The impacts of cultivar maturity and meteorological factors on main quality of potato
-
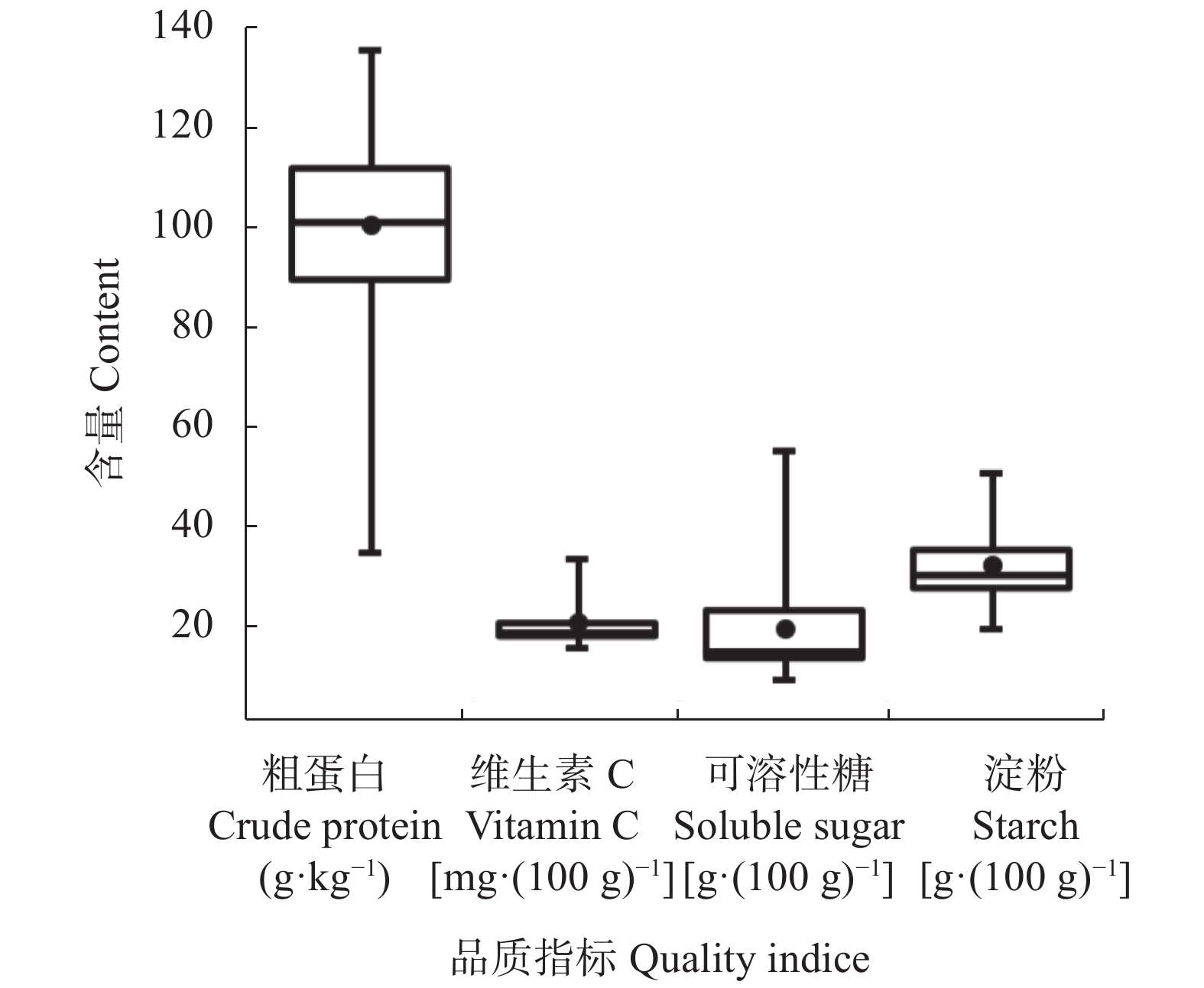
摘要: 品种和气象因子是决定马铃薯块茎品质的主要因素, 分析不同播期下生育期气象因子对不同品种马铃薯主要品质的影响对保障我国食物安全、丰富人民饮食结构具有重要意义。本文基于2018—2020年内蒙古武川马铃薯播期-品种耦合试验, 探究马铃薯块茎主要品质指标(粗蛋白、可溶性糖、淀粉和维生素C)随品种和播期的变化规律, 并解析不同品种和播期下各生育阶段气象因子对马铃薯主要品质的影响。主要结果如下: 马铃薯块茎主要品质指标变异系数为可溶性糖>淀粉>维生素C>粗蛋白; 基于隶属函数值的结果表明早熟品种‘费乌瑞它’早播(4月27日)、中熟品种‘康尼贝克’晚播(6月2日)和晚熟品种‘克新一号’中播(5月15日)的综合品质高于其他处理。播期和品种调控对马铃薯品质存在显著影响。而生殖生长阶段尤其是开花−成熟阶段的 气象因子决定了主要品质指标的形成, 限制当地马铃薯品质提升的主要气象因子为生育期平均温度和 降水量。‘费乌瑞它’粗蛋白含量随开花−成熟期的有效积温、日均温增加表现出显著下降趋势(P<0.05), 品种‘克新一号’粗蛋白含量随全生育期降水量增加表现出极显著下降趋势(P<0.01), 品种‘康尼贝克’粗蛋白含量和生育期气象因子均无显著相关。本研究定量了品种和气象因子对马铃薯块茎主要品质的影响, 结果可为优质马铃薯的品种筛选和科学种植提供理论依据。Abstract: Meteorological factors and cultivar maturity are the two determining factors of potato tuber quality. Analyzing the relationship between meteorological factors during the potato growth period and potato quality is of great significance for ensuring food security and enriching people’s dietary structure. On the basis of 2 years × 3-planting dates × 3-cultivars field experiment conducted in Wuchuan, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, the relationships between meteorological factors during different potato growth periods and the main indices of potato quality were quantified. On the basis of hydrothermal requirements during different potato growth stages, we divided the entire growth period into two periods, namely the vegetative growth period (planting-tuberization) and the reproductive growth period (tuberization-maturity), and then divided the reproductive growth period into tuberization to tuber bulking, tuber bulking to maturity. With the addition of the whole growth period and the water critical period (10 days before to 15 days after tuberization), six growth periods were set as the study phases. Five meteorological factors, namely effective accumulative temperature, mean temperature, daily temperature range, precipitation, and sunshine hours during the six growth periods were used to assess the relationships with potato quality, using correlation analysis, variance analysis, and membership function. The results showed that the average contents of crude protein, vitamin C, soluble sugar, and starch were 100.1 g∙kg−1, 19.64 mg∙(100g)−1, 18.58 g∙(100g)−1 and 31.48 g∙(100g)−1, respectively. The coefficients of variation for the main potato quality indices were in the order of soluble sugar > starch > vitamin C > crude protein. On the basis of membership function, the early maturing cultivar (‘Favorita’) with early planting (April 27), the middle maturing cultivar (‘Connibeck’) with late planting (June 2), and the late maturing cultivar (‘Kexin_1’) with middle planting (May 15) achieved the best potato quality when compared with other combinations of planting date and cultivar maturity. Ultimately, the coupling of planting date and cultivar had a significant effect on potato quality. Furthermore, meteorological factors had significant effects on potato quality during different potato growth periods. The results showed that potato tuber quality was mainly determined by meteorological factors during the potato reproductive growth period (tuberization-maturity), especially during tuber bulking to maturity.
-
Key words:
- Potato /
- Planting date /
- Cultivar /
- Starch /
- Vitamin C /
- Soluble sugar /
- Crude protein
-
图 1 2018—2020年不同播期下不同马铃薯品种的主要品质指标
箱体中的实线和“●”分别代表中值和均值, 箱体的上、下边界线分别代表75%和25%点位, 箱体外的短横线分别代表最大值和最小值。The solid line and “●” in the box body represent the median and mean values, respectively; the upper and lower boundaries of the box body represent 75% and 25% points, respectively; the short lines outside the box body represent the maximum and minimum values, respectively.
Figure 1. Main quality indices of different potato cultivars planted in different dates during 2018—2020
表 1 不同播期下不同马铃薯品种主要品质指标的平均隶属函数值
Table 1. Mean membership function values of different quality indices of different potato cultivars planted in different dates
品种
Cultivar播期(月-日)
Planting date (month-day)粗蛋白
Crude protein可溶性糖
Soluble sugar淀粉
Starch维生素C
Vitamin C平均隶属函数值
Mean membership function value费乌瑞它 Favorita 04-27 1.0 0.8 0.0 1.0 0.7 05-15 0.0 1.0 0.7 0.3 0.5 06-02 0.8 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.5 康尼贝克 Connibeck 04-27 0.9 0.7 0.0 1.0 0.7 05-15 0.0 0.0 0.8 0.0 0.2 06-02 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.3 0.8 克新一号 Kexin_1 04-27 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.3 05-15 1.0 1.0 0.4 1.0 0.8 06-02 0.4 0.9 0.0 0.9 0.5 表 2 2018—2020年播期和品种对马铃薯主要品质指标的互作效应
Table 2. Interactive effects of planting date and cultivar on main quality indices of potato during 2018−2020
年份
Year品质指标
Quality indice播期(月-日)
Planting date (month-day)品种
Cultivar显著性
Significance04-27 05-15 06-02 费乌瑞它
Favoritae康尼贝克
Connibeck克新一号
Kexin-1播期
Planting date (P)品种
Cultivar (C)播期×品种
P×C2018 粗蛋白
Crude protein (g∙kg−1)88.6±15.6a 90.3±4.9a 91.1±6.2a 88.9±6.4a 94.1±4.8a 87.0±14.0a 0.950 0.650 0.771 可溶性糖
Soluble sugar [g∙(100g)−1]28.8±8.2a 30.0±9.6a 29.2±4.6a 32.2±6.5a 24.3±3.9a 31.4±6.6a 0.971 0.198 0.473 淀粉
Starch [g∙(100g)−1]38.1±4.8a 38.0±4.5a 39.7±7.8a 39.4±5.3a 39.5±6.2a 36.9±5.1a 0.858 0.707 0.268 维生素C
Vitamin C [mg∙(100g)−1]24.7±3.6a 23.1±2.0a 23.3±2.6a 21.5±0.8a 24.4±3.8a 25.1±1.6a 0.757 0.235 0.607 2019 粗蛋白
Crude protein (g∙kg−1)101.8±18.9a 92.5±15.3a 102.0±24.9a 106.7±13.9a 102.0±24.8a 87.6±10.5b 0.356 0.019* 0.001** 可溶性糖
Soluble sugar [g∙(100g)−1]11.8±3.3a 13.1±0.1a 12.9±1.1a 11.1±2.6b 13.4±0.2a 13.3±0.2a 0.196 0.002** 0.001** 淀粉
Starch [g∙(100g)−1]24.1±5.8a 26.8±1.8a 27.1±4.0a 23.7±4.9b 26.1±3.3ab 28.3±2.2a 0.160 0.026* 0.001** 维生素C
Vitamin C [mg∙(100g)−1]18.0±1.2a 17.7±1.5a 18.0±1.2a 17.1±0.4b 19.2±0.0a 17.3±0.2b 0.830 0.001** 0.001** 2020 粗蛋白
Crude protein (g∙kg−1)115.4±6.4a 102.3±20.4a 117.0±14.7a 106.0±15.8a 108.7±18.5a 119.9±5.7a 0.144 0.203 0.040* 可溶性糖
Soluble sugar [g∙(100g)−1]14.0±0.9a 13.9±0.3a 13.4±0.4a 13.3±0.5a 13.9±0.5a 14.1±0.7a 0.495 0.269 0.700 淀粉
Starch [g∙(100g)−1]30.6±3.7a 30.4±2.6a 28.5±1.4a 27.7±0.9b 29.4±0.8b 32.4±2.6a 0.207 0.001** 0.001** 维生素C
Vitamin C [mg∙(100g)−1]17.3±0.2a 17.4±0.2a 17.3±0.1a 17.5±0.1a 17.2±0.1b 17.2±0.1b 0.858 0.038* 0.468 同行不同字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著, *表示显著影响(P<0.05), **表示极显著影响(P<0.01)。Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level. * and ** indicate significant effects at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. 表 3 马铃薯品种‘费乌瑞它’品质指标与各生长阶段气象因子线性关系的决定系数(R2)
Table 3. Coefficients of determination (R2) of linear relationships between tuber quality indices and meteorological factors at different growth stages for potato cultivar ‘Favorita’
气象因子
Meteorological factor品质指标
Quality indice全生育期
Whole growth period营养生长期
Vegetative growth period生殖生长期
Reproductive growth period现蕾—开花期
Tuberization to tuber bulking开花—成熟期
Tuber bulking to maturity水分关键期
Water critical period有效积温
Effective accumulative temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.26 0.35 −0.36 −0.03 −0.43* −0.12 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.23 −0.31 0.76** 0.47* 0.59* 0.55* 淀粉 Starch −0.42* −0.49* 0.58* 0.33 0.47* 0.66** 维生素 C Vitamin C −0.27 −0.40 0.85** 0.52* 0.66** 0.55* 日均温
Daily average temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.28 −0.03 −0.29 0.02 −0.44* −0.12 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.54* 0.03 0.29 0.26 0.81** 0.55* 淀粉 Starch 0.71** 0.21 0.57* 0.26 0.60** 0.66** 维生素C Vitamin C 0.55* 0.04 0.33 0.18 0.84** 0.55* 温度日较差
Daily temperature range粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.23 −0.14 0.32 −0.03 0.34 0.002 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.16 0.26 −0.54* 0.01 −0.49* 0.23 淀粉 Starch −0.35 0.16 −0.71** −0.04 −0.36 0.01 维生素C Vitamin C −0.19 0.25 −0.50* 0.02 −0.50* 0.16 降水量
Precipitation粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.14 0.11 −0.31 −0.10 −0.31 −0.39 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.30 −0.23 0.64** 0.35 0.60** 0.10 淀粉 Starch 0.15 −0.29 0.44* 0.54* 0.35 0.19 维生素C Vitamin C 0.33 0.26 0.72** 0.41 0.68** 0.11 日照时数
Sunshine hours粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.001 0.02 −0.24 −0.001 −0.18 −0.001 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.09 0.01 0.47* 0.08 0.21 0.36 淀粉 Starch −0.002 −0.05 0.27 0.01 0.18 0.16 维生素C Vitamin C 0.08 0.003 0.54* 0.12 0.22 0.25 *和**分别表示相关性达显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)水平, “−”表示品质指标与气象因子间呈负相关。* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. “−” indicates potato quality indice negatively correlated with meteorological factor. 表 4 马铃薯品种‘康尼贝克’品质指标与各生长阶段气象因子线性关系的决定系数(R2)
Table 4. Coefficients of determination (R2) of linear relationships between tuber quality indices and meteorological factors at different growth stages for potato cultivar ‘Connibeck’
气象因子
Meteorological factor品质指标
Quality indice全生育期
Whole growth period营养生长期
Vegetative growth period生殖生长期
Reproductive growth period现蕾—开花期
Tuberization to tuber bulking开花—成熟期
Tuber bulking to maturity水分关键期
Water critical period有效积温
Effective accumulative temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.01 −0.01 −0.001 0.004 −0.03 −0.14 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.27 −0.21 0.78** 0.44* 0.52* 0.30 淀粉 Starch −0.46* −0.36 0.53* 0.39 0.23 0.56* 维生素C Vitamin C −0.07 −0.05 0.64** 0.23 0.70** 0.14 日均温
Daily average temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.13 −0.01 −0.20 −0.11 −0.13 −0.14 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.63** 0.18 0.71** 0.03 0.56* 0.30 淀粉 Starch 0.81** 0.40 0.73** 0.15 0.39 0.56* 维生素C Vitamin C 0.37 0.02 0.39 0.03 0.68** 0.14 温度日较差
Daily temperature range粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.02 0.01 0.09 0.18 0.01 0.04 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.36 0.02 −0.84** −0.15 −0.36 −0.19 淀粉 Starch −0.43* −0.001 −0.66** −0.34 −0.18 −0.31 维生素C Vitamin C −0.20 0.02 −0.68** −0.03 −0.49* −0.002 降水量
Precipitation粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.13 −0.04 −0.09 −0.07 −0.02 −0.04 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.34 −0.14 0.69** 0.72** 0.06 0.69** 淀粉 Starch 0.16 −0.24 0.46* 0.53* 0.02 0.49* 维生素C Vitamin C 0.59* −0.001 0.75** 0.30 0.37 0.28 日照时数
Sunshine hours粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.003 −0.01 0.11 0.14 −0.02 −0.001 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.02 0.001 0.54* 0.08 0.13 −0.15 淀粉 Starch −0.03 −0.07 0.34 0.07 0.05 −0.09 维生素C Vitamin C 0.18 0.10 0.35 0.02 0.15 −0.05 *和**分别表示相关性达显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)水平, “−”表示品质指标与气象因子间呈负相关。* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. “−” indicates potato quality indice negatively correlated with meteorological factor. 表 5 马铃薯品种‘克新一号’品质指标与各生长阶段气象因子线性关系的决定系数(R2)
Table 5. Coefficients of determination (R2) of linear relationships between tuber quality indices and meteorological factors at different growth stages for potato cultivar ‘Kexin_1’
气象因子
Meteorological factor品质指标
Quality indice全生育期
Whole growth period营养生长期
Vegetative growth period生殖生长期
Reproductive growth period现蕾—开花期
Tuberization to tuber bulking开花—成熟期
Tuber bulking to maturity水分关键期
Water critical period有效积温
Effective accumulative temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.03 0.03 −0.16 −0.04 −0.14 −0.01 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.18 −0.19 0.54* 0.12 0.50* 0.48* 淀粉 Starch 0.07 0.09 0.65** 0.11 0.66** 0.38 维生素C Vitamin C −0.16 −0.16 0.61** 0.11 0.60** 0.47* 日均温
Daily average temperature粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.07 0.001 −0.15 −0.005 −0.26 −0.006 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.61** 0.25 0.89** 0.04 0.55* 0.48* 淀粉 Starch 0.15 −0.01 0.26 0.04 0.64** 0.38 维生素C Vitamin C 0.62** 0.20 0.90** 0.03 0.66** 0.47* 温度日较差
Daily temperature range粗蛋白 Crude protein 0.12 0.007 0.12 −0.001 0.16 −0.01 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar −0.57* 0.01 −0.86** −0.23 −0.55* −0.25 淀粉 Starch −0.04 0.34 −0.61** −0.01 −0.70** 0.03 维生素C Vitamin C −0.55* 0.02 −0.88** −0.20 −0.61** −0.18 降水量
Precipitation粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.86** −0.37 −0.61** −0.11 −0.54* −0.13 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.38 −0.11 0.67** 0.66** 0.16 0.54* 淀粉 Starch 0.12 −0.27 0.29 0.03 0.30 0.02 维生素C Vitamin C 0.47* −0.08 0.75** 0.66** 0.21 0.55* 日照时数
Sunshine hours粗蛋白 Crude protein −0.04 −0.06 0.004 0.001 0.003 0.07 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.04 0.001 0.47* −0.04 0.68** −0.08 淀粉 Starch 0.55* 0.47* 0.34 −0.004 0.35 0.07 维生素C Vitamin C 0.07 0.01 0.44* −0.05 0.68** −0.07 *和**分别表示相关性达显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)水平, “−”表示品质指标与气象因子间呈负相关。* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. “−” indicates potato quality indice negatively correlated with meteorological factor. -
[1] 张千友, 王万疆, 廖武霜. 马铃薯主粮化与产业开发研究综述[J]. 西昌学院学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 30(2): 1−5ZHANG Q Y, WANG W J, LIAO W S. The review of the researches on the promotion and industrialization of potatoes as the staple food[J]. Journal of Xichang College: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 30(2): 1−5 [2] 仇菊, 朱宏, 朱大洲, 等. 不同加工用途马铃薯品质特性分析[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2019, 33(6): 372−378QIU J, ZHU H, ZHU D Z, et al. Quality characteristics analyses of potatoes for different processing purposes[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2019, 33(6): 372−378 [3] VAN NIEKERK C, SCHÖNFELDT H, HALL N, et al. The role of biodiversity in food security and nutrition: a potato cultivar case study[J]. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 2016, 7(5): 371−382 doi: 10.4236/fns.2016.75039 [4] 潘峰. 马铃薯种质资源品质性状及利用价值的评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019: 12–13PAN F. Evaluation of quality characters and utilization value of potato germplasm resources[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019: 12–13 [5] 李扬, 王靖, 唐建昭, 等. 播期和品种变化对马铃薯产量的耦合效应[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(2): 296−304LI Y, WANG J, TANG J Z, et al. Coupling impacts of planting date and cultivar on potato yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(2): 296−304 [6] 宋学锋, 侯琼. 气候条件对马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2003, 24(2): 35−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2003.02.011SONG X F, HOU Q. Influence of climate conditions on potato yield[J]. Agricultural Meteorology, 2003, 24(2): 35−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2003.02.011 [7] 宋玉芝, 王连喜, 李剑萍. 气候变化对黄土高原马铃薯生产的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(3): 1018−1019 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.03.047SONG Y Z, WANG L X, LI J P. Influence of climate change on potato production in the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(3): 1018−1019 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.03.047 [8] 王榛. 浙江省不同生态环境马铃薯品质评价[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2017: 10–11WANG Z. Quality evaluation of potatoes in different ecological environment in Zhejiang Province[D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2017: 10–11 [9] 王朝晖, 钟林光, 李景龙. 主要气象因子与抗虫杂交棉纤维品质的关系[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 37(8): 101−108WANG Z H, ZHONG L G, LI J L. Study on the relationship between main meteorological factors and fiber quality of insect-resistant hybrid cotton[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 37(8): 101−108 [10] 肖国举, 仇正跻, 张峰举, 等. 增温对西北半干旱区马铃薯产量和品质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(3): 830−836XIAO G J, QIU Z J, ZHANG F J, et al. Influence of increased temperature on the potato yield and quality in a semiarid district of Northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(3): 830−836 [11] 潘小番, 张恒嘉, 邓浩亮, 等. 河西绿洲不同生育期调亏灌溉对马铃薯生长、产量及品质的影响[J]. 农业工程, 2021, 11(2): 130−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2021.02.026PAN X F, ZHANG H J, DENG H L, et al. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages on potato growth, yield and quality in Hexi oasis[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 11(2): 130−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2021.02.026 [12] 杨炳南, 张小燕, 赵凤敏, 等. 不同马铃薯品种的不同加工产品适宜性评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(20): 301−308 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.20.042YANG B N, ZHANG X Y, ZHAO F M, et al. Suitability evaluation of different potato cultivars for processing products[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(20): 301−308 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.20.042 [13] 王颖, 潘哲超, 梁淑敏, 等. 4个马铃薯品种淀粉的理化特性[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2016, 44(11): 24−28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.11.005WANG Y, PAN Z C, LIANG S M, et al. Starch physicochemical property of four potato varieties[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(11): 24−28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.11.005 [14] 张凤军, 张永成, 田丰. 不同生态环境马铃薯维生素C含量分析[J]. 种子, 2006, 25(12): 24−27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2006.12.007ZHANG F J, ZHANG Y C, TIAN F. Analysis for vitamin C content of potato in differ ecological environment[J]. Seed, 2006, 25(12): 24−27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2006.12.007 [15] 张永成, 田丰. 马铃薯试验研究方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2007ZHANG Y C, TIAN F. Research Methods of Potato Experiment[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2007 [16] 王谧, 王芳, 王舰. 应用隶属函数法对马铃薯进行抗旱性综合评价[J]. 云南农业大学学报: 自然科学, 2014, 29(4): 476−481WANG M, WANG F, WANG J. Evaluation of potato drought resistance by subordinate function[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University: Natural Science, 2014, 29(4): 476−481 [17] 李扬, 王靖, 唐建昭, 等. 农牧交错带马铃薯高产和水分高效利用的播期和品种选择[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(4): 118−126 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.04.014LI Y, WANG J, TANG J Z, et al. Selecting planting date and cultivar for high yield and water use efficiency of potato across the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(4): 118−126 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.04.014 [18] 唐建昭. 北方农牧交错带马铃薯基于缩差和增效的种植管理模式研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018: 22–28TANG J Z. A study on planting pattern of potato to narrow yield gap and increase precipitation use efficiency in the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018: 22–28 [19] 李扬. 播期和品种耦合对北方农牧交错带马铃薯产量和品质的影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2019: 36–37LI Y. A study on the coupling effects of planting date and cultivar on potato yield and quality in the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2019: 36–37 [20] 张荣华, 许庆芬, 杨艳华, 等. 不同播期对马铃薯淀粉含量与产量的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2011(4): 20–21ZHANG R H, XU Q F, YANG Y H, et al. Effects of different sowing date on starch content and yield of potato[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011(4): 20–21 [21] 李琪, 谢萍, 李剑萍, 等. 不同播期对宁夏粉用马铃薯生长和品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(12): 220−226LI Q, XIE P, LI J P, et al. Effects of different sowing periods on growth and quality of starch potato in Ningxia[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(12): 220−226 [22] 刘凯, 张琦琦, 石瑛, 等. 不同生态条件下马铃薯品种的淀粉含量分析[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2008, 22(2): 85−87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2008.02.007LIU K, ZHANG Q Q, SHI Y, et al. Starch content of six potato varieties under different ecological environments[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2008, 22(2): 85−87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2008.02.007 [23] 姚玉璧, 雷俊, 夏权, 等. 气候变化主要因子对马铃薯生物量积累及产量和品质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 1−9YAO Y B, LEI J, XIA Q, et al. Impacts of the main factors for climate change on potato biomass accumulation and potato yield and quality[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(1): 1−9 [24] 朱杰, 宿秀丽, 吴国文, 等. 不同品种马铃薯块茎品质的分析与评价[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(24): 41−44ZHU J, SU X L, WU G W, et al. Analysis and evaluation on tuber quality of different potato varieties[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 59(24): 41−44 [25] 梁烜赫, 高华援, 刘峰, 等. 影响马铃薯淀粉产量的因素研究[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2008, 22(6): 339−341 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2008.06.006LIANG H H, GAO H Y, LIU F, et al. A study on the factors of affecting potato starch[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2008, 22(6): 339−341 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2008.06.006 [26] 梁振娟, 周平, 陆燚, 等. 不同马铃薯品种叶片光合特性研究[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2020, 26(20): 17−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2020.20.008LIANG Z J, ZHOU P, LU Y, et al. A study on photosynthetic characteristics of leaves of different potato varieties[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 26(20): 17−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2020.20.008 [27] 张宝林, 高聚林, 刘克礼. 马铃薯在不同密度及施肥处理下叶片叶绿素含量的变化[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2003, 17(3): 137−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2003.03.002ZHANG B L, GAO J L, LIU K L. Chlorophyll content in leaves of potatoes treated with different density and fertilizer rate[J]. Chinese Potato, 2003, 17(3): 137−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2003.03.002 [28] 王惠群, 萧浪涛, 李合松, 等. 矮壮素对马铃薯中薯3号光合特征和磷素营养的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(6): 1143−1147 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505x.2007.06.025WANG H Q, XIAO L T, LI H S, et al. Effects of chlorocholine chloride on photosynthetic characteristics and phosphate nutrition of potato Zhongshu 3[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007, 13(6): 1143−1147 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505x.2007.06.025 [29] 王立春. 克山地区气象因子与马铃薯品质的关系[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2014, 28(2): 73−77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2014.02.003WANG L C. Relationship between meteorological factor and potato quality in Keshan[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2014, 28(2): 73−77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2014.02.003 [30] 罗爱花, 陆立银, 王一航, 等. 播期对中早熟马铃薯LK99原种产量效益及贮藏性能的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2011(4): 102–103LUO A H, LU L Y, WANG Y H, et al. Effect of sowing date on yield and storage performance of medium and early maturing potato LK99[J]. Crops , 2011(4): 102–103 [31] 云冬梅, 云存柱, 蔺淑岚, 等. 2012年和林格尔县玉米、马铃薯、大豆全生育期气候评述[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2013, 41(2): 94−96, 114YUN D M, YUN C Z, LIN S L, et al. In 2012 Helingeer County corn, potato, soybean growth period of climate comment[J]. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013, 41(2): 94−96, 114 [32] 杨宁. 内蒙古农牧交错带主要作物对气候的敏感性与适应弹性研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014: 44–58YANG N. Climate sensitivity and adaptation flexibility for five dominant crops in agro-pastoral ecotone in Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014: 44–58 [33] 景彩艳. 甘肃省气候条件对马铃薯生产安全影响浅析[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2008(3): 39–41JING C Y. The impact of climate changes on potato production safety in Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2008(3): 39–41 [34] 云文丽, 苗百岭. 内蒙古马铃薯干旱等级指标研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(2): 220−226 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2021.02.28YUN W L, MIAO B L. A study of drought index of potato in Inner Mongolia[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2021, 39(2): 220−226 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2021.02.28 [35] 代海林. 揭膜时间对全膜垄播马铃薯水肥运移规律及产量、品质的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013: 40–45DAI H L. Effects of film-uncovering time on soil moisture movement, yield and quality of potato under completely mulched with ridge planting[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013: 40–45 [36] 朴炫春, 廉美兰, 张志东, 等. 光通量和温差对马铃薯试管苗生长的影响[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2004, 26(6): 620−623 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5684.2004.06.008PIAO X C, LIAN M L, ZHANG Z D, et al. Effects of PPF and DIF on growth of potato in vitro[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2004, 26(6): 620−623 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5684.2004.06.008 [37] 于文颖, 纪瑞鹏, 冯锐, 等. 不同生育期玉米叶片光合特性及水分利用效率对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(9): 2902−2909YU W Y, JI R P, FENG R, et al. Response of water stress on photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency of maize leaves in different growth stage[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(9): 2902−2909 [38] 朱钦士. 光合作用中光反应的机制和由来(6)[J]. 生物学通报, 2019, 54(7): 5−8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2019.07.003ZHU Q S. The mechanism and origin of photosynthetic light reactions(6)[J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2019, 54(7): 5−8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2019.07.003 [39] 马文军, 武均, 宋雪峰, 等. 不同施肥处理对马铃薯农田土壤理化性状及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(15): 87−91 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0449MA W J, WU J, SONG X F, et al. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil physical and chemical properties and yield of potato[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(15): 87−91 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0449 [40] 王乾, 杨术明, 杨树川, 等. 宁夏固原地区马铃薯种植粉垄耕作试验研究[J]. 农业科学研究, 2021, 42(1): 88−92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2021.01.016WANG Q, YANG S M, YANG S C, et al. Report of smash-ridging cultivation technology on planting potato in Ningxia Guyuan Area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 42(1): 88−92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2021.01.016 [41] 任勇. 马铃薯病虫害防治技术[J]. 农家参谋, 2021(6): 96–97REN Y. Pest control technology of potato[J]. Adviser of Peasant Families, 2021(4): 96–97 [42] 张宇新, 王鹏程, 张春雨, 等. 滴灌田‘大西洋’马铃薯种植密度对产量及效益影响[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2021, 35(1): 24−29ZHANG Y X, WANG P C, ZHANG C Y, et al. Effect of planting density on yield and benefit of potato variety ‘Atlantic’ planted in drip irrigation field[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2021, 35(1): 24−29 -





 下载:
下载: