 12 h/12 h 0 (蒸馏水 Distilled water) P1N2 12 h/12 h 24 P1N3 12 h/12 h 48 P2N1 16 h/8 h 0 (蒸馏水 Distilled water) P2N2 16 h/8 h 24 P2N3 16 h/8 h 48 P3N1 20 h/4 h 0 (蒸馏水 Distilled water) P3N2 20 h/4 h 24 P3N3 20 h/4 h 48 表 2 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜株高和生物量的影响
Table 2. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on plant height and biomass of lettuce under different photoperiods
处理
Treatment株高
Plant height (cm)地上部鲜重
Overground fresh weight (g)地下部鲜重
Underground fresh weight (g)P1N1 19.33±0.33cd 25.41±1.65cd 3.17±0.05bc P1N2 19.00±0.28d 33.27±0.66bcd 3.94±0.15bc P1N3 20.33±0.33bc 33.42±0.80bcd 3.58±0.13bc P2N1 22.16±0.44a 50.53±6.16a 4.66±0.36ab P2N2 21.50±0.28ab 34.69±1.23bc 3.66±0.21bc P2N3 21.33±0.44ab 52.18±8.19a 5.49±0.97a P3N1 20.83±0.16b 36.72±3.36bc 3.96±0.41bc P3N2 17.66±0.44e 22.22±0.76d 2.78±0.17c P3N3 20.67±0.67b 45.32±0.63ab 5.80±0.78a 处理具体说明见表1。同列数据后不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). 表 3 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜光合色素含量的影响
Table 3. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on photosynthetic pigment content of lettuce under different photoperiods
µg∙g−1(FW) 处理
Treatment叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b类胡萝卜素
Carotenoid总叶绿素
Total chlorophyll叶绿素a/b
Chlorophyll a/bP1N1 438.1±12.26d 159.8±6.33d 89.7±1.76c 597.9±18.58d 2.74±0.03ef P1N2 357.2±4.49e 134.0±1.49e 69.6±1.02d 491.2±5.95e 2.66±0.01f P1N3 326.9±1.04e 112.2±2.93f 67.9±0.35d 439.0±3.97e 2.91±0.06bc P2N1 512.2±33.33bc 165.2±10.35cd 111.6±7.08b 677.4±43.55bc 3.09±0.03a P2N2 523.7±9.34b 183.1±2.99c 107.1±0.37b 706.8±12.22b 2.86±0.01cde P2N3 536.1±30.66b 178.7±12.07cd 111.9±7.19b 714.8±42.67b 3.01±0.03ab P3N1 459.0±17.63cd 158.9±4.81d 99.5±3.66bc 617.9±22.43cd 2.88±0.02bc P3N2 596.0±15.94a 207.6±3.26b 147.5±3.79a 803.6±19.11a 2.87±0.03cd P3N3 632.3±17.49a 229.3±4.78a 147.2±6.38a 861.7±21.11a 2.75±0.05def 处理具体说明见表1。同列数据后不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). 表 4 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜氨基酸含量的影响
Table 4. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on amino acid composition and contents of lettuce under different photoperiods
µg∙g−1(DW) 氨基酸
Amino acidP1N1 P1N2 P1N3 P2N1 P2N2 P2N3 P3N1 P3N2 P3N3 天冬氨酸 Aspartic acid 4.33±0.37a 4.32±0.37a 3.65±0.08b 2.18±0.10cd 1.73±0.20de 2.57±0.31c 1.58±0.13e 4.32±0.58a 1.82±0.21de 苏氨酸 L-Threonine 0.75±0.06e 0.81±1.34a 0.31±0.06e 5.99±0.35c 6.29±0.72c 9.57±1.84b 4.10±0.55d 8.59±0.26b 5.73±0.89c 丝氨酸 Serine 6.31±0.50b 7.40±0.51a 7.15±1.04ab 3.43±0.12de 2.48±0.29f 4.25±0.50cd 2.65±0.15ef 7.60±0.22a 4.95±0.59c 谷氨酸 Glutamic acid 5.88±0.51c 6.99±0.60b 5.86±1.26c 2.96±0.13d 2.58±0.28d 5.20±0.76c 3.01±0.17d 10.06±0.36a 5.39±0.61c 甘氨酸 Glycine 4.22±0.31a 4.32±0.30a 4.47±1.01a 1.79±0.03cd 1.62±0.18d 2.55±0.31b 0.89±0.05e 2.40±0.07bc 1.60±0.16d 丙氨酸 Alanine 42.96±3.67bc 46.50±3.76b 39.00±1.95c 13.09±0.74e 12.52±1.46e 20.98±3.59d 11.35±0.68e 58.53±0.84a 23.16±2.99d 缬氨酸 Valine 11.13±0.68b 12.60±1.05ab 12.10±2.49ab 4.80±0.23d 4.63±0.34d 8.00±1.21c 3.75±0.29d 13.18±0.14a 7.35±0.95c 异亮氨酸 L-Isoleucine 6.57±0.44c 7.87±0.65ab 7.21±1.47bc 2.97±0.15e 2.72±0.30e 4.90±0.73d 2.20±0.21e 8.72±0.05a 4.62±0.56d 亮氨酸 Leucine 16.96±0.88b 17.58±1.42b 19.55±0.94a 9.18±0.44d 8.57±1.07d 13.45±2.05c 8.03±0.41d 16.50±0.03b 12.77±1.58c 苯丙氨酸 Phenylalanine 9.29±0.56a 9.74±0.77a 10.03±2.02a 3.49±0.16cd 4.00±0.48c 6.38±0.95b 2.24±0.11d 7.50±0.14b 4.74±0.56c 赖氨酸 Lysine 9.94±0.31a 8.40±0.63b 9.44±1.03a 2.23±0.14d 2.56±0.30d 3.91±0.41c 0.95±0.02e 4.51±0.16c 2.40±0.25d 组氨酸 Histidine 1.32±0.09b 1.53±0.12ab 1.52±0.32ab 0.76±0.02c 0.49±0.06d 1.01±0.13c 0.45±0.03d 1.66±0.09a 1.00±0.12c 精氨酸 Arginine 10.22±0.59b 9.74±0.78b 10.83±0.85b 4.88±0.29d 3.33±0.39e 5.63±0.85d 3.52±0.27e 13.93±0.24a 7.74±1.02c 处理具体说明见表1。同行数据后不同小写字母表示各处理差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters in the same row indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). 表 5 不同光周期下叶面喷施纳米硒对生菜矿质元素含量的影响
Table 5. Effects of foliar spraying nano-Se on contents of mineral elements in lettuce under different photoperiods
处理 Treatment K (g∙kg−1) Na (g·kg−1) Ca (g∙kg−1) Mg (g∙kg−1) Fe (mg∙kg−1) Zn (mg∙kg−1) Mn (mg∙kg−1) Se (μg∙kg−1) P1N1 0.30±0.006b 0.26±0.008bc 0.34±0.012a 8.37±0.064a 34.47±2.474ab 248.76±13.212b 62.05±1.084a 33.62±0.178e P1N2 0.31±0.017b 0.27±0.04bc 0.33±0.001a 8.07±0.203a 29.57±0.311cd 226.28±10.084b 52.43±1.888b 34.56±0.227d P1N3 0.31±0.015b 0.23±0.032c 0.36±0.015a 7.95±0.186a 32.23±1.31bc 341.25±8.7007a 45.88±3.427c 34.86±0.160cd P2N1 0.35±0.013a 0.30±0.03abc 0.22±0.024b 5.65±0.114c 27.31±0.793de 234.69±14.004b 21.56±0.483e 35.72±0.200b P2N2 0.29±0.01b 0.35±0.035a 0.26±0.015ab 6.21±0.069b 28.73±0.76cde 144.35±4.417c 16.48±0.489fg 35.93±0.291ab P2N3 0.32±0.004ab 0.36±0.026a 0.33±0.025a 5.70±0.083c 38.47±1.287a 138.45±2.733c 30.12±0.991d 36.56±0.257a P3N1 0.24±0.004c 0.21±0.023c 0.12±0.013c 4.08±0.064e 20.91±0.22f 55.41±2.962d 15.06±0.243g 34.18±0.219de P3N2 0.35±0.018a 0.33±0.019ab 0.27±0.019ab 5.85±0.284bc 25.05±2.465e 50.53±3.357d 20.62±1.982ef 34.79±0.103cd P3N3 0.32±0.004ab 0.26±0.014bc 0.19±0.081bc 4.83±0.05d 18.75±0.344f 50.96±4.316d 12.62±1.004g 35.40±0.620bc 处理具体说明见表1。同列数据后不同小写字母表示各处理差异显著(P<0.05)。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). 表 6 生菜生长和品质主成分分析的各因子载荷矩阵
Table 6. Principal component analysis of lettuce growth and quality of each factor load matrix
主成分
Principal componentX1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X12 Ⅰ 0.514 0.693 0.724 0.557 0.855 0.773 0.785 0.838 0.457 0.583 0.194 0.699 Ⅱ 0.764 0.656 0.397 0.463 −0.490 −0.608 −0.590 −0.522 0.516 0.729 0.099 −0.405 Ⅲ 0.047 −0.271 −0.474 0.246 0.002 −0.075 0.049 −0.018 0.340 −0.018 0.843 0.134 X1: 株高; X2: 地上部鲜重; X3: 地下部鲜重; X4: 根系活力; X5: 叶绿素a; X6: 叶绿素b; X7: 类胡萝卜素; X8: 总叶绿素; X9: 叶绿素a/b; X10: 可溶性糖; X11: 还原糖; X12: 可溶性蛋白。X1: plant height; X2: fresh weight of aboveground part; X3: fresh weight of underground part; X4: root activity; X5: chlorophyll a; X6: chlorophyll b; X7: carotenoids; X8: total chlorophyll; X9: chlorophyll a/b; X10: soluble sugar; X11: reducing sugar; X12: soluble protein. 表 7 各处理综合因子得分(Y值)及排序
Table 7. Comprehensive factor score (Y value) and ranking of each treatment
处理 Treatment Y1 Y2 Y3 Y 排序 Order P1N1 −2.60 −0.76 −0.11 −1.39 9 P1N2 −2.88 0.09 −1.21 −1.37 8 P1N3 −2.87 1.53 −0.20 −0.83 6 P2N1 1.64 2.10 0.30 1.38 2 P2N2 0.54 −0.23 0.35 0.21 5 P2N3 2.41 1.73 −0.78 1.50 1 P3N1 0.44 0.93 2.24 0.70 4 P3N2 0.15 −3.91 0.75 −1.03 7 P3N3 3.17 −1.47 −1.34 0.83 3 处理具体说明见表1。The description of each treatment is shown in the table 1. -
[1] 马英辉, 李利军, 卢美欢, 等. 微生物纳米硒研究进展[J]. 中国酿造, 2020, 39(9): 25−29 doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.09.005MA Y H, LI L J, LU M H, et al. Research progress of microbial nano-selenium[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(9): 25−29 doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.09.005 [2] TAN L C, NANCHARAIAH Y V, VAN HULLEBUSCH E D, et al. Selenium: environmental significance, pollution, and biological treatment technologies[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(5): 886−907 doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.05.005 [3] 魏艳秋, 景艺卓, 郭笑恒, 等. 外源硒对植物抗盐性的影响研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2021, (2): 15−21WEI Y Q, JING Y Z, GUO X H, et al. Research progress on the effect of exogenous selenium on salt resistance of plants[J]. Crops, 2021, (2): 15−21 [4] 袁伟玲, 刘志雄, 吴金平, 等. 硒对生菜生长、品质、养分吸收和硒转化率的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(S1): 189−194 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191595YUAN W L, LIU Z X, WU J P, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium on the nutritional quality and mineral element absorption of lettuce[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(S1): 189−194 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191595 [5] 孙崇庆, 马晓春, 高艳明, 等. 硒肥对植物工厂水培生菜生长及品质的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2020, 33(6): 24−29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2020.06.005SUN C Q, MA X C, GAO Y M, et al. Effect of selenium fertilizers on growth and quality of hydroponic lettuce in plant factory[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2020, 33(6): 24−29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2020.06.005 [6] 胡万行, 石玉, 程玉琦, 等. 纳米硒对紫色马铃薯生长及其矿质元素含量和品质特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(2): 296−303HU W X, SHI Y, CHENG Y Q, et al. Effects of nano-selenium on the growth and its mineral element contents and quality characteristics of purple potatoes[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(2): 296−303 [7] LI Y H, LIN Z F, ZHAO M Q, et al. Multifunctional selenium nanoparticles as carriers of HSP70 siRNA to induce apoptosis of HepG2 cells[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2016, 11: 3065−3076 doi: 10.2147/IJN.S109822 [8] BIAN Z H, LEI B, CHENG R F, et al. Selenium distribution and nitrate metabolism in hydroponic lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.): Effects of selenium forms and light spectra[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19(1): 133−144 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62775-9 [9] 孔凡丽, 张恩萍, 曹庆军, 等. 硒的生理功能及在主要作物中的吸收富集[J]. 东北农业科学, 2020, 45(6): 115−118KONG F L, ZHANG E P, CAO Q J, et al. Physiological function and absorption enrichment of selenium in staple crops[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 45(6): 115−118 [10] 李列, 仝宇欣, 李锦, 等. 不同光质组合对生菜生长和能量利用效率的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(9): 114−120LI L, TONG Y X, LI J, et al. Effect of different combinations of light wavelengths on growth and energy use efficiency of lettuce[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 48(9): 114−120 [11] 杜彦修, 季新, 张静, 等. 弱光对水稻生长发育影响研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(11): 1307−1317 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01307DU Y X, JI X, ZHANG J, et al. Research progress on the impacts of low light intensity on rice growth and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(11): 1307−1317 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01307 [12] 傅国海, 杨其长, 刘文科. LED补光和根区加温对日光温室起垄内嵌式基质栽培甜椒生长及产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(2): 230−238FU G H, YANG Q C, LIU W K. Effect of LED supplemental lighting and root zone heating on growth and yield of soil ridged substrate-embedded sweet pepper in solar greenhouses in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(2): 230−238 [13] SONG J L, HUANG H, SONG S W, et al. Effects of photoperiod interacted with nutrient solution concentration on nutritional quality and antioxidant and mineral content in lettuce[J]. Agronomy, 2020, 10(7): 920 doi: 10.3390/agronomy10070920 [14] 吉家曾, 李聪聪, 丁慧霞, 等. 光强及光周期对红叶生菜生长及品质的影响[J]. 照明工程学报, 2019, 30(6): 163−166JI J Z, LI C C, DING H X, et al. Effects of light intensity and photoperiod on growth and quality of red leaf lettuce[J]. China Illuminating Engineering Journal, 2019, 30(6): 163−166 [15] KELLY N, CHOE D, MENG Q W, et al. Promotion of lettuce growth under an increasing daily light integral depends on the combination of the photosynthetic photon flux density and photoperiod[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2020, 272: 109565 doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109565 [16] 刘杰, 胡笑涛, 王文娥, 等. 光强和光周期对水培生菜光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(8): 1784−1790LIU J, HU X T, WANG W E, et al. Effects of light intensity and photoperiod on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence of hydroponic lettuce[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(8): 1784−1790 [17] 查凌雁, 刘文科. LED红蓝光连续光照对五种生菜生长、光合和叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(9): 1735−1741ZHA L Y, LIU W K. Effect of continuous light with red and blue LED lamps on growth and characteristics of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of five lettuce cultivars[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2017, 53(9): 1735−1741 [18] SAMUOLIENĖ G, VIRŠILĖ A, MILIAUSKIENĖ J, et al. The physiological response of lettuce to red and blue light dynamics over different photoperiods[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11: 610174 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.610174 [19] 佟静, 吴萍, 季延海, 等. 叶用莴苣(生菜)单粒播种、一次成苗穴盘育苗技术[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2019, (9): 99−100TONG J, WU P, JI Y H, et al. The technique of single seed sowing and one time seedling raising of lettuce[J]. China Vegetables, 2019, (9): 99−100 [20] 翟克清, 张昕昱, 周念念, 等. 光学干涉膜下生菜的生理指标变化及品质分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(9): 1493−1501 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2019.09.13ZHAI K Q, ZHANG X Y, ZHOU N N, et al. Changes of physiological indexes and quality analysis of lettuce under optical interference film[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(9): 1493−1501 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2019.09.13 [21] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006LI H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006 [22] 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006GAO J F. Plant Physiology Experimental Guidance[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006 [23] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1976, 72(1/2): 248−254 [24] 林海明, 张文霖. 主成分分析与因子分析的异同和SPSS软件−兼与刘玉玫、卢纹岱等同志商榷[J]. 统计研究, 2005, 22(3): 65−69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4565.2005.03.015LIN H M, ZHANG W L. The relationship between principal component analysis and factor analysis and SPSS software — to discuss with Liu Yumei, Lu Wendai etc[J]. Statistical Research, 2005, 22(3): 65−69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4565.2005.03.015 [25] 张玉彬, 刘文科, 杨其长, 等. 采收前LED红蓝光连续照射对水培生菜品质的提升作用[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(7): 436−445 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.07.004ZHANG Y B, LIU W K, YANG Q C, et al. Improvement effects of red and blue LED continuous lighting before harvest on quality of hydroponic lettuce[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(7): 436−445 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.07.004 [26] CRAIG D S, RUNKLE E S. An intermediate phytochrome photoequilibria from night-interruption lighting optimally promotes flowering of several long-day plants[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 121: 132−138 doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.04.004 [27] 任旭妍, 张婵, 张亚, 等. 不同红蓝LED光照强度对紫叶生菜生长及营养品质的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(6): 89−96 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190484REN X Y, ZHANG C, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of different red and blue LED light intensities on the growth and nutritional quality of purple leaf lettuce[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(6): 89−96 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190484 [28] YAN Z N, HE D X, NIU G H, et al. Evaluation of growth and quality of hydroponic lettuce at harvest as affected by the light intensity, photoperiod and light quality at seedling stage[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 248: 138−144 doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.01.002 [29] 林魁, 黄枝, 金心怡, 等. 植物生长光调控应用研究进展[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(6): 1163−1170 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.06.029LIN K, HUANG Z, JIN X Y, et al. Progress of research in light regulation for plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(6): 1163−1170 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.06.029 [30] WANG C R, CHENG T T, LIU H T, et al. Nano-selenium controlled cadmium accumulation and improved photosynthesis in indica rice cultivated in lead and cadmium combined paddy soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 103: 336−346 doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.11.005 [31] 何久兴, 赵解春, 白文波, 等. 叶面喷施寡糖对生菜生长和品质的调节作用[J]. 中国农业气象, 2019, 40(12): 783−792 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2019.12.005HE J X, ZHAO J C, BAI W B, et al. Effect of different oligosaccharides by spraying on plant growth and quality in lettuce[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2019, 40(12): 783−792 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2019.12.005 [32] VIRŠILĖ A, BRAZAITYTĖ A, VAŠTAKAITĖ-KAIRIENĖ V, et al. Lighting intensity and photoperiod serves tailoring nitrate assimilation indices in red and green baby leaf lettuce[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2019, 99(14): 6608−6619 doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9948 [33] 高勇, 李清明, 刘彬彬, 等. 不同光质配比对紫叶生菜光合特性和品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(11): 3649−3657GAO Y, LI Q M, LIU B B, et al. Effects of light quality ratio on photosynthetic characteristics and quality of purple lettuce[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(11): 3649−3657 [34] ATIF M J, AMIN B, GHANI M I, et al. Variation in morphological and quality parameters in garlic (Allium sativum L.) bulb influenced by different photoperiod, temperature, sowing and harvesting time[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(2): 155 doi: 10.3390/plants9020155 [35] LEI B, BIAN Z H, YANG Q C, et al. The positive function of selenium supplementation on reducing nitrate accumulation in hydroponic lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2018, 17(4): 837−846 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61759-3 [36] 周晚来, 刘文科, 闻婧, 等. 短期连续光照下水培生菜品质指标变化及其关联性分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(6): 1319−1323ZHOU W L, LIU W K, WEN J, et al. Changes in and correlation analysis of quality indices of hydroponic lettuce under short-term continuous light[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(6): 1319−1323 [37] 吕兵兵, 姚攀锋, 王官凤, 等. 光周期对苦荞芽菜生长与品质的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(10): 1785−1794LÜ B B, YAO P F, WANG G F, et al. Effect of photoperiod on growth and quality of Tartary buckwheat sprouts[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(10): 1785−1794 [38] 黄小兰, 何旭峰, 杨勤, 等. 不同产地地参中17种氨基酸的测定与分析[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(2): 255−261 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200108-090HUANG X L, HE X F, YANG Q, et al. Determination of 17 amino acids in the dried rhizome of Lycopus lucidus Turcz. var. hirtus Regel from different habitats[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(2): 255−261 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200108-090 [39] 宋奇超, 曹凤秋, 巩元勇, 等. 高等植物氨基酸吸收与转运及生物学功能的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6): 1507−1517SONG Q C, CAO F Q, GONG Y Y, et al. Current research progresses of amino acids uptake, transport and their biological roles in higher plants[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(6): 1507−1517 [40] 崔剑波, 尹昭汉. 外源Se对农作物籽实中Se的化学形态及其品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 1993, 4(3): 303−307 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.03.017CUI J B, YIN Z H. Influence of supplemented selenium on chemical forms of selenium in crop seeds and their quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1993, 4(3): 303−307 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.03.017 [41] 苏苑君, 胡笑涛, 王文娥, 等. 磷对水培生菜生长及矿质元素动态吸收的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(10): 1244−1252SU Y J, HU X T, WANG W E, et al. Effect of phosphorus on dynamic growth and nutrient absorption of hydroponic lettuce[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(10): 1244−1252 [42] 刘文科, 张玉彬, 查凌雁, 等. 采收前连续光照光质对三种供氮水平的水培生菜营养元素含量的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(12): 3884−3889LIU W K, ZHANG Y B, ZHA L Y, et al. Effects of continuous light before harvest on nutrient element contents of hydroponic lettuce cultivated supplied with three nitrogen levels and two LED red and blue light qualities[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(12): 3884−3889 [43] 查凌雁, 张玉彬, 李宗耕, 等. LED红蓝光连续光照及其光强对生菜生长及矿质元素吸收的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(8): 2474−2480ZHA L Y, ZHANG Y B, LI Z G, et al. Effect of continuous red/blue LED light and its light intensity on growth and mineral elements absorption of lettuce[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(8): 2474−2480 [44] 李海云, 刘焕红. 夜间补光对黄瓜幼苗激素含量及养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(16): 74−78 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2012-3699LI H Y, LIU H H. Effects of supplementary illumination at night on hormones content and nutrient absorption of cucumber seedlings[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(16): 74−78 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2012-3699 -






 下载:
下载: