Quantitative mechanism analysis of the improved P availability in red soil during maize/soybean intercropping
-
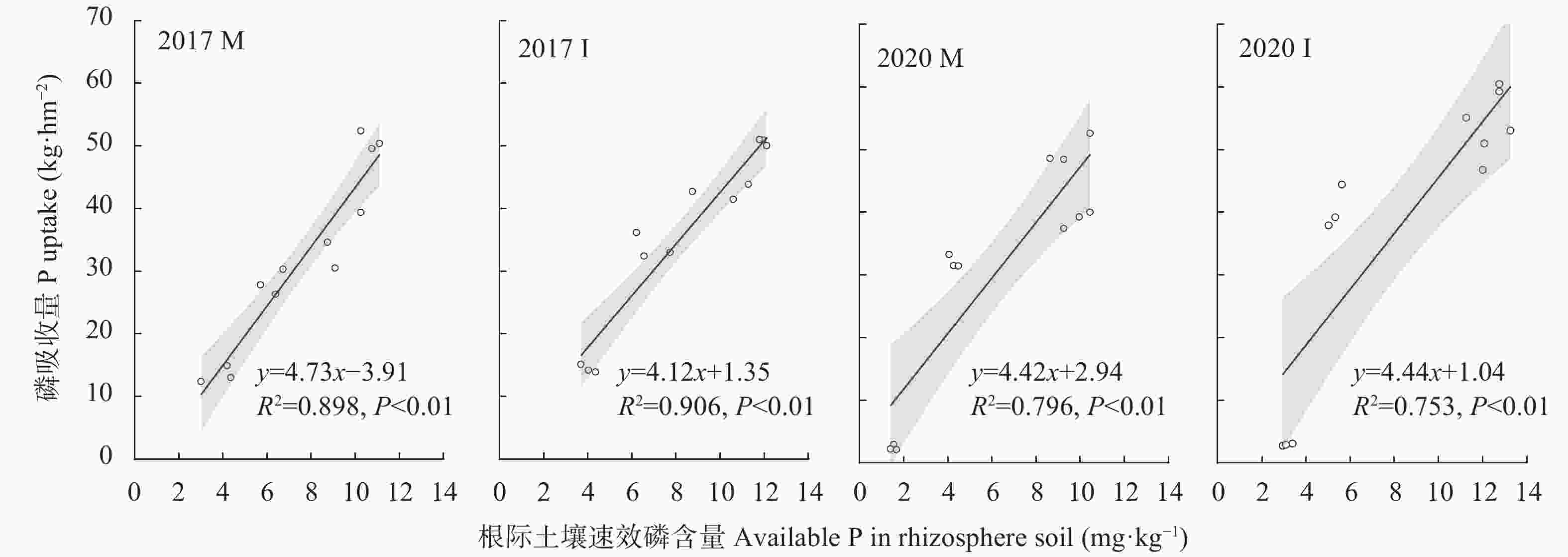
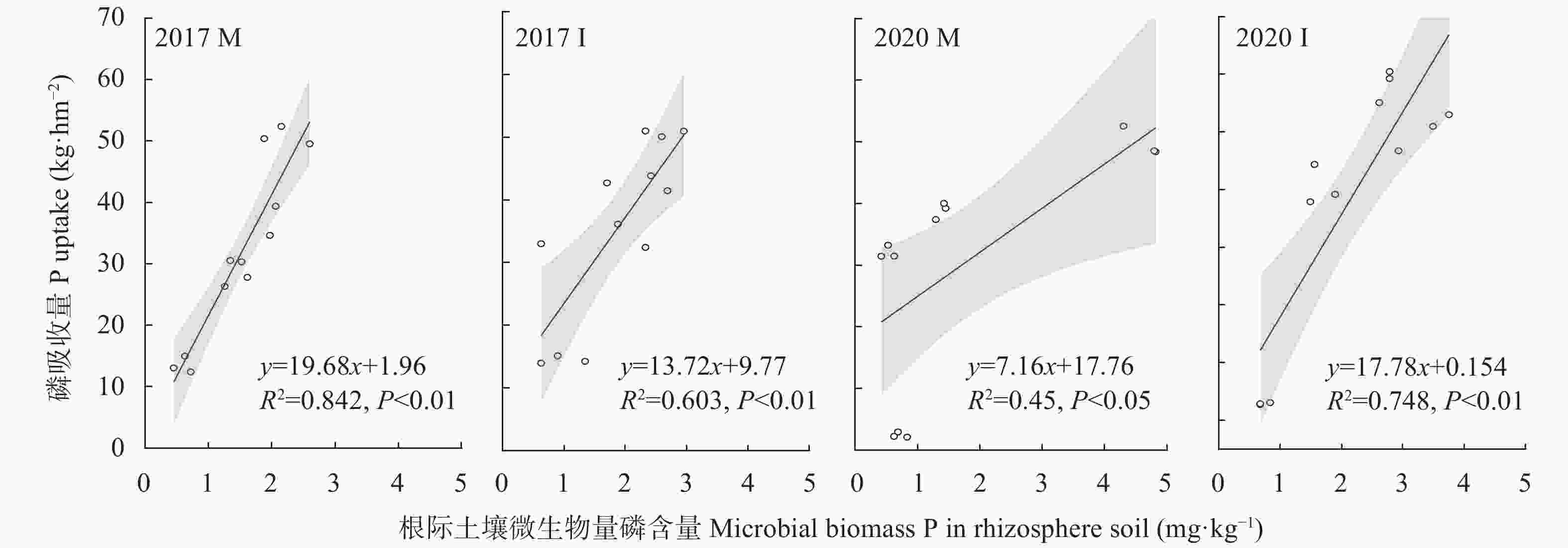
摘要: 间作可提高红壤磷有效性, 但缺乏田间试验条件下土壤生物学活性与磷有效性之间关系的定量解析。通过4年的田间定位试验, 研究2017年和2020年玉米||大豆间作和玉米单作2种种植模式在4个施磷水平[P0: 0 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2; P60: 60 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2; P90: 90 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2; P120: 120 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2]下, 土壤磷有效性及其与主要土壤因素的关系, 通过回归分析、冗余分析与结构方程模型分析, 定量解析间作提高红壤磷有效性的机制。结果表明: 玉米干物质量土地当量比(LER)和磷吸收土地当量比(LERp)均大于1, 2020年LER随施磷水平的增加而降低, 但LERp不受磷水平影响。与单作相比, 间作显著提高了土壤速效磷含量, 且种植模式对土壤速效磷含量的影响由2017年的显著水平变化为2020年的极显著水平。回归分析表明, 单作条件下, 相比2017年, 2020年土壤有效磷(速效磷和微生物量磷)与作物磷吸收的线性关系斜率有所降低, 而间作条件下该斜率有所提高。冗余分析表明, 土壤速效磷和微生物量碳的增加对促进玉米磷吸收的解释量分别由单作中的37.6%和10.0%变化为间作中的33.3%和13.8%。通过结构方程模型分析发现, 碱性磷酸酶活性的提高能够直接提高土壤速效磷含量, 而酸性磷酸酶则通过提高微生物量磷含量进而提高土壤速效磷水平。因此, 在低磷条件下, 间作能够通过提高玉米根际土壤微生物量与磷酸酶活性而增强红壤磷有效性, 从而具有维持玉米干物质量及磷吸收量的能力。Abstract: Intercropping has been shown to improve P availability in red soil, but a quantitative mechanistic analysis of the relationships between soil biological activity and P availability has not been conducted in field experiments. The aim of this study was to determine the specific effect of soil biological activity on P availability in red soil. In this study, maize/soybean intercropping and maize monocropping with four P application levels [0 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, 60 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, 90 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, and 120 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, labeled as P0, P60, P90, and P120, respectively] were used to analyze P availability and its relationship with major soil factors during a 4 year field experiment, which compared the values in the first and last years (2017 and 2020). Regression, redundancy, and structural equation model analyses were conducted to determine these relationships. The results showed that the land equivalent ratio of dry matter mass (LER) and land equivalent ratio of P uptake (LERp) were both greater than 1, indicating that intercropping increases biomass production and P uptake of crops. LER significantly (P<0.05) decreased with an increase in P application level in 2020, but LERp did not. This indicates that the advantage of P absorption in intercropping was not affected by P level, and low P levels still had the ability to maintain this advantage. Compared with monocropping, intercropping significantly (P<0.05) increased the soil available P content in maize rhizosphere; the increasing amplitude was from 24% to 103%, and the role of planting pattern changed from a significant level (P<0.05) in 2017 to an extremely significant level (P<0.01) in 2020. This indicates the effects of intercropping and P application on maize rhizosphere P availability in red soil with low fertility over multiple planting years. Regression analysis showed that the slope of the linear relationship between both Olsen-P and microbial biomass P (MBP) with maize P absorption in 2020 was lower than that in 2017 under monoculture (varied from 4.73 to 4.42 in Olsen-P and 19.68 to 7.16 in MBP), whereas the slope increased under intercropping (varied from 4.12 to 4.44 in Olsen-P and 13.72 to 17.78 in MBP). Redundancy analysis showed that the increase in soil available P and microbial biomass carbon (MBC) accounted for P absorption varied from 37.6% and 10.0% in monoculture to 33.3% and 13.8% in intercropping, respectively. This result shows that intercropping decreased the effect of available P on P uptake and increased the role of MBC. Through structural equation model analysis, increasing the activity of alkaline phosphatase was found to directly increase the content of soil available P, whereas acid phosphatase could increase soil available P by increasing MBP. These two enzymes are speculated to affect P availability in rhizosphere soil via different mechanisms. Therefore, under low P application levels, intercropping can enhance P availability in red soil by increasing soil microbial biomass and phosphatase activity in the maize rhizosphere, thus maintaining the dry matter mass and phosphorus uptake of maize. The quantitative contribution of microbial processes should be further studied.
-
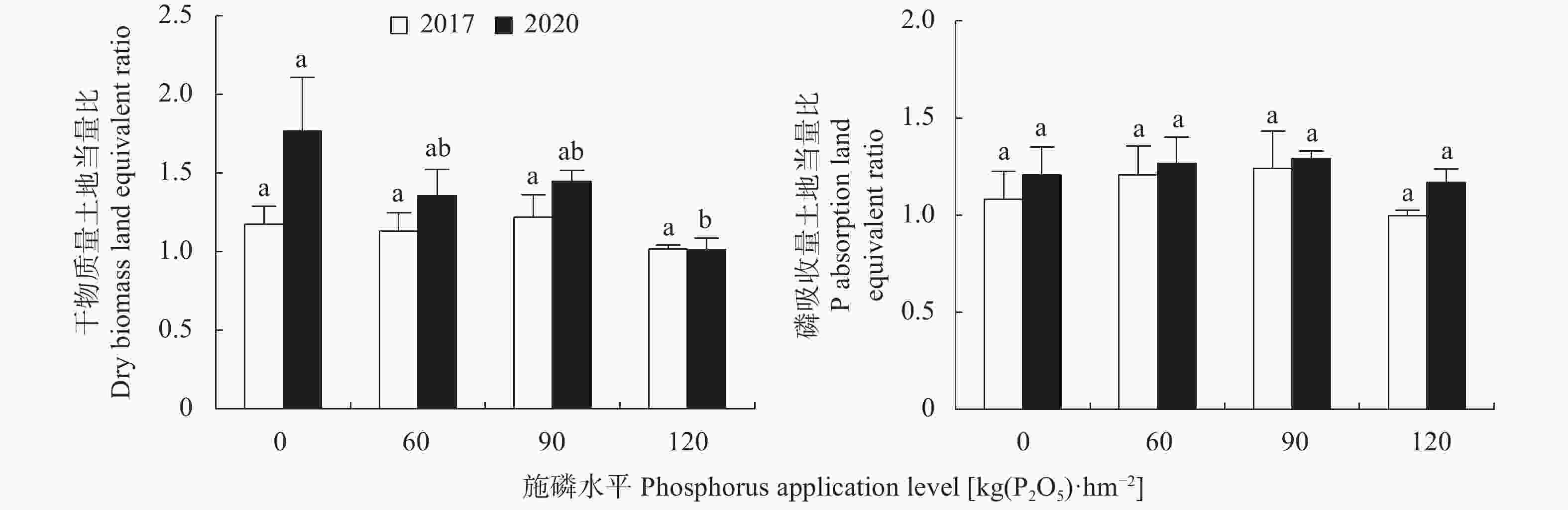
图 2 2017年和2020年不同施磷水平对玉米||大豆间作系统土地当量比的影响
不同小写字母表示同一年份施磷处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among P application levels in the same year (P<0.05).
Figure 2. Effects of P application levels on land equivalent ratio of maize/soybean intercropping system in 2017 and 2020
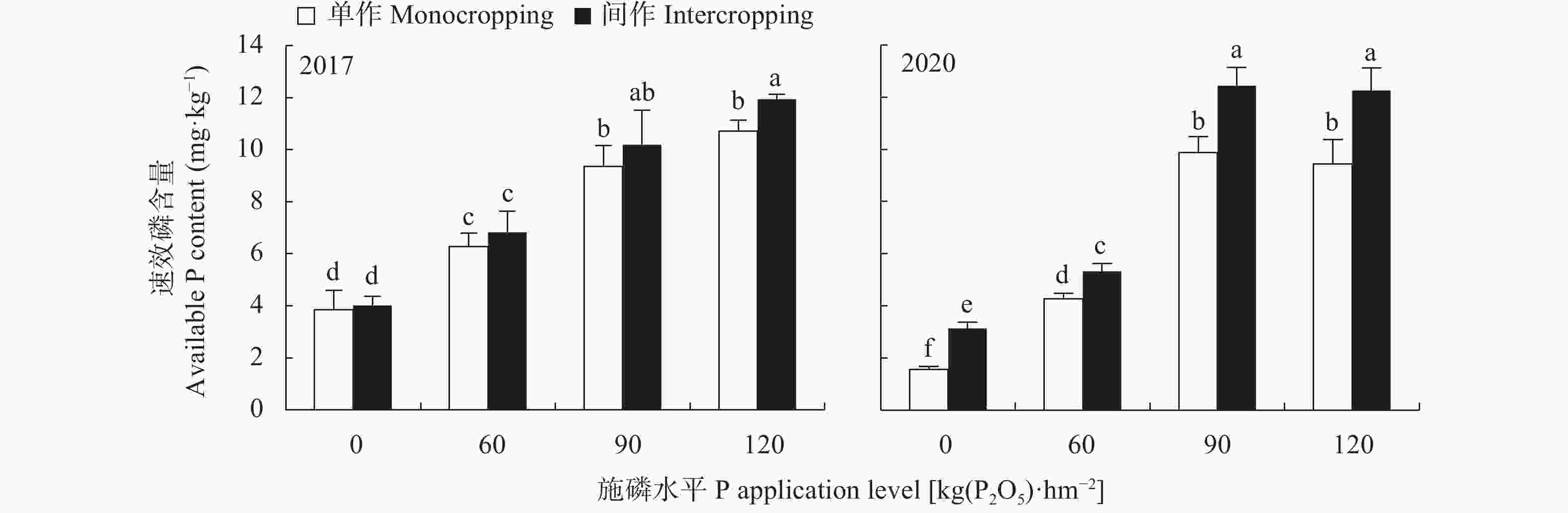
图 3 2017年和2020年不同施磷水平及与大豆间作对玉米根际土壤速效磷含量的影响
不同小写字母表示不同种植模式和不同施磷水平间差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different P application levels of different planting patterns (P<0.05).
Figure 3. Effects of P application levels and intercropping with soybean on available P content in maize rhizosphere soil in 2017 and 2020
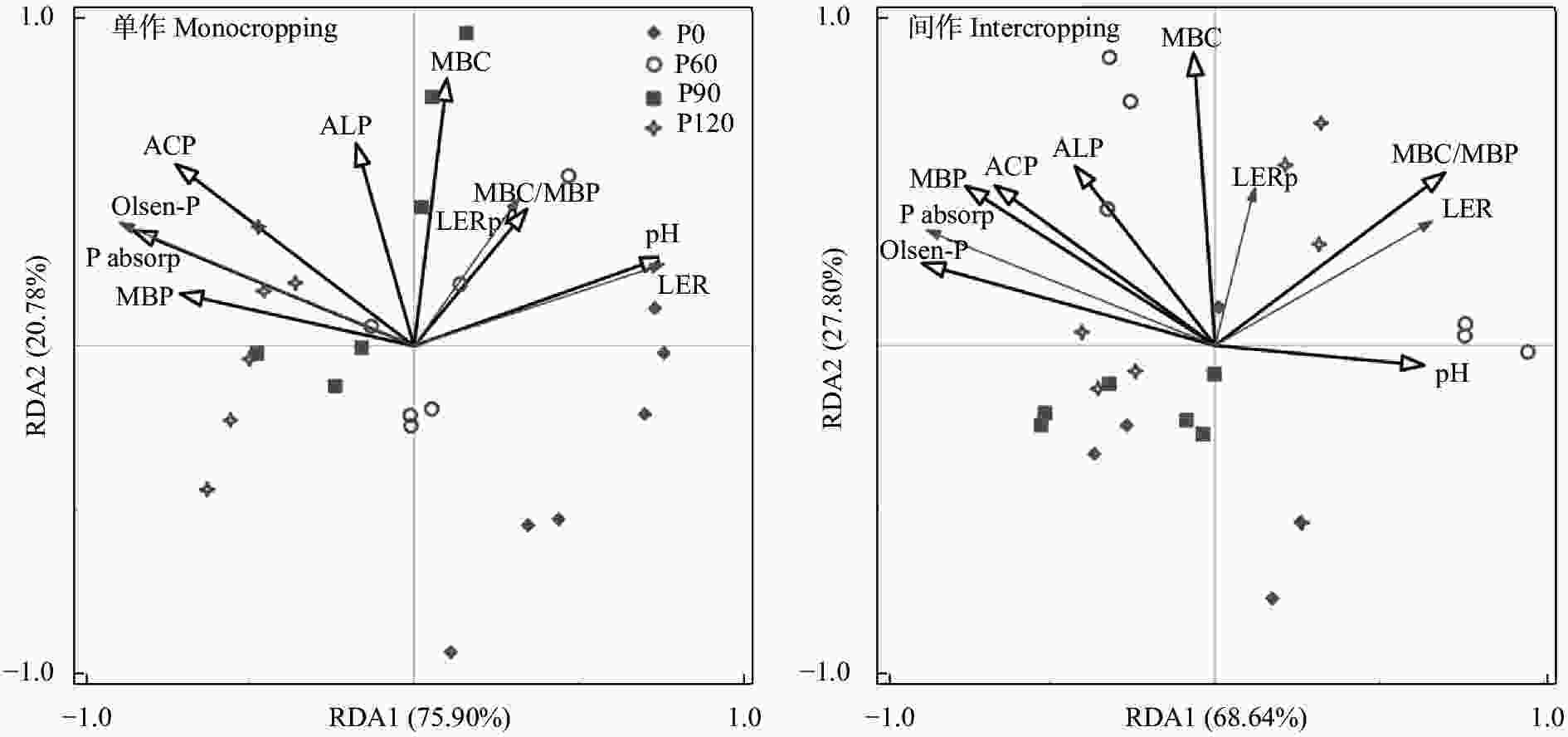
图 6 单作及与大豆间作玉米磷吸收量与根际土壤因子的冗余分析
MBC: 微生物量碳; ACP: 酸性磷酸酶; ALP: 碱性磷酸酶; MBP: 微生物量磷; P absorp: 磷吸收量; LERp: 磷吸收土地当量比; LER: 干物质量土地当量比。P0、P60、P90和P120分别为施磷水平0 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2、60 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2、90 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2和120 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2。
Figure 6. Redundancy analysis of P uptake and rhizosphere soil factors of monocropped maize and maize intercropped with soybean
MBC: microbial biomass carbon; ACP: acid phosphatase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; MBP: microbial biomass P; P absorp: P uptake; LERp: P uptake land equivalent ratio; LER: dry biomass land equivalent ratio. P0, P60, P90 and P120 represent P application levels of 0 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, 60 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, 90 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2 and 120 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2, respectively.
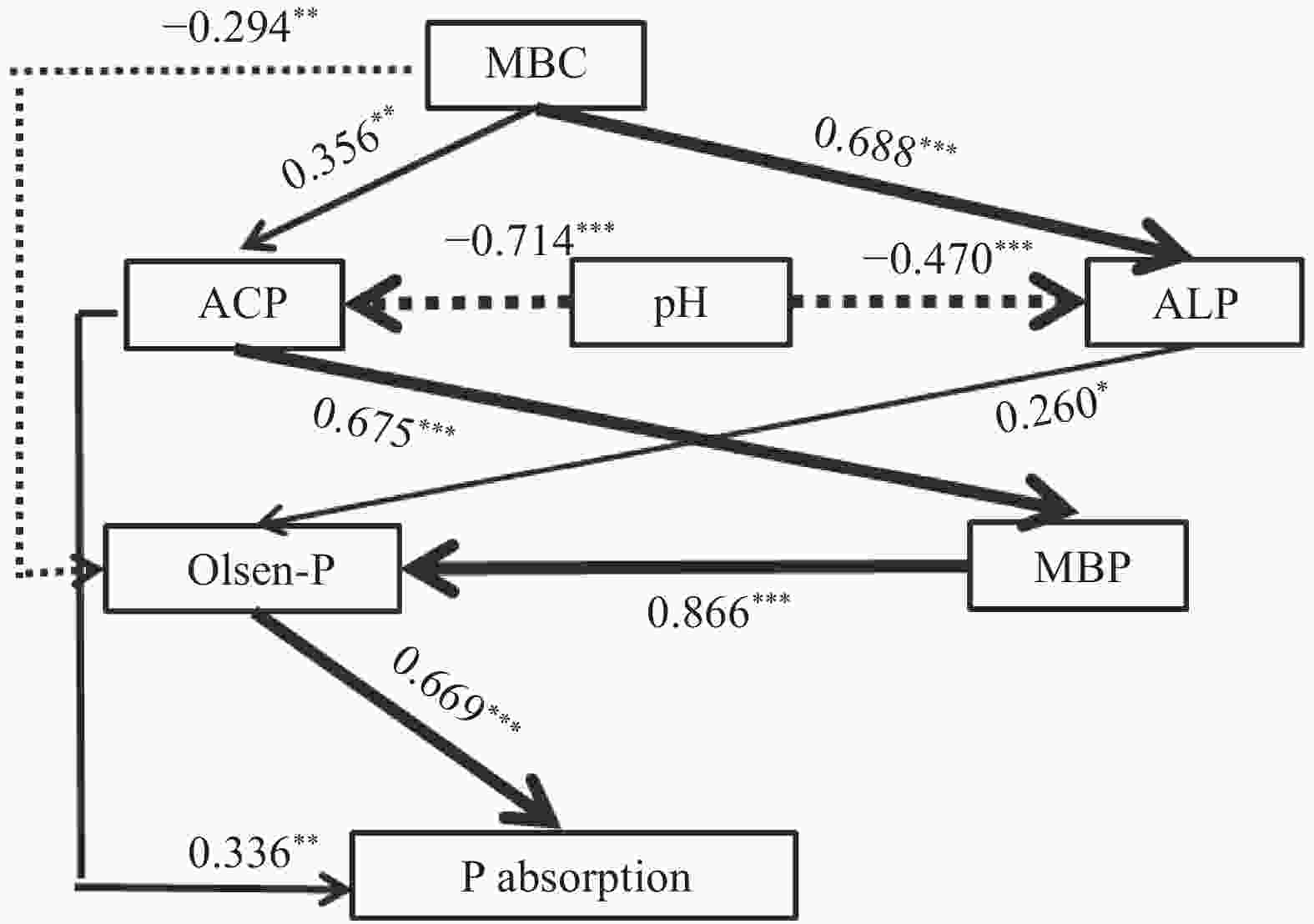
图 7 结构方程模型分析土壤生物学活性对玉米磷吸收量的影响
x2=11.061, P=0.438, GFI=0.888, RMSEA=0.016. ***: P<0.001, **: P<0.01, *: P<0.05。黑色直线表示促进作用, 虚线表示抑制作用, 粗细程度表示影响大小, 数字表示标准化总影响系数。MBC: 微生物量碳; ACP: 酸性磷酸酶; ALP: 碱性磷酸酶; MBP: 微生物量磷。
Figure 7. Structural equation analysis of the influence of soil factors on P uptake
The black line represents the positive effect, the dotted line represents the negative effect, and the width of arrow line indicates strength of normalized path coefficients, the numbers on the line represent the standardized total effects. MBC: microbial biomass carbon; ACP: acid phosphatase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; MBP: microbial biomass P.
表 1 2017年和2020年施磷水平和种植模式对玉米干物质量、磷吸收量和根际土壤速效磷含量的影响
Table 1. Effects of P application level and cropping pattern on dry biomass, P uptake and available P content in rhizosphere soil of maize in 2017 and 2020
因子
Factor2017 2020 干物质量
Dry biomass磷吸收量
P uptake根际土壤速效磷含量
Available P content in rhizosphere soil干物质量
Dry biomass磷吸收量
P uptake根际土壤速效磷含量
Available P content in rhizosphere soil磷水平
P application level (T)** ** ** ** ** ** 种植模式
Cropping pattern (M)** ** * ** ** ** 磷水平×种植模式
T×M* * ns ** ** ns *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01. -
[1] RICHARDSON A E, SIMPSON R J. Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 989−996 doi: 10.1104/pp.111.175448 [2] QUESADA C A, LLOYD J, ANDERSON L O, et al. Soils of Amazonia with particular reference to the RAINFOR sites[J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(6): 1415−1440 doi: 10.5194/bg-8-1415-2011 [3] SHEN J B, YUAN L X, ZHANG J L, et al. Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 997−1005 doi: 10.1104/pp.111.175232 [4] TANG X Y, PLACELLA S A, DAYDÉ F, et al. Phosphorus availability and microbial community in the rhizosphere of intercropped cereal and legume along a P-fertilizer gradient[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 407(1/2): 119−134 [5] SUN B R, GAO Y Z, WU X, et al. The relative contributions of pH, organic anions, and phosphatase to rhizosphere soil phosphorus mobilization and crop phosphorus uptake in maize/alfalfa polyculture[J]. Plant and Soil, 2020, 447(1/2): 117−133 [6] HE Y, DING N, SHI J C, et al. Profiling of microbial PLFAs: Implications for interspecific interactions due to intercropping which increase phosphorus uptake in phosphorus limited acidic soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2013, 57: 625−634 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.07.027 [7] HINSINGER P, BETENCOURT E, BERNARD L, et al. P for two, sharing a scarce resource: soil phosphorus acquisition in the rhizosphere of intercropped species[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1078−1086 doi: 10.1104/pp.111.175331 [8] LI C J, HOFFLAND E, KUYPER T W, et al. Syndromes of production in intercropping impact yield gains[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 653−660 doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0680-9 [9] TANG X Y, ZHANG C C, YU Y, et al. Intercropping legumes and cereals increases phosphorus use efficiency; a meta-analysis[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 460(1/2): 89−104 [10] 王宇蕴, 李兰, 郑毅, 等. 基于根系形态对磷吸收的贡献解析小麦||蚕豆间作促进磷吸收的作用[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(7): 954−959WANG Y Y, LI L, ZHENG Y, et al. Contribution of root morphology to phosphorus absorption in wheat and faba bean intercropping system[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(7): 954−959 [11] 刘彦伶, 李渝, 张艳, 等. 长期施用磷肥和有机肥黄壤微生物量磷特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(6): 1188−1198 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.06.010LIU Y L, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Characteristics of microbial biomass phosphorus in yellow soil under long-term application of phosphorus and organic fertilizer[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(6): 1188−1198 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.06.010 [12] SEELING B, ZASOSKI R J. Microbial effects in maintaining organic and inorganic solution phosphorus concentrations in a grassland topsoil[J]. Plant and Soil, 1993, 148(2): 277−284 doi: 10.1007/BF00012865 [13] CHEN Y, SUN R B, SUN T T, et al. Evidence for involvement of keystone fungal taxa in organic phosphorus mineralization in subtropical soil and the impact of labile carbon[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 148: 107900 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107900 [14] 王蕾, 王艳玲, 李欢, 等. 长期施肥下红壤旱地磷素有效性影响因子的冗余分析[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(1): 17−25 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19549WANG L, WANG Y L, LI H, et al. Redundancy analysis of influencing factors of phosphorus availability in red soil upland under long-term fertilization[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(1): 17−25 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19549 [15] 王一帆. 地上地下互作提高小麦间作玉米水分利用效率的机理[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018WANG Y F. Mechanism of above- and below-ground interaction intensity improving water use efficiency in wheat-maize intercropping system[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural Univerisity, 2018 [16] 鲁如坤. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999LU R K. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1999 [17] TANG X Y, BERNARD L, BRAUMAN A, et al. Increase in microbial biomass and phosphorus availability in the rhizosphere of intercropped cereal and legumes under field conditions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 75: 86−93 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.04.001 [18] JIANG Y J, QIAN H Y, WANG X Y, et al. Nematodes and microbial community affect the sizes and turnover rates of organic carbon pools in soil aggregates[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 119: 22−31 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.01.001 [19] 张梦瑶, 肖靖秀, 汤利, 等. 不同磷水平下小麦蚕豆间作对根际有效磷及磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(7): 1157−1165 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18346ZHANG M Y, XIAO J X, TANG L, et al. Effects of wheat and faba bean intercropping on the available phosphorus contents in rhizospheric soil and phosphorus uptake by crops under different phosphorus levels[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(7): 1157−1165 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18346 [20] CARPENTER S R. Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: Bistability and soil phosphorus[J]. PNAS, 2005, 102(29): 10002−10005 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503959102 [21] 覃潇敏, 农玉琴, 骆妍飞, 等. 施磷量对玉米-大豆间作根际红壤无机磷形态及磷吸收的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5498.S.20210813.1044.002.htmlQIN X M, NONG Y Q, LUO Y F, et al. Effects of phosphorus application rate on inorganic phosphorus forms and phosphorus uptake in the rhizosphere of maize-soybean intercropping in red soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5498.S.20210813.1044.002.html [22] XU Z, LI C J, ZHANG C C, et al. Intercropping maize and soybean increases efficiency of land and fertilizer nitrogen use: a meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 246: 107661 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107661 [23] 张丽, 柳勇, 谷林静, 等. 外源磷与AMF对间作玉米种植红壤无机磷形态的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(1): 26−33 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20160105ZHANG L, LIU Y, GU L J, et al. Effect of phosphorus addition and different AMF on inorganic phosphorus forms in red soil under intercropping maize plants[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(1): 26−33 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20160105 [24] MALTAIS-LANDRY G. Legumes have a greater effect on rhizosphere properties (pH, organic acids and enzyme activity) but a smaller impact on soil P compared to other cover crops[J]. Plant and Soil, 2015, 394(1/2): 139−154 [25] Barber S A. Soil Nutrient Bioavailability: A Mechanistic Approach[M]. New York: Wiley, 1995 [26] HINSINGER P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review[J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237(2): 173−195 doi: 10.1023/A:1013351617532 [27] DEVAU N, HINSINGER P, CADRE E, et al. Root-induced processes controlling phosphate availability in soils with contrasted P-fertilized treatments[J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 348(1/2): 203−218 [28] GEELHOED J S, VAN RIEMSDIJK W H, FINDENEGG G R. Simulation of the effect of citrate exudation from roots on the plant availability of phosphate adsorbed on goethite[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 1999, 50(3): 379−390 doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.1999.00251.x [29] DEVAU N, LE CADRE E, HINSINGER P, et al. A mechanistic model for understanding root-induced chemical changes controlling phosphorus availability[J]. Annals of Botany, 2010, 105(7): 1183−1197 doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq098 [30] WANG D, YI W B, ZHOU Y L, et al. Intercropping and N application enhance soil dissolved organic carbon concentration with complicated chemical composition[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 210: 104979 doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.104979 [31] WANG D M, MARSCHNER P, SOLAIMAN Z, et al. Growth, P uptake and rhizosphere properties of intercropped wheat and chickpea in soil amended with iron phosphate or phytate[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2007, 39(1): 249−256 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.07.013 [32] 陈利, 肖靖秀, 郑毅. 间作玉米大豆根系分泌物中有机酸的变化特征[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2016, 36(5): 78−83CHEN L, XIAO J X, ZHENG Y. Characteristics of organic acids from root exudation in maize and soybean intercropping[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2016, 36(5): 78−83 [33] MCLAUGHLIN M J, ALSTON A M, MARTIN J K. Phosphorus cycling in wheat pasture rotations. Ⅱ. The role of the microbial biomass in phosphorus cycling[J]. Soil Research, 1988, 26(2): 333 doi: 10.1071/SR9880333 [34] 孙瑞莲, 赵秉强, 朱鲁生, 等. 长期定位施肥田土壤酶活性的动态变化特征[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(5): 2059−2063SUN R L, ZHAO B Q, ZHU L S, et al. Dynamic changes of soil enzyme activities in long-term fertilization soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(5): 2059−2063 [35] CUI H, ZHOU Y, GU Z H, et al. The combined effects of cover crops and symbiotic microbes on phosphatase gene and organic phosphorus hydrolysis in subtropical orchard soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 82: 119−126 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.01.003 -





 下载:
下载: