Effects of rotation tillage on available nutrients and structural characteristics of dissolved organic carbon of Fluvo-aquic soil in northern Henan Province
-
摘要: 本研究以豫北潮土为研究对象, 采用大田小区试验研究不同轮耕模式对不同深度土壤速效养分与可溶性有机碳结构特性的影响, 以筛选适合豫北潮土的轮耕模式。本研究于小麦季实施5种不同的耕作模式, 3年为一个周期: 1)连续旋耕(RT-RT-RT); 2)深耕-旋耕-旋耕(DT-RT-RT); 3)深耕-旋耕-条旋耕(DT-RT-SRT); 4)深耕-条旋耕-条旋耕(DT-SRT-SRT); 5)深耕-条旋耕-旋耕(DT-SRT-RT)。测定并分析土壤碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾、可溶性有机碳含量及其腐殖化程度、有机质分子量与聚合度、疏水组分比例、芳香化程度与分子量。结果显示, 各处理间的差异主要表现在0~40 cm土层。相较于RT-RT-RT, 轮耕处理对各项指标均有显著影响, 其中以DT-SRT-RT处理对各指标的影响最为突出, 具体表现为DT-SRT-RT处理显著增加了0~40 cm土层碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾含量(P<0.05), 最高增加17.8%、17.2%和19.6%。在0~40 cm土层中, DT-SRT-RT处理较RT-RT-RT最高增加了20.2%土壤可溶性有机碳含量(P<0.05)、53.1%腐殖化程度和27.4%疏水组分比例(P<0.05)。DT-RT-SRT处理较RT-RT-RT处理显著增加20~30 cm土层芳香化程度与分子量(P<0.05), 最高增加21.0%, 10~30 cm土层有机质分子量与聚合度显著降低36.7% (P<0.05)。土层深度与轮耕处理的单因素以及二者之间的交互效应均显著影响土壤速效养分和可溶性有机碳及其结构特性(P<0.05)。所有处理各指标间的相关性随土层深度的增加而减弱。综上所述, 相较于连续旋耕(RT-RT-RT), 深耕-条旋耕-旋耕模式(DT-SRT-RT)提高了土壤速效养分和可溶性有机碳含量, 增加可溶性有机碳的结构复杂性, 推荐为豫北潮土区适宜的轮耕模式。Abstract: Tillage is an important practice for improving soil quality. The effects of tillage on soil nutrient contents are well known. However, the understanding of the effects of tillage on soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and its structure is rare. This study aimed to select optimum tillage mode by exploring the effect of tillage mode on DOC and its structure in Fluvo-aquic soil in northern Henan Province. A field experiment was carried out using five treatments designed with different tillage rotation modes during the wheat season. The treatments were as follows: 1) continuous rotary tillage (RT-RT-RT); 2) deep tillage-rotary tillage-rotary tillage (DT-RT-RT); 3) deep tillage-rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage (DT-RT-SRT); 4) deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage (DT-SRT-SRT); 5) deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-rotary tillage (DT-SRT-RT). The contents of alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), available potassium (AK), DOC, degree of humification, molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter, proportion of hydrophobic components, degree of aromatization and molecular weight of soil were measured and analyzed. The results showed that the difference in all the indexes among treatments was mainly demonstrated in the 0–40 cm soil layer. Compared with those under RT-RT-RT in the 0–40 cm soil layer, the AN, AP, and AK increased by 17.8%, 17.2%, and 19.6% (P<0.05), respectively, under DT-SRT-RT, whereas the DOC content, degree of humification, and proportion of hydrophobic components increased by 20.2%, 53.1%, and 27.4% (P<0.05), respectively, under DT-SRT-RT. Compared with those under RT-RT-RT, the aromatization degree and molecular weight in the 20–30 cm soil layer increased by 21.0% (P<0.05), and the molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter in the 10–30 cm soil layer decreased by 36.7% (P<0.05) under DT-RT-SRT. Available soil nutrients and DOC and its structural characteristics were affected by soil depth, tillage mode, and the interaction between soil depths and tillage modes. The correlation among different indices decreased with increasing soil depth. In summary, compared with continuous rotary tillage, DT-SRT-RT improved soil available nutrients and DOC content and increased the complexity of the DOC structure. Therefore, the DT-SRT-RT mode was suggested as a suitable rotation tillage mode in the Fluvo-aquic soil areas of northern Henan.
-
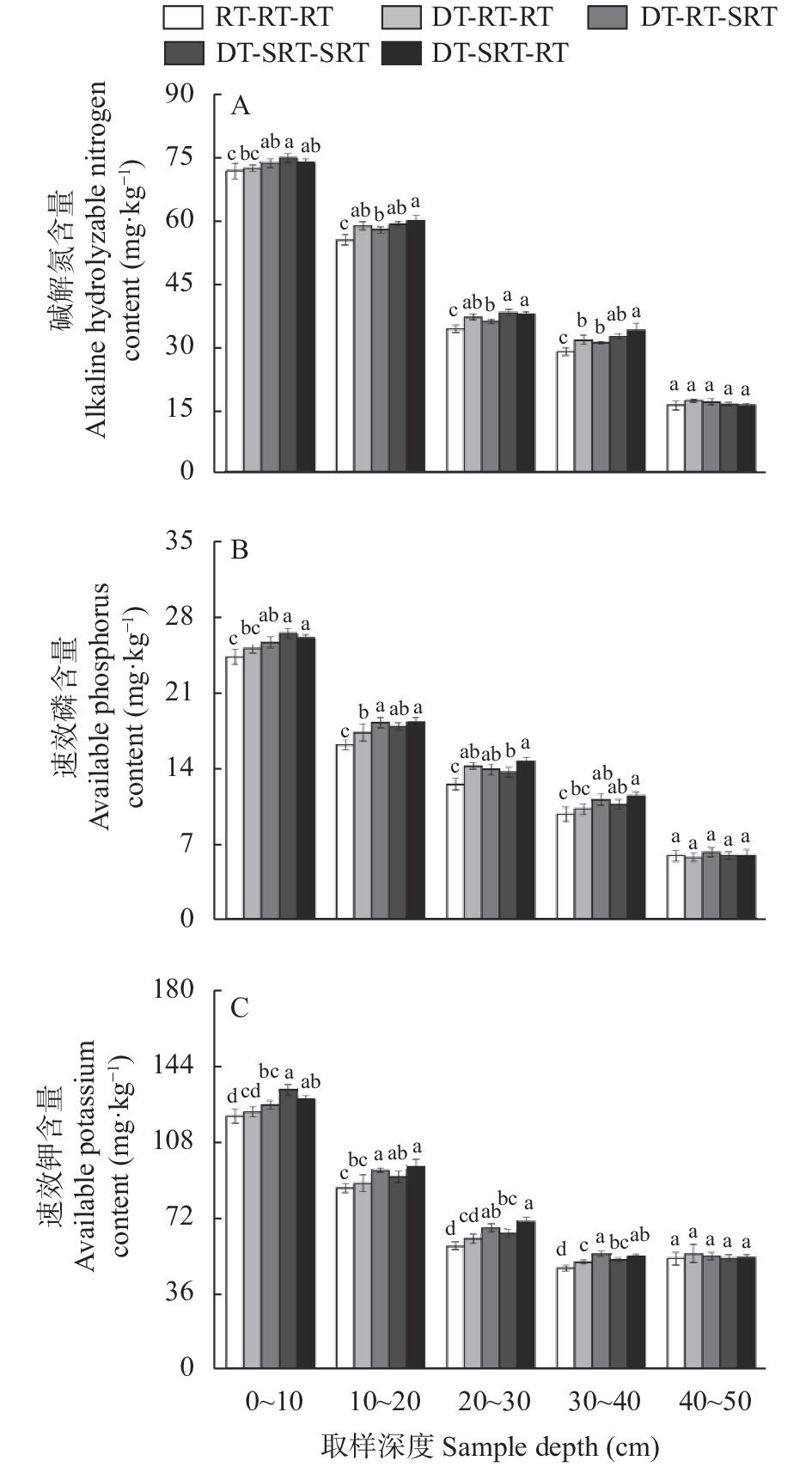
图 1 不同处理下不同土层土壤碱解氮(A)、速效磷(B)和速效钾(C)含量
RT-RT-RT: 连续旋耕; DT-RT-RT: 深耕-旋耕-旋耕; DT-RT-SRT: 深耕-旋耕-条旋耕; DT-SRT-SRT: 深耕-条旋耕-条旋耕; DT-SRT-RT: 深耕-条旋耕-旋耕。不同小写字母表示同一取样深度不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。RT-RT-RT: continuous rotary tillage; DT-RT-RT: deep tillage-rotary tillage-rotary tillage; DT-RT-SRT: deep tillage-rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage; DT-SRT-SRT: deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage; DT-SRT-RT: deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-rotary tillage. Different lowercase letters mean significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level in the same sample depth.
Figure 1. Alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen (A), available phosphorus (B) and available potassium (C) contents in different soil layers under different treatments
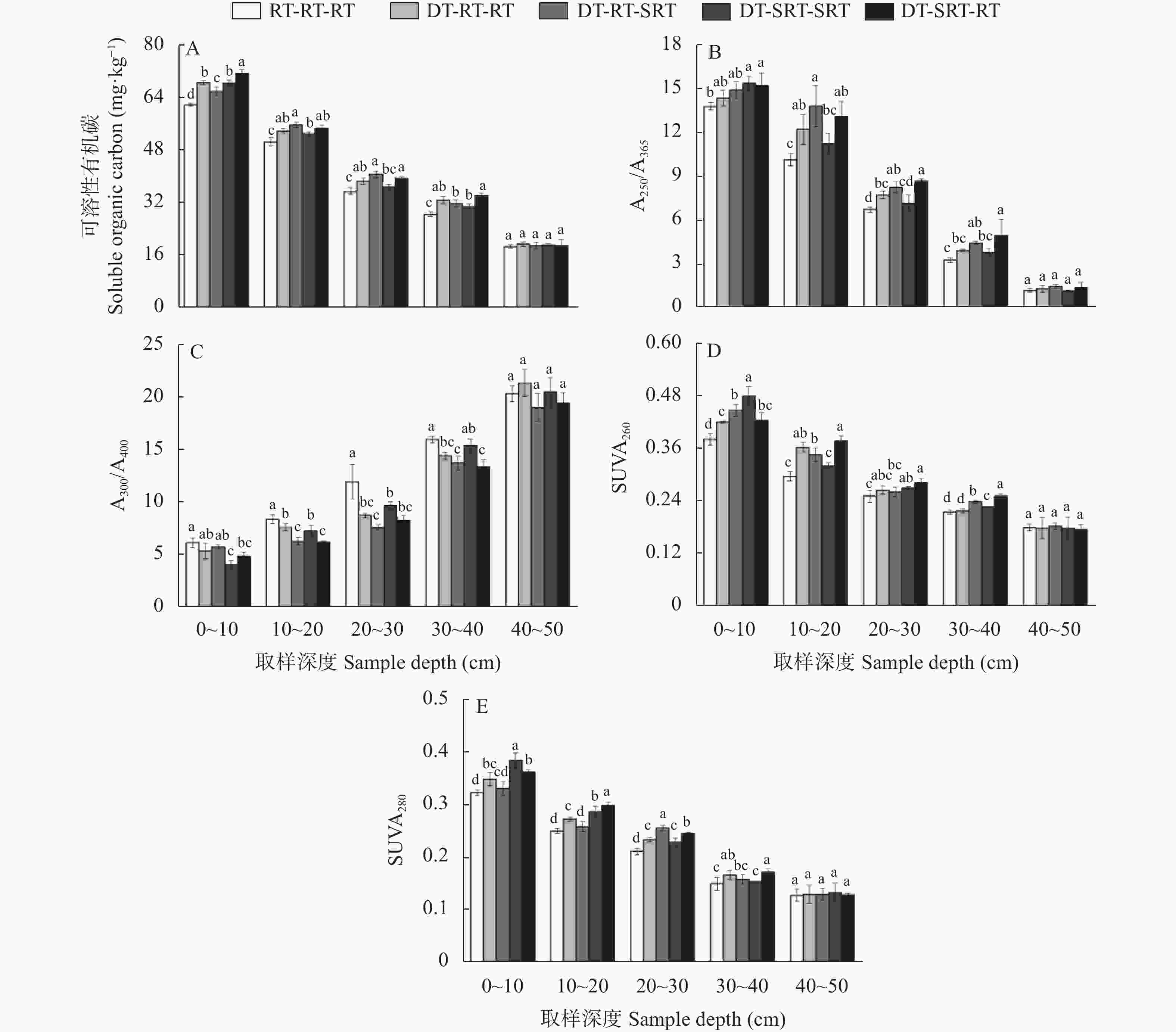
图 2 不同处理不同土层土壤可溶性有机碳含量(A)、腐殖化程度(A250/A365, B)、有机质分子量与聚合度(A300/A400, C)、疏水组分比例(SUVA260, D)和芳香化程度与分子量大小(SUVA280, E)
RT-RT-RT: 连续旋耕; DT-RT-RT: 深耕-旋耕-旋耕; DT-RT-SRT: 深耕-旋耕-条旋耕; DT-SRT-SRT: 深耕-条旋耕-条旋耕; DT-SRT-RT: 深耕-条旋耕-旋耕。不同小写字母表示同一取样深度不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。RT-RT-RT: continuous rotary tillage; DT-RT-RT: deep tillage-rotary tillage-rotary tillage; DT-RT-SRT: deep tillage-rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage; DT-SRT-SRT: deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-strip rotary tillage; DT-SRT-RT: deep tillage-strip rotary tillage-rotary tillage. Different lowercase letters mean significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level in the same sample depth.
Figure 2. Soil dissolved organic carbon content (A), degree of humification (A250/A365, B), molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter (A300/A400, C), proportions of hydrophobic components (SUVA260, D) and degree of aromatization and molecular weight (SUVA280, E) in different soil layers under different treatments
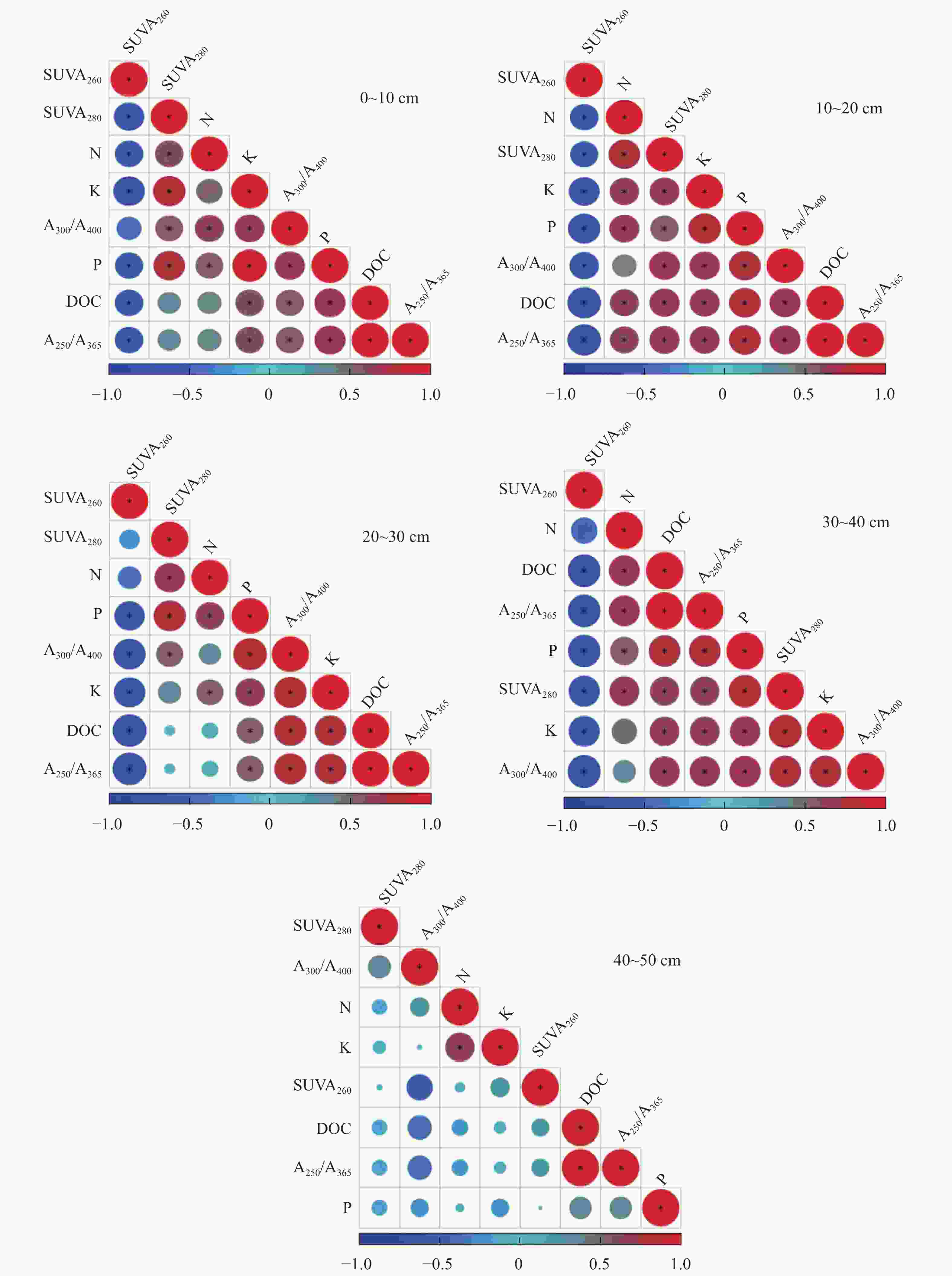
图 3 0~50 cm土层不同深度土壤养分指标与可溶性有机物紫外光谱参数的相关性分析
N、P、K 分别代表碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾; DOC、A250/A365、A300/A400、SUVA260、SUVA280分别代表可溶性有机碳、腐殖化程度、有机质分子量与聚合度、疏水组分比例、芳香化程度与分子量大小。 N, P, K represent alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium; DOC, A250/A365, A300/A400, SUVA260 and SUVA280 represent dissolved organic carbon, degree of humification, molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter, hydrophobic components, degree of aromatization and molecular weight.
Figure 3. Correlation analysis of soil nutrient indices and UV spectral parameters of dissolved organic matter in different depthes of 0−50 cm soil layer
表 1 可溶性有机物(DOM)的紫外–可见光谱特征参数描述及表征意义
Table 1. Description and significance of characteristic parameters of ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter (DOM)
吸光度
Wavelength (nm)定义
Definition意义
SignificanceA250/A365 DOM滤出液在250 nm和365 nm处吸光度的比值
The ratio of absorbance of DOM filtrate at 250 nm and 365 nm表征DOM腐殖化程度[20]
Indicates the degree of DOM humificationA300/A400 DOM滤出液在300 nm和400 nm处吸光度的比值
The ratio of absorbance of DOM filtrate at 300 nm and 400 nm表征DOM分子量与聚合度[21]
Indicates the molecular weight and degree of polymerization of DOMSUVA260 单位DOM浓度在波长260 nm处的吸收系数
Absorption coefficient of unit DOM concentration at wavelength 260 nm表征DOM疏水性组分比例[16-17]
Indicates the proportion of DOM hydrophobic componentsSUVA280 单位DOM浓度在波长280 nm处的吸收系数
Absorption coefficient of unit DOM concentration at wavelength 280 nm表征DOM芳香化程度和分子量大小[18-19]
Indicates the degree of aromatization and molecular weight of DOM表 2 轮耕模式对不同土层土壤速效养分含量的主体间效应检验
Table 2. Tests on the intersubjective effects of rotation tillage patterns on soil available nutrients contents in different soil layers
源
Source土壤养分
Soil nutrientⅢ 型平方和
Sum of squared deviations from meandf 均方
Mean squareF P 土层
Soil layer碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen 30 433.346 4 7608.34 8956.67 0 有效磷 Available phosphorus 3279.283 4 819.82 3538.85 0 速效钾 Available potassium 59 707.959 4 14 926.99 2893.77 0 轮耕
rotation tillage碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen 92.541 4 23.14 27.24 0 有效磷 Available phosphorus 21.505 4 5.38 23.21 0 速效钾 Available potassium 523.974 4 130.99 25.40 0 土层×轮耕
Soil layer ×
rotation tillage碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen 39.188 16 2.45 2.88 0.002 有效磷 Available phosphorus 9.668 16 0.60 2.61 0.005 速效钾 Available potassium 320.027 16 20.002 3.88 0 表 3 轮耕模式对不同土层土壤可溶性有机碳及其结构特性主体间效应的检验
Table 3. Tests on the intersubjective effects of rotation tillage patterns on soil dissolved organic carbon and its structural characteristics in different soil layers
源
Source因变量
Dependent variableⅢ 型平方和
Sum of squared deviations from meandf 均方
Mean squareF P 土层
Soil layer可溶性有机碳含量 Dissolved organic carbon content 21 246.08 4 5311.52 4180.36 0 腐殖化程度 Degree of humification 1839.13 4 459.78 1363.44 0 有机质分子量与聚合度
Molecular weight and polymerization degreee of organic matter2199.53 4 549.88 1036.17 0 疏水组分比例 Hydrophobic components 0.59 4 0.15 942.02 0 芳香化程度与分子量大小
Degree of aromatization and molecular weight0.47 4 0.12 1305.51 0 轮耕
Rotation tillage可溶性有机碳含量 Dissolved organic carbon content 192.42 4 48.10 37.86 0 腐殖化程度 Degree of humification 27.15 4 6.79 20.13 0 有机质分子量与聚合度
Molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter45.66 4 11.41 21.51 0 疏水组分比例 Hydrophobic components 0.012 4 0.003 20.04 0 芳香化程度与分子量大小
Degree of aromatization and molecular weight0.007 4 0.002 20.86 0 土层×轮耕
Soil layer × rotation tillage可溶性有机碳含量 Dissolved organic carbon content 114.126 16 7.13 5.61 0 腐殖化程度 Degree of humification 16.671 16 1.04 3.09 0.001 有机质分子量与聚合度
Molecular weight and polymerization degree of organic matter30.861 16 1.93 3.64 0 疏水组分比例 Hydrophobic components 0.02 16 0.001 8.15 0 芳香化程度与分子量大小
Degree of aromatization and molecular weight0.009 16 0.001 6.32 0 -
[1] 曹志磊, 俞花美, 葛成军, 等. 可溶性有机物对土霉素在土壤中吸附-解吸的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(4): 825−831 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.04.034CAO Z L, YU H M, GE C J, et al. Effects of dissolved organic matter on adsorption-desorption behavior of oxytetracycline in soil system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(4): 825−831 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.04.034 [2] 张浩, 吕茂奎, 谢锦升. 红壤侵蚀区芒萁对土壤可溶性有机质光谱特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 862−871 doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2016.0363ZHANG H, LYU M K, XIE J S. Effect of Dicranopteris dichotoma on spectroscopic characteristic of dissolved organic matter in red soil erosion area[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(8): 862−871 doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2016.0363 [3] 周国模, 姜培坤. 不同植被恢复对侵蚀型红壤活性碳库的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(6): 68−70, 83 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.06.016ZHOU G M, JIANG P K. Changes in active organic carbon of erosion red soil by vegetation recovery[J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2004, 18(6): 68−70, 83 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.06.016 [4] 刘翥, 杨玉盛, 司友涛, 等. 植被恢复对侵蚀红壤可溶性有机质含量及光谱学特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(11): 1174−1183 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00113LIU Z, YANG Y S, SI Y T, et al. Effects of vegetation restoration on content and spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matter in eroded red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(11): 1174−1183 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00113 [5] 陈兰, 唐晓红, 魏朝富. 土壤腐殖质结构的光谱学研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(8): 233−239 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2007.08.051CHEN L, TANG X H, WEI C F. Spectroscopies of soil humic substances: a review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 23(8): 233−239 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2007.08.051 [6] 侯贤清, 李荣, 韩清芳, 等. 轮耕对宁南旱区土壤理化性状和旱地小麦产量的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(3): 592−600 doi: 10.11766/trxb201107290282HOU X Q, LI R, HAN Q F, et al. Effects of alternate tillage on soil physicochemical properties and yield of dryland wheat in arid areas of south Ningxia[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(3): 592−600 doi: 10.11766/trxb201107290282 [7] 王丽, 李军, 李娟, 等. 轮耕与施肥对渭北旱作玉米田土壤团聚体和有机碳含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(3): 759−768WANG L, LI J, LI J, et al. Effects of tillage rotation and fertilization on soil aggregates and organic carbon content in corn field in Weibei Highland[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(3): 759−768 [8] 王健波. 耕作方式对旱地冬小麦土壤有机碳转化及水分利用影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014WANG J B. Effect of different tillage practices on soil organic carbon transformation and water use in dryland winter wheat[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014 [9] 丁晋利, 武继承, 杨永辉, 等. 免耕对农田土壤有机碳及可溶性有机碳的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2020, 43(3): 27−31DING J L, WU J C, YANG Y H, et al. Impacts of no-tillage on soil organic carbon and soil dissolved organic carbon in farmland[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2020, 43(3): 27−31 [10] 叶新新, 王冰清, 刘少君, 等. 耕作方式和秸秆还田对砂姜黑土碳库及玉米小麦产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(14): 112−118 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.14.014YE X X, WANG B Q, LIU S J, et al. Influence of tillage and straw retention on soil carbon pool and maize-wheat yield in Shajiang black soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(14): 112−118 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.14.014 [11] 孙国峰, 徐尚起, 张海林, 等. 轮耕对双季稻田耕层土壤有机碳储量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(18): 3776−3783 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.18.011SUN G F, XU S Q, ZHANG H L, et al. Effects of rotational tillage in double rice cropping region on organic carbon storage of the arable paddy soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(18): 3776−3783 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.18.011 [12] LIU M, ZHANG Z J, HE Q, et al. Exogenous phosphorus inputs alter complexity of soil-dissolved organic carbon in agricultural riparian wetlands[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 95: 572−580 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.117 [13] YANG Y S, XIE J S, SHENG H, et al. The impact of land use/cover change on storage and quality of soil organic carbon in midsubtropical mountainous area of southern China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2009, 19(1): 49−57 doi: 10.1007/s11442-009-0049-5 [14] 谢理, 杨浩, 渠晓霞, 等. 滇池典型陆生和水生植物溶解性有机质组分的光谱分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(1): 72−79XIE L, YANG H, QU X X, et al. Characterization of water extractable organic matters from the dominant plants in Lake Dianchi by multiple spectroscopic techniques[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 26(1): 72−79 [15] 常单娜, 曹卫东, 白金顺, 等. 绿肥对华北潮土土壤可溶性有机物的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(1): 221−226CHANG D N, CAO W D, BAI J S, et al. Effects of green manures on soil dissolved organic matter in moisture soil in North China[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(1): 221−226 [16] DILLING J, KAISER K. Estimation of the hydrophobic fraction of dissolved organic matter in water samples using UV photometry[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(20): 5037−5044 doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00365-2 [17] JAFFRAIN J, GÉRARD F, MEYER M, et al. Assessing the quality of dissolved organic matter in forest soils using ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2007, 71(6): 1851−1858 doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0202 [18] LIN D S, GREENWOOD P F, GEORGE S, et al. The development of soil organic matter in restored biodiverse Jarrah forests of South-Western Australia as determined by ASE and GCMS[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2011, 18(7): 1070−1078 doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0433-9 [19] KORSHIN G V, CROUÉ J P, LI C W, et al. Comprehensive Study of UV Absorption and Fluorescence Spectra of Suwannee River Nom Fractions[M]//Understanding Humic Substances. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 147–156 [20] WANG L Y, WU F C, ZHANG R Y, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter fractions from Lake Hongfeng, Southwestern China Plateau[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(5): 581−588 doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62311-6 [21] ARTINGER R, BUCKAU G, GEYER S, et al. Characterization of groundwater humic substances: influence of sedimentary organic carbon[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(1): 97−116 doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00021-9 [22] 张伟, 王克林, 刘淑娟, 等. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被演替过程中土壤养分的积累及影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(7): 1801–1808ZHANG W, WANG K L, LIU S J, et al. Soil nutrient accumulation and its affecting factors during vegetation succession in Karst peak-cluster depressions of South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24 (7): 1801–1808 [23] 黄倩, 吴靖霆, 陈杰, 等. 土壤吸附可溶性有机碳研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(3): 446−452HUANG Q, WU J T, CHEN J, et al. Adsorption of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) on soil: A review[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(3): 446−452 [24] 张勉. 夏闲期轮耕对旱地麦田土壤理化性状及有机碳组分的影响[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2017ZHANG M. Effects of tillage during summer fallow on soil physicochemical properties and organic carbon components in dryland wheat fields[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017 [25] 陶贞, 沈承德, 高全洲, 等. 土地利用变化对高寒草甸土壤有机质更新的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2007, 29(2): 217−225TAO Z, SHEN C D, GAO Q Z, et al. The impact of land use change on soil organic matter turnover of alpine meadow in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2007, 29(2): 217−225 [26] 刘霞娇, 段亚峰, 叶莹莹, 等. 耕作扰动对喀斯特土壤可溶性有机质及其组分迁移淋失的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(19): 6981−6991LIU X J, DUAN Y F, YE Y Y, et al. The impacts of tillage on soil soluble organic matter and its movement and leaching in Karst area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(19): 6981−6991 [27] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2000 [28] BORISOVER M, LORDIAN A, LEVY G J. Water-extractable soil organic matter characterization by chromophoric indicators: effects of soil type and irrigation water quality[J]. Geoderma, 2012, 179/180: 28−37 doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.02.019 [29] 唐海明, 孙国峰, 肖小平, 等. 轮耕对双季稻田土壤全氮、有效磷、速效钾质量分数及水稻产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(3): 420−424 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.03.005TANG H M, SUN G F, XIAO X P, et al. Effects of rotational tillage treatments on soil total nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium and grain yield of rice in double-rice cropping field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(3): 420−424 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.03.005 [30] 张琦, 王浩, 王淑兰, 等. 深松轮耕模式对黄土旱塬春玉米土壤理化性质和作物产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(2): 459−466ZHANG Q, WANG H, WANG S L, et al. Effects of tillage alternation pattern with subsoiling on soil physical and chemical properties and spring maize yield in the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(2): 459−466 [31] 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 等. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123−133 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2019403ZHANG J J, DANG Y, ZHAO G, et al. Effect of no-tillage with film and stubble residues on soil nutrients, microbial populations and enzyme activity in dryland maize fields[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(2): 123−133 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2019403 [32] 彭光爵, 王志勇, 胡桐, 等. 粉垄深耕对长沙稻作烟区土壤物理特性及烤烟根系发育的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(1): 134−142 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190952PENG G J, WANG Z Y, HU T, et al. Effects of deep vertical rotary tillage on soil physical characteristics and root development of flue-cured tobacco in paddy-tobacco growing area in Changsha[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(1): 134−142 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190952 [33] 何鑫. 不同耕作方式对农田黑土理化性质及玉米叶片PSⅡ功能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2017HE X. Effects of different tillage on physicochemical properties of farmland mollisoil and PSⅡ function of maize leaves[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017 [34] 孔凡磊, 张海林, 孙国峰, 等. 轮耕措施对小麦玉米两熟制农田土壤碳库特性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(2): 150−154, 183KONG F L, ZHANG H L, SUN G F, et al. Rotational tillage effects on characteristics of soil carbon pool for the wheat-corn system[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(2): 150−154, 183 [35] 杨景清, 王铮, 元晓春, 等. 不同森林更新方式下亚热带土壤可溶性有机质的数量及质量[J]. 河南科技学院学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(3): 16−25YANG J Q, WANG Z, YUAN X C, et al. The quantity and quality of dissolved organic matter under different regeneration modes in subtropical soil[J]. Journal of Henan Institute of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 45(3): 16−25 [36] 汪景宽, 李丛, 于树, 等. 不同肥力棕壤溶解性有机碳、氮生物降解特性[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(12): 6165−6171 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.046WANG J K, LI C, YU S, et al. The biodegradation of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in brown earth with different fertility levels[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(12): 6165−6171 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.046 [37] HAO Q J, CHENG B H, JIANG C S. Long-term tillage effects on soil organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in a purple paddy soil of Southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 260−265 doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2013.07.005 [38] 杨景成, 韩兴国, 黄建辉, 等. 土地利用变化对陆地生态系统碳贮量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(8): 1385−1390 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.08.038YANG J C, HAN X G, HUANG J H, et al. Effects of land use change on carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(8): 1385−1390 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.08.038 [39] 靳世蕊. 利用方式对土壤水溶性有机物紫外光谱特性影响评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2014JIN S R. Assessment of the impact on UV spectral characteristics of soil water soluble organic matter in the soils using in different ways[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2014 [40] 苏冬雪, 王文杰, 邱岭, 等. 落叶松林土壤可溶性碳、氮和官能团特征的时空变化及与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(21): 6705−6714 doi: 10.5846/stxb201109141347SU D X, WANG W J, QIU L, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of DOC, DON and their function group characteristics in larch plantations and possible relations with other physical-chemical properties[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(21): 6705−6714 doi: 10.5846/stxb201109141347 [41] 潘雅文, 樊军, 郝明德, 等. 黄土塬区长期不同耕作、覆盖措施对表层土壤理化性状和玉米产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与 肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1558−1567PAN Y W, FAN J, HAO M D, et al. Effects of long-term tillage and mulching methods on properties of surface soil and maize yield in tableland region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(6): 1558−1567 [42] DE MORAES SÁ J C, LAL R. Stratification ratio of soil organic matter pools as an indicator of carbon sequestration in a tillage chronosequence on a Brazilian Oxisol[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2009, 103(1): 46−56 doi: 10.1016/j.still.2008.09.003 [43] ZHAO Z H, GAO S F, LU C Y, et al. Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice-wheat rotation system[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 212: 105071 doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.105071 [44] 熊丽, 杨玉盛, 朱锦懋, 等. 可溶性有机碳在米槠天然林不同土层中的迁移特征[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(17): 5711−5720XIONG L, YANG Y S, ZHU J M, et al. Transport characteristics of dissolved organic carbon in different soil horizons in natural Castanopsis carlesii forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(17): 5711−5720 -





 下载:
下载: