Suitability evaluation of suitable-for-mechanization transformation of cultivated land based on topographic complexity in Chongqing, China
-
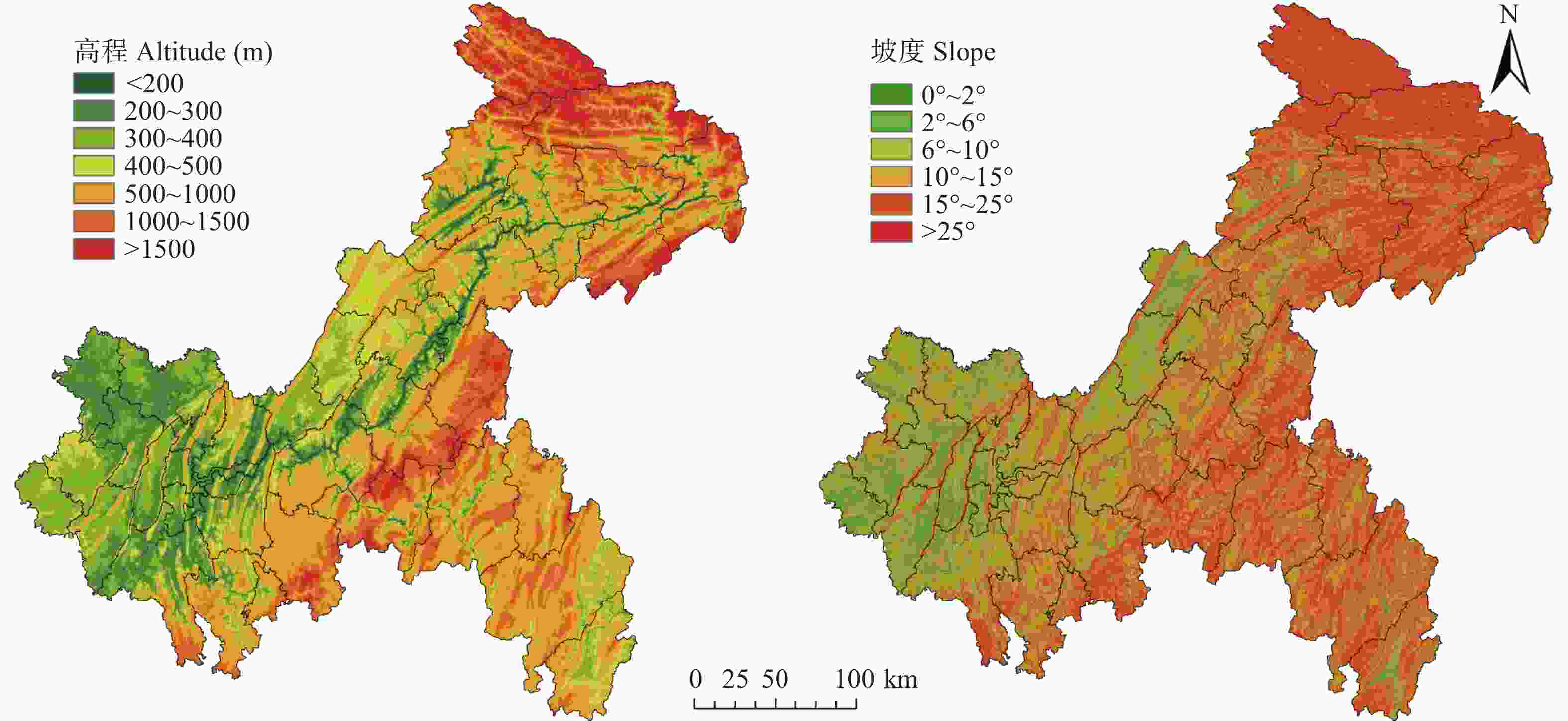
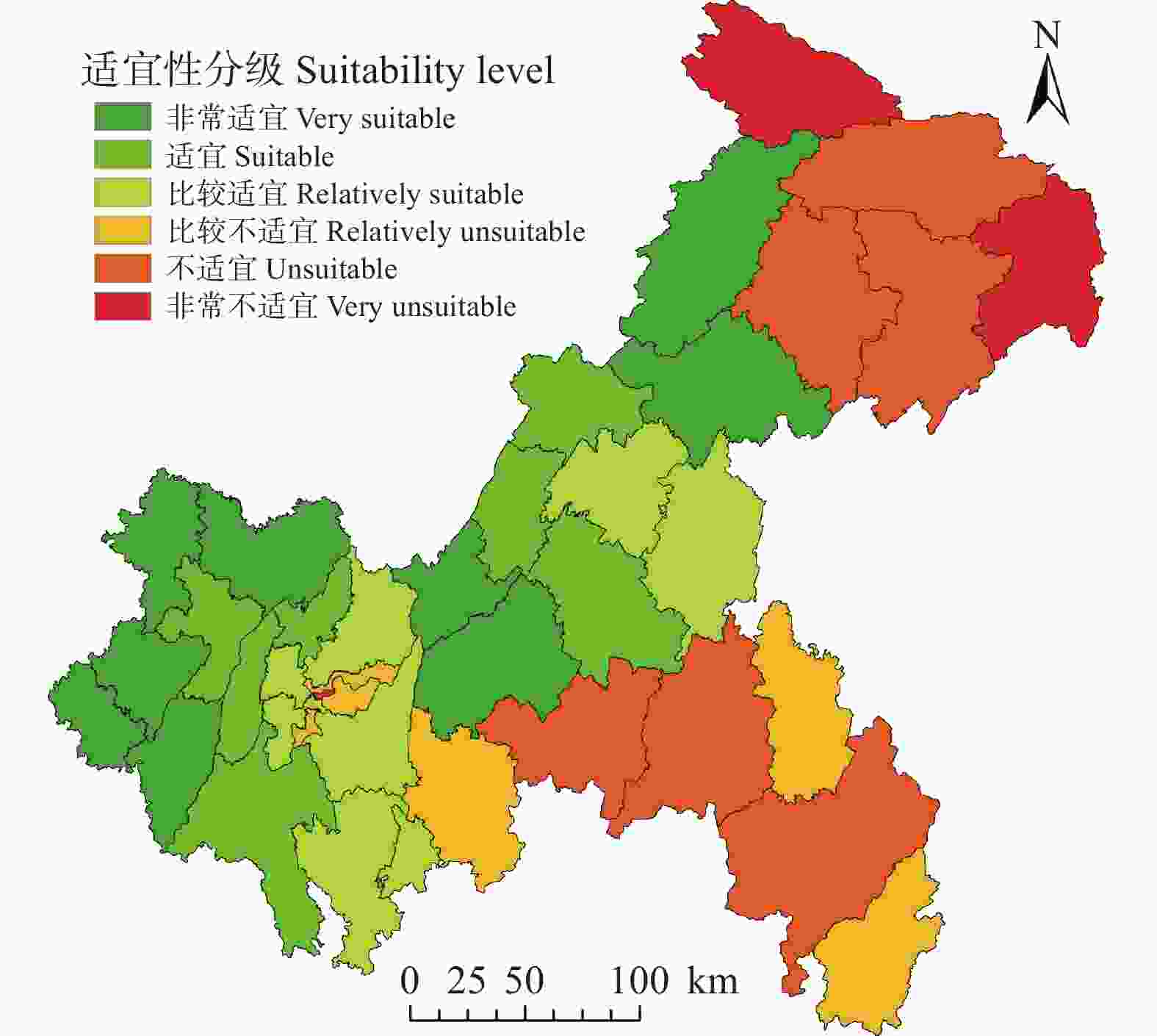
摘要: “宜机化”改造是推进丘陵山地农业机械化发展的根本之路, 对其进行科学的适宜性评价能合理规划改造进程, 对提高丘陵山地“宜机化”改造的效率和准度具有重要意义。本文选取高程、坡度和地块破碎度等3个地形限制因素, 以重庆市各区县为评价单元, 结合GIS空间分析功能及数据包络法(DEA), 对耕地进行“宜机化”改造适宜性评价。结果表明: 1)重庆市耕地小而碎, 主要分布在中部和西部。2)耕地主要分布在坡度为6°~15°、海拔高度为200~500 m区域, 其中海拔在300~400 m范围内的耕地是“宜机化”改造最理想的区域, 占主要耕地的48.88%。3)通过自然间断点分级法(Jenks)将综合地形复杂度指数分段后得到6个适宜程度: 非常适宜、适宜、比较适宜、比较不适宜、不适宜和非常不适宜; 低于平均地形复杂度指数值的区县共25个, 包括处于非常适宜区的潼南区等9个区县、处于适宜区的璧山区等7个区县和处于比较适宜区的綦江区等9个区县。评价结果与重庆市地貌格局高度重合, 建议优先考虑在适宜性程度高的区县进行“宜机化”改造。因此, 在GIS空间分析功能的支撑下, 基于地形复杂度的适宜性评价方法能有效评价丘陵山地耕地“宜机化”改造的适宜性, 对耕地坡度<15°的区域进行“宜机化”改造将大大提升重庆市农业机械化程度, 重庆市耕地“宜机化”改造潜力大。Abstract: Suitable-for-mechanization transformation is the fundamental way to promote the development of agricultural mechanization in hilly areas. Scientific evaluation of its suitability can reasonably plan the transformation process, which is significant in improving the efficiency and accuracy of agriculture mechanized transformation in hilly areas. The study selected three topographic limiting factors: elevation, slope and fragmentation with different districts and counties in Chongqing as evaluation units, to evaluate the suitability of suitable-for-mechanization transformation of cultivated land by integrating GIS spatial analysis function and data envelopment method (DEA). The results showed that: 1) the cultivated land plots in Chongqing was small and fragmented, mainly distributed in the central and western regions. The area and density of cultivated land in the eastern part of Chongqing were obviously less than that in other regions, consistent with the topography of high in the east and low in the west. The spatial distribution characteristics of paddy field and cultivated land were similar, and the terrain requirement of dryland was lower than that of paddy field. 2) The cultivated land was mainly distributed in the slope of 6°−15° and the elevation of 200−500 m, among which the cultivated land with the elevation of 300−400 m was the most ideal area for mechanization transformation, accounting for 48.88% of the main cultivated land. 3) According to the classification method of natural disjunctions (Jenks), the comprehensive topographical complexity index was segmented into six sections of the suitability degree of mechanization reconstruction in Chongqing City including very suitable, suitable, relatively suitable, relatively unsuitable, unsuitable and very unsuitable. The average value of terrain complexity index of each district and county was 0.925, and a total of 25 districts and counties were below that index, including 9 districts and counties in the very suitable area such as Tongnan District, 7 districts and counties in the suitable area such as Bishan District, and 9 districts and counties in the relatively suitable area such as Qijiang District, which were relatively suitable. The evaluation results, which consider the limiting factors of developing the agricultural mechanization of hilly areas, were highly coincident with the actual geomorphic layout of Chongqing City, which was conducive to group integrated development. So it is suggested that the places with high suitability should be given priority for mechanization reconstruction for further landing. Therefore, the suitability evaluation method based on the terrain complexity can effectively evaluate the suitability of hilly mountain land in reconstructing appropriate machine for cultivated land, with the support of GIS spatial analysis function. Futrthermore, the appropriate machine renovation for the cultivated land located in a region of gradient less than 15° will greatly improve the degree of agricultural mechanization in Chongqing municipality; thus, the appropriate machine reconstruction for cultivated land is potential.
-
Key words:
- Chongqing City /
- Terrain complexity /
- Suitable for mechanization /
- Suitability evaluation
-
表 1 2018年重庆市各区县耕地面积统计表
Table 1. Statistics of cultivated land areas in various districts (counties) of Chongqing in 2018
km² 地域范围
Territorial scope行政区
Administrative district耕地
Cultivated land耕地 Cultivated land 水田 Paddy field 旱地 Dry land 中心城区
Central urban area渝中区 Yuzhong District 0 0 0 大渡口 Dadukou District 35.86 11.73 24.13 江北区 Jiangbei District 77.96 31.36 46.60 南岸区 Nan’an District 118.95 55.76 63.19 沙坪坝区 Shapingba District 172.16 90.09 82.07 九龙坡区 Jiulongpo District 195.86 72.78 123.08 巴南区 Banan District 1351.01 503.28 847.73 北碚区 Beibei District 436.04 132.47 303.57 渝北区 Yubei District 863.37 279.59 583.78 主城新区
New developed area of city万盛经济技术开发区
Wansheng Economic and Technological Development Zone251.63 52.47 199.16 璧山区 Bishan District 634.25 333.00 301.25 长寿区 Changshou District 995.95 555.54 440.42 荣昌区 Rongchang District 890.18 266.92 623.25 永川区 Yongchuan District 1042.19 259.41 782.78 铜梁区 Tongliang District 1072.06 583.54 488.52 綦江区 Qijiang District 1156.51 407.01 749.51 潼南区 Tongnan District 1428.10 484.61 943.49 涪陵区 Fuling District 1586.12 678.09 908.03 江津区 Jiangjin District 1532.61 412.57 1120.04 南川区 Nanchuan District 965.47 300.79 664.69 合川区 Hechuan District 1911.50 689.59 1221.91 大足区 Dazu District 1206.91 429.93 776.98 渝东北地区
Northeast Chongqing area城口县 Chengkou County 797.43 41.14 756.29 巫山县 Wushan County 750.52 24.26 726.25 巫溪县 Wuxi County 1063.99 24.98 1039.01 奉节县 Fengjie County 1162.17 144.50 1017.67 丰都县 Fengdu County 1318.78 367.20 951.57 垫江县 Dianjiang County 1257.55 714.77 542.78 云阳县 Yunyang County 1443.52 166.62 1276.90 开州县 Kaizhou County 2019.41 506.85 1512.56 万州区 Wanzhou District 1721.26 464.43 1256.83 梁平区 Liangping District 1239.73 636.00 603.73 忠县 Zhong County 1274.83 336.16 938.66 渝东南地区
Southeast Chongqing area石柱土家族自治县
Shizhu Tujia Autonomous County915.84 284.57 631.28 黔江区 Qianjiang District 711.10 250.14 460.96 武隆区 Wulong District 821.41 121.97 699.45 秀山土家族苗族自治县
Xiushan Tujia and Miao Autonomous County594.62 114.18 480.44 彭水苗族土家族自治县
Pengshui Miao and Tujia Autonomous County1195.97 210.71 985.25 酉阳土家族苗族自治县
Youyang Tujia and Miao Autonomous County1334.46 181.19 1153.27 总计 Sum 37 547.29 11 220.21 26 327.09 表 2 重庆市海拔高程与坡度分级组合下耕地面积统计
Table 2. Statistics of cultivated land area under the combination of altitude and slope in Chongqing
海拔高程
Altitude (m)地形坡度 Slope 总计
Sum (km²)占比
Proportion (%)<4° 4°~6° 6°~10° 10°~15° 15°~25° 33~200 0.04 5.40 25.58 44.82 8.10 83.93 0.27 200~300 4.99 339.07 2274.45 1896.25 130.80 4645.55 14.83 300~400 4.90 395.82 4006.79 5109.17 389.93 9906.61 31.63 400~500 0.79 48.38 2339.56 3022.82 771.73 6183.28 19.74 500~1000 0.12 9.31 543.39 4662.58 3226.08 8441.48 26.95 1000~1500 0.00 0.16 42.52 747.00 981.00 1770.68 5.65 1500~2743 0.00 0.54 17.31 104.51 167.94 290.30 0.93 总计 Sum (km²) 10.84 798.67 9249.60 15 587.16 5675.57 31 321.84 100.00 占比 Proportion (%) 0.03 2.55 29.53 49.76 18.12 100.00 表 3 重庆市各区县耕地地形因子复杂度及综合地形复杂度结果
Table 3. Complexities of topographic factors and the comprehensive topographic complexity of cultivated land in various districts (counties) of Chongqing
行政区
Administrative district海拔复杂度
Altitude complexity (CE1)坡度复杂度
Slope complexity (CE2)地块破碎度
Land fragmentation (CE3)综合地形复杂度
Comprehensive topographic
complexity (CE)潼南区 Tongnan District 0.229 0.373 0.733 0.452 永川区 Yongchuan District 0.249 0.291 0.900 0.486 大足区 Dazu District 0.238 0.336 0.870 0.488 荣昌区 Rongchang District 0.263 0.369 0.902 0.518 合川区 Hechuan District 0.196 0.367 0.963 0.519 开州县 Kaizhou County 0.180 0.482 0.954 0.552 万州区 Wanzhou District 0.293 0.438 0.980 0.579 长寿区 Changshou District 0.318 0.370 1.036 0.581 涪陵区 Fuling District 0.218 0.334 1.212 0.598 璧山区 Bishan District 0.252 0.305 1.328 0.637 江津区 Jiangjin District 0.136 0.306 1.440 0.641 铜梁区 Tongliang District 0.178 0.349 1.359 0.641 丰都县 Fengdu County 0.210 0.436 1.243 0.642 垫江县 Dianjiang County 0.164 0.371 1.48 0.686 北碚区 Beibei District 0.175 0.408 1.434 0.687 梁平区 Liangping District 0.290 0.299 1.455 0.689 綦江区 Qijiang District 0.358 0.489 1.232 0.702 渝北区 Yubei District 0.175 0.398 1.592 0.737 巴南区 Banan District 0.419 0.320 1.585 0.780 万盛经济技术开发区
Wansheng Economic and Technological
Development Zone0.323 0.519 1.568 0.817 石柱土家族自治县
Shizhu Tujia Autonomous County0.438 0.370 1.635 0.820 云阳县 Yunyang County 1.894 0.502 1.793 1.359 忠县 Zhong County 1.438 0.448 0.832 0.876 沙坪坝区 Shapingba District 0.331 0.320 1.966 0.883 九龙坡区 Jiulongpo District 0.270 0.220 2.201 0.909 南岸区 Nan’an District 0.335 0.452 2.467 1.102 黔江区 Qianjiang District 0.327 0.392 2.952 1.243 南川区 Nanchuan District 0.302 0.419 2.96 1.248 江北区 Jiangbei District 0.243 0.452 3.059 1.276 大渡口区 Dadukou District 0.220 0.445 3.125 1.289 武隆区 Wulong District 0.251 0.400 3.195 1.306 彭水苗族土家族自治县
Pengshui Miao and Tujia Autonomous County0.465 0.290 3.222 1.339 巫溪县 Wuxi County 0.445 0.345 3.426 1.422 酉阳土家族苗族自治县
Youyang Tujia and Miao Autonomous County0.250 0.433 3.506 1.422 奉节县 Fengjie County 1.099 0.413 2.989 1.494 秀山土家族苗族自治县
Xiushan Tujia and Miao Autonomous County0.247 0.383 3.336 1.286 巫山县 Wushan County 1.438 0.493 3.267 1.720 城口县 Chengkou County 0.402 0.628 4.375 1.834 -
[1] 李卫, 薛彩霞, 朱瑞祥, 等. 中国农机装备水平区域不平衡的测度与分析[J]. 经济地理, 2014, 34(7): 116−122LI W, XUE C X, ZHU R X, et al. An imbalance analysis of China’ s agricultural machinery distribution[J]. Economic Geography, 2014, 34(7): 116−122 [2] 杨敏丽, 李世武, 恽竹恬. 区域农业机械化发展问题研究[J]. 中国农机化, 2010(1): 8–13Yang L M, LI S W, YUN Z T. Study on regional development of agricultural mechanization in China[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2010(1): 8–13 [3] 刘玉, 刘巧芹, 唐秀美, 等. 平原区耕作单元地块细碎化对小麦机收效率的影响分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(2): 225−231 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.02.029LIU Y, LIU Q Q, TANG X M, et al. Effects of fragmentation of cultivated land unit on mechanical harvesting efficiency of wheat in plain area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(2): 225−231 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.02.029 [4] 湛小梅, 聂华林, 李亚丽, 等. 宜机化整治地区油菜生产全程机械化作业体系研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2019, 40(7): 197−203ZHAN X M, NIE H L, LI Y L, et al. Study on mechanized operation system of rapeseed production in suitable for remediation areas[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40(7): 197−203 [5] 王梅. 丘陵山区农机化与乡村产业振兴[J]. 山东农机化, 2020(3): 20–21WANG M. Agricultural mechanization in hilly areas and rural industry revitalization[J]. Shandong Mechanization of Agriculture, 2020(3): 20–21 [6] 陈建. 我国丘陵山区应对农机化两大困境的新对策−基于宜机化土地整治[J]. 农机化研究, 2019, 41(4): 1−4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2019.04.001CHEN J. A new countermeasure against two severe difficulties in agricultural mechanization in China’s hilly and mountainous Areas— based on land consolidation for fitting large-medium farm machinery[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(4): 1−4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2019.04.001 [7] 陈印军, 肖碧林, 方琳娜, 等. 中国耕地质量状况分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(17): 3557−3564 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.17.008CHEN Y J, XIAO B L, FANG L N, et al. The quality analysis of cultivated land in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(17): 3557−3564 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.17.008 [8] 曾雄生. 从零碎化到园田化: 农田整治的历史反思[J]. 中国经济史研究, 2015(2): 89–102ZENG X S. From fragmentation to gardenization-historical reflections on farmland consolidation[J]. Researches in Chinese Economic History, 2015(2): 89–102 [9] 高强, 高桥五郎. 日本农地制度改革及对我国的启示[J]. 调研世界, 2012(5): 60–64GAO Q, GAO Q W L. Agricultural land System reform in Japan and its enlightenment to China[J]. The World of Survey and Research, 2012(5): 60–64 [10] KIM K U. Farm mechanization policies in Korea[J]. Asian Agricultural and Biological Engineering Association, 2009, 2(4): 132−143 doi: 10.11165/eaef.2.132 [11] 杨洲, 梁松练. 中国台湾农业机械化发展经验与启示[J]. 世界农业, 2006(8): 21–23YANG Z, LIANG S L. Experience of agricultural mechanization development in Taiwan, China[J]. World Agriculture, 2006(8): 21–23 [12] 罗锡文. 对发展丘陵山区农业机械化的思考[J]. 农机科技推广, 2011(2): 17–20LUO X W. Reflections on agricultural mechanization in developing hilly and mountainous areas[J]. Agriculture Machinery Technology Extension, 2011(2): 17–20 [13] 陈建, 陈川, 陈洪. 西南地区微耕机面临的三大新挑战及对策探讨[J]. 农机化研究, 2014, 36(10): 245−248CHEN J, CHEN C, CHEN H. Three new challenges micro tillers face in southwest China and study of countermeasures[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(10): 245−248 [14] 刘小伟. “改地适机”是丘陵山区农机化发展的治本之策[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2017, 38(7): 1–2LIU X W. Fundamental strategy for developing agricultural mechanization in hilly areas is adapting land for mechanization[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2017, 38(7): 1–2 [15] 崔思远, 金雪婷, 曹光乔. 我国丘陵山区农机化水平影响因素及区划研究−基于全国丘陵山区238个县(市)的调研数据[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(11): 129−134CUI S Y, JIN X T, CAO G Q. Study on the factors affecting the level of agricultural mechanization and regional division in hilly and mountainous areas of China — based on 238 counties (cities) investigations in hilly and mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(11): 129−134 [16] 敖方源, 秦大春, 周兵, 等. 重庆市丘陵山区宜机化地块整理整治实践[J]. 农业工程, 2017, 7(4): 122−124 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2017.04.036AO F Y, QIN D C, ZHOU B, et al. Application of land consolidation suitable for mechanization in hilly and mountainous areas of Chongqing City[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 7(4): 122−124 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2017.04.036 [17] 秦大春, 周兵, 敖方源. 重庆市丘陵山区农业机械化发展实践[J]. 农业工程, 2017, 7(1): 29−31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2017.01.008QIN D C, ZHOU B, AO F Y. Development practice of agricultural mechanization in hilly and mountainous areas of Chongqing City[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 7(1): 29−31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2017.01.008 [18] 陈伟, 朱继平, 陈小兵, 等. 我国坡耕地农业机械化发展现状[J]. 农机化研究, 2017, 39(5): 1−5, 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2017.05.001CHEN W, ZHU J P, CHEN X B, et al. The current situation of the development of agricultural mechanization of slope-farmland in our country[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2017, 39(5): 1−5, 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2017.05.001 [19] 王图展. 丘陵山区农业机械化发展的制约因素及对策−以重庆为例[J]. 农机化研究, 2013, 35(3): 24−28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2013.03.005WANG T Z. The restriction factor and countermeasure of agricultural mechanization in mountain and hill areas — A case study of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013, 35(3): 24−28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2013.03.005 [20] 田阡, 邓军. 丘陵山区农业机械化发展研究−重庆经验[J]. 农机化研究, 2012, 34(5): 16−20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2012.05.004TIAN Q, DENG J. Study on the development of agricultural mechanization in hilly and mountain areas — Chongqing experience[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2012, 34(5): 16−20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2012.05.004 [21] 湛小梅, 李亚丽, 李龙峰, 等. 重庆丘陵山区农业机械化发展战略研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2019, 40(1): 168−173ZHAN X M, LI Y L, LI L F, et al. Study on the development strategy of agricultural mechanization in the hilly and mountainous of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40(1): 168−173 [22] 封志明, 杨艳昭, 张晶, 等. 从栅格到县域: 中国粮食生产的资源潜力区域差异分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(5): 747−755, 854 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2007.05.009FENG Z M, YANG Y Z, ZHANG J, et al. A GIS based study on the grain productivity and potential yield increase at multi-levels in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2007, 22(5): 747−755, 854 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2007.05.009 [23] 胡义萍, 陈超, 曹磊, 等. 改进土地整治技术、推进丘陵山区农业机械化[J]. 国土资源导刊, 2014, 11(10): 19−22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2014.10.005HU Y P, CHEN C, CAO L, et al. Improve land consolidation technology and promote agricultural mechanization in hilly and mountainous areas[J]. Land & Resources Herald, 2014, 11(10): 19−22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2014.10.005 [24] 陈梅, 曹中华. 丘陵山区宜机化土地整治项目综合效益评价研究−基于改进AHP—模糊综合评价法[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2019, 40(1): 145−151CHEN M, CAO Z H. Research on comprehensive benefits evaluation of land consolidation in hilly and mountainous areas based on method of improved AHP-Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40(1): 145−151 [25] STERNER F. Resource suitability: Methods for analyses[J]. Environmental Management, 1983, 7(5): 401−420 doi: 10.1007/BF01867120 [26] 韦少凡, 华璀. 基于GIS的隆安县耕地土地适宜性评价[J]. 大众科技, 2012, 14(3): 106−108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2012.03.042WEI S F, HUA C. Cultivated land suitability assessment of Long’an County based on GIS[J]. Popular Science & Technology, 2012, 14(3): 106−108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2012.03.042 [27] 崔艳, 白中科, 张继栋, 等. 露天矿区农用地复垦适宜性评价的方法与应用[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(S1): 181−184CUI Y, BAI Z K, ZHANG J D, et al. Methods and application of agricultural land suitability evaluation in open-cast mining area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2008, 24(S1): 181−184 [28] 张清, 赵曜. 县域未利用地适宜性评价−以袁州区为例[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014, 42(29): 10364−10365 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2014.29.117ZHANG Q, ZHAO Y. The unused land suitability evaluation of the County — A case study of Yuanzhou District[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(29): 10364−10365 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2014.29.117 [29] WOTLOLAN D L, LOWRY J H, WALES N A, et al. Land suitability evaluation for multiple crop agroforestry planning using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis: A case study in Fiji[J]. Agroforestry Systems, 2021, DOI: 10.1007/S10457-021-00661-3 [30] YAO M L, SHAO D G, LV C H, et al. Evaluation of arable land suitability based on the suitability function — A case study of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 787(3): 147414 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147414 [31] KNAAPEN J P, HARMS BERT M H. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning[J]. Elsevier, 1992, 23(1): 1−16 [32] 李平星, 陈东, 樊杰. 基于最小费用距离模型的生态可占用性分析−以广西西江经济带为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(2): 227−236 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.02.006LI P X, CHEN D, FAN J. Research of ecological occupiability based on least-cost distance model — a case study on Xijiang River Economic Belt in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011, 26(2): 227−236 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.02.006 [33] 李涛, 廖和平, 潘卓, 等. 主体功能区国土空间开发利用效率评估−以重庆市为例[J]. 经济地理, 2015, 35(9): 157−164LI T, LIAO H P, PAN Z, et al. Evaluation of efficiency differentiation in land spatial development and utilization of major functional areas based on DEA model — a case study of Chongqing City[J]. Economic Geography, 2015, 35(9): 157−164 [34] 刘焱序, 彭建, 韩忆楠, 等. 基于OWA的低丘缓坡建设开发适宜性评价−以云南大理白族自治州为例[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(12): 3188−3197LIU Y X, PENG J, HAN Y N, et al. Suitability assessment for building land consolidation on gentle hillside based on OWA operator: a case in Dali Bai Nationality Borough in Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(12): 3188−3197 [35] 张晖, 王晓峰, 余正军. 基于ArcGIS的坡面复杂度因子提取与分析−以黄土高原为例[J]. 华中师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 43(2): 323−326ZHANG H, WANG X F, YU Z J. Slope surface complexity factor extract and analysis based on ArcGIS[J]. Journal of Huazhong Normal University: Natural Sciences, 2009, 43(2): 323−326 [36] 贾兴利, 许金良, 杨宏志, 等. 基于GIS的地表破碎指数计算[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2012, 35(11): 126−130 doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2012.11.021JIA X L, XU J L, YANG H Z, et al. Calculation of broken index of surface based on GIS[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2012, 35(11): 126−130 doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2012.11.021 [37] 杨雪, 谈明洪. 北京市耕地功能空间差异及其演变[J]. 地理研究, 2014, 33(6): 1106−1118YANG X, TAN M H. Spatial differences and evolution of arable land functions in Beijing[J]. Geographical Research, 2014, 33(6): 1106−1118 [38] 毛雪, 陈良松, 马友华, 等. 基于GIS的六安市茶叶种植适宜性评价研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(1): 188−194MAO X, CHEN L S, MA Y H, et al. Evaluation on suitability for the tea planting in Lu’ an City based on GIS[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(1): 188−194 [39] 张金光, 韦薇, 承颖怡, 等. 基于GIS适宜性评价的中小城市公园选址研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 44(1): 171−178ZHANG J G, WEI W, CHENG Y Y, et al. Study on site selection of small and medium-sized city parks based on GIS suitability evaluation[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 44(1): 171−178 [40] 易中懿, 曹光乔, 张宗毅. 我国南方丘陵山区农业机械化宏观影响因素分析[J]. 农机化研究, 2010, 32(8): 229−233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2010.08.059YI Z Y, CAO G Q, ZHANG Z Y. The analysis on macro-affected factors for agricultural mechanization in Chinese southern mountain and hill areas[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(8): 229−233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2010.08.059 [41] 傅幸之. 市县级国土空间农业生产适宜性评价方法优化[J]. 规划师, 2020, 36(8): 20−25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2020.08.003FU X Z. Improving agricultural production suitability evaluation of national land use and space at city and county levels[J]. Planners, 2020, 36(8): 20−25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2020.08.003 [42] 李春梅, 邵景安, 郭跃, 等. 基于地貌因子的高标准农田建设潜力研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(7): 1067−1079LI C M, SHAO J A, GUO Y, et al. Construction potential of high-standard farmland based on landform factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(7): 1067−1079 [43] 刘光盛, 赵乐松, 程迎轩, 等. 基于限制因子的粤北丘陵山区耕地宜机化整治分区[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(12): 262−270 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.12.030LIU G S, ZHAO L S, CHENG Y X, et al. Land consolidation zoning of northern Guangdong for suitable mechanization transformation in hilly and mountainous areas based on limiting factors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(12): 262−270 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.12.030 [44] 邓子怡. 重庆市万州区农用地整治潜力评价研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018DENG Z Y. Evaluation research of farmland consolidation potential in Wanzhou District of Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018 -





 下载:
下载: