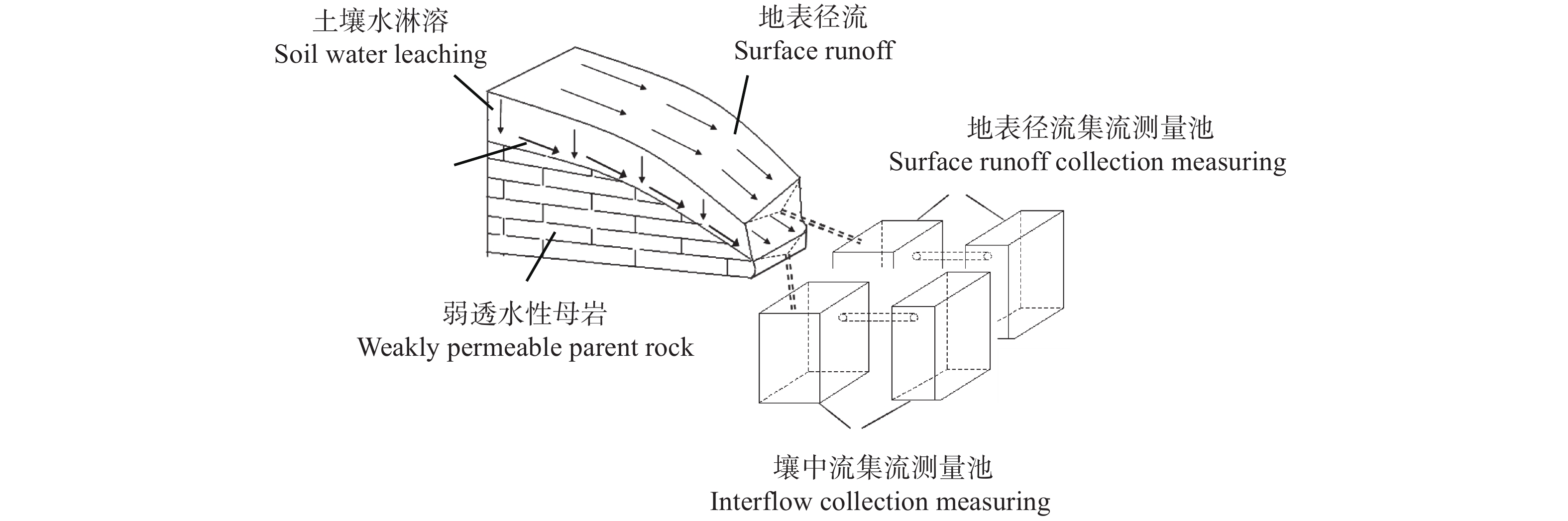
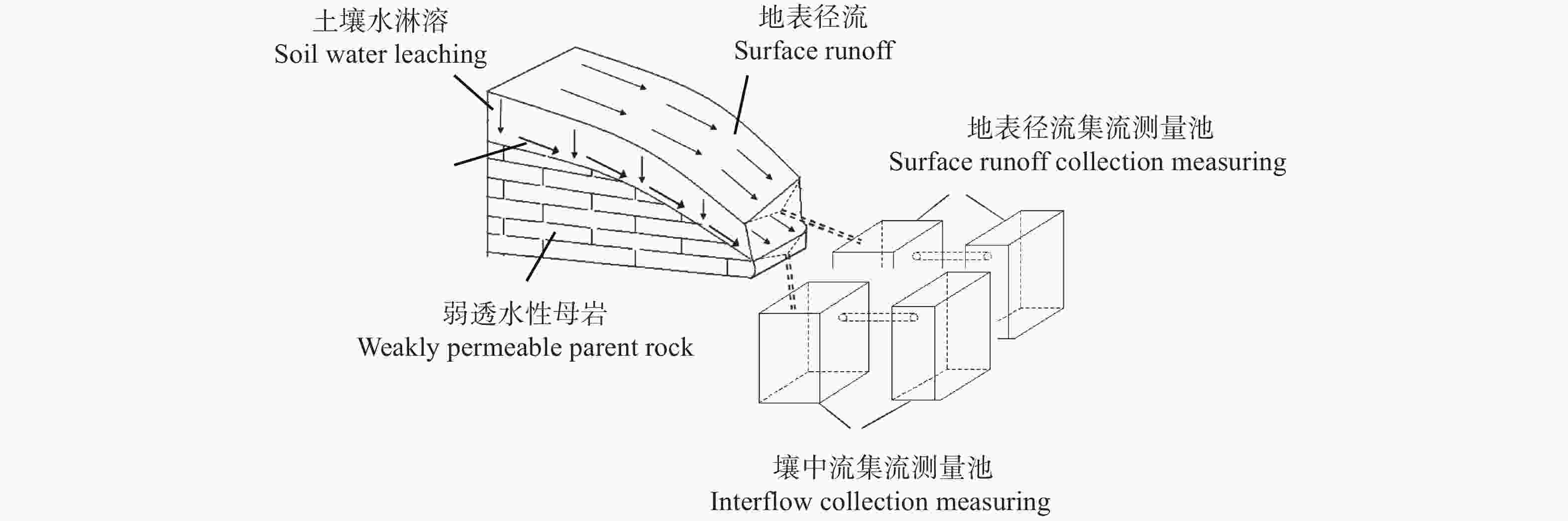
Impact of substitution of synthetic nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizers on nitrogen loss from sloping cropland of purple soil
-
摘要: 为明确紫色土有机肥替代化肥的农学与环境效应, 减少紫色土氮素面源污染, 进一步为紫色土化肥“零增长”策略提供科学依据, 利用紫色土坡地养分管理长期试验平台, 结合自由排水采集器(Free-drain Lysimeter)定位观测, 研究紫色土坡耕地小麦-玉米轮作期间(2012—2013年)不同施肥方式下的土壤无机氮动态、作物产量、氮素流失路径与总量。等氮下设置5个施肥处理: 单施化学氮肥(N)、常规化肥(NPK)、猪厩肥(猪厩肥替代100%的化肥氮, OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(猪厩肥替代30%的化肥氮, OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(秸秆替代15%的化肥氮, CRNPK), 以不施肥(NF)为对照。结果表明, 紫色土坡耕地壤中流流量占总径流量的54.5%~84.6%, 随壤中流淋失的氮占氮流失总量的90.6%, 以壤中流为介导的氮淋失是紫色土坡耕地氮素流失的首要途径, 且氮淋失量高达12.53~76.72 kg(N)·hm−2, 远高于我国其他地区农田氮淋失量, 紫色土地区是氮淋失的热点区域。与常规施肥(NPK)相比, 有机肥替代化肥显著降低紫色土氮素流失量, 其中猪厩肥(OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(CRNPK)总氮素流失量分别减少32.1% (P<0.05)、27.5% (P<0.05)与21.2% (P<0.05), 其关键机制在于有机肥替代化肥对氮淋失的减控作用, 通过壤中流淋失的氮素分别减少32.0% (P<0.05)、26.7% (P<0.05)与18.0% (P<0.05); 此外, 氮流失系数分别降低44.8%、38.5%及24.3%, 玉米-小麦轮作系统年产量分别增加23.0%、17.8%及4.1%。因此, 长期有机肥替代化肥能在减量施用化肥的基础上保证作物产量, 同时显著降低紫色土坡耕地氮流失风险, 是当前紫色土坡耕地可推荐的减氮增效技术。Abstract: Excessive N fertilizer application not only increases crop productivity, but also induces substantial environmental N losses that cause large environmental pollution risks. This study aimed to examine the effects of substituting synthetic N fertilizers with organic fertilizers on the reduction in environmental N losses from croplands in purple soil areas. Therefore, we conducted a one year field investigation to measure N-loss pathways and fluxes, crop productivity, and soil environmental variables in a wheat-maize rotation system under long-term different fertilization regimes with the same N rate, including the control (no fertilizer; NF); synthetic N fertilizer only (N); pig manure substituting 100% synthetic N fertilizer (pig manure; OM); regular synthetic N, P, and K fertilizer (NPK); combination of pig manure with synthetic N, P, and K fertilizer (OMNPK; pig manure substituting 30% synthetic N fertilizer); and combination of straw residue returned with synthetic N, P, and K fertilizer (CRNPK; straw residue substituting 15% synthetic N fertilizer). The results showed that N losses via surface runoff and sediment were in the range of 1.12–3.52 kg(N)∙hm−2 and 1.48–7.26 kg(N)∙hm−2, respectively. The N leaching losses via interflow ranged from 12.53 to 76.72 kg(N)∙hm−2, which were over 10 times greater than those for surface runoff; nevertheless, N leaching losses accounted for 90.6% of the total hydrological N losses. These results indicate that N leaching via interflow is the predominant pathway of hydrological N losses, thereby highlighting that sloping cropland of purple soil is one of the hotspots of N leaching losses from agricultural soils in China. Compared with that of the NPK treatment, the substitution of synthetic N fertilizer with organic fertilizers (OM, OMNPK, and CRNPK treatments) decreased the total hydrological N losses by 32.1%, 27.5%, and 21.2%, respectively. This was mainly because practices with substitution of synthetic N fertilizer with organic fertilizers significantly decreased N leaching losses via interflow compared with the application of synthetic N fertilizer only. Furthermore, considering the crop yields, the substitution of synthetic N fertilizer with organic fertilizer treatments (OM, OMNPK, and CRNPK treatments) significantly increased the total annual crop yields by 23.0%, 17.8%, and 4.1%, respectively, and decreased the yield-scaled total hydrological N losses by 24.3% to 44.8%. Therefore, the long-term substitution of synthetic N fertilizer with organic fertilizer can not only increase the crop productivity of both wheat and maize, but also decrease environmental N losses, thereby decreasing the risk of agricultural non-point source pollution in the purple soil region. Overall, the substitution of synthetic N fertilizer with organic fertilizers can be recommended as an optimized agricultural N management strategy to reduce synthetic N fertilizer rates and improve N use efficiency in agricultural systems of the purple soil region.
-
Key words:
- Purple soil /
- Sloping cropland /
- Interflow /
- Nitrogen loss /
- Nitrogen leaching /
- Organic fertilizer /
- Improved fertilization
-
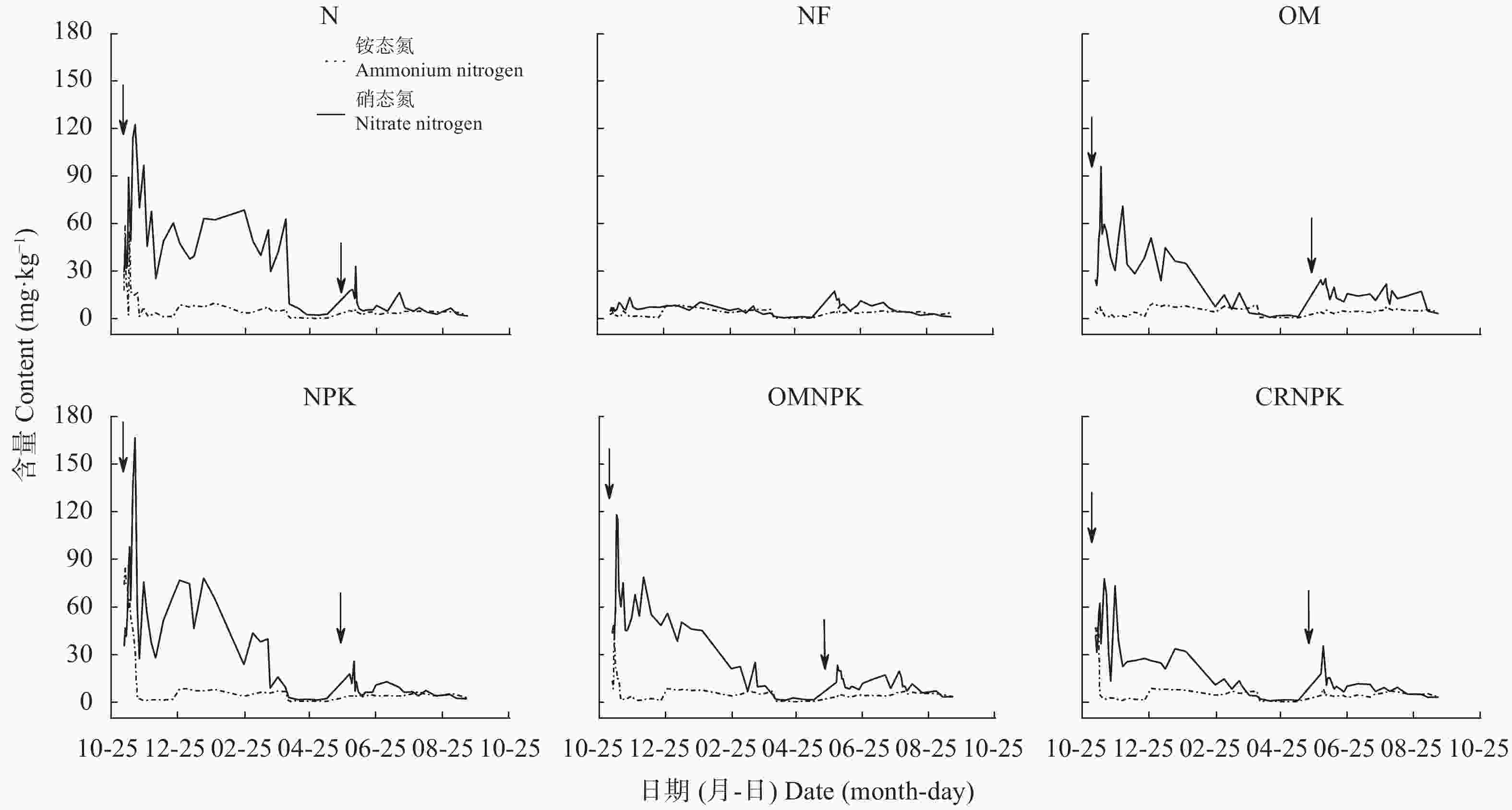
图 3 不同施肥方式下的紫色土表土(0~10 cm)无机氮含量变化
图中各施肥处理分别为单施氮肥(N)、常规施肥(NPK)、猪厩肥(OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(CRNPK)及不施肥(NF)。图中两个箭头分别指示小麦季(11月5日)和玉米季(6月1日)施肥。
Figure 3. Changes of topsoil (0−10 cm) inorganic nitrogen contents under different fertilization regimes on sloping cropland of purple soil
Fertilization treatments in the figure are: nitrogen fertilizer only (N), regular synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (NPK), pig manure (OM), combination of pig manure with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (OMNPK), combined application of straw residue with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (CRNPK). Two arrows in the figures indicate fertilization on November 5 in wheat season and on June 1 in maize season, respectively.
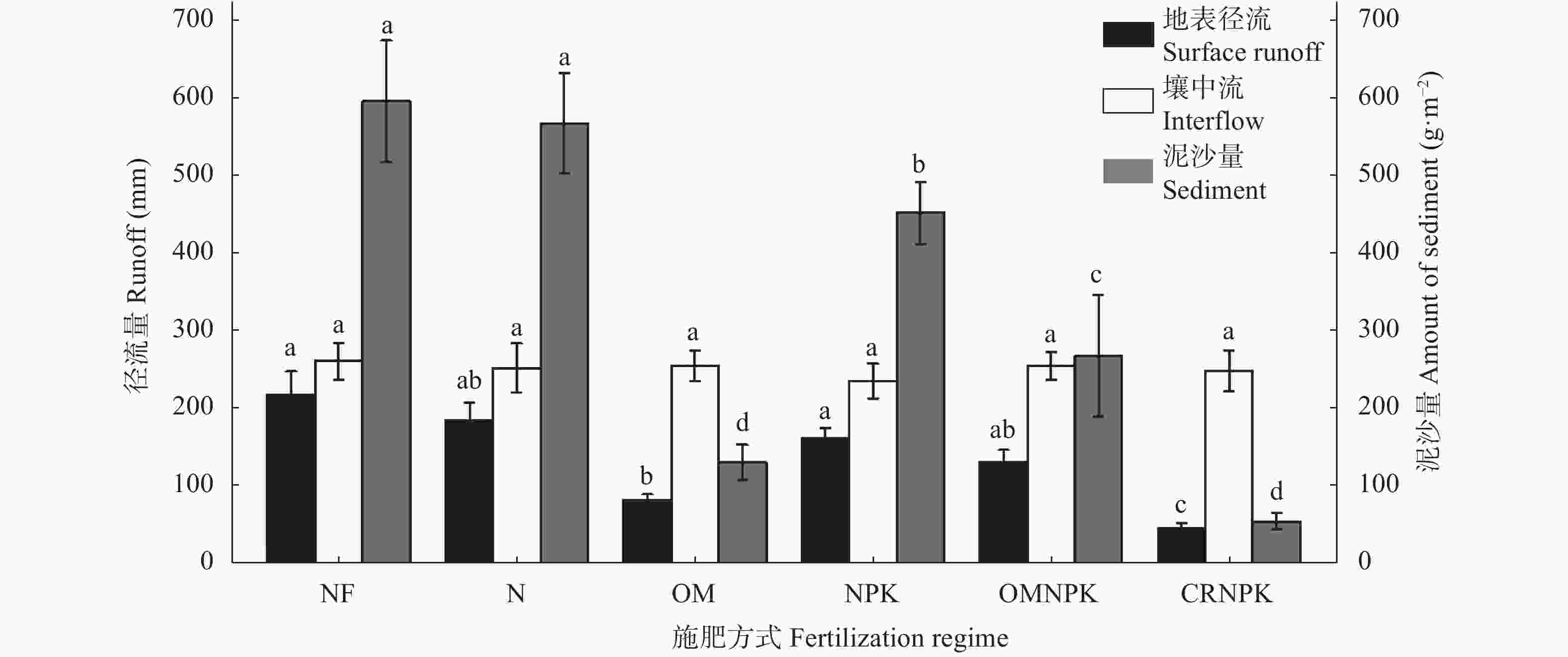
图 4 不同施肥方式下紫色土坡耕地的地表径流、壤中流流量和泥沙量
图中各施肥处理分别为单施氮肥(N)、常规施肥(NPK)、猪厩肥(OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(CRNPK)及不施肥(NF)。不同小写字母代表施肥处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4. Discharge of overland runoff, interflow and sediment yield under different fertilization regimes on sloping cropland of purple soil
Fertilization treatments in the figure are: nitrogen fertilizer only (N), regular synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (NPK), pig manure (OM), combination of pig manure with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (OMNPK), combination of straw residue with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (CRNPK). Different lowercases letters in the figure indicate significant differences among ferilization regimes at P<0.05 level .
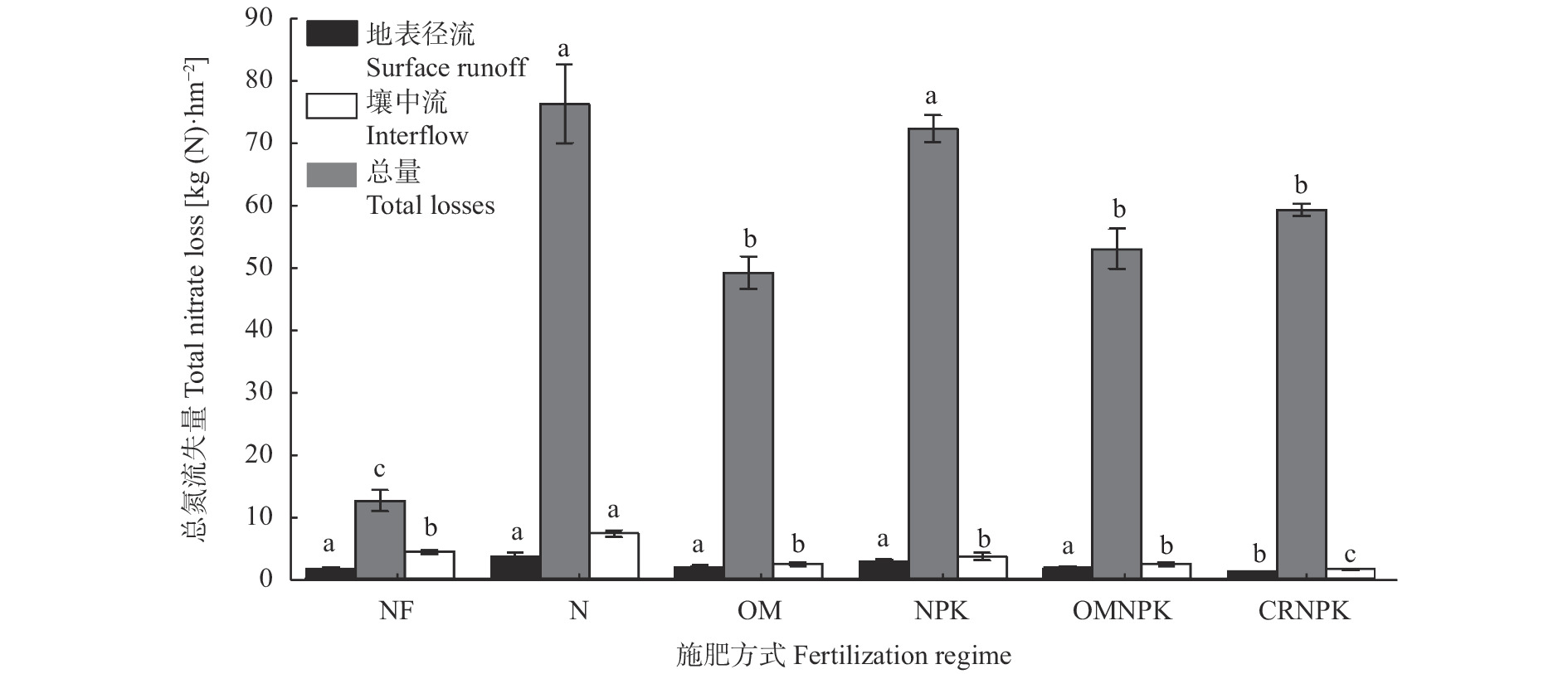
图 5 不同施肥方式下紫色土坡耕地氮素流失路径与总量
图中各施肥处理分别为单施氮肥(N)、常规施肥(NPK)、猪厩肥(OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(CRNPK)及不施肥(NF)。不同小写字母代表施肥处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5. Nitrogen loss pathways and fluxes from sloping cropland of purple soil under different fertilization regimes
Fertilization treatments in the figure are: nitrogen fertilizer only (N), regular synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (NPK), pig manure (OM), combination of pig manure with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (OMNPK), combination of straw residue with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (CRNPK). Different lowercases letters in the figure indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
表 1 不同施肥方式下小麦-玉米轮作系统的作物生物量、产量、总氮流失量及氮流失系数(2012—2013年)
Table 1. Biomass, crop yield, nitrogen loss and nitrogen loss coefficient of wheat-maize rotation system under different fertilization regimes (2012−2013)
施肥方式
Fertilization regime生物量
Biomass (t∙hm−2)产量
Crop yield (t∙hm−2)总氮流失量Total nitrogen loss
[kg(N)∙hm−2]基于单位产量的氮流失系数Nitrogen loss per unit yield (kg∙hm−2∙t−1) 小麦
Wheat玉米
Maize小麦
Wheat玉米
Maize合计
TotalNF 3.12±0.41b 2.51±0.77d 0.84±0.18b 1.84±0.62d 2.68±0.87c 18.26±3.16a 6.81 N 2.19±0.48b 4.89±1.03c 0.81±0.20b 3.23±0.61cd 4.04±0.76c 87.50±8.51b 21.66 OM 7.80±0.18a 10.55±1.01a 2.74±0.26a 7.21±1.38a 9.95±1.41a 53.58±2.69c 5.38 NPK 6.62±1.66a 9.11±0.44ab 2.39±0.36a 5.70±0.32ab 8.09±0.30ab 78.91±3.34b 9.75 OMNPK 7.40±0.90a 9.79±1.17a 2.50±0.11a 7.03±1.37a 9.53±1.47ab 57.20±2.38c 6.00 CRNPK 7.82±0.79a 7.76±0.74b 2.69±0.13a 5.73±1.37bc 8.42±1.39b 62.15±1.25c 7.38 图中各施肥处理分别为单施氮肥(N)、常规施肥(NPK)、猪厩肥(OM)、猪厩肥与氮磷钾配施(OMNPK)、秸秆还田与氮磷钾配施(CRNPK)及不施肥(NF)。不同小写字母代表施肥处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。Fertilization treatments in the figure are: nitrogen fertilizer only (N), regular synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (NPK), pig manure (OM), combination of pig manure with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (OMNPK), combination of straw residue with synthetic nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (CRNPK). Different lowercases letters in the figure indicate significant differences among fertilization regimes at P<0.05 level. -
[1] 张福锁, 张卫峰, 马文奇. 中国化肥产业技术与展望[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 32–33ZHANG F S, ZHANG W F, MA W Q. Fertilizer Technology and Development in China[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007: 32–33 [2] 国家统计局. 国家统计年鉴2018[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018National Bureau of Statistics. National Statistical Yearbook 2018[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018 [3] EVANS J E, LEVINE N S, ROBERTS S J, et al. Assessment using GIS and sediment routing of the proposed removal of ballville dam, Sandusky River, Ohio[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2002, 38(6): 1549−1565 doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2002.tb04364.x [4] JU X T, KOU C L, ZHANG F S, et al. Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: Comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 143(1): 117−125 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.005 [5] GAO W, HOWARTH R W, SWANEY D P, et al. Enhanced N input to lake Dianchi basin from 1980 to 2010: drivers and consequences[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 505: 376−384 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.016 [6] RADWAN S, AWAD N M. Effect of soil amendment with various organic wastes with multi-biofertilizer on yield of peanut plants in sandy soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences of Mansoura University, 2002, 27(5): 3129−3138 [7] MICHAEL A T. Effect of tillage, biochar, poultry manure and NPK 15-15-15 fertilizer, and their mixture on soil properties, growth and carrot (Daucus carota L.) yield under tropical conditions[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(6): 1−11 [8] HAAS G, BERG M, KOPKE U. Nitrate leaching: comparing conventional, integrated and organic agricultural production systems[C]. IAHS Publication, 2000: 131–136 [9] 沈灵凤, 白玲玉, 曾希柏, 等. 施肥对设施菜地土壤硝态氮累积及pH的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(7): 1350−1356SHEN L F, BAI L Y, ZENG X B, et al. Effects of fertilization on NO3–-N accumulation in greenhouse soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(7): 1350−1356 [10] 裴雪霞, 党建友, 张定一, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥对旱地小麦产量、品质和水分利用率的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 250−258PEI X X, DANG J Y, ZHANG D Y, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer on the yield, quality, and water use efficiency of dryland wheat[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 250−258 [11] 杨凯, 董青君, 李其胜, 等. 餐余蚓粪替代化肥对白菜和西兰花光合、抗氧化性及品质的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(5): 934−942 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1189YANG K, DONG Q J, LI Q S, et al. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by vermicompost from food waste on the photosynthesis, antioxidant capacity, and quality of Chinese cabbage and broccoli[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(5): 934−942 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1189 [12] 刘亦丹, 迟凤琴, 谷思玉, 等. 有机肥替代部分化学氮肥对春小麦产量与氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(2): 442−448LIU Y D, CHI F Q, GU S Y, et al. Effects of organic fertilizer substituted by mineral nitrogen fertilizer on yield of spring wheat and nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(2): 442−448 [13] 韩笑, 席运官, 田伟, 等. 有机肥施用模式对环水有机蔬菜种植氮磷径流的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(3): 465−473HAN X, XI Y G, TIAN W, et al. Effects of different organic fertilization patterns on the nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses in organic agriculture in watershed areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(3): 465−473 [14] 张康宁, 俞巧钢, 叶静, 等. 有机替代对农田土壤肥力及氮磷流失的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2019, 60(7): 1154−1158ZHANG K N, YU Q G, YE J, et al. Effect of substituting chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer on soil fertility status, soil N and P loss of farmland[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 60(7): 1154−1158 [15] 宁建凤, 邹献中, 杨少海, 等. 有机无机氮肥配施对土壤氮淋失及油麦菜生长的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(11): 95−100 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.11.016NING J F, ZOU X Z, YANG S H, et al. Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on the soil nitrogn leaching and the growth of leaf-used lettuce[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2007, 23(11): 95−100 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.11.016 [16] ZHU B, WANG T, KUANG F H, et al. Measurements of nitrate leaching from a hillslope cropland in the central Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2009, 73(4): 1419−1426 doi: 10.2136/sssaj2008.0259 [17] 曹瑞霞, 刘京, 邓开开, 等. 三峡库区典型紫色土小流域径流及氮磷流失特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12): 5330−5339CAO R X, LIU J, DENG K K, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus losses and runoff in a typical purple soil watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(12): 5330−5339 [18] ZHOU M H, ZHU B, BUTTERBACH-BAHL K, et al. Nitrate leaching, direct and indirect nitrous oxide fluxes from sloping cropland in the purple soil area, southwestern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 162: 361−368 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.001 [19] 韦高玲, 卓慕宁, 廖义善, 等. 不同施肥水平下菜地耕层土壤中氮磷淋溶损失特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(6): 1023−1031WEI G L, ZHUO M N, LIAO Y S, et al. Leaching characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in vegetable soils under different fertilization levels[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(6): 1023−1031 [20] 谢军, 赵亚南, 陈轩敬, 等. 有机肥氮替代化肥氮提高玉米产量和氮素吸收利用效率[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(20): 3934−3943 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.20.008XIE J, ZHAO Y N, CHEN X J, et al. Nitrogen of organic manure replacing chemical nitrogenous fertilizer improve maize yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(20): 3934−3943 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.20.008 [21] 汪涛, 朱波, 况福虹, 等. 有机-无机肥配施对紫色土坡耕地氮素淋失的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(4): 781−788WANG T, ZHU B, KUANG F H, et al. Effects of a combination of organic and inorganic fertilization on nitrogen leaching from purple soil with sloping cropland[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(4): 781−788 [22] 徐泰平, 朱波, 汪涛, 等. 不同降雨侵蚀力条件下紫色土坡耕地的养分流失[J]. 水土保持研究, 2006(6): 139–141, 144XU T P, ZHU B, WANG T, et al. Nutrient loss from slope cropland of purple soil under different rainfall erosivities[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, (6): 139–141, 144 [23] 朱波, 汪涛, 况福虹, 等. 紫色土坡耕地硝酸盐淋失特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(3): 525−533 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.03.018ZHU B, WANG T, KUANG F H, et al. Characteristics of nitrate leaching from hilly cropland of purple soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(3): 525−533 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.03.018 [24] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000LU R K. Methods for Agricultural Chemical Analysis of Soils[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Scientech Press, 2000 [25] WANG J, ZHU B, ZHANG J B, et al. Mechanisms of soil N dynamics following long-term application of organic fertilizers to subtropical rain-fed purple soil in China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 91: 222−231 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.039 [26] 曹建生, 刘昌明, 张万军, 等. 太行山区坡地水文地质特性与渗流集蓄技术研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2005, 16(2): 216−221 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.02.011CAO J S, LIU C M, ZHANG W J, et al. Slope hydrogeology and collecting seepage water techniques in gneiss area in the Taihang Mountains[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2005, 16(2): 216−221 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.02.011 [27] NAEF F, SCHERRER S, WEILER M. A process based assessment of the potential to reduce flood runoff by land use change[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 267(1/2): 74−79 [28] 秦雪超, 潘君廷, 郭树芳, 等. 化肥减量替代对华北平原小麦-玉米轮作产量及氮流失影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(7): 1558−1567 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1364QIN X C, PAN J T, GUO S F, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction combined with biogas fertilizer on crop yield of wheat-maize rotation and soil nitrogen loss in North China Plain[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(7): 1558−1567 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1364 [29] 曹宏磊, 朱宁远, 颜廷梅, 等. 生物炭/DCD对于淮河流域主要类型土壤NO3–-N淋失的影响[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学, 2016, 52(01): 56−64CAO H L, ZHU N Y, YAN T M, et al. Impact of biochar / DCD on NO3–-N leaching in the main soil types in Huai-river basin[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Science, 2016, 52(01): 56−64 [30] 王秀丽, 孙波. 红壤旱地施用有机肥的氮素淋失过程[J]. 土壤学报, 2008(4): 745–749WANG X L, SUN B. Nitrogen leaching in upland red soil applied with dairy manure[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008(4): 745–749 [31] WANG T, ZHU B. Nitrate loss via overland flow and interflow from a sloped farmland in the hilly area of purple soil, China[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2011, 90(3): 309−319 doi: 10.1007/s10705-011-9431-7 [32] JIA H Y, LEI A, LEI J S, et al. Effects of hydrological processes on nitrogen loss in purple soil[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2007, 89(1/2): 89−97 [33] WANG J, SUN N, XU M G, et al. The influence of long-term animal manure and crop residue application on abiotic and biotic N immobilization in an acidified agricultural soil[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 337: 710−717 doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.10.022 [34] 朱兆良. 中国土壤氮素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 778−783 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.05.003ZHU Z L. Research on soil nitrogen in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(5): 778−783 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.05.003 [35] XIA L L, LAM S K, WOLF B, et al. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(12): 5919−5932 doi: 10.1111/gcb.14466 [36] FAN J L, XIAO J, LIU D Y, et al. Effect of application of dairy manure, effluent and inorganic fertilizer on nitrogen leaching in clayey fluvo-aquic soil: a lysimeter study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 592: 206−214 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.060 [37] 汪涛, 朱波, 武永锋, 等. 不同施肥制度下紫色土坡耕地氮素流失特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005(5): 67–70WANG T , ZHU B, WU Y F, et al. Nitrogen Loss from Slope Cropland of Purple Soil under Different Fertilization[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005(5): 67–70 -





 下载:
下载: