Effects of Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation on Cd uptake, rhizosphere soils enzyme activities and Cd bioavailability in rice (Oryza sativa) varieties with different Cd tolerance
-
摘要: 为探究假单胞菌TCd-1降低水稻镉吸收的根际生态机制, 以高镉耐性水稻品种‘特优671’和低镉耐性水稻品种‘百香139’为材料, 通过盆栽土培试验, 研究了接种TCd-1菌株对10 mg∙kg−1镉处理水稻镉吸收、根际土壤镉形态及酶活性的影响。结果表明: 接种菌株后高、低镉耐性水稻品种各部位的镉含量显著降低(P<0.05), 镉富集系数分别降低35.14%和47.79%, 转移系数无显著变化; 根际土壤可交换态镉含量分别显著降低15.89%和23.81% (P<0.05) , 铁锰氧化结合态镉含量显著提高39.58%和28.81% (P<0.05), 有机态镉含量显著提高36.11%和25.00% (P<0.05); 低镉耐性水稻品种根际土壤酸性磷酸酶、脲酶、蔗糖酶、纤维素酶和过氧化氢酶活性依次提高26.74%、12.07%、62.50%、81.17%和5.13%, 多酚氧化酶活性降低12.40%, 高镉耐性水稻的酸性磷酸酶、脲酶、蔗糖酶、纤维素酶和多酚氧化酶活性依次降低7.19%、9.39%、25.53%、16.20%和11.44%, 过氧化氢酶活性提高5.13%。可见, 假单胞菌TCd-1主要通过降低根际土壤镉的生物有效性、恢复土壤酶活性, 进而提高水稻耐镉能力并抑制水稻对镉的吸收与积累, 对高、低不同镉耐性水稻品种, 接种TCd-1菌株后其镉富集特性、根际土壤酶活性及不同镉形态含量占比均表现出显著差异。Abstract: Heavy metal contamination in rice (Oryza sativa) is a serious problem. Microbial remediation is a promising technique to reduce Cd accumulation in rice. To explore the rhizosphere-associated ecological mechanism of Pseudomonas TCd-1-induced reduction of Cd uptake in rice, two rice varieties, high Cd-tolerant variety ‘Teyou 671’ and low Cd-tolerant variety ‘Baixiang 139’, were used. A set of soil culture pots treated with 10 mg∙kg−1 Cd were employed to evaluate the effects of Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation on rice Cd uptake and enzymes activities in rhizosphere soils. The results showed that the Cd content in different parts of both the high and low Cd-tolerant rice varieties significantly decreased (P<0.05) after inoculation of Pseudomonas TCd-1, and the bioconcentration factor (BCF) of Cd decreased by 35.14% and 47.79% (P<0.05), respectively. However, no significant changes were found in the translocation factor (TF). Meanwhile, in rhizosphere soils of the high and low Cd-tolerant rice varieties, the content of exchangeable Cd decreased by 15.89% and 23.81% (P<0.05), Fe-Mn oxide bound Cd increased by 39.58% and 28.81% (P<0.05), and organic matter Cd increased by 36.11% and 25.00% (P<0.05), respectively. In addition, the activities of acid phosphatase, urease, saccharase, cellulase, and catalase significantly increased by 26.74%, 12.07%, 62.50%, 81.17%, and 5.13%, respectively; while the polyphenol oxidase activity decreased by 12.40% in the rhizosphere soils of low Cd-tolerant rice variety. In rhizosphere soils of high Cd-tolerant rice variety, the activities of acid phosphatase, urease, sucrase, cellulase, and polyphenol oxidase decreased by 7.19%, 9.39%, 25.53%, 16.20%, and 11.44%, respectively; while catalase activity increased by 5.13%. There were significant differences in enrichment characteristics, rhizosphere soil enzymes activities, and the proportions of different chemical forms of Cd in rhizosphere soils of different Cd-tolerant rice varieties after inoculation with the TCd-1 strain. The results indicated that inoculation with the strain may partly remediate the changes in soil enzymes activities caused by Cd pollution. In conclusion, Pseudomonas TCd-1 can improve Cd tolerance and inhibit Cd uptake and accumulation in rice, mainly by reducing the bioavailability of soil Cd and restoring the changes in soil enzymes activities caused by Cd pollution.
-
Key words:
- Rice /
- Cd pollution /
- Pseudomonas TCd-1 /
- Soil Cd form /
- Bioavailability /
- Soil enzyme activity /
- Microbial remediation
-
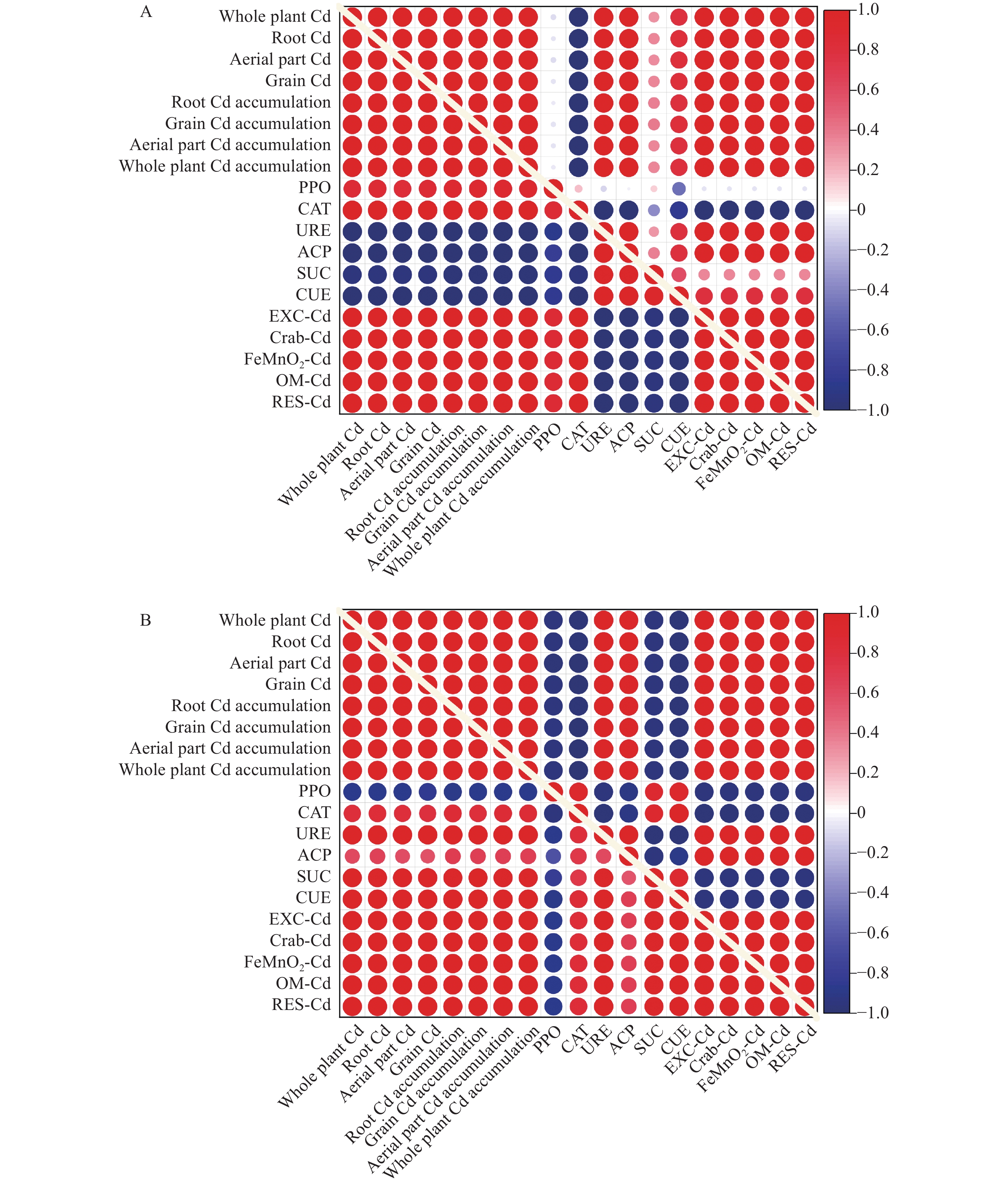
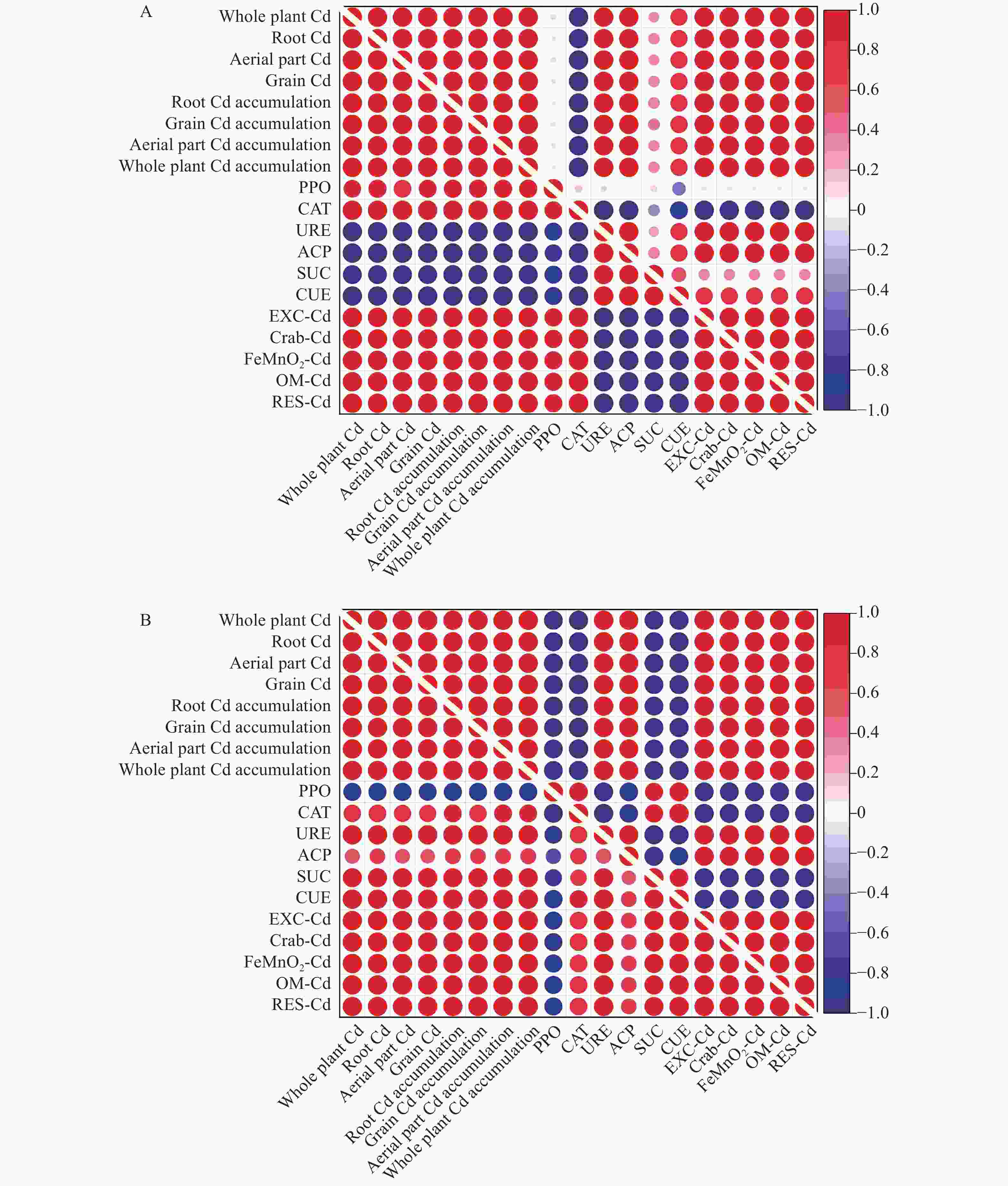
图 1 高镉耐性(上三角矩阵)和低镉耐性(下三角矩阵)水稻接种假单胞菌TCd-1前(A)后(B)的镉含量、镉富集量、土壤酶活性及镉形态的相关性
Whole plant Cd: 全株镉含量; Root Cd: 根镉含量; Aerial part Cd: 地上部镉含量; Grain Cd: 籽粒镉含量; Root Cd accumulation: 根部镉富集量; Grain Cd accumulation: 籽粒镉富集量; Aerial part Cd accumulation: 地上部镉富集量; Whole plant Cd accumulation: 全株镉富集量; PPO: 多酚氧化酶活性; CAT: 过氧化氢酶活性; URE: 脲酶活性; ACP: 酸性磷酸酶活性; SUC: 纤维素酶活性; CUE: 蔗糖酶活性; EXC-Cd: 可交换态镉含量; Crab-Cd: 碳酸盐结合态镉含量; FeMnO2-Cd: 铁锰氧化物结合态镉含量; OM-Cd: 有机结合态镉含量; RES-Cd: 残渣态镉含量。蓝色表示负相关, 红色表示正相关, 颜色越深, 相关性越强。右边的数值代表Pearson相关性指数。
Figure 1. Correlation among Cd content, Cd accumulation, soil enzyme activity and soil Cd forms contents for high Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Teyou 671’ (upper triangular matrix) and low Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Baixiang 139’ (lower triangular matrix) before (A) and after (B) Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation
PPO: polyphenol oxidase activity; CAT: catalase activity; URE: urease activity; ACP: acid phosphatase activity; SUC: cellulase activity; CUE: invertase activity; EXC-Cd: exchangeable Cd content; Crab-Cd: carbonate bound Cd content; FeMnO2-Cd: Fe-Mn oxides bound Cd content; OM-Cd: organic matter Cd content; RES-Cd: residual Cd content. Blue indicates a negative correlation, red indicates a positive correlation, the darker the color, the stronger the correlation. The numbers on the right represent the Pearson index.
表 1 菌和Cd互作处理对不同镉耐性水稻各部位镉含量、富集系数(BCF)、转移系数(TF)及镉富集量的影响
Table 1. Effects of Pseudomonas TCd-1, Cd and their interaction on Cd contents, bioconcentration factor (BCF), translocation factor (TF) and Cd accumulation of different Cd-tolerant varieties of rice
处理
Treatment镉含量 Cadmium content (mg∙kg−1) 富集系数
BCF转移系数
TF镉富集量 Cadmium accumulation (μg∙plant−1) 根部
Root地上部
Aerial part籽粒
Grain全株
Whole plant根部
Root地上部
Aerial part籽粒
Grain全株
Whole plantTY-CK 0.28±0.04g 0.05±0.02f 0.03±0.00d 0.09±0.02e 0.52±0.10de 0.18±0.03d 4.05±0.31f 3.51±1.06f 0.99±0.24d 7.56±1.38f TY-CKB 0.33±0.03g 0.09±0.03f 0.06±0.01d 0.12±0.03e 0.67±0.18cde 0.26±0.08d 4.07±0.22f 6.99±2.58f 2.25±0.38d 11.06±2.88f TY-Cd 35.72±0.21a 3.47±0.21c 0.84±0.01b 7.53±0.42b 0.74±0.04cd 0.10±0.01e 342.60±13.33a 231.57±5.70b 28.94±2.62a 574.17±16.71a TY-CdB 24.83±0.10b 2.07±0.10d 0.60±0.03c 4.93±0.16c 0.48±0.02e 0.08±0.00e 227.06±5.92b 131.69±6.66c 20.37±1.46c 358.75±12.58b BX-CK 0.55±0.03f 1.50±0.06e 0.02±0.01d 1.39±0.05d 7.74±0.28b 2.75±0.08d 3.84±0.33f 81.81±3.74c 0.67±0.31d 85.64±4.01e BX-CKB 1.69±0.07e 1.46±0.02e 0.08±0.02d 1.49±0.02d 8.26±0.10a 0.86±0.04b 16.13±0.57e 100.47±5.83d 2.69±0.67d 116.60±6.40d BX-Cd 13.18±0.02c 8.47±0.43a 1.33±0.01a 9.07±0.40a 0.89±0.39c 0.64±0.03c 65.34±2.39c 289.05±8.20a 22.96±2.22b 354.38±10.56b BX-CdB 6.30±0.06d 4.52±0.25b 0.81±0.08b 4.74±0.23c 0.47±0.02e 0.72±0.03c 45.87±1.03d 235.69±1.55b 22.98±1.09b 281.56±2.33c 显著性 Significance 水稻品种
Rice variety (V)** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** NS ** 镉处理
Cadmium treatment (Cd)** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** 菌处理
Bacterial treatment (B)** ** ** ** NS ** ** ** * ** V×Cd ** ** ** ** ** ** ** NS NS ** V×B ** ** ** ** NS ** ** ** ** ** Cd×B ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** V×Cd×B ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** 表中同列不同小写字母表示处理间在 P<0.05水平差异显著; *和**分别表示在 P<0.05和 P<0.01水平差异显著; NS表示无显著性差异。TY: 高镉耐性水稻品种‘特优671’; BX: 低镉耐性品种‘百香139’; CK: 不加镉且不接种菌株; CKB: 不加镉但接种菌株; Cd: 加镉但不接种菌株; CdB: 加镉且接种菌株。In the table, different lowercase letters in the same column mean significant differences among treatments at P<0.05. * and ** mean significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. NS means no significant difference. TY: high Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Teyou 671’; BX: low Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Baixiang 139; CK: control treatment without Cd and Pseudomonas TCd-1; CKB: control treatment without Cd but with Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation; Cd: treatment of 10 mg·kg−1 Cd; CdB: treatment with inoculation of Pseudomonas TCd-1 and 10 mg·kg−1 Cd. 表 2 菌和Cd互作处理对不同镉耐性水稻品种根际土壤酶活性的影响
Table 2. Effect of Pseudomonas TCd-1, Cd and their interaction on enzymes activities in rhizosphere soil of different Cd-tolerant varieties of rice
处理
Treatment酸性磷酸酶
Acid phosphatase (ACP)
[mg∙g−1(FW)∙(24 h)−1]脲酶
Urease (URE)
[mg∙g−1(FW)∙
(24 h)−1]蔗糖酶
Sucrase (SUC)
[mg∙g−1(FW)∙
(24 h)−1]纤维素酶
Cellulase
(CUE)
[mg∙g−1(FW)∙(24 h)−1]过氧化氢酶
Catalase
(CAT)
[mL∙g−1(FW)∙(20 min−1]多酚氧化酶
Polyphenol oxidase (PPO)
[mg∙g−1(FW)∙
(24 h)−1]TY-CK 1.06±0.01d 1.47±0.02f 0.46±0.01a 13.02±0.86b 0.46±0.01a 16.16±1.00a TY-CKB 1.20±0.01c 1.49±0.00f 0.46±0.03a 14.09±0.11a 0.45±0.00a 17.07±0.30a TY-Cd 1.39±0.01a 1.81±0.02c 0.47±0.02a 14.44±0.34a 0.39±0.00c 16.08±0.48a TY-CdB 1.29±0.01b 1.64±0.00e 0.35±0.00c 12.10±0.50c 0.41±0.01b 14.24±0.77b BX-CK 0.98±0.01e 2.16±0.01a 0.29±0.01d 8.88±0.030d 0.36±0.00d 14.59±0.46b BX-CKB 0.96±0.01e 1.33±0.02g 0.29±0.00d 9.18±0.13d 0.39±0.01c 16.01±0.74a BX-Cd 0.86±0.00f 1.74±0.02d 0.24±0.01e 7.70±0.030e 0.39±0.00c 16.37±0.75a BX-CdB 1.09±0.12d 1.95±0.03b 0.39±0.02b 13.95±0.04a 0.41±0.01b 14.34±0.24b 显著性 Significance 水稻品种
Rice variety (V)** ** ** ** ** * 镉处理
Cd treatment (Cd)** ** NS ** ** * 菌处理
Bacterial treatment (B)** ** NS ** ** * V×Cd ** ** ** ** ** * V×B * ** ** ** ** NS Cd×B NS ** NS ** NS ** V×Cd×B ** ** ** ** ** NS 表中同列不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著; *和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著; NS表示无显著性差异。TY: 高镉耐性水稻品种‘特优671’; BX: 低镉耐性品种‘百香139’; CK: 不加镉且不接种菌株; CKB: 不加镉但接种菌株; Cd: 加镉但不接种菌株; CdB: 加镉且接种菌株。In the table, different lowercase letters in the same column mean significant differences among treatments at P<0.05. * and ** mean significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. NS means no significant difference. TY: high Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Teyou 671’; BX: low Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Baixiang 139; CK: control treatment without Cd and Pseudomonas TCd-1; CKB: control treatment without Cd but with Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation; Cd: treatment of 10 mg·kg−1 Cd; CdB: treatment with inoculation of Pseudomonas TCd-1 and 10 mg·kg−1 Cd. 表 3 菌和镉互作处理对不同镉耐性水稻根际土壤中不同形态镉含量的影响
Table 3. Effect of Pseudomonas TCd-1, Cd and their interaction on different forms of cadmium in rhizosphere soil of different Cd-tolerant varieties of rice
处理
Treatment可交换态镉
Exchangeable cadmium
(EXC-Cd)碳酸盐结合态镉
Carbonate bound cadmium
(Crab-Cd)铁锰氧化结合态镉
Fe-Mn oxides bound cadmium
(FeMnO2-Cd)有机态镉
Organic matter cadmium
(OM-Cd)残渣态镉
Residual cadmium
(RES-Cd)mg·kg−1 TY-CK 0.08±0.00e 0.04±0.00c 0.03±0.00d 0.01±0.01c 0.01±0.00c TY-CKB 0.06±0.01e 0.05±0.01c 0.03±0.00d 0.02±0.00c 0.01±0.00c TY-Cd 4.09±0.55a 2.05±0.30a 1.92±0.29b 0.72±0.12b 0.59±0.09b TY-CdB 3.44±0.28b 1.81±0.15a 2.68±0.20a 0.98±0.08a 0.70±0.06b BX-CK 0.04±0.01e 0.02±0.01c 0.02±0.00d 0.01±0.00c 0.07±0.01c BX-CKB 0.05±0.01e 0.02±0.01c 0.01±0.00d 0.01±0.00c 0.08±0.01c BX-Cd 2.73±0.11c 1.39±0.23b 0.59±0.03c 0.80±0.07b 3.94±0.53a BX-CdB 2.08±0.14d 1.85±0.11a 0.76±0.05c 1.00±0.08a 4.07±0.24a 显著性 Significance 水稻品种 Rice variety (V) ** * ** NS ** 镉处理 Cadmium treatment (Cd) ** ** ** ** ** 菌处理 Bacterial treatment (B) * NS ** ** NS V×Cd ** * ** NS ** V×B NS * * NS NS Cd×B * NS ** ** NS V×Cd×B NS * * NS NS 表中同列不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著; *和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著; NS表示无显著性差异。TY: 高镉耐性水稻品种‘特优671’; BX: 低镉耐性品种‘百香139’; CK: 不加镉且不接种菌株; CKB: 不加镉但接种菌株; Cd: 加镉但不接种菌株; CdB: 加镉且接种菌株。In the table, different lowercase letters in the same column mean significant differences among treatments at P<0.05. * and ** mean significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. NS means no significant difference. TY: high Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Teyou 671’; BX: low Cd-tolerant rice variety ‘Baixiang 139; CK: control treatment without Cd and Pseudomonas TCd-1; CKB: control treatment without Cd but with Pseudomonas TCd-1 inoculation; Cd: treatment of 10 mg·kg−1 Cd; CdB: treatment with inoculation of Pseudomonas TCd-1 and 10 mg·kg−1 Cd. -
[1] SHARMA R K, ARCHANA G. Cadmium minimization in food crops by cadmium resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 107: 66−78 doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.05.009 [2] CHEN H P, TANG Z, WANG P, et al. Geographical variations of cadmium and arsenic concentrations and arsenic speciation in Chinese rice[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 238: 482−490 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.048 [3] 杨海, 黄新, 林子增, 等. 重金属污染土壤微生物修复技术研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(6): 1417−1422 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.06.039YANG H, HUANG X, LIN Z Z, et al. Research progress on microbial remediation technology for heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(6): 1417−1422 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.06.039 [4] 陆仲烟, 宋正国, 郭军康, 等. 伯克氏菌对水稻种子萌发及初生幼苗耐镉性的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2013, 30(6): 87−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.06.018LU Z Y, SONG Z G, GUO J K, et al. Effects of Burkholderia on rice seed germination and Cd-tolerance of rice seedlings[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2013, 30(6): 87−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.06.018 [5] 何小三, 王微, 肖清铁, 等. 铜绿假单胞菌对镉胁迫水稻苗期生长与镉积累的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(6): 884−891HE X S, WANG W, XIAO Q T, et al. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the growth and cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling under Cd stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(6): 884−891 [6] LI Y, PANG H D, HE L Y, et al. Cd immobilization and reduced tissue Cd accumulation of rice (Oryza sativa Wuyun-23) in the presence of heavy metal-resistant bacteria[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 138: 56−63 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.12.024 [7] 汪敦飞, 郑新宇, 肖清铁, 等. 铜绿假单胞菌对镉胁迫苗期水稻根系活力及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(8): 2767−2774WANG D F, ZHENG X Y, XIAO Q T, et al. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on root activity and leaf physiological characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling under cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(8): 2767−2774 [8] WANG Y J, ZHENG X Y, HE X S, et al. Effects of Pseudomonas TCd-1 on rice (Oryza sativa) cadmium uptake, rhizosphere soils enzyme activities and cadmium bioavailability under cadmium contamination[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 218: 112249 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112249 [9] 文欢欢, 郑新宇, 肖清铁, 等. 镉污染条件下水稻对假单胞菌TCd-1微生物修复的生理响应[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5): 1924−1933WEN H H, ZHENG X Y, XIAO Q T, et al. Physiological response of cadmium-contaminated rice to Pseudomonas TCd-1 microbial repair[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(5): 1924−1933 [10] 朱胜男. 不同镉耐性水稻间作系统对镉污染的生理响应[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2020ZHU S N. Physiological response of rice intercropping systems with different cadmium tolerance to cadmium pollution[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2020 [11] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986GUAN S Y. Soil Enzyme and Its Study Method[M]. Beijing: Beijing Agricultural Press, 1986 [12] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844−851 doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [13] 孙亚莉, 徐庆国, 贾巍. 镉胁迫对水稻的影响及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(10): 1−6 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16050157SUN Y L, XU Q G, JIA W. Advance in cadmium stress on rice and its regulation and control technology[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(10): 1−6 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16050157 [14] LI Z M, LIANG Y, HU H W, et al. Speciation, transportation, and pathways of cadmium in soil-rice systems: a review on the environmental implications and remediation approaches for food safety[J]. Environment International, 2021, 156: 106749 doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106749 [15] SIRIPORNADULSIL S, SIRIPORNADULSIL W. Cadmium-tolerant bacteria reduce the uptake of cadmium in rice: potential for microbial bioremediation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 94: 94−103 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.002 [16] MA Y, OLIVEIRA R S, FREITAS H, et al. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of plant-microbe-metal interactions: relevance for phytoremediation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 918 [17] 马莹, 骆永明, 滕应, 等. 根际促生菌及其在污染土壤植物修复中的应用[J]. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(5): 1021−1031MA Y, LUO Y M, TENG Y, et al. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and their role in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(5): 1021−1031 [18] 娄庭, 杨丽娟. 土壤重金属的生物有效性及对植物的毒害作用[J]. 吉林农业科学, 2009, 34(5): 28−32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8701.2009.05.010LOU T, YANG L J. Bioavailability of heavy metals in the soil and the toxic effect of plant[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 34(5): 28−32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8701.2009.05.010 [19] 罗海艳, 李丹阳, 刘寿涛, 等. 铁锰改性椰壳炭对土壤镉形态及水稻吸收积累镉的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(5): 857−865LUO H Y, LI D Y, LIU S T, et al. Effects of Fe-Mn modified coconut shell biochar on cadmium speciation and accumulation in rice[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(5): 857−865 [20] 刘霞, 刘树庆, 王胜爱, 等. 重金属复合污染对土壤微生物生态特征的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(S1): 17−21LIU X, LIU S Q, WANG S A, et al. Influence on ecological characteristics of microorganisms in soils polluted by compound heavy metals[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(S1): 17−21 [21] 张芬, 杨长明, 潘睿捷. 青山水库表层沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(9): 2625−2630ZHANG F, YANG C M, PAN R J. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Qingshan Reservoir in Lin’an City, Zhejiang Province of East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(9): 2625−2630 [22] 张锡洲, 张洪江, 李廷轩, 等. 水稻镉耐性差异及镉低积累种质资源的筛选[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(11): 1434−1440 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01434ZHANG X Z, ZHANG H J, LI T X, et al. Differences in Cd-tolerance of rice and screening for Cd low-accumulation rice germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(11): 1434−1440 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.01434 [23] 于辉, 杨中艺, 杨知建, 等. 不同类型镉积累水稻细胞镉化学形态及亚细胞和分子分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(10): 2221−2226YU H, YANG Z Y, YANG Z J, et al. Chemical forms and subcellular and molecular distribution of Cd in two Cd-accumulation rice genotypes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(10): 2221−2226 [24] 张连忠, 路克国, 王宏伟, 等. 重金属和生物有机肥对苹果根区土壤微生物的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(2): 92−95 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.02.024ZHANG L Z, LU K G, WANG H W, et al. Effect of heavy metal and bio-fertilizer on microorganisms in soil of apple root[J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2005, 19(2): 92−95 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.02.024 [25] 曾路生, 廖敏, 黄昌勇, 等. 镉污染对水稻土微生物量、酶活性及水稻生理指标的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(11): 2162−2167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.11.031ZENG L S, LIAO M, HUANG C Y, et al. Effects of Cd contamination on paddy soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities and rice physiological indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(11): 2162−2167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.11.031 [26] 宫占元, 张国庆, 于文莹, 等. 哈茨木霉菌对水稻幼苗根际土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2013, 31(4): 167−171 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7601.2013.04.031GONG Z Y, ZHANG G Q, YU W Y, et al. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum on microorganisms and enzymatic activities in rhizosphere soil during rice seedling stage[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2013, 31(4): 167−171 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7601.2013.04.031 [27] 耿玉清, 王冬梅. 土壤水解酶活性测定方法的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(4): 387−394 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2012.00387GENG Y Q, WANG D M. Research advances on the measurement methods for soil hydrolytic enzymes activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(4): 387−394 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2012.00387 [28] 许云翔, 何莉莉, 刘玉学, 等. 施用生物炭6年后对稻田土壤酶活性及肥力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(4): 1110−1118XU Y X, HE L L, LIU Y X, et al. Effects of biochar addition on enzyme activity and fertility in paddy soil after six years[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(4): 1110−1118 [29] 刘树庆. 保定市污灌区土壤的Pb、Cd污染与土壤酶活性关系研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1996, 33(2): 175−182 doi: 10.11766/trxb199505260208LIU S Q. Relationship between soil Pb and Cd pollution and enzyme activities in waste water irrigated area of Baoding City[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1996, 33(2): 175−182 doi: 10.11766/trxb199505260208 [30] 和文祥, 陈会明, 冯贵颖, 等. 汞铬砷元素污染土壤的酶监测研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2000, 20(3): 338−343HE W X, CHEN H M, FENG G Y, et al. Study on enzyme index in soils polluted by mercury, chromium and arsenic[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2000, 20(3): 338−343 [31] 蒲生彦, 王宇, 陈文英, 等. 植物根际土壤酶对重金属污染的响应机制研究综述[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(4): 11−20PU S Y, WANG Y, CHEN W Y, et al. Review on the mechanism of plant rhizosphere soil enzyme response to heavy metal pollution[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(4): 11−20 [32] 罗虹, 刘鹏, 宋小敏. 重金属镉、铜、镍复合污染对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2006, 20(2): 94−96, 121 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2006.02.023LUO H, LIU P, SONG X M. Effect of compound pollution of Cd, Cu and Ni on soil enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(2): 94−96, 121 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2006.02.023 [33] 刘辉, 吴小芹, 任嘉红, 等. 荧光假单胞菌与红绒盖牛肝菌共接种对杨树根际土壤酶活性及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(1): 22−30 doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20190103LIU H, WU X Q, REN J H, et al. Effect of co-inoculation with Pseudomonas fluorescens and Xerocomus chrysenteron on the soil enzyme activity and microbial diversity in poplar rhizosphere[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2019, 55(1): 22−30 doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20190103 [34] QIAN X, LÜ Q X, HE X S, et al. Pseudomonas sp. TCd-1 significantly alters the rhizosphere bacterial community of rice in Cd contaminated paddy field[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 290: 133257 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133257 -





 下载:
下载: