Factors influencing soil water content during dry period in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
-
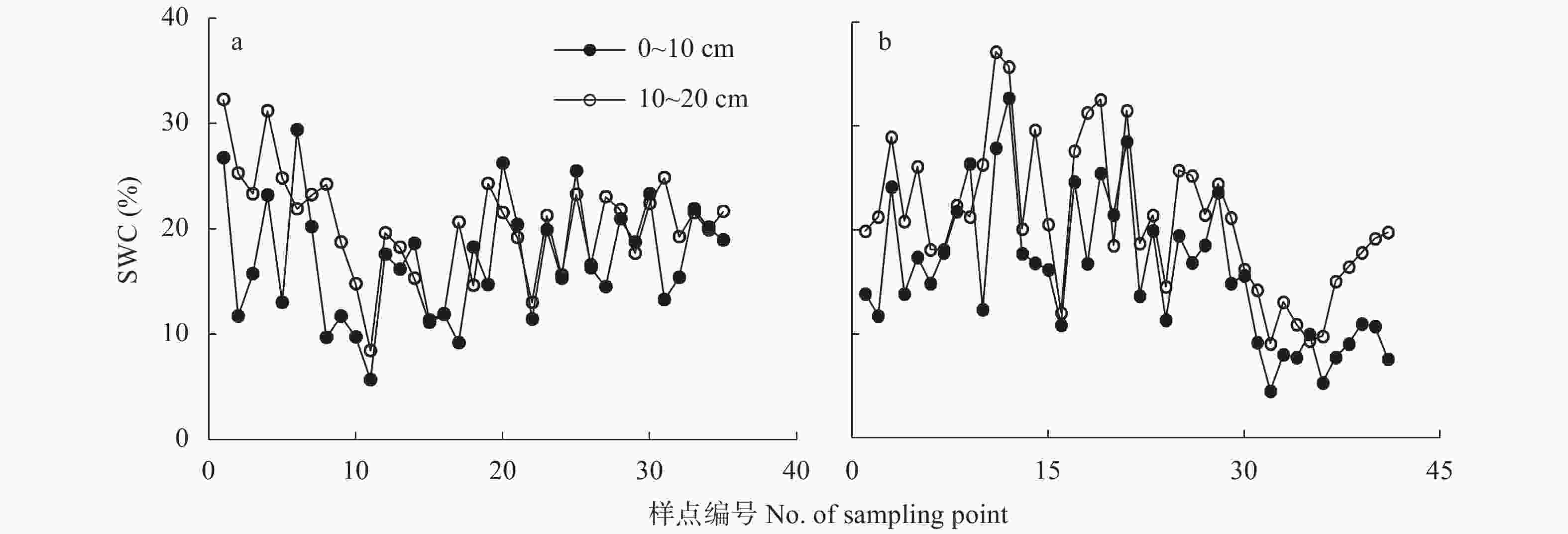
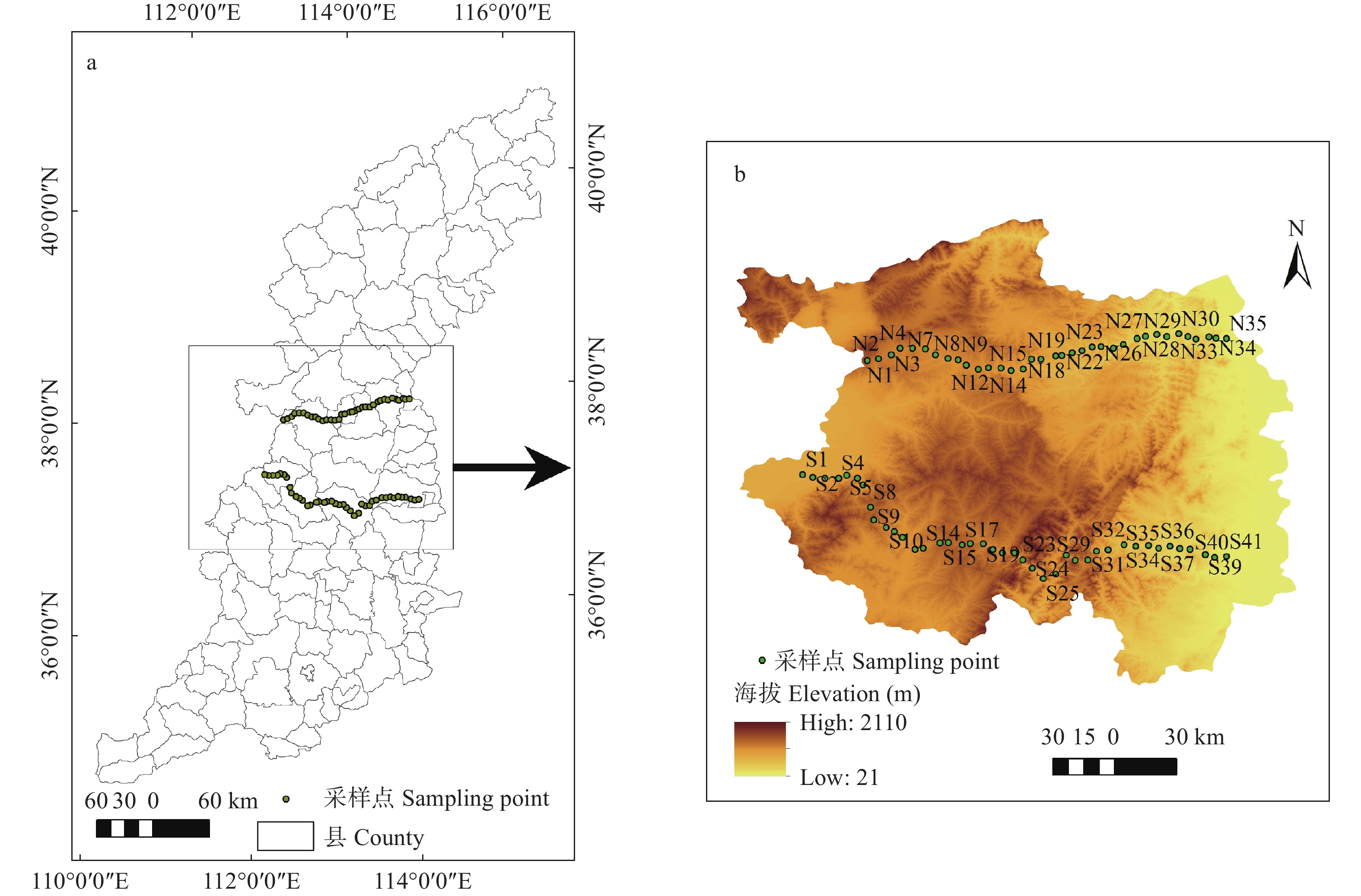
摘要: 太行山脉为我国第二、第三阶梯的重要分界线, 海拔自西向东迅速降低, 在这种自然条件复杂的地理空间过渡带内, 土壤含水量(SWC)空间格局特征及其影响因素亦复杂而不明确, 限制了对山区土壤水文过程的认知。本研究通过在太行山区中段设置间距约85 km的两条样线(长度分别为140 km和164 km), 在旱季采集土壤样品, 测定SWC、容重、毛管孔隙度、非毛管孔隙度、有机碳含量、机械组成等理化性质, 详细调查样点的地形条件(坡度、坡向、海拔等)和植被条件(植被类型、枯落物情况等), 利用经典统计和地统计的方法, 并结合结构方程模型, 分析了表层(0~10 cm)和次表层(10~20 cm) SWC在海拔梯度上的变异特征, 探讨了其主要影响因素。结果表明, 太行山区中段两条样线均表现为表层SWC显著小于次表层, 两条样线之间没有显著差异。地统计分析表明, 表层和次表层SWC分别适用线性模型和指数模型模拟, 说明表层SWC影响因素更加复杂, 随机因素占主导地位; 次表层呈现出块基效应, 随机因素和结构因素共同起作用。两条样线次表层SWC块基比分别为48.01%和31.62%, 说明次表层SWC属中等程度的空间相关性。影响SWC的主要环境因子为海拔和降水量, 坡度、坡向及植被类型没有达到显著水平; 土壤性质中, 表层SWC主要受容重的影响, 次表层主要受毛管孔隙度和黏粒含量的影响。结构方程模型显示, 土壤性质是影响旱季SWC的直接因素, 环境因子是间接因素。环境因子对旱季SWC的影响超过80%是通过土壤性质产生的间接影响。以上结果有助于深入了解太行山区SWC特征, 为水-土过程的深入研究提供科学依据。Abstract: Taihang Mountain is an important natural boundary between the second and third steps in China. The elevation of this mountains decreases drastically from west to east. Owing to the complex environment in this transition zone, the spatial pattern of and the factors influencing soil water content (SWC) are complex and unclear. This limits further understanding of the soil hydrological processes. In this study, two line transects (140 km and 164 km long, respectively) were set in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain, which are 85 km apart. Both disturbed and undisturbed soils were sampled along two line transects during the dry period in the middle part of Taihang Mountain region. Soil water content, bulk density (BD), capillary porosity (CP), non-capillary porosity (NCP), soil organic carbon (SOC), and soil particle composition (sand, silt, and clay contents) were measured. Topographical conditions (including slope gradient, slope aspect, and elevation) and vegetation conditions (including vegetation type, vegetation cover, and litter information) were also investigated for each sampling point. Classical statistical, geostatistical, and structural equation modeling methods were used to study the variation and influencing factors of the SWC in the surface (0–10 cm) and subsurface (10–20 cm) layers along the two line transects in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain. The results showed that the SWC of the surface soil layer was significantly lower than that of the subsurface layer. No significant differences were observed between the two studied line transects. In geostatistical analysis, the most suitable SWC model was a linear model for the surface soil layer, but an exponential model for the subsurface layer. This indicated that random factors played a dominant role, and the influencing factors may be more complex for the surface soil layer. For the subsurface layer, an obvious nugget effect was observed, suggesting the coexistence of random and structural factors. The nugget to sill value of the subsurface layer was 48.01% and 31.62%, respectively, for the two-line transects. This indicated that both line transects showed moderate spatial dependence. Among the considered environmental factors, precipitation and elevation significantly influenced the SWC. Other environmental factors showed no significant effects. Among the studied soil properties, BD significantly influenced the SWC of the surface layer, whereas the CP and clay content significantly influenced the SWC of the subsurface soil layer. Structural equation modeling showed that soil properties were the direct factor, and environmental factors were indirect factors of SWC. Over 80% of the environmental factors acted through the soil properties. These results can be helpful in further understanding the soil water characteristics in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain and provide a scientific basis for studying soil hydrological processes in similar mountainous areas.
-
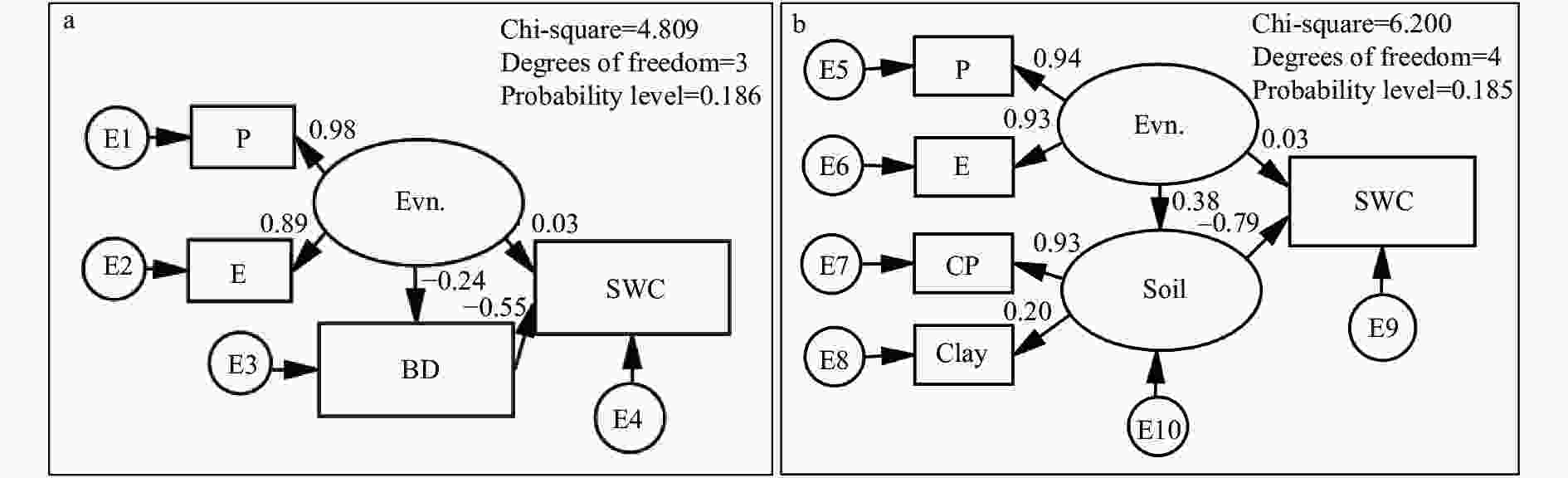
图 3 太行山中段不同层次土壤含水量影响因素的结构方程模型
a: 0~10 cm; b: 10~20 cm。Evn.为环境因子, Soil为土壤性质, SWC为土壤含水量, P为年降雨量, E为海拔, BD为土壤容重, CP为毛管孔隙度, Clay为黏粒含量, E为误差项。
Figure 3. Structural equation modeling of soil water content of different layers in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
Evn. means the environmental factors, Soil means the soil properties, SWC means soil water content, P means annual precipitation, E means elevation, BD means bulk density, CP means capillary porosity, E means error.
表 1 太行山中段两条样线不同层次土壤属性及环境因子数据分布特征
Table 1. Data distribution of soil properties of different layers and environmental factors in two line transects of the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
类别
Category性质
Property数据分布特征及转换 Data distribution and transformation 0~10 cm 10~20 cm 土壤属性 Soil property 含水量 Soil water content 正态分布 Normal distribution 正态分布 Normal distribution 容重 Bulk density 正态分布 Normal distribution log转换 Logarithmic transformation 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity 秩排序 Rank cases Lngamma转换 Lngamma transformation 非毛管孔隙度 Non-capillary porosity 秩排序 Rank cases log转换 Logarithmic transformation 有机碳含量 Soil organic carbon 平方根转换 Square root transformation 正态分布 Normal distribution 砂粒 Sand content log转换 Logarithmic transformation log转换 Logarithmic transformation 粉粒 Silt content Lngamma转换 Lngamma transformation 秩排序 Rank cases 黏粒 Clay content 平方根转换 Square root transformation 正态分布 Normal distribution 自然因子 Natural factor 年降水量 Annual precipitation 正态分布 Normal distribution 海拔 Elevation 秩排序 Rank cases 坡度 Slope gradient log转换 Logarithmic transformation 坡向 Slope aspect 正态分布 Normal distribution NDVI 正态分布 Normal distribution 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness log转换 Logarithmic transformation 表 2 太行山中段两条样线不同层次土壤含水量描述性统计
Table 2. Describe statistic of soil water contents of different layers in two line transects of the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
样线
Line transect土层
Soil layer (cm)样本数
Sampling number平均值
Mean (%)标准偏差
Standard deviation (%)变异系数
Coefficient of variation北样线
North transect0~10 35 17.56bA 6.42 0.37 10~20 35 20.62aA 5.84 0.28 南样线
South transect0~10 41 16.06bA 6.85 0.43 10~20 41 21.08aA 7.03 0.33 不同小写字母表示不同层次之间差异显著(P<0.05), 不同大写字母表示不同样线之间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences between two soil layers at P<0.05, different capital letters mean significant differences between two line transects. 表 3 太行山区中段不同样线不同层次土壤含水量地统计学特征
Table 3. Geostatistical characteristic of soil water contents of different layers in two line transects of the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
样线
Line transect土层
Soil layer (cm)模型
ModelC0 C0+C C0/(C0+C)
(%)变程
Range (km)R2 北样线
North transect0~10 线性
Linear42.46 42.46 100.00 65.7 0.22 10~20 指数
Exponential24.21 50.43 48.01 145.5 0.47 南样线
South transect0~10 线性
Linear52.08 60.48 86.11 80.2 0.24 10~20 指数
Exponential21.00 66.42 31.62 128.4 0.90 表 4 太行山区中段不同层次土壤属性对土壤含水量的回归分析
Table 4. Regression analysis of soil water content of different layers and other soil properties in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
土层
Soil layer (cm)模型变量
Independent variableR2 调整后R2
Adjusted R2标准估算的错误
Estimated standard error0~10 容重 Bulk density 0.407 0.356 5.34 10~20 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity 0.565 0.560 4.45 黏粒含量 Clay content 0.596 0.585 4.32 表 5 太行山区中段不同层次土壤含水量与地形因素的相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis between soil water contents of different layers and geographical factors in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
土层
Soil layer (cm)参数
Parameter年降水量
Annual precipitation海拔
Elevation坡度
Slope gradient坡向
Slope aspectNDVI 枯落物厚度
Litter thickness0~10 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R) 0.306** 0.282* –0.045 –0.201 0.018 0.037 P 0.007 0.014 0.698 0.082 0.876 0.750 样本数 Samples number 76 76 76 76 76 76 10~20 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R) 0.310** 0.306** –0.125 –0.205 0.137 0.151 P 0.006 0.007 0.282 0.075 0.238 0.194 样本数 Samples number 76 76 76 76 76 76 表 6 太行山中段不同层次土壤含水量在不同地形部位和不同土地利用类型的方差分析
Table 6. Variance analysis of soil water contents of different layers at different topographical locations and land use types in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
土层
Soil layer (cm)源
Source平方和
Sum of squares自由度
Degree均方
Root mean squareF 显著性
Significant value0~10 校正模型
Corrected model364.468 11 33.13 0.72 0.72 截距
Intercept21 322.11 1 21 322.11 461.40 0 地形部位
Topographical location203.49 3 67.83 1.47 0.23 土地利用
Land use31.65 2 15.83 0.34 0.71 地形部位×土地利用
Topographical location×land use129.31 6 21.55 0.47 0.83 10~20 校正模型
Corrected model758.85 11 68.99 1.69 0.10 截距
Intercept26 603.80 1 26 603.80 650.16 0 地形部位
Topographical location289.61 3 96.54 2.36 0.08 土地利用
Land use121.62 2 60.81 1.49 0.23 地形部位×土地利用
Topographical location×land use347.62 6 57.94 1.42 0.22 表 7 太行山中段不同层次土壤性质和环境因子对土壤含水量的直接影响和间接影响
Table 7. Direct and indirect effects of soil properties and environmental factors on soil water contents of different layers in the middle part of the Taihang Mountain
土层
Soil layer (cm)环境因子 Environmental factor 土壤因子 Soil factor 直接
Direct effect百分比
Percentage (%)间接
Indirect effect百分比
Percentage (%)环境因子总效应
Total effect直接
Direct effect间接
Indirect effect0~10 0.03 18.75 0.13 81.25 0.16 −0.55 0 10~20 0.03 10.00 0.30 90.00 0.33 −0.79 0 -
[1] CASTILLO V M, GÓMEZ-PLAZA A, MARTı́NEZ-MENA M. The role of antecedent soil water content in the runoff response of semiarid catchments: a simulation approach[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 284(1/2/3/4): 114−130 [2] WU Y Y, HE G J, OUYANG W, et al. Differences in soil water content and movement drivers of runoff under climate variations in a high-altitude catchment[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 587: 125024 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125024 [3] NAN W G, LIU S Q, YANG S J, et al. Changes of Sabina vulgaris growth and of soil moisture in natural stands and plantations in semi-arid Northern China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2020, 21: e00859 doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00859 [4] 易小波. 西北干旱区土壤含水量时空变化特征及土壤物理性质模拟试验研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017YI X B. Spatial and temporal variation of soil water content and modeling of soil physical properties in arid region of northwest China[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2017 [5] ZHANG J G, CHEN H S, SU Y R, et al. Spatial variability of surface soil moisture in a depression area of Karst region[J]. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 2011, 39(7): 619−625 doi: 10.1002/clen.201000528 [6] BARONI G, ORTUANI B, FACCHI A, et al. The role of vegetation and soil properties on the spatio-temporal variability of the surface soil moisture in a maize-cropped field[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 489: 148−159 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.03.007 [7] WANG Y Q, SHAO M A, LIU Z P, et al. Regional spatial pattern of deep soil water content and its influencing factors[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2012, 57(2): 265−281 doi: 10.1080/02626667.2011.644243 [8] YANG J, CHEN H S, NIE Y P, et al. Dynamic variations in profile soil water on Karst hillslopes in Southwest China[J]. CATENA, 2019, 172: 655−663 doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.032 [9] LEE Y, JUNG C, KIM S. Spatial distribution of soil moisture estimates using a multiple linear regression model and Korean geostationary satellite (COMS) data[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 213: 580−593 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.004 [10] 付同刚, 陈洪松, 张伟, 等. 喀斯特小流域土壤含水率空间异质性及其影响因素[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(14): 124−131 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.14.016FU T G, CHEN H S, ZHANG W, et al. Spatial variability of soil moisture content and its influencing factors in small Karst catchment during dry period[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(14): 124−131 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.14.016 [11] GAO L, SHAO M G. Temporal stability of shallow soil water content for three adjacent transects on a hillslope[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2012, 110: 41−54 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2012.03.012 [12] 唐敏, 赵西宁, 高晓东, 等. 黄土丘陵区不同土地利用类型土壤水分变化特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(3): 765−774TANG M, ZHAO X N, GAO X D, et al. Characteristics of soil moisture variation in different land use types in the hilly region of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(3): 765−774 [13] 徐飞, 赖晓明, 朱青, 等. 太湖流域丘陵区两种土地利用类型土壤水分分布控制因素[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(3): 592−599XU F, LAI X M, ZHU Q, et al. The controlling factors of soil moisture distribution under two typical land-use hillslopes in a hilly region of Taihu Lake Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(3): 592−599 [14] 任启文, 王鑫, 李联地, 等. 小五台山不同海拔土壤理化性质垂直变化规律[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(1): 241−247REN Q W, WANG X, LI L D, et al. Vertical variation of soil physical and chemical properties at different altitudes in Xiaowutai Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(1): 241−247 [15] FAMIGLIETTI J S, RUDNICKI J W, RODELL M. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect: Rattlesnake Hill, Texas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1998, 210(1/2/3/4): 259−281 [16] 宋献方, 李发东, 刘昌明, 等. 太行山区水循环及其对华北平原地下水的补给[J]. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(3): 398−408 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2007.03.009SONG X F, LI F D, LIU C M, et al. Water cycle in Taihang Mountains and its recharge to groundwater in North China Plain[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2007, 22(3): 398−408 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2007.03.009 [17] 曹建生. 太行山区岩土二元介质水分运移机制及高效利用研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011CAO J S. Research on water movement and high-efficient utilization on slope characterized by a soil-rock binary medium in mountain area of Taihang Mountain[D]. Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011 [18] 张志华, 郭加伟, 桑玉强, 等. 太行山南麓鱼鳞坑工程对坡面土壤水分空间变异性的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(9): 85−92ZHANG Z H, GUO J W, SANG Y Q, et al. Spatial variation in soil water content over hillslopes engineered by fish-scale pits in Taihang Mountainous region[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(9): 85−92 [19] 王齐瑞, 谭晓风, 高峻. 太行山山前坡地不同土地利用方式下土壤水分的时空变异特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2008, 22(4): 100−103 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.04.022WANG Q R, TAN X F, GAO J. Spatiotemporal variability of soil moisture under different land use patterns of Taihang Mountains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 22(4): 100−103 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.04.022 [20] 朱奎, 夏军, 邓群, 等. 太行山山地丘陵区雨季土壤水分动态规律研究−以崇陵流域为研究区[J]. 水利水电技术, 2007, 38(10): 6−9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2007.10.002ZHU K, XIA J, DENG Q, et al. Study on dynamic law of soil moisture during rainy season in hilly area of Taihang Mountain: A case study on Chongling Watershed[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2007, 38(10): 6−9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2007.10.002 [21] 司梦可, 曹建生, 阳辉, 等. 太行山区不同植被条件下土壤水分动态变化特征研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(11): 1766−1777SI M K, CAO J S, YANG H, et al. Soil water variation of different vegetation community in Taihang Mountain Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(11): 1766−1777 [22] 史薪钰, 刘洋, 齐国辉, 等. 太行山片麻岩山地坡面土壤含水率及其影响因子−以河北省阜平县为例[J]. 林业资源管理, 2015(3): 114−120SHI X Y, LIU Y, QI G H, et al. Study on soil moisture content and its impact factors in Taihangshan low gneiss mountainous area — take Fuping County, Hebei Province as an example[J]. Forest Resource Management, 2015(3): 114−120 [23] WANG L, WANG Q J, WEI S P, et al. Soil desiccation for loess soils on natural and regrown areas[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(7): 2467−2477 doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2008.01.006 [24] FU T G, CHEN H S, FU Z Y, et al. Surface soil water content and its controlling factors in a small Karst catchment[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(21): 1−11 [25] 戴军杰, 章新平, 吕殿青, 等. 南方红壤丘陵区樟树林土壤水分动态变化[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4): 123−131DAI J J, ZHANG X P, LYU D Q, et al. Dynamics of soil water in Cinnamomum camphora forest in the red soil hilly region of South China[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4): 123−131 [26] 邱扬, 傅伯杰, 王军, 等. 黄土丘陵小流域土壤水分的空间异质性及其影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(5): 715−720 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.05.016QIU Y, FU B J, WANG J, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture content on the Loess Plateau, China and its relation to influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(5): 715−720 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.05.016 [27] 王珊. 土壤水肥空间变异及对作物产量影响的研究[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2019WANG S. Spatial variation of soil water and fertilizer and its effects on crop yield[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agriculture University, 2019 [28] PENNA D, BROCCA L, BORGA M, et al. Soil moisture temporal stability at different depths on two alpine hillslopes during wet and dry periods[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 477: 55−71 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.052 [29] ZHU Q, NIE X F, ZHOU X B, et al. Soil moisture response to rainfall at different topographic positions along a mixed land-use hillslope[J]. CATENA, 2014, 119: 61−70 doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2014.03.010 [30] SUN F X, LÜ Y, WANG J L, et al. Soil moisture dynamics of typical ecosystems in response to precipitation: a monitoring-based analysis of hydrological service in the Qilian Mountains[J]. CATENA, 2015, 129: 63−75 doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.03.001 [31] 韩姣姣, 段旭, 赵洋毅, 等. 干热河谷不同土地利用类型坡面土壤水分时空变异[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(2): 129−136HAN J J, DUAN X, ZHAO Y Y, et al. Spatial and temporal variability of soil moisture on sloping lands of different land use types in a dry-hot valley[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(2): 129−136 [32] ZHAO W J, CUI Z, ZHANG J Y, et al. Temporal stability and variability of soil-water content in a gravel-mulched field in northwestern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 552: 249−257 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.031 [33] 刘佩伶, 陈乐, 刘效东, 等. 鼎湖山不同演替阶段森林土壤水分时空变异研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(5): 1798−1807LIU P L, CHEN L, LIU X D, et al. Temporal and spatial variability of soil moisture in a forest succession series in Dinghushan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(5): 1798−1807 [34] CHEN H S, ZHANG W, WANG K L, et al. Soil moisture dynamics under different land uses on Karst hillslope in northwest Guangxi, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 61(6): 1105−1111 doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0428-3 [35] 赵鑫, 辛一凡, 张应龙, 等. 不同植被类型对毛乌素沙地背风坡土壤水分时空变化的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(3): 36−43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.03.06ZHAO X, XIN Y F, ZHANG Y L, et al. Effects of different vegetation types on temporal and spatial variation of soil moisture on leeward slope of Mu Us sandy land[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(3): 36−43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.03.06 [36] LLOYD C D. Assessing the effect of integrating elevation data into the estimation of monthly precipitation in Great Britain[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 308(1/2/3/4): 128−150 [37] 张伟, 陈洪松, 王克林, 等. 喀斯特地区典型峰丛洼地旱季表层土壤水分空间变异性初探[J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(4): 554−562 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.04.004ZHANG W, CHEN H S, WANG K L, et al. Spatial variability of surface soil water in typical depressions between hills in Karst region in dry season[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(4): 554−562 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.04.004 [38] 李增尧, 赵兴凯, 朱清科. 陕北黄土区陡坡坡面因子对土壤水分的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2017, 35(9): 798−805 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8530.16.0114LI Z Y, ZHAO X K, ZHU Q K. Effects of farmland slope on soil moisture in semi-arid loess plateau of Northern Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2017, 35(9): 798−805 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8530.16.0114 [39] 陈有君, 关世英, 李绍良, 等. 内蒙古浑善达克沙地土壤水分状况的分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2000, 14(1): 80−85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2000.01.014CHEN Y J, GUAN S Y, LI S L, et al. Soil water regime of Hunshandake sandy land in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2000, 14(1): 80−85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2000.01.014 [40] 李奕, 满秀玲, 蔡体久, 等. 大兴安岭山地樟子松天然林土壤水分物理性质及水源涵养功能研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(2): 87−91, 96LI Y, MAN X L, CAI T J, et al. Research on physical properties of soil moisture and water conservation of scotch pine forest in Da Xing’an Mountains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(2): 87−91, 96 [41] 张敏, 刘爽, 刘勇, 等. 黄土丘陵缓坡风沙区不同土地利用类型土壤水分变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(3): 115−120, 128ZHANG M, LIU S, LIU Y, et al. Soil moisture variation characteristics of different land use types in the moderate slope sandy area of loess hilly region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(3): 115−120, 128 [42] BUTTAFUOCO G, CASTRIGNANÒ A, BUSONI E, et al. Studying the spatial structure evolution of soil water content using multivariate geostatistics[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 311(1/2/3/4): 202−218 [43] 赵世伟, 周印东, 吴金水. 子午岭北部不同植被类型土壤水分特征研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2002, 16(4): 119−122, 94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2002.04.031ZHAO S W, ZHOU Y D, WU J S. Soil moisture characteristics of different vegetations in northern of Ziwuling[J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2002, 16(4): 119−122, 94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2002.04.031 [44] 任婷婷, 王瑄, 孙雪彤, 等. 不同土地利用方式土壤物理性质特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(2): 123−126REN T T, WANG X, SUN X T, et al. Characterization of soil physical properties under different land use types[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(2): 123−126 -





 下载:
下载: