Suitability of the cosmic-ray fast neutron soil moisture monitoring method in a low-latitude plateau
-
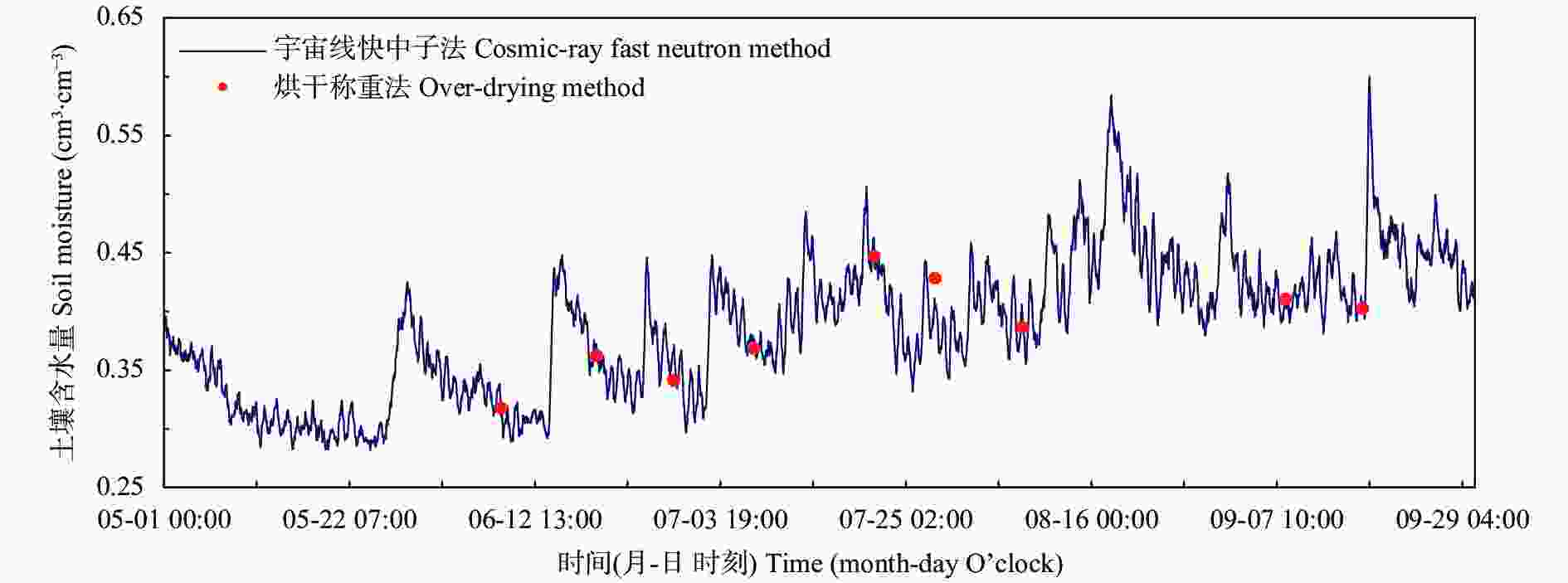
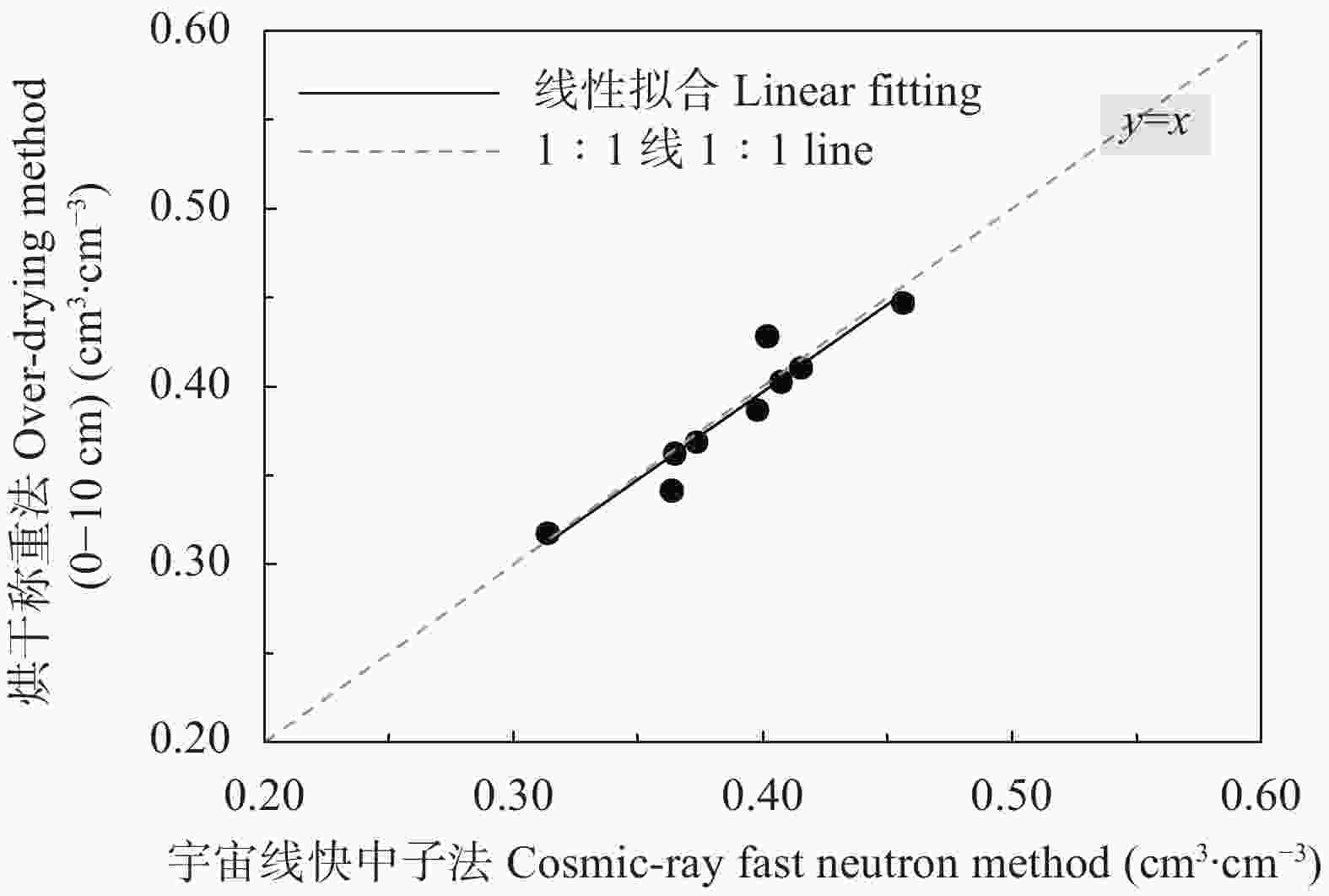
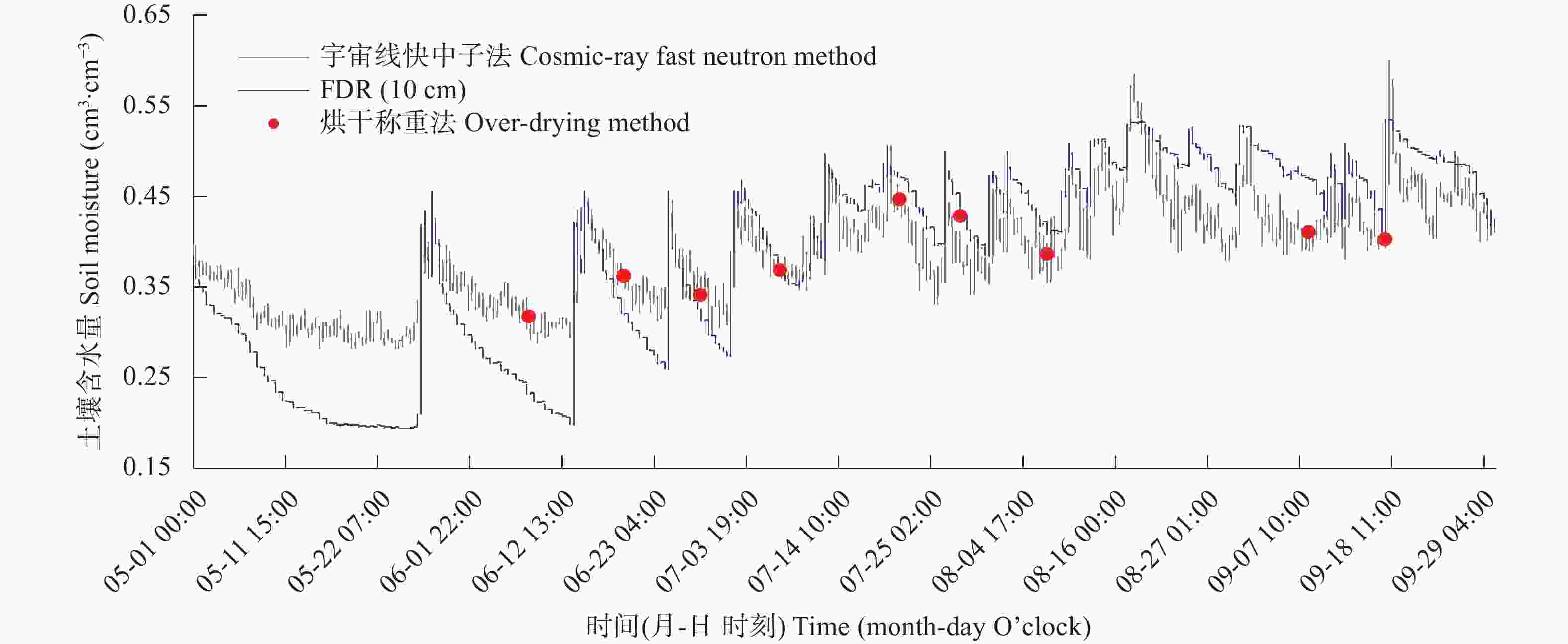
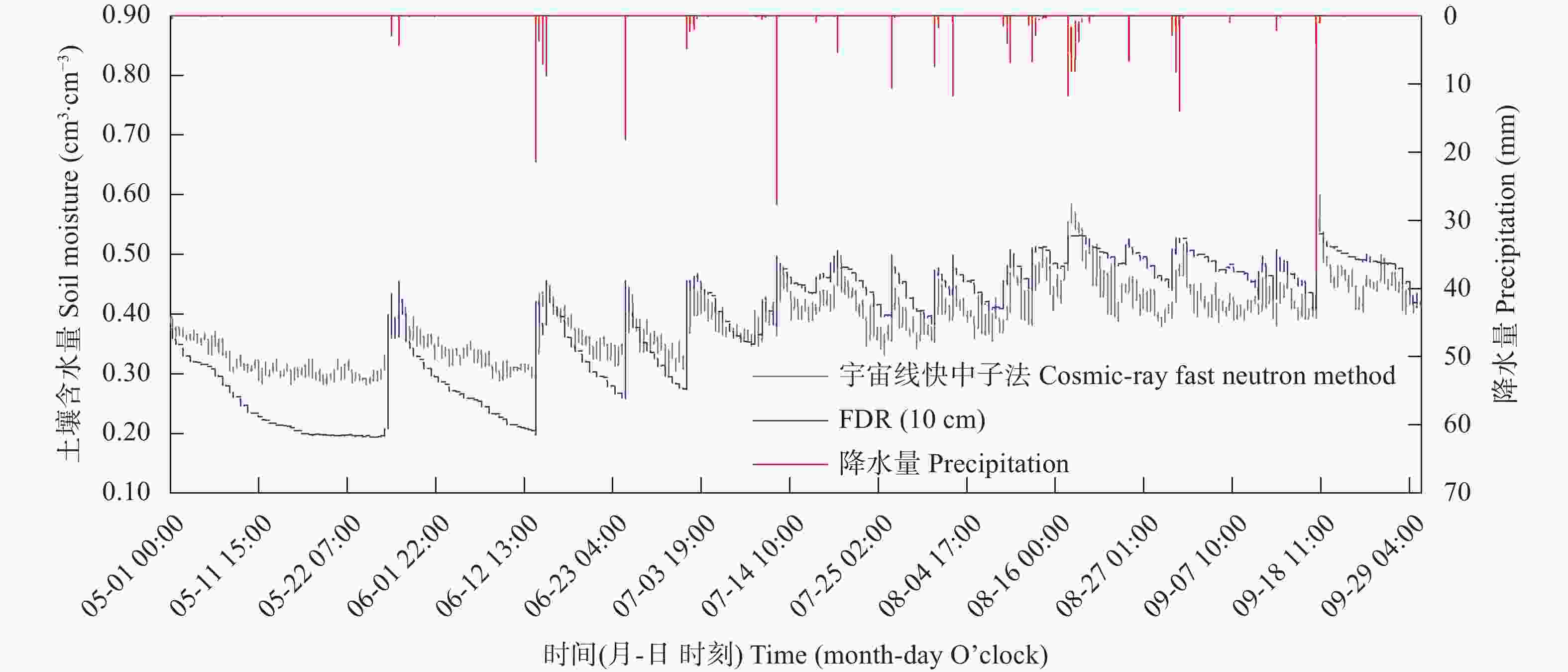
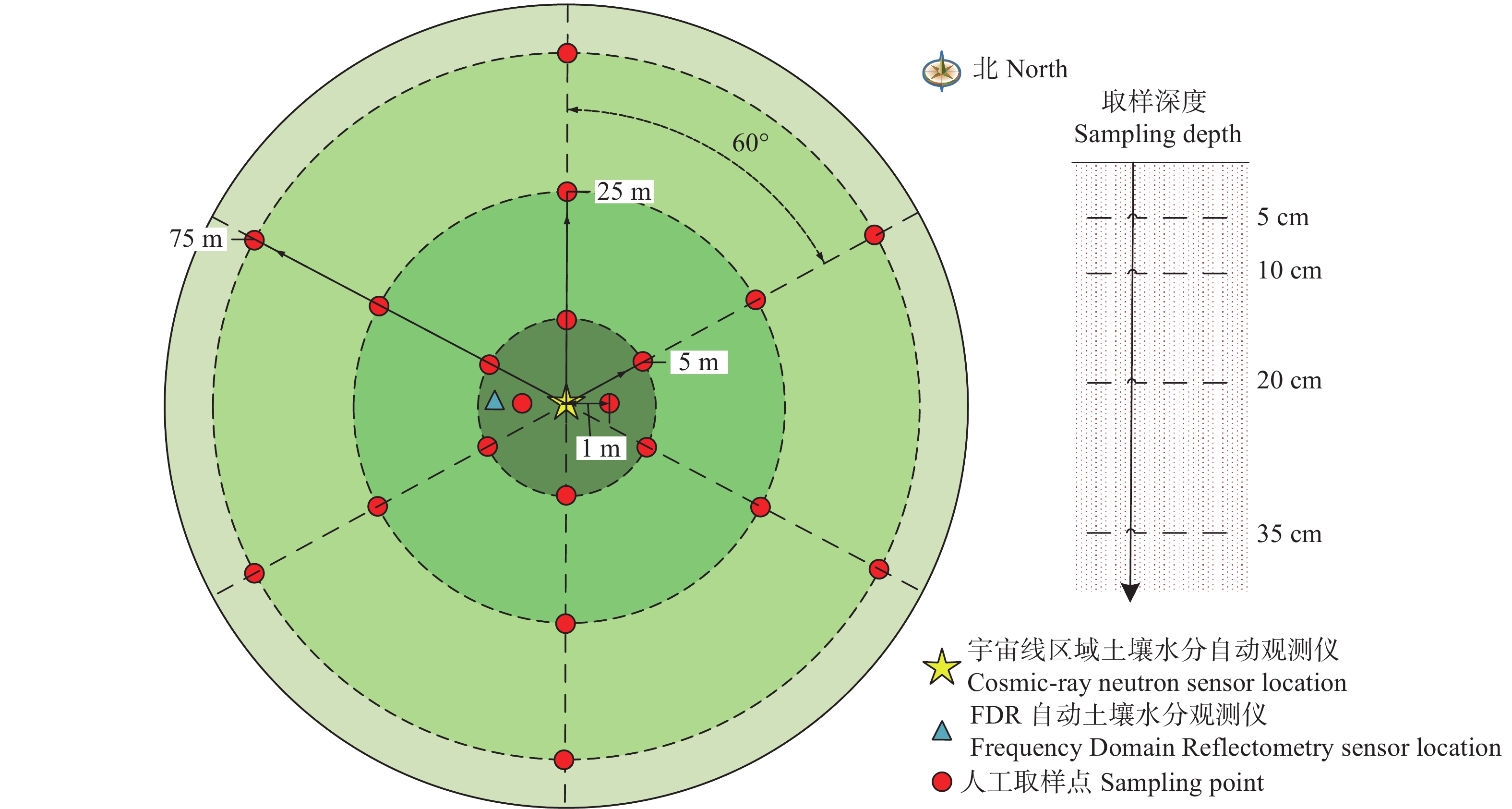
摘要: 宇宙线快中子土壤水分监测方法具有监测范围大、不受土壤盐碱程度影响、实时无损原位测量的特点, 对旱涝预警、节水灌溉、生态环境保护及土壤生产力提升等具有重要意义。为明确宇宙线快中子土壤水分监测方法在低纬度高原的适宜性, 本研究在中国南部开展了大范围烘干称重法测量, 验证宇宙线快中子法准确性, 以频域反射法做连续监测对比, 分析土壤水分相关性, 并结合雨量站观测数据, 研究其对土壤水分连续变化的响应能力。试验结果表明, 宇宙线快中子法与多点烘干称重法的线性拟合优度、均方根误差及绝对误差分别为0.898、0.013 cm3∙cm–3和0.027 cm3∙cm–3, 说明宇宙线快中子法在低纬度高原能够准确测量区域土壤含水量。在较长时间序列上, 宇宙线快中子法与频域反射法10 cm的土壤水分变化趋势完全一致, 线性拟合优度为0.839; 在对降水响应的灵敏性上, 降水量2 mm以上的降水过程, 两种方法均有明显响应, 降水量2 mm以下的降水过程, 宇宙线快中子法要略优于频域反射法。在本试验中, 宇宙线快中子土壤水分监测方法在低纬度高原区是适宜的, 对土壤水分空间变异性不敏感, 对百米级范围的平均土壤含水量的测量准确可信, 测量性能满足当前土壤含水量观测要求, 且能够提供实时土壤水分信息, 有效提高中尺度土壤水分监测效率与精度, 为相关土壤水分监测研究与应用提供参考, 对低纬度高原土地资源开发利用、环境保护、粮食自给等具有重要意义。Abstract: The cosmic-ray fast neutron soil moisture monitoring method has a large monitoring range, is unaffected by soil salinity, allows real-time and non-destructive in situ measurement, and is of significance for drought and flood warning, water-saving irrigation, ecological environment protection, and soil productivity improvement. To clarify the suitability of the cosmic-ray fast neutron soil moisture monitoring method in the low-latitude plateau, this study conducted a large-scale soil moisture investigation using oven-drying method in the southern Chinese city of Dali (25°42ʹ14″N, 100°10ʹ34″E) from May to September 2020 to verify the accuracy of the cosmic-ray fast neutron method. At the experimental site, a cosmic-ray fast neutron soil moisture station, frequency domain reflectometer (FDR) soil moisture station, and rainfall monitoring station were installed. FDR was used for continuous monitoring and comparison, and the correlation of soil moisture in the 0–50 cm soil layer was analyzed. Combined with the observation data of rainfall stations, the response ability of cosmic-ray fast neutrons and FDR to continuous changes in soil moisture was studied. The experimental results showed that the determination coefficient of the linear equation (R2), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and absolute error between the soil moisture content measured by the cosmic-ray fast neutron method and by the multi-point mean value of the oven-drying method were 0.898, 0.013 cm3∙cm–3, and 0.027 cm3∙cm–3, respectively. This shows that the cosmic-ray fast neutron method can accurately measure the regional soil water content in low-latitude plateaus. In the long time series, the cosmic-ray fast neutron method and FDR have a consistent trend of soil moisture changes in the 10 cm soil layer, and the determination coefficient of the linear equation (R2) was 0.839. This shows that the cosmic-ray fast neutron method can respond to soil moisture changes over time, similar to FDR. In terms of sensitivity to precipitation, if the precipitation amount was more than 2 mm for the precipitation process, and both methods had obvious responses. For the precipitation process with precipitation below 2 mm, the cosmic-ray fast neutron method was slightly better than FDR. However, more obvious sensitivity was not observed in this experiment, especially for the precipitation process with precipitation below 1 mm, which may be related to the loose texture of the surface soil in the experimental area and the rapid shift of sunny and rainy weather. In this experiment, the cosmic-ray fast neutron soil moisture monitoring method was suitable in the low-latitude plateau region, was not sensitive to the spatial variability of soil moisture, and was accurate and reliable for measuring the average soil moisture content in the range of 100 m. It meets the current soil moisture observation requirements, can provide real-time soil moisture information, effectively improving the efficiency and accuracy of mesoscale soil moisture monitoring, and provides a reference for related soil moisture monitoring research and applications.
-
Key words:
- Cosmic-ray /
- Fast neutron /
- Soil moisture /
- Low-latitude plateau /
- Oven-drying method /
- Frequency Domain Reflectometry
-
表 1 宇宙线快中子法与FDR法测定的土壤含水量的相关性分析
Table 1. Correlation analysis of soil moisture between cosmic-ray fast neutron method and Frequency Domain Reflectometry method
深度 Depth (cm) 0~10 0~20 0~30 0~40 0~50 R2 0.839 0.826 0.805 0.809 0.792 RMSE (cm3·cm–3) 0.057 0.045 0.044 0.037 0.036 -
[1] 雷志栋, 胡和平, 杨诗秀. 土壤水研究进展与评述[J]. 水科学进展, 1999, 10(3): 311−318 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.1999.03.015LEI Z D, HU H P, YANG S X. A review of soil water research[J]. Advances in Water Science, 1999, 10(3): 311−318 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.1999.03.015 [2] BRUNETTI G, ŠIMŮNEK J, BOGENA H, et al. On the information content of cosmic-ray neutron data in the inverse estimation of soil hydraulic properties[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2019, 18(1): 1−24 [3] 张静, 可文静, 刘娟, 等. 不同深度土壤控水对稻田土壤微生物区系及细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(2): 277−285ZHANG J, KE W J, LIU J, et al. Influence of water controlling depth on soil microflora and bacterial community diversity in paddy soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(2): 277−285 [4] BROCCA L, CIABATTA L, MASSARI C, et al. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: open questions and new opportunities[J]. Water, 2017, 9(2): 140 doi: 10.3390/w9020140 [5] TIAN J, ZHANG B Q, HE C S, et al. Dynamic response patterns of profile soil moisture wetting events under different land covers in the mountainous area of the Heihe River Watershed, Northwest China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2019, 271: 225−239 doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.03.006 [6] 邸兰杰, 王卫, 成贺玺, 等. 基于ATI和TVDI模型的河北平原土壤湿度遥感反演[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(6): 737−743DI L J, WANG W, CHENG H X, et al. Remote sensing inversion of soil moisture in Hebei Plain based on ATI and TVDI models[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2014, 22(6): 737−743 [7] RIVERA VILLARREYES C A, BARONI G, OSWALD S E. Integral quantification of seasonal soil moisture changes in farmland by cosmic-ray neutrons[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011, 15(12): 3843−3859 doi: 10.5194/hess-15-3843-2011 [8] ZHANG L H, HE C S, ZHANG M M. Multi-scale evaluation of the SMAP product using sparse in situ network over a high mountainous watershed, Northwest China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(11): 1111 doi: 10.3390/rs9111111 [9] 朱安宁, 吉丽青, 张佳宝, 等. 基于探地雷达的土壤水分测定方法研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(5): 1039−1044 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2009.01039ZHU A N, JI L Q, ZHANG J B, et al. Research progress on soil moisture measurement via ground-penetrating radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(5): 1039−1044 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2009.01039 [10] KÖHLI M, SCHRÖN M, ZREDA M, et al. Footprint characteristics revised for field-scale soil moisture monitoring with cosmic-ray neutrons[J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 51(7): 5772−5790 doi: 10.1002/2015WR017169 [11] ZREDA M, DESILETS D, FERRÉ T P A, et al. Measuring soil moisture content non-invasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(21): L21402 doi: 10.1029/2008GL035655 [12] DESILETS D, ZREDA M, FERRÉ T P A. Nature’s neutron probe: land surface hydrology at an elusive scale with cosmic rays[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(11): W11505 [13] SCHRÖN M, KÖHLI M, SCHEIFFELE L, et al. Improving calibration and validation of cosmic-ray neutron sensors in the light of spatial sensitivity[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2017, 21(10): 5009−5030 doi: 10.5194/hess-21-5009-2017 [14] HEIDBÜCHEL I, GÜNTNER A, BLUME T. Use of cosmic-ray neutron sensors for soil moisture monitoring in forests[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2016, 20(3): 1269−1288 doi: 10.5194/hess-20-1269-2016 [15] 楼惠新. 云贵高原土地利用[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2000(1): 9−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2000.01.004LOU H X. Sustainable landuse in Yun-Gui Plateau[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Stuty, 2000(1): 9−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2000.01.004 [16] 张雪芹, 葛全胜. 青藏高原土地利用结构、特征及合理开发战略[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2002, 23(1): 14−19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9121.2002.01.004ZHANG X Q, GE Q S. The structure, characteristics of land use in the Tibetan Plateau and its rationed development strategy[J]. Journal of China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2002, 23(1): 14−19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9121.2002.01.004 [17] ZREDA M, SHUTTLEWORTH W J, ZENG X, et al. COSMOS: the COsmic-ray Soil Moisture Observing System[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2012, 16(11): 4079−4099 doi: 10.5194/hess-16-4079-2012 [18] DESILETS D, ZREDA M, PRABU T. Extended scaling factors for in situ cosmogenic nuclides: new measurements at low latitude[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 246(3/4): 265−276 [19] ROSOLEM R, SHUTTLEWORTH W J, ZREDA M, et al. The effect of atmospheric water vapor on neutron count in the cosmic-ray soil moisture observing system[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(5): 1659−1671 doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-12-0120.1 [20] DESILETS D, ZREDA M. Footprint diameter for a cosmic-ray soil moisture probe: theory and Monte Carlo simulations[J]. Water Resources Research, 2013, 49(6): 3566−3575 doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20187 [21] FRANZ T E, ZREDA M, FERRE T P A, et al. Measurement depth of the cosmic ray soil moisture probe affected by hydrogen from various sources[J]. Water Resources Research, 2012, 48(8): W08515 [22] 赵原, 李晓鹏, 纪景纯, 等. 宇宙射线中子法在土壤水分监测研究中的应用进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(5): 545−553ZHAO Y, LI X P, JI J C, et al. Advances in soil moisture monitoring using cosmic ray neutron probe method[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019, 35(5): 545−553 -





 下载:
下载: