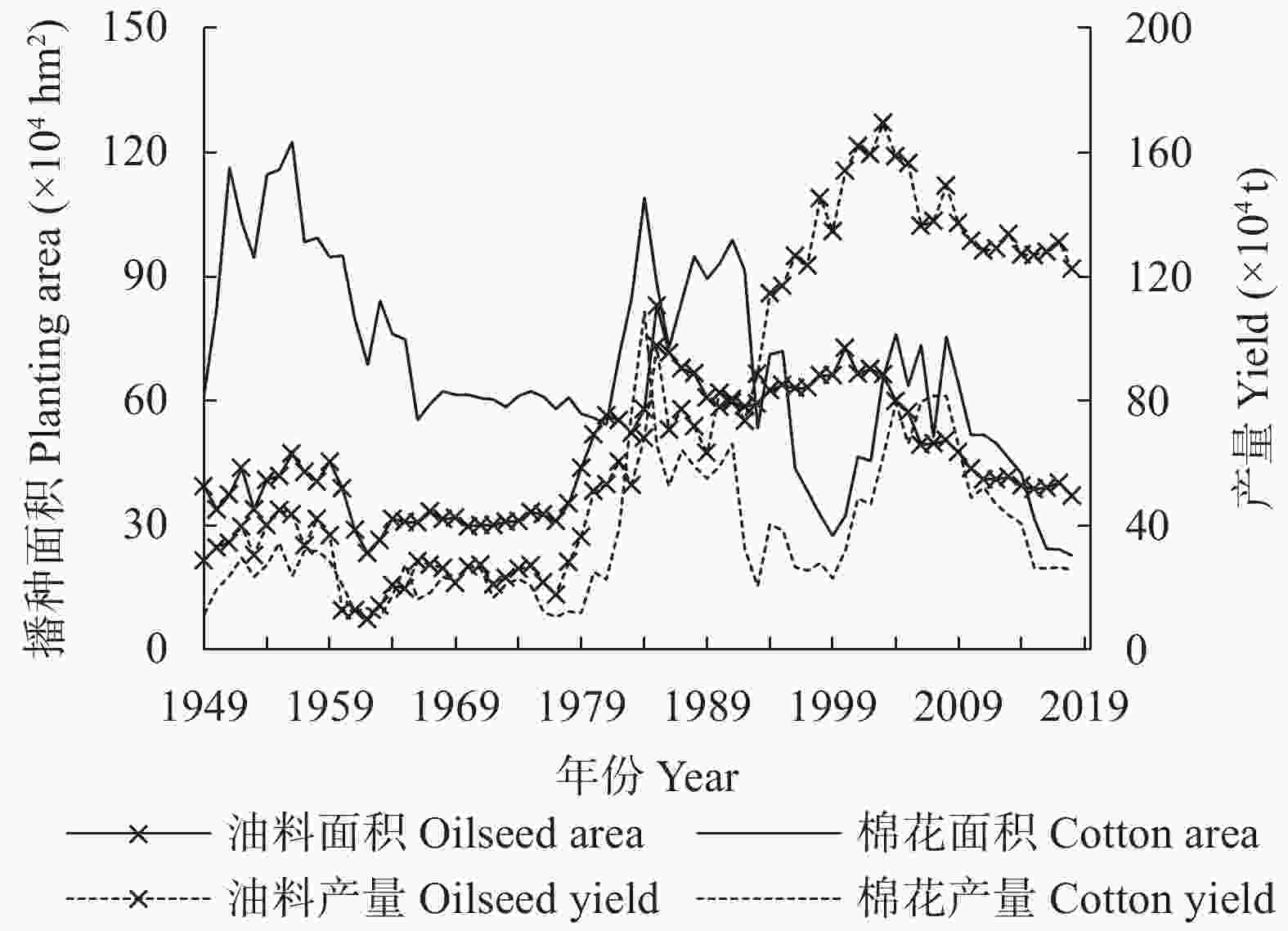
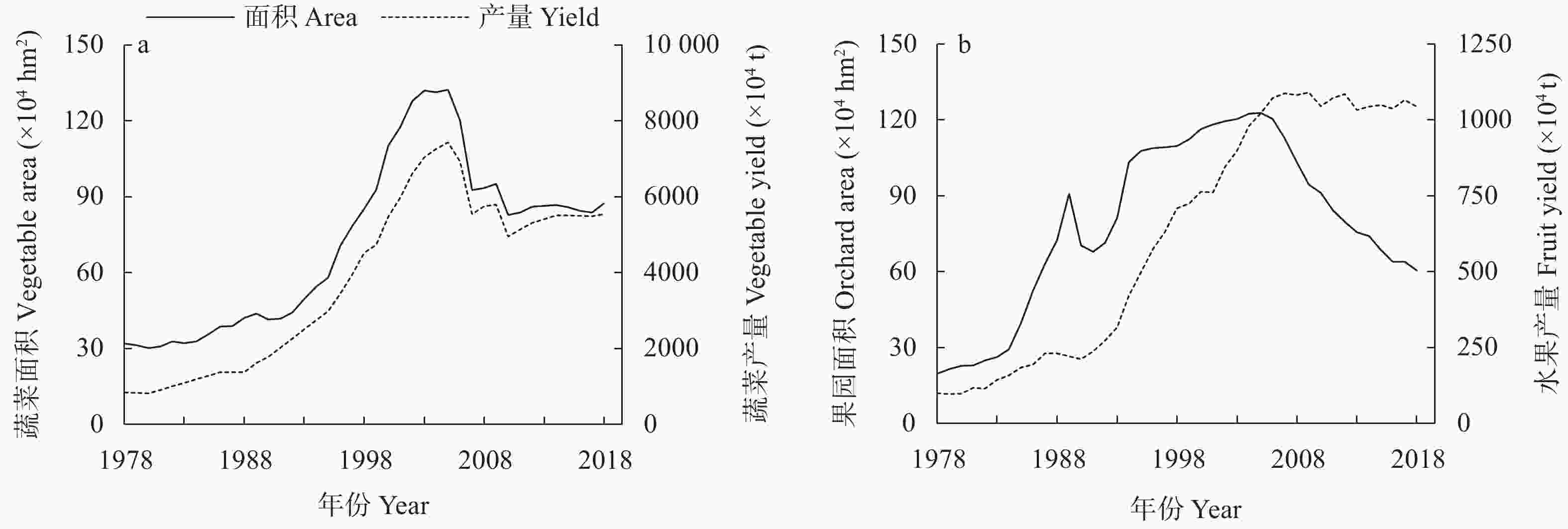
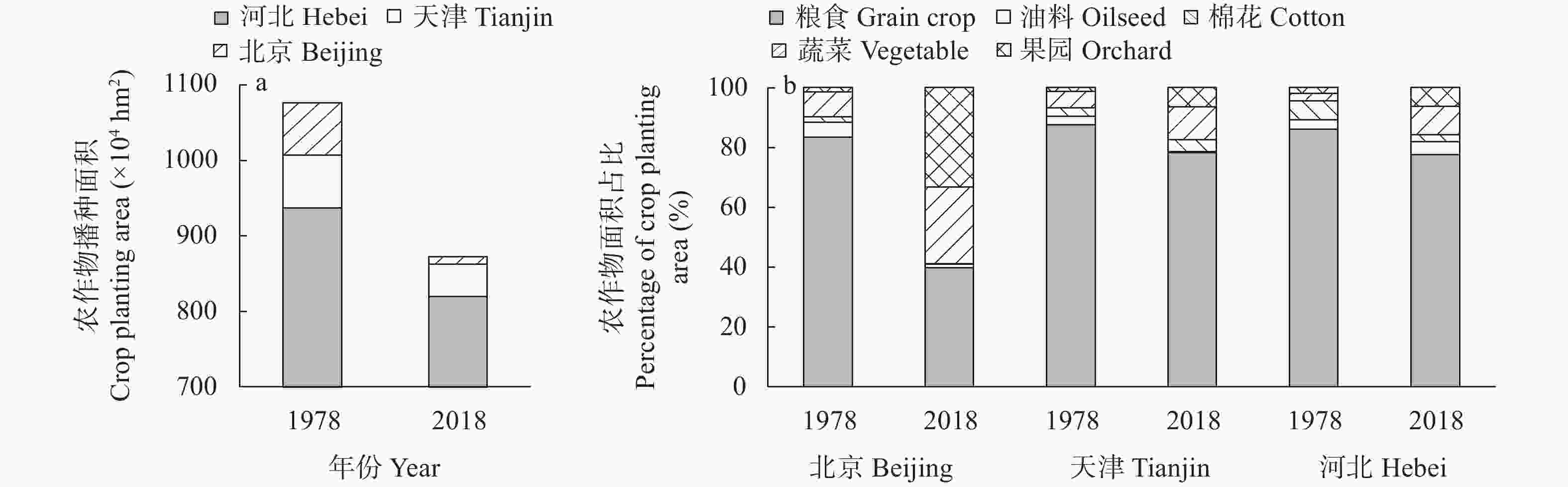
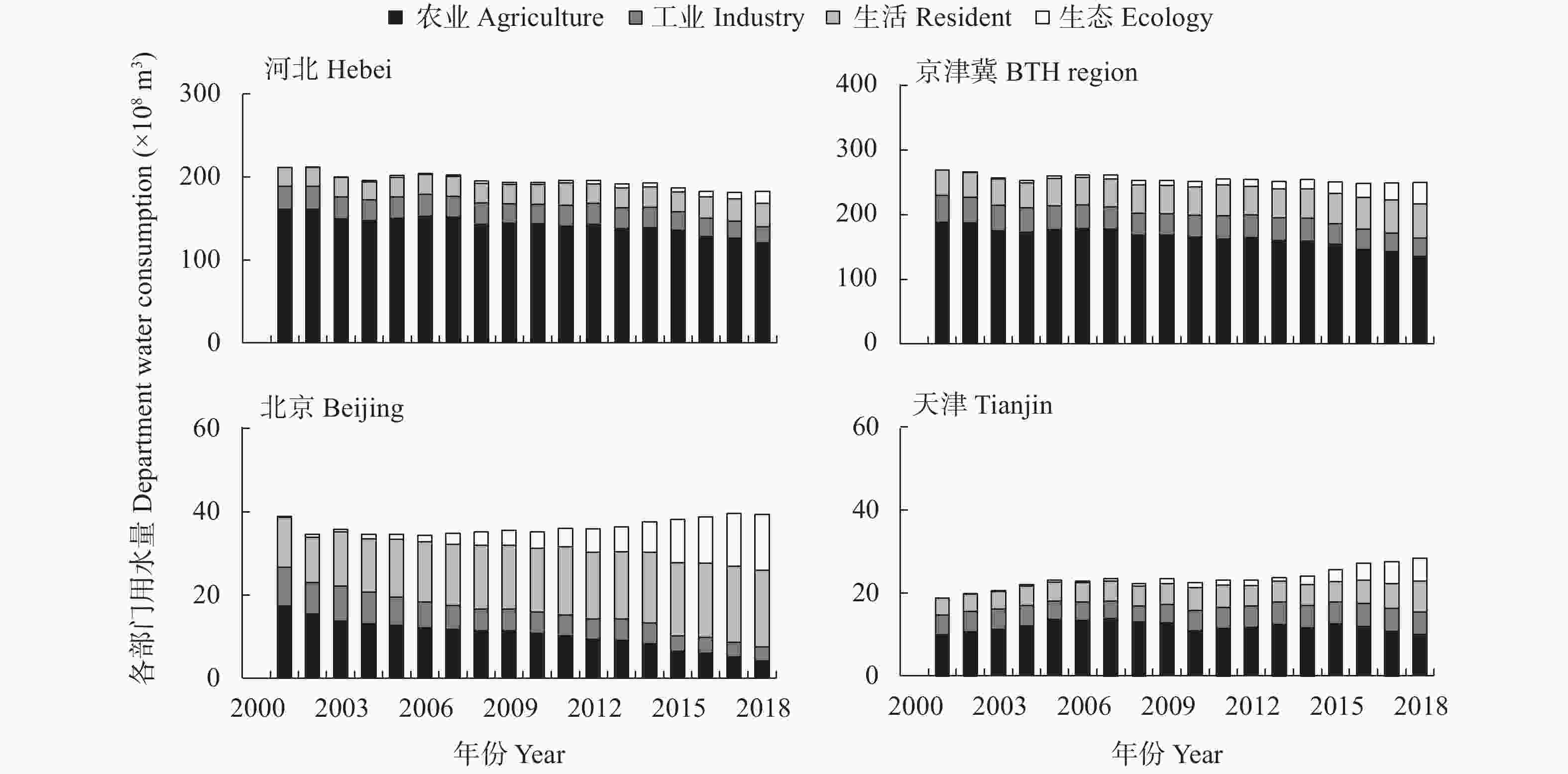
| [1] |
YUAN Z J, SHEN Y J. Estimation of agricultural water consumption from meteorological and yield data: a case study of Hebei, North China[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e58685 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058685
|
| [2] |
SHEN Y J, ZHANG Y C, SCANLON B R, et al. Energy/water budgets and productivity of the typical croplands irrigated with groundwater and surface water in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2013, 181: 133−142 doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2013.07.013
|
| [3] |
沈彦俊, 胡春胜, 张喜英, 等. 生态学长期研究促进资源高效利用和区域农业可持续发展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(6): 648−655SHEN Y J, HU C S, ZHANG X Y, et al. Long-term ecological research (LTER) promotes natural resources use efficiency and agricultural sustainable development in North China Plain[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(6): 648−655
|
| [4] |
张光辉, 费宇红, 王金哲. 华北灌溉农业与地下水适应性研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012ZHANG G H, FEI Y H, WANG J Z. Research on Adaptability of Irrigated Agriculture and Groundwater in North China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012
|
| [5] |
胡春胜, 张喜英, 程一松, 等. 太行山前平原地下水动态及超采原因分析[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2002, 18(2): 89−91 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2002.02.003HU C S, ZHANG X Y, CHENG Y S, et al. An analysis on dynamics of water table and overdraft of groundwater in the Piedmont of Mt. Taihang[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 2002, 18(2): 89−91 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2002.02.003
|
| [6] |
HU Y K, MOIWO J P, YANG Y H, et al. Agricultural water-saving and sustainable groundwater management in Shijiazhuang Irrigation District, North China Plain[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 393(3/4): 219−232
|
| [7] |
沈彦俊, 刘昌明. 华北平原典型井灌区农田水循环过程研究回顾[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(5): 1004−1010SHEN Y J, LIU C M. Agro-ecosystems water cycles of the typical irrigated farmland in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(5): 1004−1010
|
| [8] |
夏军. 华北地区水循环与水资源安全: 问题与挑战[J]. 地理科学进展, 2002, 21(6): 517−526 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2002.06.001XIA J. A perspective on hydrological base of water security problem and its application study in North China[J]. Progress in Geography, 2002, 21(6): 517−526 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2002.06.001
|
| [9] |
刘昌明. 建设节水型社会 缓解地下水危机[J]. 中国水利, 2007(15): 10−13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2007.15.005LIU C M. Building water-saving society and alleviating groundwater crisis[J]. China Water Resources, 2007(15): 10−13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2007.15.005
|
| [10] |
康绍忠. 水安全与粮食安全[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(8): 880−885KANG S Z. Towards water and food security in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2014, 22(8): 880−885
|
| [11] |
XIAO D P, SHEN Y J, QI Y Q, et al. Impact of alternative cropping systems on groundwater use and grain yields in the North China Plain region[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2017, 153: 109−117 doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.01.018
|
| [12] |
LUO J M, SHEN Y J, QI Y Q, et al. Evaluating water conservation effects due to cropping system optimization on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain, China[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2018, 159: 32−41 doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.10.002
|
| [13] |
郭步庆, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 等. 华北平原不同粮作模式下作物水分利用[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2013, 18(1): 53−60 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2013.01.008GUO B Q, TAO H B, WANG P, et al. Water utilization of different cropping production systems in North China Plain[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2013, 18(1): 53−60 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2013.01.008
|
| [14] |
YANG X L, CHEN Y Q, STEENHUIS T S, et al. Mitigating groundwater depletion in North China Plain with cropping system that alternate deep and shallow rooted crops[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 980 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00980
|
| [15] |
张敏, 隋鹏, 陈源泉, 等. 太行山山前平原节水替代模式耗水特征分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(20): 251−257ZHANG M, SUI P, CHEN Y Q, et al. Water consumption characteristics of alternative crop rotations in the piedmont of Mt. Taihang[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(20): 251−257
|
| [16] |
赵华甫, 张凤荣, 李佳, 等. 北京都市农业种植制度的发展方向−春玉米一熟制[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(2): 469−474 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00469ZHAO H F, ZHANG F R, LI J, et al. Direction of agricultural development of urban Beijing — Single-harvest spring-maize farming method[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008, 16(2): 469−474 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00469
|
| [17] |
刘明, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 等. 华北平原水氮优化条件下不同种植制度的水分效应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2008, 22(2): 116−120, 125 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.02.027LIU M, TAO H B, WANG P, et al. Water consumption, soil water content variation and water utilization efficiency of different cropping system in China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 22(2): 116−120, 125 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.02.027
|
| [18] |
闫鹏, 陈源泉, 张学鹏, 等. 河北低平原区春玉米一熟替代麦玉两熟制的水生态与粮食安全分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(11): 1491−1499YAN P, CHEN Y Q, ZHANG X P, et al. Security of water-ecology and food under replacement of winter wheat-summer maize rotation with spring maize mono-cropping in Hebei Lowland Plains[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(11): 1491−1499
|
| [19] |
SUN H Y, ZHANG X Y, WANG E L, et al. Quantifying the impact of irrigation on groundwater reserve and crop production — A case study in the North China Plain[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2015, 70: 48−56 doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2015.07.001
|
| [20] |
河北省地方志编纂委员会. 河北省志·第16卷·农业志[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1995Hebei Local History Compilation Committee. Hebei Provincial History, Volume 16, Agricultural History[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1995
|
| [21] |
高玲玲. 近代河北农作物种植结构变迁研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2020GAO L L. The study on the changes of crop planting structure in modern Hebei[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2020
|
| [22] |
杨英法, 杜献宁. 河北解放前历代农田水利设施状况考察[J]. 经济视角(中旬), 2011(12): 162−163YANG Y F, DU X N. Investigation on the status of farmland water conservancy facilities in the past dynasties of Hebei[J]. Economic Vision, 2011(12): 162−163
|
| [23] |
潘明涛. 海河平原水环境与水利研究(1360—1945)[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2014PAN M T. The research on the water environment and water conservancy in the Haihe River Plain Basin (1360−1945)[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2014
|
| [24] |
国家统计局. 国家数据[DB/OL]. 北京: 国家统计局, [2020-11-04]. http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01National Bureau of Statistics. National Data[DB/OL]. Beijing: National Bureau of Statistics, [2020-11-04]. http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01
|
| [25] |
崔瑞敏, 田海燕, 刘素恩, 等. 河北省棉花生产的历史回顾[J]. 中国棉花, 2016, 43(8): 10−15 doi: 10.11963/issn.1000-632X.201608003CUI R M, TIAN H Y, LIU S E, et al. Historical review on cotton production in Hebei Province[J]. China Cotton, 2016, 43(8): 10−15 doi: 10.11963/issn.1000-632X.201608003
|
| [26] |
郭元章, 霍艳爽. 河北省油料产业的发展现状 问题与对策[J]. 河北农业科学, 2013, 17(3): 81−85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2013.03.023GUO Y Z, HUO Y S. Development situation, problems and countermeasures of oil industry in Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 17(3): 81−85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2013.03.023
|
| [27] |
孔祥智, 程泽南. 京津冀农业差异性特征及协同发展路径研究[J]. 河北学刊, 2017, 37(1): 115−121KONG X Z, CHENG Z N. The research for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region’s agricultural characteristics of difference and collaborative development path[J]. Hebei Academic Journal, 2017, 37(1): 115−121
|
| [28] |
张希涛. 民国时期华北农家农业生产资料与生活消费研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2012ZHANG X T. A study on the agricultural production materials and living consumption of farmers in North China in the period of the Republic of China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2012
|
| [29] |
惠富平, 阚国坤. 民国时期华北小麦生产与农民生活考察[J]. 中国农史, 2009, 28(2): 101−111HUI F P, KAN G K. Study on wheat production and peasants’ lives in North China during the Republic of China[J]. Agricultural History of China, 2009, 28(2): 101−111
|
| [30] |
徐秀丽. 近代华北平原的农业耕作制度[J]. 近代史研究, 1995(3): 112−131XU X L. The farming system in the North China Plain in modern times[J]. Modern Chinese History Studies, 1995(3): 112−131
|
| [31] |
罗建美. 京津冀平原农业种植结构优化及其节水效应研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019LUO J M. Evaluating water saving effects due to planting structure optimization in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019
|
| [32] |
张光辉, 连英立, 刘春华, 等. 华北平原水资源紧缺情势与因源[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(2): 172−176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.02.012ZHANG G H, LIAN Y L, LIU C H, et al. Situation and origin of water resources in short supply in North China Plain[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(2): 172−176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.02.012
|
| [33] |
YANG Y H, WATANABE M, ZHANG X Y, et al. Optimizing irrigation management for wheat to reduce groundwater depletion in the piedmont region of the Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2006, 82(1/2): 25−44
|
| [34] |
MOIWO J P, YANG Y H, LI H L, et al. Impact of water resource exploitation on the hydrology and water storage in Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2010, 24(21): 3026−3039 doi: 10.1002/hyp.7716
|
| [35] |
吴炳方, 闫娜娜, 曾红伟, 等. 节水灌溉农业的空间认知与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(1): 70−77WU B F, YAN N N, ZENG H W, et al. Outlook on water saving agriculture[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(1): 70−77
|
| [36] |
ZHANG Y C, LEI H M, ZHAO W G, et al. Comparison of the water budget for the typical cropland and pear orchard ecosystems in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 198: 53−64 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2017.12.027
|
| [37] |
裴宏伟. 华北平原灌溉农业对地下水资源的影响及其可持续性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016PEI H W. Impact of irrigation agriculture on groundwater resources and the sustainability analysis in the North China Plain[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016
|
| [38] |
陈飞, 丁跃元, 李原园, 等. 华北地区地下水超采治理实践与思考[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2020, 18(2): 191−198CHEN F, DING Y Y, LI Y Y, et al. Practice and consideration of groundwater overexploitation in North China Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2020, 18(2): 191−198
|
| [39] |
户作亮. 华北地下水超采综合治理经验与思考[J]. 中国水利, 2020(13): 17−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.014HU Z L. Experiences and thinkings on comprehensive treatment of groundwater overexploitation in North China[J]. China Water Resources, 2020(13): 17−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.014
|
| [40] |
LU Y, ZHANG X Y, CHEN S Y, et al. Changes in water use efficiency and water footprint in grain production over the past 35 years: a case study in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 116: 71−79 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.008
|
| [41] |
FANG Q X, MA L, GREEN T R, et al. Water resources and water use efficiency in the North China Plain: Current status and agronomic management options[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(8): 1102−1116 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2010.01.008
|
| [42] |
PEI H W, SCANLON B R, SHEN Y J, et al. Impacts of varying agricultural intensification on crop yield and groundwater resources: comparison of the North China Plain and US High Plains[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2015, 10(4): 044013
|
| [43] |
杜朝阳, 于静洁. 京津冀地区适水发展问题与战略对策[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2018, 16(4): 17−25DU C Y, YU J J. Issues on the sustainable development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on the limited water resources[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2018, 16(4): 17−25
|
| [44] |
YANG X L, CHEN Y Q, PACENKA S, et al. Effect of diversified crop rotations on groundwater levels and crop water productivity in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 522: 428−438 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.010
|
| [45] |
YANG X L, CHEN Y Q, PACENKA S, et al. Recharge and groundwater use in the North China Plain for six irrigated crops for an eleven year period[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(1): e0115269 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115269
|





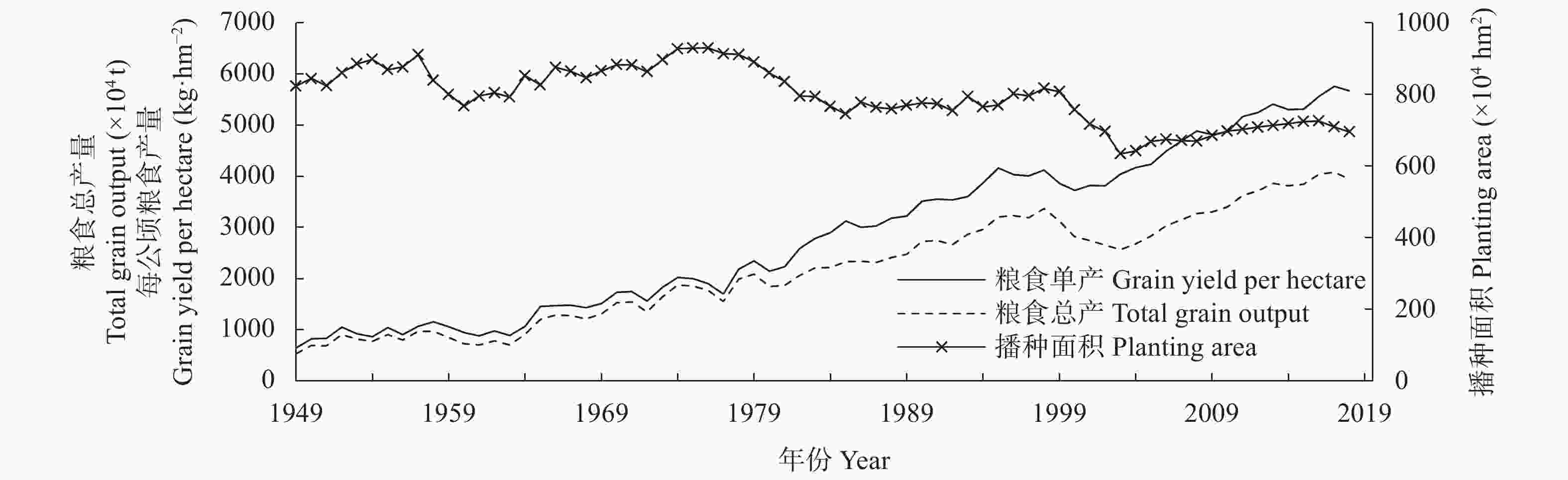
 下载:
下载: