Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions in China’s agricultural sector: Current status and future perspectives
-
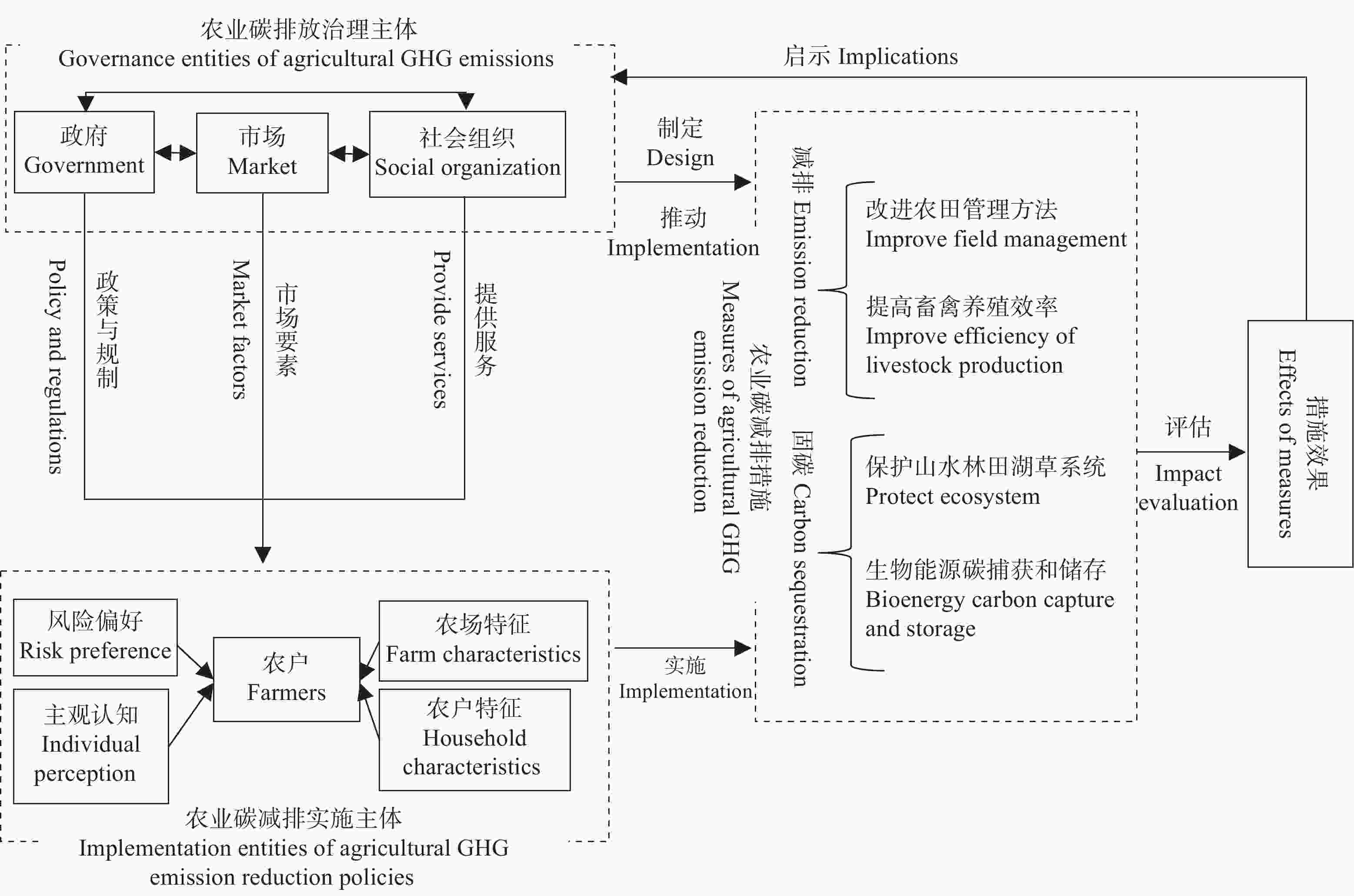
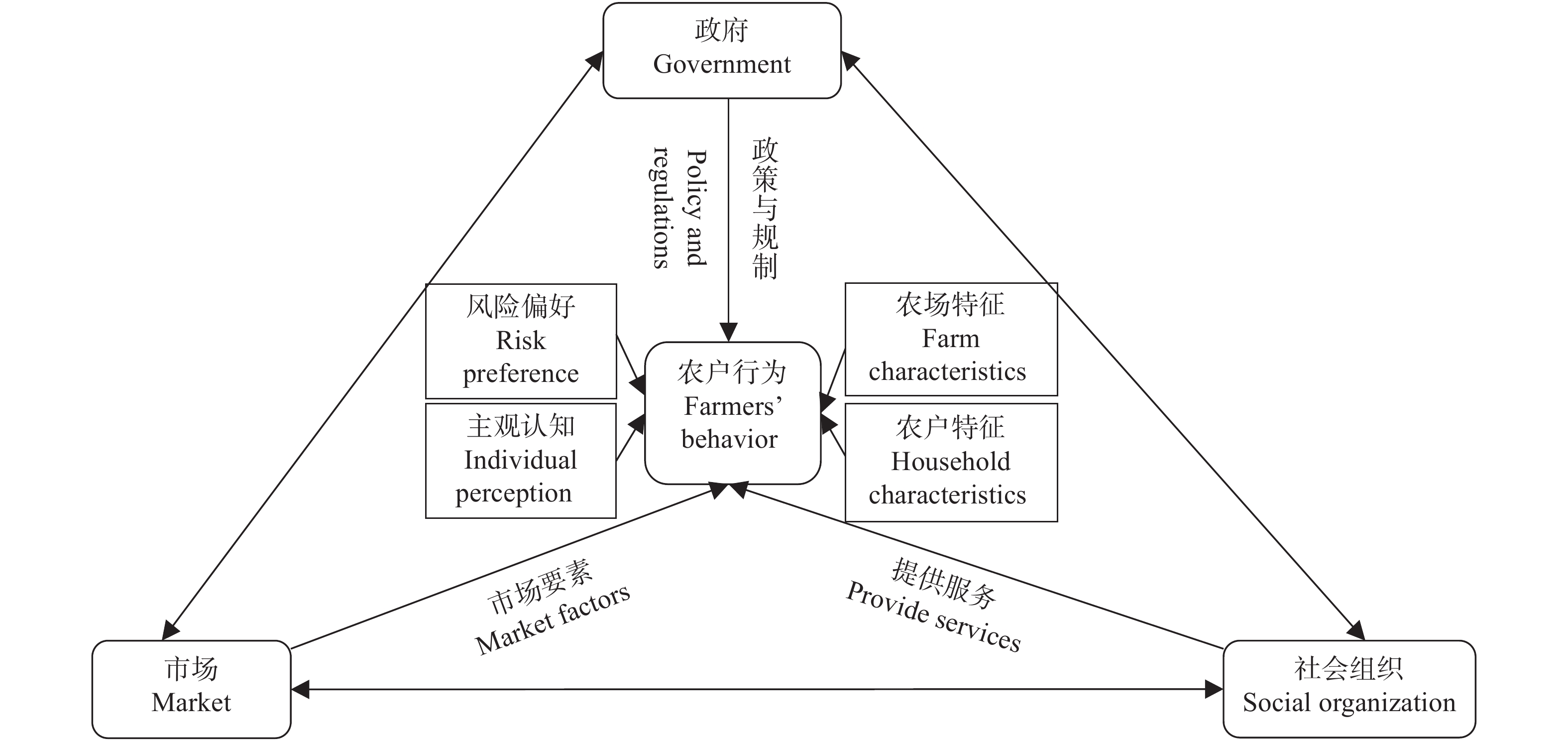
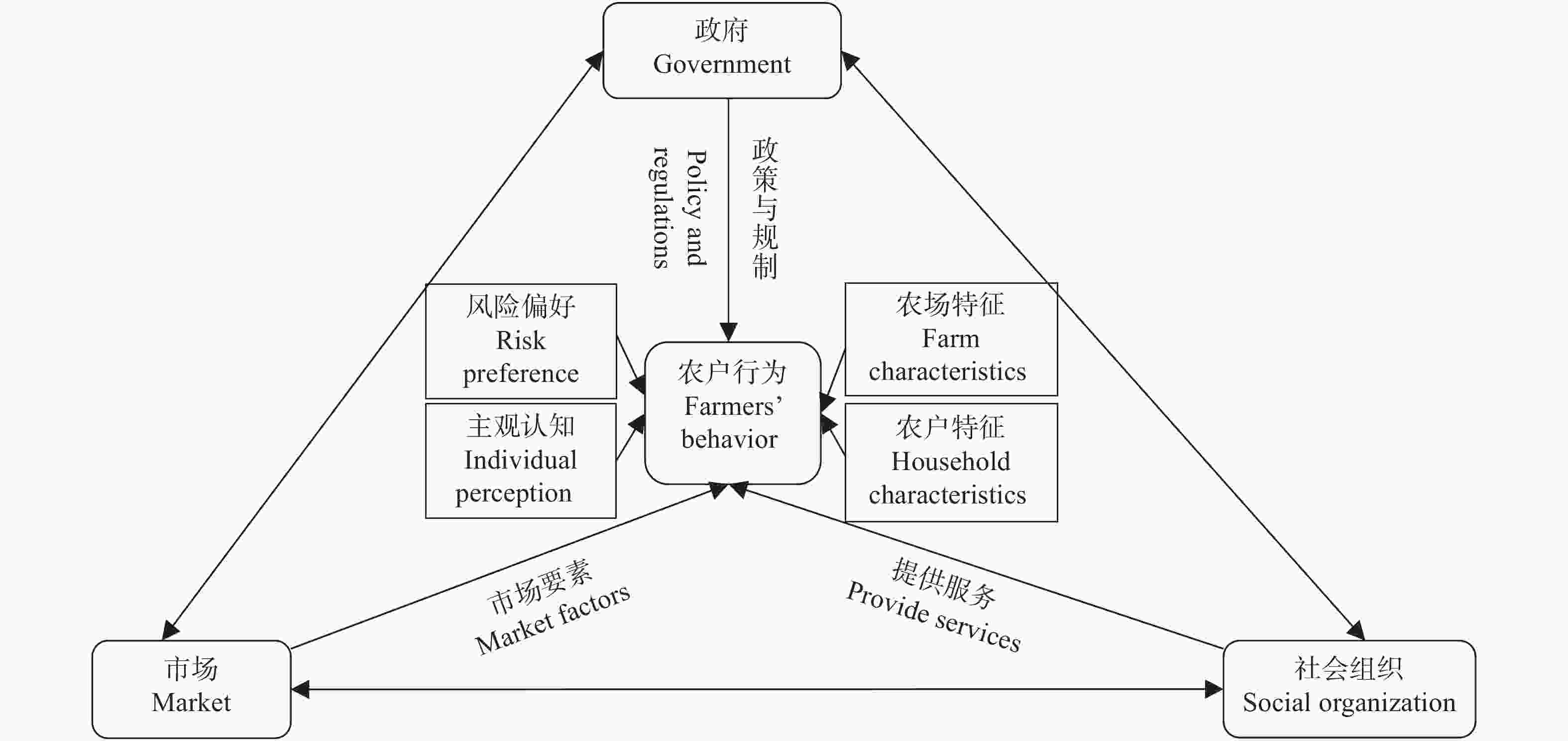
摘要: 中国正处在农业绿色转型与高质量发展的关键期, 减少农业温室气体排放对促进农业可持续发展及实现2060年碳中和有重要作用。本文在系统回顾近年来中国农业碳减排的相关政策与研究进展的基础上, 梳理了中国农业碳减排的治理结构。中国已初步形成农业碳中和的政策体系, 涵盖了农业减排固碳的主要方面, 但政策目标仍有待明确和细化, 且需进一步推动技术创新和提升资源利用效率。当前研究围绕低碳农业开展了大量实证和模型分析, 研究内容从农业碳排放测算逐步转向农业碳减排措施设计与效果评估、农业碳减排措施的实施与落实等方面。然而, 相关研究仍需进一步完善农业碳排放的核算, 并在考虑农业发展受到多目标制约的前提条件下综合评估农业碳减排措施的环境及社会经济影响。在农业碳减排的治理结构方面, 形成了以政府、市场和社会组织为治理主体与农户作为实施主体的农业碳减排治理框架, 但仍需加强中观和微观层面政策措施的制定, 并综合考虑治理主体和实施主体的协作互动, 通过直接和间接手段激发农户碳减排的积极性。本研究可为进一步制定农业碳减排政策措施和开展相关研究提供科学依据。Abstract: Reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in China’s agricultural sector is essential to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. China has been promoting the green transformation of its agricultural sector. This study systematically reviewed the policies and researches that are related to the reduction of GHG emissions in China’s agricultural sector, and established a governance framework for guiding future research that focuses on emission reduction in agriculture. Our results showed that China’s agriculture-related policies have already covered the main aspects of GHG emission reduction and carbon sequestration in the agricultural sector; however, technological innovation and resource use efficiency improvements should be further endorsed along with explicit policy targets. Among the existing literature, researches have focused on the estimation of agricultural GHG emissions to impact the evaluation of specific policies and measures. Future research on the improvement of agricultural GHG emission accounting and integrated assessment of emission reduction measures is needed. A governance framework for mitigating GHG emissions in agriculture has been identified in China, in which the government, market, and social organizations are the main governance entities, and the farmers are the implementation entities. Hence, to encourage farmers to reduce GHG emissions, the interactions between governmental entities and implementation entities should be considered when designing effective policies. This study summarized the current status of policies and research that are related to the mitigation of China’s agricultural GHG emissions and provided future perspectives on policy design and research foci.
-
表 1 中国农业碳减排相关法律政策文件
Table 1. Policies and regulations related to greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction in agricultural sector in China
类别 Category 领域/方面 Field 法律政策文件(发布时间) Documents (release time) 综合性政策
Integrated policies全领域
Whole fields《中国应对气候变化国家方案》(2007)
China’s National Climate Change Program (2007)《中国应对气候变化的政策与行动(2011)》(2011)
Responding to Climate Change: China’s Policies and Actions (2011)《“十三五”控制温室气体排放工作方案》(2016)
The 13th Five-Year Plan for Controlling Greenhouse Gas Emissions (2016)《“十三五”节能减排综合工作方案》(2016)
The 13th Five-Year Comprehensive Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Work Plan (2016)《关于完整准确全面贯彻新发展理念做好碳达峰碳中和工作的意见》(2021)
Opinions on the Complete, Accurate, and Comprehensive Implementation of the New Development Concept to Do a Good Job in Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality (2021)《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》(2021)
Action Plan for Carbon Emission Peak Before 2030 (2021)农业领域
Agricultural field《全国农业可持续发展规划(2015—2030年)》(2015)
National Sustainable Agricultural Development Plan (2015−2030) (2015)《“十三五”农业农村科技创新专项规划》(2017)
The 13th Five-Year Plan for Science and Technology Innovation in Agriculture (2017)《关于创新体制机制推进农业绿色发展的意见》(2017)
Opinions on Innovating System and Mechanism to Promote Agricultural Green Development (2017)《“十四五”全国农业绿色发展规划》(2021)
The 14th Five-Year Plan of National Agricultural Green Development (2021)农业碳减排
Measures for mitigating agricultural GHG emissions投入品减量
Reduction of agricultural inputs《到2020年化肥使用量零增长行动方案》(2015)
Action Plan for Zero Growth in Chemical Fertilizer Use by 2020 (2015)《到2020年农药使用量零增长行动方案》(2015)
Action Plan for Zero Growth in Pesticide Use by 2020 (2015)《建立以绿色生态为导向的农业补贴制度改革方案》(2016)
Reformation Plan for Establishing a Green and Ecology Oriented Agricultural Subsidy System (2016)《开展果菜茶有机肥替代化肥行动方案》(2017)
Action Plan for Replacing Chemical Fertilizers by Organic Fertilizers in Fruits, Vegetables, and Tea Plantations (2017)《果菜茶有机肥替代化肥技术方案》(2017)
Technology Schemes for Replacing Chemical Fertilizers by Organic Fertilizers in Fruits, Vegetables, and Tea Plantations (2017)循环利用
Recycling《中华人民共和国循环经济促进法》(2008)
Circular Economy Promotion Law of People’s Republic of China (2008)《禽畜规模养殖污染防治条例》(2014)
Regulation on the Prevention and Control of Pollution from Large-scale Breeding of Livestock and Poultry (2014)农业固碳增汇
Measures for increasing carbon sequestration in agricultural sector森林
Forest《中华人民共和国森林法》(1984)
Forest Law of the People’s Republic of China (1984)草地
Grassland《中华人民共和国草原法》(1985)
Grassland Law of the People’s Republic of China (1985)《全国草原保护建设利用总体规划》(2007)
National Grassland Protection and Construction Plan (2007)《全国草原保护建设利用“十三五”规划》(2016)
The 13th Five-Year National Grassland Protection and Construction Plan (2016)《关于加强草原保护修复的若干意见》(2021)
Several Opinions on Strengthening Grassland Protection and Restoration (2021)农田
Farmland《东北黑土地保护规划纲要(2017—2030年)》(2017)
Outline of the Black Soil Protection Plan in Northeast China (2017−2030) (2017)《全国高标准农田建设总体规划》(2013)
National High-Sandard Farmland Construction Plan (2013)《全国高标准农田建设规划(2021—2030年)》(2021)
National High-Standard Farmland Construction Plan (2021−2030) (2021)山水林田湖草系统治理
Systematic management of landscape, water, forests, farmland, lakes, and grassland《关于推进山水林田湖生态保护修复工作的通知》(2016)
Notice on Promoting the Ecological Protection and Restoration of Landscape, Water, Forests, Farmland, and Lakes (2016)《山水林田湖草生态保护修复工程指南(试行)》(2020)
Guideline for Ecological Protection and Restoration Projects of Landscape, Water, Forests, Farmland, Lakes, and Grassland (Trial) (2020) -
[1] 董红敏, 李玉娥, 陶秀萍, 等. 中国农业源温室气体排放与减排技术对策[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(10): 269−273 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.10.055DONG H M, LI Y E, TAO X P, et al. China greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities and its mitigation strategy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2008, 24(10): 269−273 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.10.055 [2] 谭秋成. 中国农业温室气体排放: 现状及挑战[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2011, 21(10): 69−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2011.10.011TAN Q C. Greenhouse gas emission in China’s agriculture: situation and challenge[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2011, 21(10): 69−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2011.10.011 [3] 田云, 张俊飚, 何可, 等. 农户农业低碳生产行为及其影响因素分析−以化肥施用和农药使用为例[J]. 中国农村观察, 2015(4): 61−70TIAN Y, ZHANG J B, HE K, et al. Analysis of farmers’ agricultural low-carbon production behavior and its influencing factors: Based on the application of fertilizer and pesticide[J]. China Rural Survey, 2015(4): 61−70 [4] 吴贤荣, 张俊飚. 中国省域农业碳排放: 增长主导效应与减排退耦效应[J]. 农业技术经济, 2017(5): 27−36WU X R, ZHANG J B. Agricultural carbon emissions at provincial level in China: Growth dominant effect and emission reduction decoupling effect[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2017(5): 27−36 [5] STEVANOVIĆ M, POPP A, BODIRSKY B L, et al. Mitigation strategies for greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture and land-use change: consequences for food prices[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(1): 365−374 [6] 付允, 马永欢, 刘怡君, 等. 低碳经济的发展模式研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2008, 18(3): 14−19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2008.03.003FU Y, MA Y H, LIU Y J, et al. Development patterns of low carbon economy[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2008, 18(3): 14−19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2008.03.003 [7] 冉光和, 王建洪, 王定祥. 我国现代农业生产的碳排放变动趋势研究[J]. 农业经济问题, 2011, 32(2): 32−38, 110RAN G H, WANG J H, WANG D X. Study on the changing tendency and counter-measures of carbon emission produced by agricultural production in China[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2011, 32(2): 32−38, 110 [8] 胡川, 韦院英, 胡威. 农业政策、技术创新与农业碳排放的关系研究[J]. 农业经济问题, 2018(9): 66−75HU C, WEI Y Y, HU W. Research on the relationship between agricultural policy, technological innovation and agricultural carbon emissions[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2018(9): 66−75 [9] 田云, 吴海涛. 产业结构视角下的中国粮食主产区农业碳排放公平性研究[J]. 农业技术经济, 2020(1): 45−55TIAN Y, WU H T. Research on fairness of agricultural carbon emissions in China’s major grain producing areas from the perspective of industrial structure[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2020(1): 45−55 [10] TUBIELLO F N, SALVATORE M, FERRARA A F, et al. The contribution of agriculture, forestry and other land use activities to global warming, 1990–2012[J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(7): 2655−2660 doi: 10.1111/gcb.12865 [11] GRASSI G, HOUSE J, DENTENER F, et al. The key role of forests in meeting climate targets requires science for credible mitigation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2017, 7(3): 220−226 doi: 10.1038/nclimate3227 [12] ROE S, STRECK C, OBERSTEINER M, et al. Contribution of the land sector to a 1.5 ℃ world[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2019, 9(11): 817−828 doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0591-9 [13] FEDERICI S, TUBIELLO F N, SALVATORE M, et al. New estimates of CO2 forest emissions and removals: 1990–2015[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2015, 352: 89−98 doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2015.04.022 [14] LE QUÉRÉ C, ANDREW R M, FRIEDLINGSTEIN P, et al. Global carbon budget 2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2018, 10(1): 405−448 doi: 10.5194/essd-10-405-2018 [15] 王金南, 董战峰, 蒋洪强, 等. 中国环境保护战略政策70年历史变迁与改革方向[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(10): 1636−1644WANG J N, DONG Z F, JIANG H Q, et al. Historical evolution and reform of China’s environmental strategy and policy during the past seventy years (1949–2019)[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(10): 1636−1644 [16] 杜志雄, 金书秦. 从国际经验看中国农业绿色发展[J]. 世界农业, 2021(2): 4−9, 18DU Z X, JIN S Q. China’s green agricultural development from the perspective of international experience[J]. World Agriculture, 2021(2): 4−9, 18 [17] 金书秦, 牛坤玉, 韩冬梅. 农业绿色发展路径及其“十四五”取向[J]. 改革, 2020(2): 30−39JIN S Q, NIU K Y, HAN D M. The path of agricultural green development and its orientation in the 14th five-year plan period[J]. Reform, 2020(2): 30−39 [18] 宋长青, 叶思菁. 提升我国耕地系统碳增汇减排能力[N]. 中国科学报, 2021-11-09(3)SONG C Q, YE S J. To enhance the capacity of China’s arable land system to increase carbon sink and reduce emissions[N]. China Science Daily, 2021-11-09(3) [19] 王惠, 卞艺杰. 农业生产效率、农业碳排放的动态演进与门槛特征[J]. 农业技术经济, 2015(6): 36−47WANG H, BIAN Y J. Dynamic evolution and threshold characteristics of agricultural production efficiency and agricultural carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2015(6): 36−47 [20] 黄祖辉, 米松华. 农业碳足迹研究−以浙江省为例[J]. 农业经济问题, 2011, 32(11): 40−47, 111HUANG Z H, MI S H. Agricultural sector carbon footprint accounting: a case of Zhejiang, China[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2011, 32(11): 40−47, 111 [21] 刘华军, 鲍振, 杨骞. 中国农业碳排放的地区差距及其分布动态演进−基于Dagum基尼系数分解与非参数估计方法的实证研究[J]. 农业技术经济, 2013(3): 72−81LIU H J, BAO Z, YANG Q. Regional disparities and dynamic evolution of agricultural carbon emissions in China: Based on the Dagum Gini coefficient decomposition and nonparametric estimation methods[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2013(3): 72−81 [22] 田云, 张俊飚, 尹朝静, 等. 中国农业碳排放分布动态与趋势演进−基于31个省(市、区)2002—2011年的面板数据分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2014, 24(7): 91−98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.07.014TIAN Y, ZHANG J B, YIN C J, et al. Distributional dynamics and trend evolution of China’s agricultural carbon emissions — an analysis on panel data of 31 provinces from 2002 to 2011[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2014, 24(7): 91−98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.07.014 [23] 陈儒, 邓悦, 姜志德. 基于修正碳计量的区域农业碳补偿时空格局[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(6): 168−177CHEN R, DENG Y, JIANG Z D. Spatial and temporal pattern of regional agricultural carbon compensation based on the modified carbon measurement[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(6): 168−177 [24] 高鸣, 宋洪远. 中国农业碳排放绩效的空间收敛与分异−基于Malmquist-luenberger指数与空间计量的实证分析[J]. 经济地理, 2015, 35(4): 142−148, 185GAO M, SONG H Y. Dynamic changes and spatial agglomeration analysis of the Chinese agricultural carbon emissions performance[J]. Economic Geography, 2015, 35(4): 142−148, 185 [25] 陈罗烨, 薛领, 雪燕. 中国农业净碳汇空间集聚与分异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(11): 1777−1784CHEN L Y, XUE L, XUE Y. Spatial agglomeration and variation of China’s agricultural net carbon sink[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(11): 1777−1784 [26] 吴昊玥, 黄瀚蛟, 何宇, 等. 中国农业碳排放效率测度、空间溢出与影响因素[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(10): 1762−1773WU H Y, HUANG H J, HE Y, et al. Measurement, spatial spillover and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions efficiency in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(10): 1762−1773 [27] ZHANG W F, DOU Z X, HE P, et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(21): 8375−8380 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210447110 [28] KAHRL F, LI Y J, SU Y F, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogen fertilizer use in China[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2010, 13(8): 688−694 [29] WANG Z B, CHEN J, MAO S C, et al. Comparison of greenhouse gas emissions of chemical fertilizer types in China’s crop production[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 141: 1267−1274 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.120 [30] 胡向东, 王济民. 中国畜禽温室气体排放量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(10): 247−252 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2010.10.042HU X D, WANG J M. Estimation of livestock greenhouse gases discharge in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(10): 247−252 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2010.10.042 [31] 虞祎, 刘俊杰. 农业产业整体减排实现路径研究−以长三角及周边地区猪肉生产流通为例[J]. 农业经济问题, 2013, 34(10): 15−21, 110YU Y, LIU J J. Approaches for actualization of carbon emission reduction in agricultural industry[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2013, 34(10): 15−21, 110 [32] MATTHEWS H S, HENDRICKSON C T, WEBER C L. The importance of carbon footprint estimation boundaries[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(16): 5839−5842 [33] HUMPENÖDER F, POPP A, DIETRICH J P, et al. Investigating afforestation and bioenergy CCS as climate change mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2014, 9(6): 064029 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/9/6/064029 [34] ZHANG X, DAVIDSON E A, MAUZERALL D L, et al. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development[J]. Nature, 2015, 528(7580): 51−59 doi: 10.1038/nature15743 [35] ZHANG W F, CAO G X, LI X L, et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7622): 671−674 doi: 10.1038/nature19368 [36] KRAUSE M, LOTZE-CAMPEN H, POPP A, et al. Conservation of undisturbed natural forests and economic impacts on agriculture[J]. Land Use Policy, 2013, 30(1): 344−354 doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.03.020 [37] 陈静, 张建国, 赵英, 等. 秸秆和生物炭添加对关中地区玉米-小麦轮作农田温室气体排放的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(5): 170−178CHEN J, ZHANG J G, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of straw and biochar amendment on greenhouse gases emission in wheat-maize rotation cropland in Guanzhong area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(5): 170−178 [38] BOYSEN L R, LUCHT W, GERTEN D, et al. Impacts devalue the potential of large-scale terrestrial CO2 removal through biomass plantations[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11(9): 095010 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/9/095010 [39] MURATORI M, CALVIN K, WISE M, et al. Global economic consequences of deploying bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS)[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11(9): 095004 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/9/095004 [40] BODIRSKY B L, POPP A, LOTZE-CAMPEN H, et al. Reactive nitrogen requirements to feed the world in 2050 and potential to mitigate nitrogen pollution[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3858 doi: 10.1038/ncomms4858 [41] CHEN X P, CUI Z L, FAN M S, et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 486−489 doi: 10.1038/nature13609 [42] CUI Z L, ZHANG H Y, CHEN X P, et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers[J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7696): 363−366 doi: 10.1038/nature25785 [43] GU B J, JU X T, CHANG S X, et al. Nitrogen use efficiencies in Chinese agricultural systems and implications for food security and environmental protection[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2017, 17(4): 1217−1227 doi: 10.1007/s10113-016-1101-5 [44] 张靖, 朱潇, 沈健林, 等. 生物有机肥与化肥配施对稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(1): 15−25 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210355ZHANG J, ZHU X, SHEN J L, et al. Effects of combined application of microbial organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer on ammonia volatilization in a paddy field with double rice cropping[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(1): 15−25 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210355 [45] 王书伟, 林静慧, 吴正贵, 等. 氮肥深施对太湖地区稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(12): 2002−2012WANG S W, LIN J H, WU Z G, et al. The effects of nitrogen fertilizer deep placement on the ammonia volatilization from paddy fields in the Taihu Lake region of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(12): 2002−2012 [46] 罗佳琳, 赵亚慧, 于建光, 等. 麦秸与氮肥配施对水稻根际区土壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(9): 1582−1591LUO J L, ZHAO Y H, YU J G, et al. Effects of wheat straw and nitrogen fertilizer application on the soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in the rhizosphere of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(9): 1582−1591 [47] 李昊, 李世平, 南灵. 农药施用技术培训减少农药过量施用了吗?[J]. 中国农村经济, 2017(10): 80−96LI H, LI S P, NAN L. Can technical training reduce pesticide overuse?[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2017(10): 80−96 [48] 童洪志, 刘伟. 农户秸秆还田技术采纳行为影响因素实证研究−基于311户农户的调查数据[J]. 农村经济, 2017(4): 108−114TONG H Z, LIU W. Empirical study on the influencing factors of farmers’ adoption behavior of straw returning technology: Based on the survey of 311 rural households[J]. Rural Economy, 2017(4): 108−114 [49] SPRINGMANN M, CLARK M, MASON-D’CROZ D, et al. Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7728): 519−525 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0594-0 [50] BRIGGS A D M, KEHLBACHER A, TIFFIN R, et al. Assessing the impact on chronic disease of incorporating the societal cost of greenhouse gases into the price of food: an econometric and comparative risk assessment modelling study[J]. BMJ Open, 2013, 3(10): e003543 doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003543 [51] SHEWMAKE S, OKRENT A, THABREW L, et al. Predicting consumer demand responses to carbon labels[J]. Ecological Economics, 2015, 119: 168−180 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.08.007 [52] ZIMMERMAN A R, GAO B, AHN M Y. Positive and negative carbon mineralization priming effects among a variety of biochar-amended soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(6): 1169−1179 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.02.005 [53] KUZYAKOV Y, FRIEDEL J K, STAHR K. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2000, 32(11/12): 1485−1498 [54] KARHU K, MATTILA T, BERGSTRÖM I, et al. Biochar addition to agricultural soil increased CH4 uptake and water holding capacity — Results from a short-term pilot field study[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2011, 140(1/2): 309−313 [55] 华春林, 陆迁, 姜雅莉, 等. 农业教育培训项目对减少农业面源污染的影响效果研究−基于倾向评分匹配方法[J]. 农业技术经济, 2013(4): 83−92HUA C L, LU Q, JIANG Y L et al. Impacts of agricultural education and training programs on reducing agricultural non-point source pollution: Based on the PSM method[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2013(4): 83−92 [56] 葛继红, 周曙东, 朱红根, 等. 农户采用环境友好型技术行为研究−以配方施肥技术为例[J]. 农业技术经济, 2010(9): 57−63GE J H, ZHOU S D, ZHU H G, et al. Research on farmers’ behavior of adopting environment-friendly technology: Take the directive fertilization technology as an example[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2010(9): 57−63 [57] HUANG J, XIANG C, JIA X, et al. Impacts of training on farmers’ nitrogen use in maize production in Shandong, China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 67(4): 321−327 doi: 10.2489/jswc.67.4.321 [58] HONG C, BURNEY J A, PONGRATZ J, et al. Global and regional drivers of land-use emissions in 1961–2017[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7843): 554−561 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03138-y [59] POORE J, NEMECEK T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6392): 987−992 doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0216 [60] HU Y, SU M, WANG Y, et al. Food production in China requires intensified measures to be consistent with national and provincial environmental boundaries[J]. Nature Food, 2020, 1(9): 572−582 doi: 10.1038/s43016-020-00143-2 [61] 卜容燕, 李敏, 韩上, 等. 有机无机肥配施对双季稻轮作系统产量、温室气体排放和土壤养分的综合效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(1): 145−153BU R Y, LI M, HAN S, et al. Comprehensive effects of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizer on yield, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil nutrient in double-cropping rice systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(1): 145−153 [62] 孙磊, 王丽华, 高中超, 等. 减氮配合增效剂和缓释肥对玉米田土壤温室气体排放和产量的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(1): 185−194SUN L, WANG L H, GAO Z C, et al. Effects of reduction of nitrogen fertilizer combined with synergist and slow release fertilizer on greenhouse gas emissions and yield in corn field[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(1): 185−194 [63] 朱晓晴, 安晶, 马玲, 等. 秸秆还田深度对土壤温室气体排放及玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(5): 977−989 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.05.010ZHU X Q, AN J, MA L, et al. Effects of different straw returning depths on soil greenhouse gas emission and maize yield[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(5): 977−989 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.05.010 [64] WANG X X, BIEWALD A, DIETRICH J P, et al. Taking account of governance: Implications for land-use dynamics, food prices, and trade patterns[J]. Ecological Economics, 2016, 122: 12−24 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.11.018 [65] WANG X X, DIETRICH J P, LOTZE-CAMPEN H, et al. Beyond land-use intensity: Assessing future global crop productivity growth under different socioeconomic pathways[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2020, 160: 120208 doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120208 [66] 金书秦, 周芳, 沈贵银. 农业发展与面源污染治理双重目标下的化肥减量路径探析[J]. 环境保护, 2015, 43(8): 50−53JIN S Q, ZHOU F, SHEN G Y. Feasible routes for reducing chemical fertilizer use with dual goals of agricultural development and non-point source pollution prevention[J]. Environmental Protection, 2015, 43(8): 50−53 [67] 金书秦, 张惠, 吴娜伟. 2016年化肥、农药零增长行动实施结果评估[J]. 环境保护, 2018, 46(1): 45−49JIN S Q, ZHANG H, WU N W. Evaluation on the implementation of zero-growth action of chemical fertilizer and pesticide use of 2016[J]. Environmental Protection, 2018, 46(1): 45−49 [68] 金书秦, 张惠, 唐佳丽. 化肥使用量零增长实施进展及“十四五”减量目标和路径[J]. 南京工业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2020, 19(3): 66−74, 112JIN S Q, ZHANG H, TANG J L. On progress in implementing zero growth of chemical fertilizer use and the target & path of fertilizer reducing in the “14th five-year plan”[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University: Social Science Edition, 2020, 19(3): 66−74, 112 [69] 代云云, 徐翔. 农户蔬菜质量安全控制行为及其影响因素实证研究−基于农户对政府、市场及组织质量安全监管影响认知的视角[J]. 南京农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2012, 12(3): 48−53, 59DAI Y Y, XU X. Study on the farmers behavior in controlling vegetable quality and safety and their influencing factors: based on the regulatory impact of government, market and organization[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University: Social Sciences Edition, 2012, 12(3): 48−53, 59 [70] 代云云. 我国蔬菜质量安全管理现状与调控对策分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2013, 23(S2): 66−69DAI Y Y. Analysis of the status quo of vegetable quality and safety management and regulation countermeasures in China[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2013, 23(S2): 66−69 [71] 王常伟, 顾海英. 市场VS政府, 什么力量影响了我国菜农农药用量的选择?[J]. 管理世界, 2013(11): 50−66, 187WANG C W, GU H Y. The market VS the government: what forces affect the selection of amount of pesticide used by China’s vegetable grower?[J]. Management World, 2013(11): 50−66, 187 [72] 王建华, 马玉婷, 王晓莉. 农产品安全生产: 农户农药施用知识与技能培训[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2014, 24(4): 54−63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.04.008WANG J H, MA Y T, WANG X L. Agricultural production safety: farmers’ pesticide application knowledge and technical training[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2014, 24(4): 54−63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.04.008 [73] 黄祖辉, 钟颖琦, 王晓莉. 不同政策对农户农药施用行为的影响[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26(8): 148−155 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.08.020HUANG Z H, ZHONG Y Q, WANG X L. Study on the impacts of government policy on farmers’ pesticide application behavior[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2016, 26(8): 148−155 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.08.020 [74] EMMANUEL D, OWUSU-SEKYERE E, OWUSU V, et al. Impact of agricultural extension service on adoption of chemical fertilizer: Implications for rice productivity and development in Ghana[J]. NJAS - Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences, 2016, 79: 41−49 doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2016.10.002 [75] 耿宇宁, 郑少锋, 王建华. 政府推广与供应链组织对农户生物防治技术采纳行为的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 社会科学版, 2017, 17(1): 116−122GENG Y N, ZHENG S F, WANG J H. Impact of the government technology promotion and supply chain organization on farmers’ biological technology adoption behavior[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University: Social Science Edition, 2017, 17(1): 116−122 [76] 卢瑜, 向平安, 余亮. 农户采纳有机农业的影响因素及其空间效应−基于新疆农户调查数据[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(1): 153−165 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210587LU Y, XIANG P A, YU L. Influencing factors and spatial effects of organic agriculture adoption: Based on survey data of farmers in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(1): 153−165 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210587 [77] LIU J Y, FUJIMORI S, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Identifying trade-offs and co-benefits of climate policies in China to align policies with SDGs and achieve the 2 ℃ goal[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2019, 14(12): 124070 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab59c4 [78] 童锐, 王永强. 农产品基地认证促进农户农药安全使用了吗?−基于陕西省苹果种植户的实证研究[J]. 生态经济, 2019, 35(11): 112−116TONG R, WANG Y Q. Does agro-product certification promote the use of unrestricted pesticides: based on the empirical study of apple farmers in Shaanxi Province[J]. Ecological Economy, 2019, 35(11): 112−116 [79] 侯博, 应瑞瑶. 分散农户低碳生产行为决策研究−基于TPB和SEM的实证分析[J]. 农业技术经济, 2015(2): 4−13HOU B, YING R Y. Research on decision making of decentralized farmers’ low-carbon production behavior: Based on the empirical analysis of TPB and SEM[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2015(2): 4−13 [80] PAUDEL K P, LOHR L, MARTIN N R Jr. Effect of risk perspective on fertilizer choice by sharecroppers[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2000, 66(2): 115−128 doi: 10.1016/S0308-521X(00)00039-1 [81] 吴雪莲, 张俊飚, 何可, 等. 农户水稻秸秆还田技术采纳意愿及其驱动路径分析[J]. 资源科学, 2016, 38(11): 2117−2126WU X L, ZHANG J B, HE K, et al. Farmer willingness to adopt rice straw returning technology and driving path[J]. Resources Science, 2016, 38(11): 2117−2126 [82] 黄季焜, 齐亮, 陈瑞剑. 技术信息知识、风险偏好与农民施用农药[J]. 管理世界, 2008(5): 71−76HUANG J K, QI L, CHEN R J. Technical information knowledge, risk preference and pesticide application by farmers[J]. Management World, 2008(5): 71−76 [83] 蔡键. 风险偏好、外部信息失效与农药暴露行为[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2014, 24(9): 135−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.09.019CAI J. Risk preference, external information failure and pesticide exposure[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2014, 24(9): 135−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.09.019 [84] LIU E M, HUANG J K. Risk preferences and pesticide use by cotton farmers in China[J]. Journal of Development Economics, 2013, 103: 202−215 doi: 10.1016/j.jdeveco.2012.12.005 [85] 仇焕广, 栾昊, 李瑾, 等. 风险规避对农户化肥过量施用行为的影响[J]. 中国农村经济, 2014(3): 85−96QIU H G, LUAN H, LI J, et al. Impacts of risk aversion on farmers’ behavior of excessive fertilizer application[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2014(3): 85−96 [86] 米建伟, 黄季焜, 陈瑞剑, 等. 风险规避与中国棉农的农药施用行为[J]. 中国农村经济, 2012(7): 60−71, 83MI J W, HUANG J K, CHEN R J, et al. Risk aversion and pesticide application behavior of cotton farmers in China[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2012(7): 60−71, 83 [87] 畅华仪, 张俊飚, 何可. 技术感知对农户生物农药采用行为的影响研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(1): 202−211CHANG H Y, ZHANG J B, HE K. Technology perception and biological pesticides adoption[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(1): 202−211 [88] TAN X P, WANG X Y, ZAIDI S H A. What drives public willingness to participate in the voluntary personal carbon-trading scheme? A case study of Guangzhou Pilot, China[J]. Ecological Economics, 2019, 165: 106389 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106389 [89] WALLACE A A, IRVINE K N, WRIGHT A J, et al. Public attitudes to personal carbon allowances: findings from a mixed-method study[J]. Climate Policy, 2010, 10(4): 385−409 doi: 10.3763/cpol.2009.004 [90] 李红梅, 傅新红, 吴秀敏. 农户安全施用农药的意愿及其影响因素研究−对四川省广汉市214户农户的调查与分析[J]. 农业技术经济, 2007(5): 99−104 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6370.2007.05.016LI H M, FU X H, WU X M. Study on farmers’ willingness to use pesticides safely and its influencing factors: Based on the survey of 214 rural households in Guanghan City, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2007(5): 99−104 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6370.2007.05.016 [91] CLARKE C, SHACKLETON S, POWELL M. Climate change perceptions, drought responses and views on carbon farming amongst commercial livestock and game farmers in the semiarid Great Fish River Valley, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa[J]. African Journal of Range & Forage Science, 2012, 29(1): 13−23 [92] 蒋琳莉, 张露, 张俊飚, 等. 稻农低碳生产行为的影响机理研究−基于湖北省102户稻农的深度访谈[J]. 中国农村观察, 2018(4): 86−101JIANG L L, ZHANG L, ZHANG J B, et al. The influence mechanism of rice farmers’ low-carbon production behaviors: an analysis based on in-depth interviews with 102 rice farmers in Hubei Province[J]. China Rural Survey, 2018(4): 86−101 [93] DOSS C R, MORRIS M L. How does gender affect the adoption of agricultural innovations?[J]. Agricultural Economics, 2000, 25(1): 27−39 doi: 10.1111/j.1574-0862.2001.tb00233.x [94] 周建华, 杨海余, 贺正楚. 资源节约型与环境友好型技术的农户采纳限定因素分析[J]. 中国农村观察, 2012(2): 37−43ZHOU J H, YANG H Y, HE Z C. Analysis on the limiting factors of farmers’ adoption of resource-saving and environment-friendly technologies[J]. China Rural Survey, 2012(2): 37−43 [95] 江激宇, 柯木飞, 张士云, 等. 农户蔬菜质量安全控制意愿的影响因素分析−基于河北省藁城市151份农户的调查[J]. 农业技术经济, 2012(5): 35−42JIANG J Y, KE M F, ZHANG S Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of farmers’ intention to control vegetable quality and safety: Based on the survey of 151 rural households in Gaocheng City, Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2012(5): 35−42 [96] 纪月清, 刘亚洲, 陈奕山. 统防统治: 农民兼业与农药施用[J]. 南京农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2015, 15(6): 61−67, 138JI Y Q, LIU Y Z, CHEN Y S. Part-time jobs and pesticide input: a perspective of collective prevention[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University: Social Sciences Edition, 2015, 15(6): 61−67, 138 [97] ZEWELD W, VAN HUYLENBROECK G, TESFAY G, et al. Smallholder farmers’ behavioural intentions towards sustainable agricultural practices[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 187: 71−81 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.014 [98] 刘明明, 雷锦锋. 我国农业实现碳中和的法制保障研究[J]. 广西社会科学, 2021(9): 30−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6917.2021.09.004LIU M M, LEI J F. Research on legal guarantee of carbon neutrality in China’s agriculture[J]. Social Sciences in Guangxi, 2021(9): 30−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6917.2021.09.004 [99] KASYMOV U, WANG X, ZIKOS D, et al. Institutional barriers to sustainable forest management: Evidence from an experimental study in Tajikistan[J]. Ecological Economics, 2022, 193: 107276 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107276 [100] BUSCH J, RING I, AKULLO M, et al. A global review of ecological fiscal transfers[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2021, 4(9): 756−765 doi: 10.1038/s41893-021-00728-0 [101] 李明月, 陈凯. 农户绿色农业生产意愿与行为的实证分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2020(4): 10−19, 173LI M Y, CHEN K. An empirical analysis of farmers’ willingness and behaviors in green agriculture production[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University: Social Sciences Edition, 2020(4): 10−19, 173 [102] 尚惠芳, 易小燕, 张宗芳. 农户耕地质量提升行为的逻辑路径与驱动力: 研究进展与展望[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(7): 1253−1261SHANG H F, YI X Y, ZHANG Z F. Logic paths and driving forces of cultivated land quality improvement behavior of farmers: research progress and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(7): 1253−1261 [103] JACQUET F, BUTAULT J P, GUICHARD L. An economic analysis of the possibility of reducing pesticides in French field crops[J]. Ecological Economics, 2011, 70(9): 1638−1648 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.04.003 [104] 罗小锋, 杜三峡, 黄炎忠, 等. 种植规模、市场规制与稻农生物农药施用行为[J]. 农业技术经济, 2020(6): 71−80LUO X F, DU S X, HUANG Y Z, et al. Planting scale, market regulation and rice farmers’ biological pesticide application behavior[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2020(6): 71−80 [105] TAKESHIMA H, LIVERPOOL-TASIE L S O. Fertilizer subsidies, political influence and local food prices in sub-Saharan Africa: evidence from Nigeria[J]. Food Policy, 2015, 54: 11−24 doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2015.04.003 [106] TAKESHIMA H, ADHIKARI R P, SHIVAKOTI S, et al. Heterogeneous returns to chemical fertilizer at the intensive margins: insights from Nepal[J]. Food Policy, 2017, 69: 97−109 doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2017.03.007 [107] PEMSL D, WAIBEL H, GUTIERREZ A P. Why do some Bt-cotton farmers in China continue to use high levels of pesticides?[J]. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability, 2005, 3(1): 44−56 doi: 10.1080/14735903.2005.9684743 [108] 何浩然, 张林秀, 李强. 农民施肥行为及农业面源污染研究[J]. 农业技术经济, 2006(6): 2−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6370.2006.06.001HE H R, ZHANG L X, LI Q. Research on farmers’ fertilization behavior and agricultural non-point source pollution[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2006(6): 2−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6370.2006.06.001 [109] PAN D, KONG F B, ZHANG N, et al. Knowledge training and the change of fertilizer use intensity: Evidence from wheat farmers in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 197: 130−139 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.069 [110] 占辉斌, 胡庆龙. 农地规模、市场激励与农户施肥行为[J]. 农业技术经济, 2017(11): 72−79ZHAN H B, HU Q L. Farm size, market incentive and farmers’ fertilization behavior[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2017(11): 72−79 [111] ZHAO L, WANG C W, GU H Y, et al. Market incentive, government regulation and the behavior of pesticide application of vegetable farmers in China[J]. Food Control, 2018, 85: 308−317 doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.09.016 [112] 方伟, 梁俊芬, 林伟君, 等. 食品企业质量控制动机及“优质优价”实现状态分析−基于300家国家级农业龙头企业调研[J]. 农业技术经济, 2013(2): 112−120FANG W, LIANG J F, LIN W J, et al. Research on motivation of quality control and realization of high quality and competitive price in food enterprises: Based on the survey in the 300 national agricultural leading enterprises[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2013(2): 112−120 [113] GOODHUE R E, KLONSKY K, MOHAPATRA S. Can an education program be a substitute for a regulatory program that bans pesticides? Evidence from a panel selection model[J]. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 2010, 92(4): 956−971 doi: 10.1093/ajae/aaq032 [114] JENA P R, GROTE U. Impact evaluation of traditional basmati rice cultivation in Uttarakhand State of northern India: what implications does it hold for geographical indications?[J]. World Development, 2012, 40(9): 1895−1907 doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2012.04.004 [115] LELAND H E. Quacks, lemons, and licensing: a theory of minimum quality standards[J]. Journal of Political Economy, 1979, 87(6): 1328−1346 doi: 10.1086/260838 [116] 黄森慰, 张春霞, 郑逸芳. 林业合作社运行效率类别差异研究[J]. 林业经济, 2019, 41(1): 98−103HUANG S W, ZHANG C X, ZHENG Y F. Study on the difference of operational efficiency of forest professional cooperatives[J]. Forestry Economics, 2019, 41(1): 98−103 [117] 周峰, 王爱民. 垂直协作方式对农户肥料使用行为的影响−基于南京市的调查[J]. 江西农业学报, 2007, 19(4): 124−126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8581.2007.04.051ZHOU F, WANG A M. Impacts of vertical cooperation on fertilizer application behavior of rural households: Based on the survey in Nanjing[J]. Acta Agriculture Jiangxi, 2007, 19(4): 124−126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8581.2007.04.051 [118] 张利国. 垂直协作方式对水稻种植农户化肥施用行为影响分析−基于江西省189户农户的调查数据[J]. 农业经济问题, 2008, 29(3): 50−54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6389.2008.03.009ZHANG L G. Impacts of vertical cooperation on fertilizer application behavior of rice farmers: Evidence from 189 households in Jiangxi Province[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2008, 29(3): 50−54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6389.2008.03.009 [119] 蔡荣, 汪紫钰, 钱龙, 等. 加入合作社促进了家庭农场选择环境友好型生产方式吗? −以化肥、农药减量施用为例[J]. 中国农村观察, 2019(1): 51−65CAI R, WANG Z Y, QIAN L, et al. Do cooperatives promote family farms to choose environmental-friendly production practices? an empirical analysis of fertilizers and pesticides reduction[J]. China Rural Survey, 2019(1): 51−65 [120] 毛飞, 孔祥智. 农户安全农药选配行为影响因素分析−基于陕西5个苹果主产县的调查[J]. 农业技术经济, 2011(5): 4−12MAO F, KONG X Z. Analysis of influencing factors of farmers’ pesticide behavior: Evidence from 5 major apple producing counties in Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2011(5): 4−12 [121] 张朝辉, 刘怡彤. 加入农业合作社能促进果农采纳新型生物农药技术吗[J]. 林业经济, 2020, 42(12): 20−26, 92ZHANG Z H, LIU Y T. The effect of joining cooperatives on the adoption of new bio-pesticides technology by farmers[J]. Forestry Economics, 2020, 42(12): 20−26, 92 [122] 史恒通, 赵敏娟, 霍学喜. 农户施肥投入结构及其影响因素分析−基于7个苹果主产省的农户调查数据[J]. 华中农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2013(2): 1−7SHI H T, ZHAO M J, HUO X X. Farmer’s fertilizer input structure and its influencing factors — an empirical analysis on survey data of growers in seven apple main producing provinces[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University: Social Sciences Edition, 2013(2): 1−7 [123] 陈中督, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 等. 长江下游地区稻麦轮作模式碳足迹研究−基于生命周期评价[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2019, 40(12): 81−90CHEN Z D, LI F B, FENG J F, et al. Study on carbon footprint for rice-wheat rotation system in the lower reaches of Yangtze River — based on the life cycle assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2019, 40(12): 81−90 [124] 孙建卫, 陈志刚, 赵荣钦, 等. 基于投入产出分析的中国碳排放足迹研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2010, 20(5): 28−34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2010.05.006SUN J W, CHEN Z G, ZHAO R Q, et al. Research on carbon emission footprint of China based on input-output model[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2010, 20(5): 28−34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2010.05.006 [125] LIN B, WANG X X, JIN S Q, et al. Impacts of cooperative membership on rice productivity: Evidence from China[J]. World Development, 2022, 150: 105669 doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105669 -





 下载:
下载: