Climatic resources and drought characteristics of maize sown in different dates in the hilly area of central Sichuan: A case study of Zhongjiang, Sichuan
-
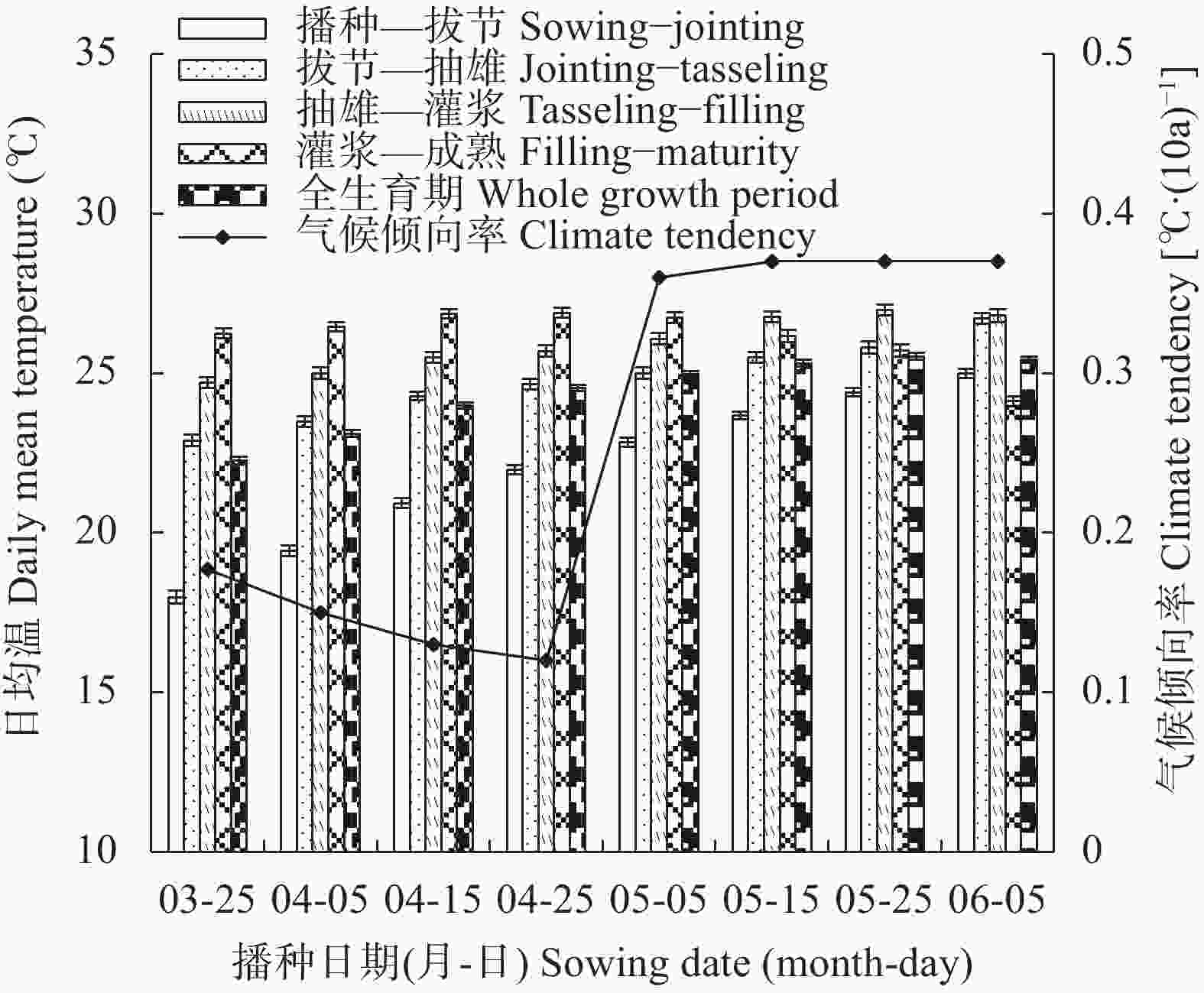
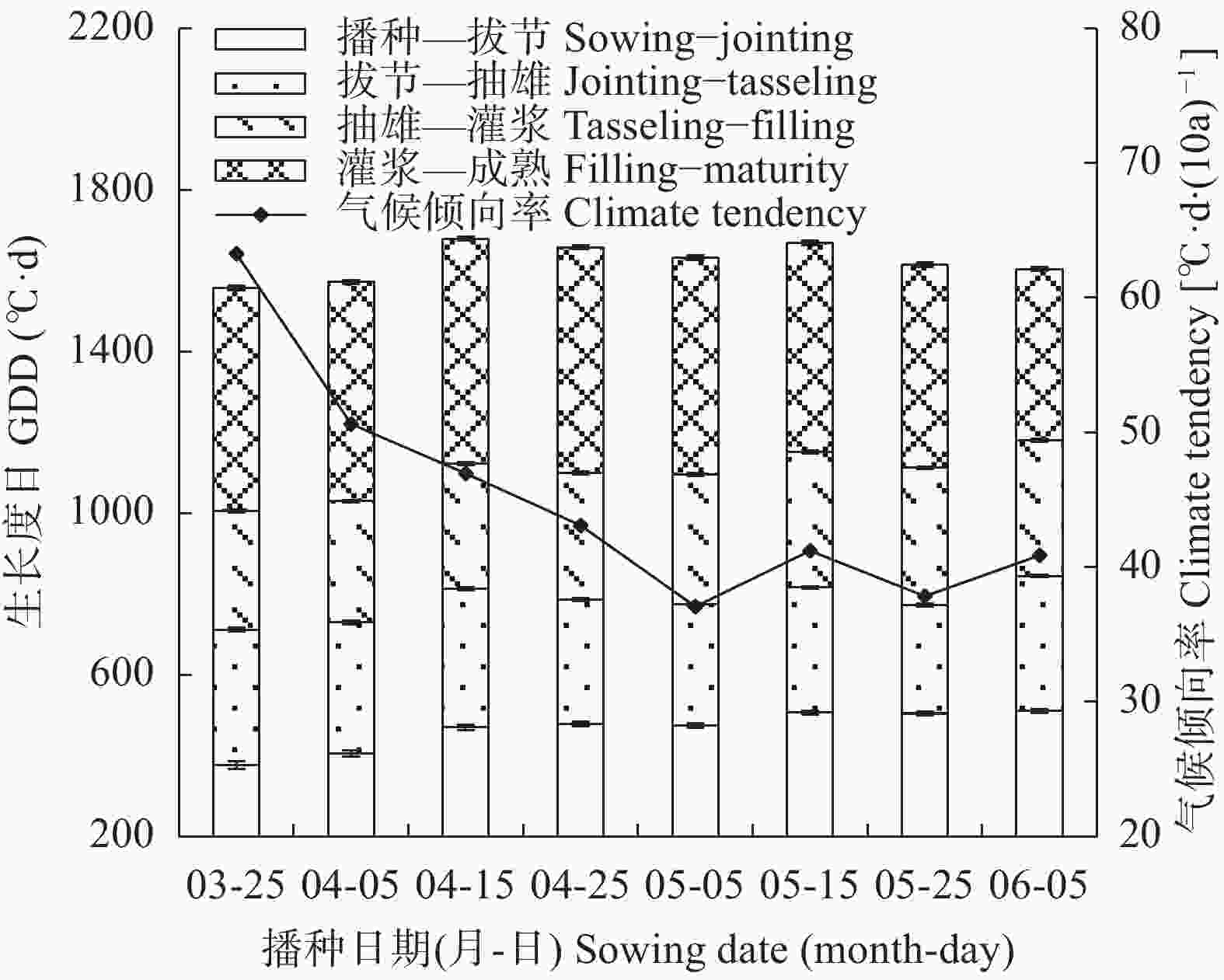
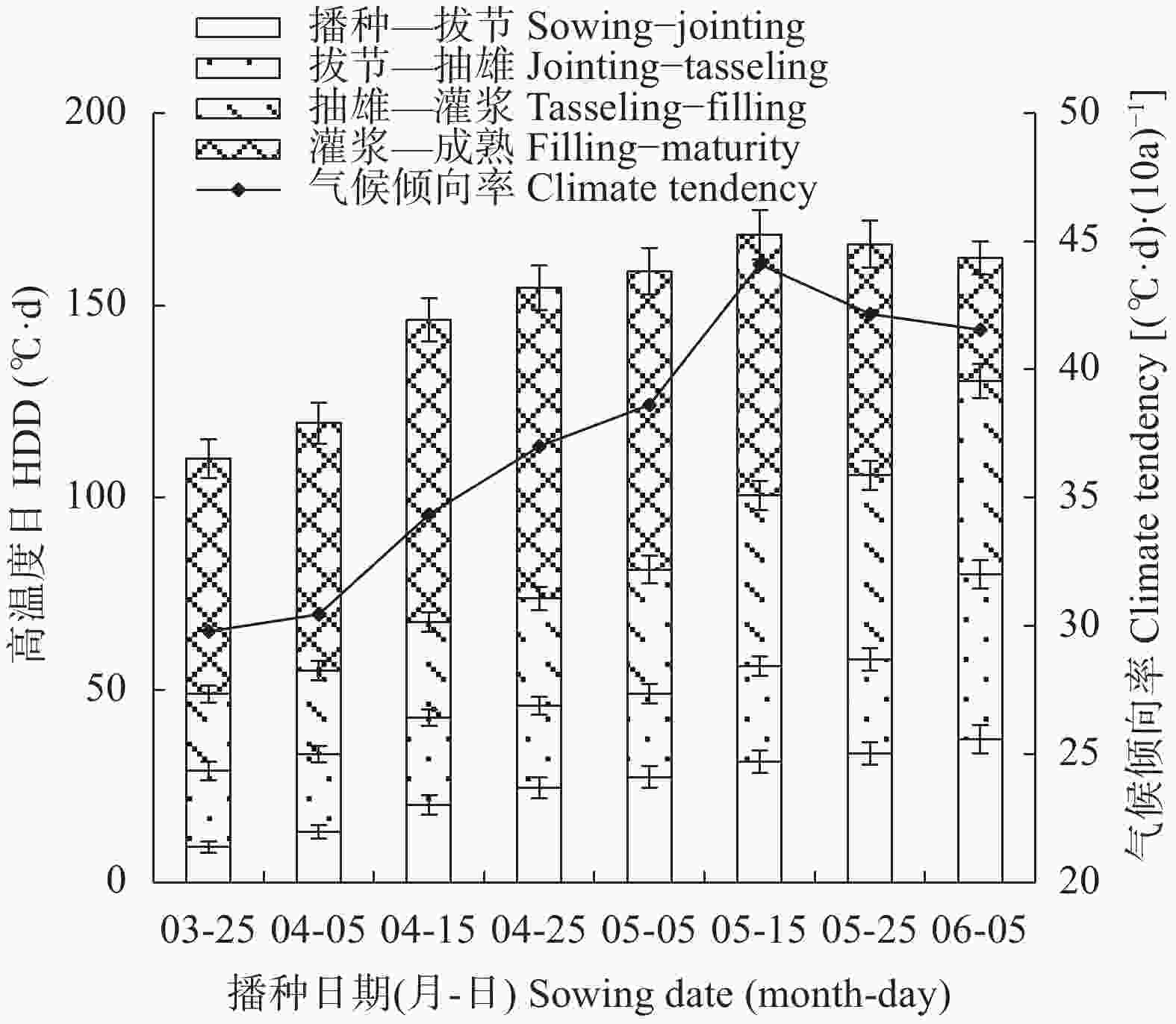
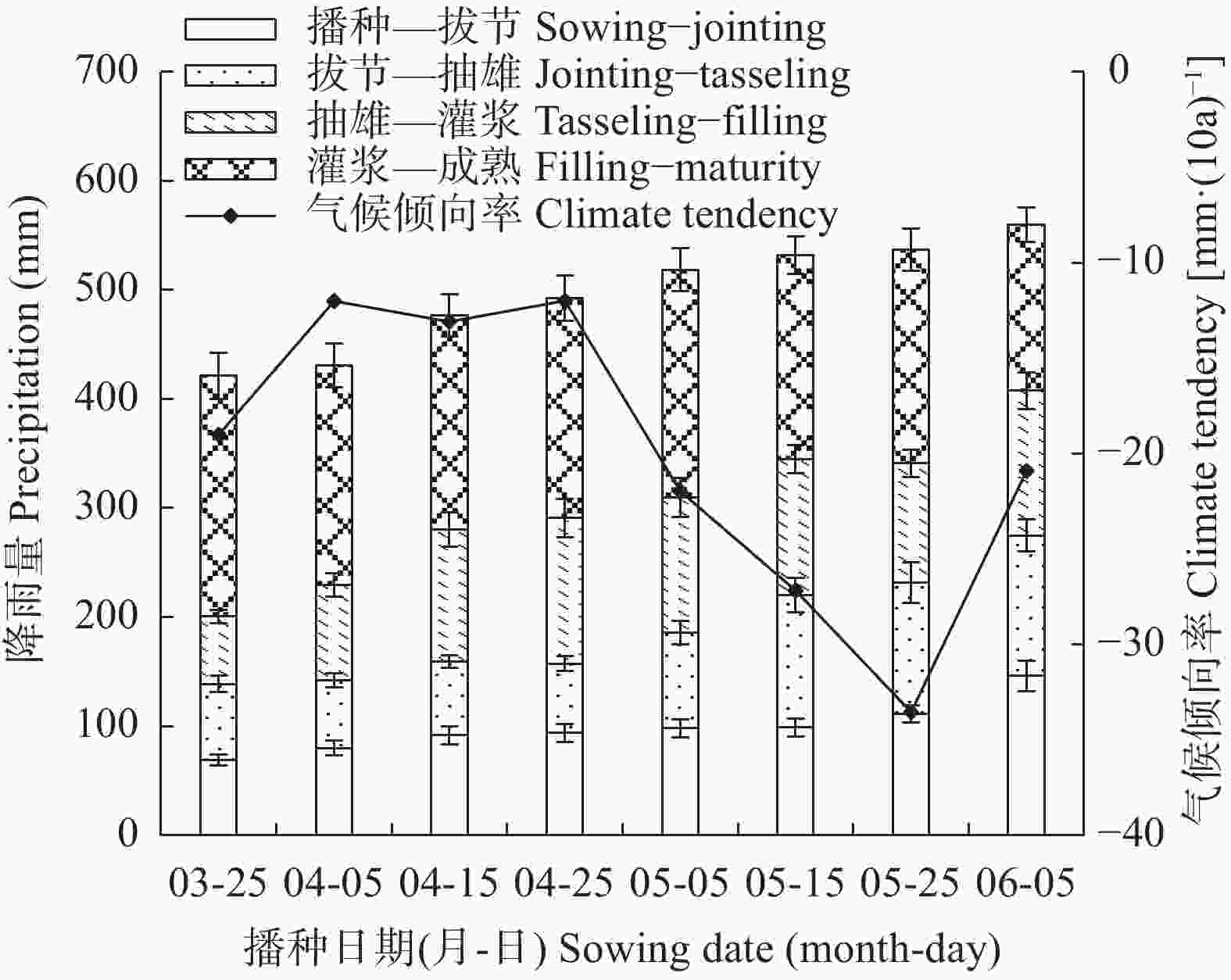
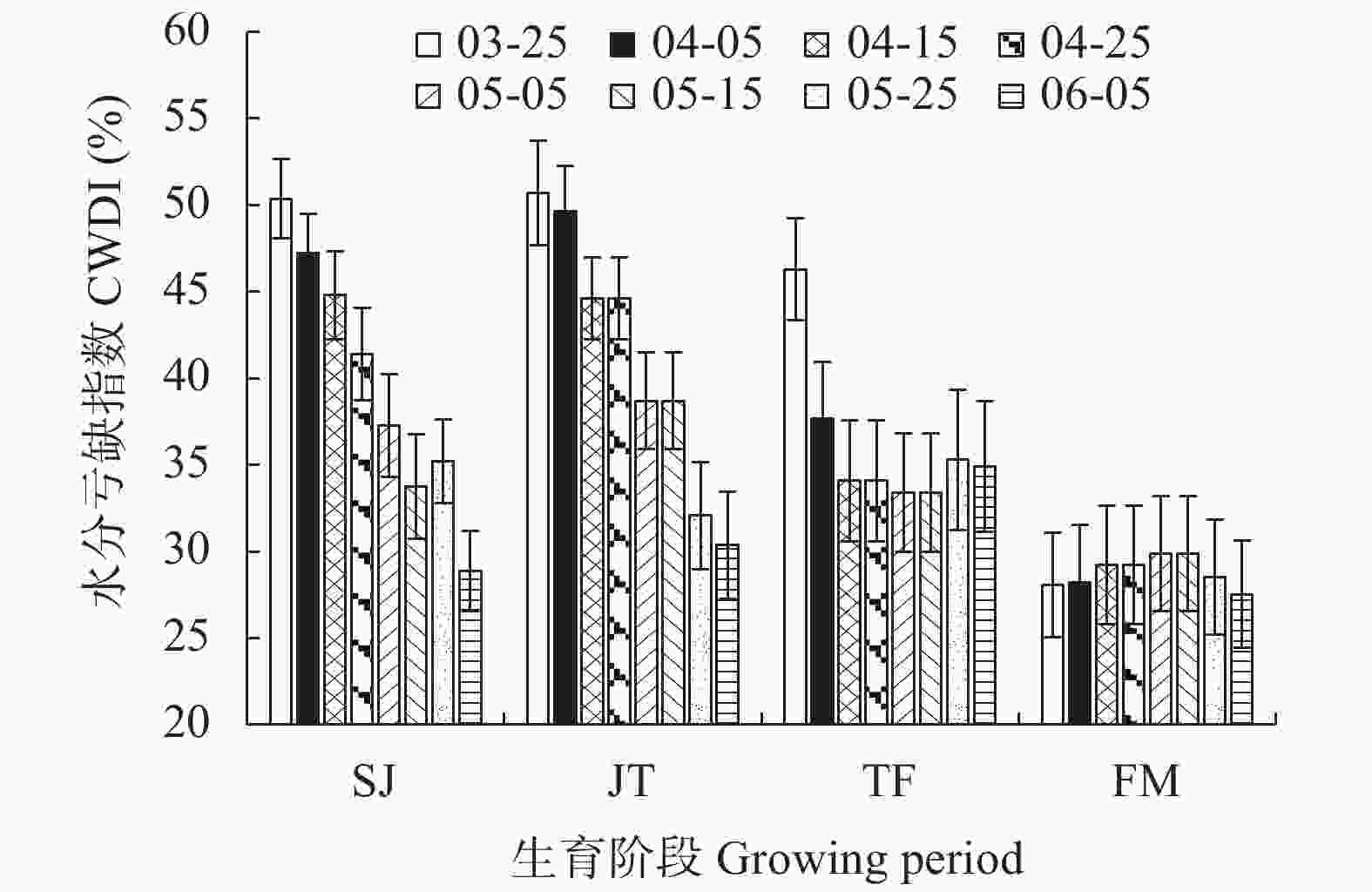
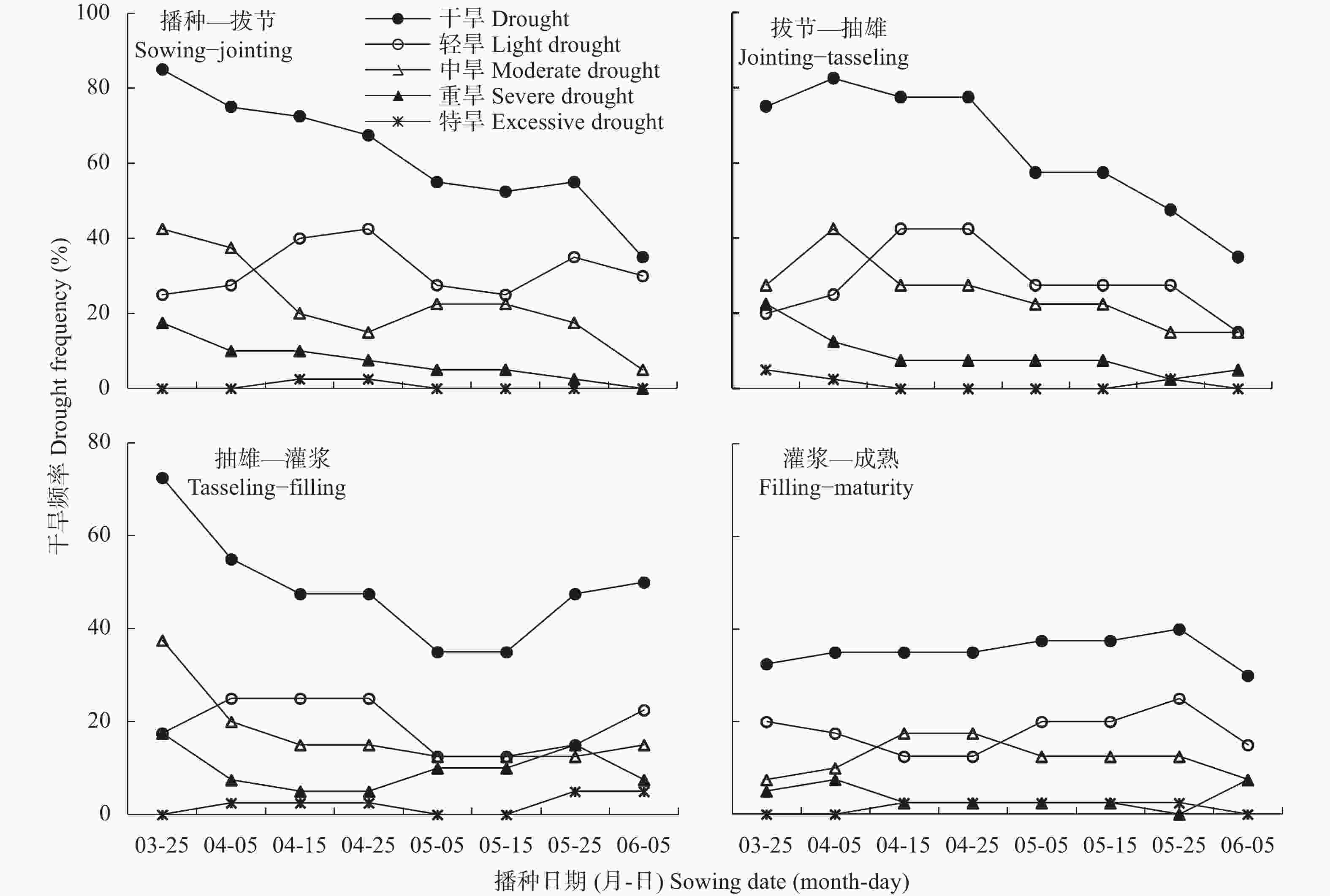
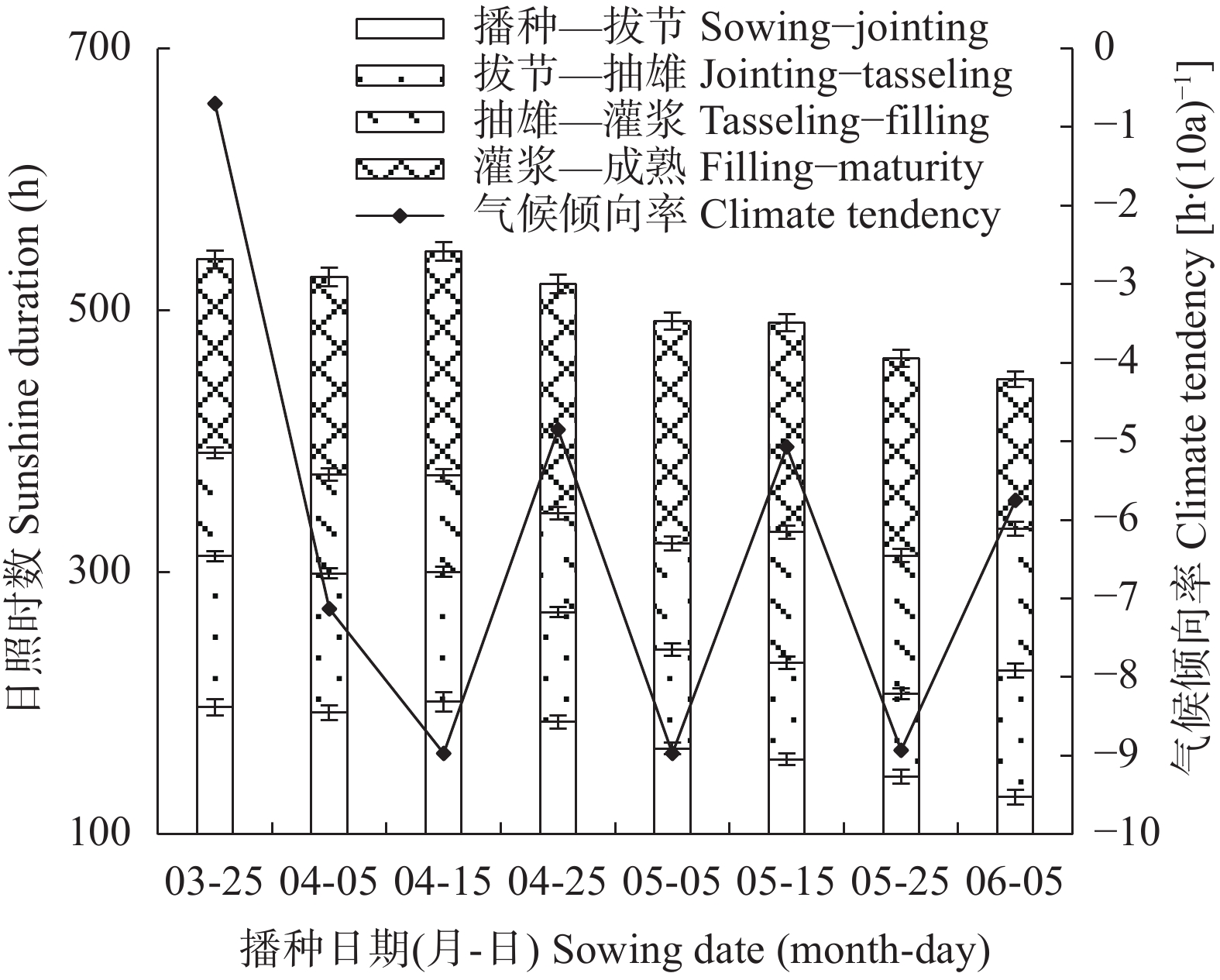
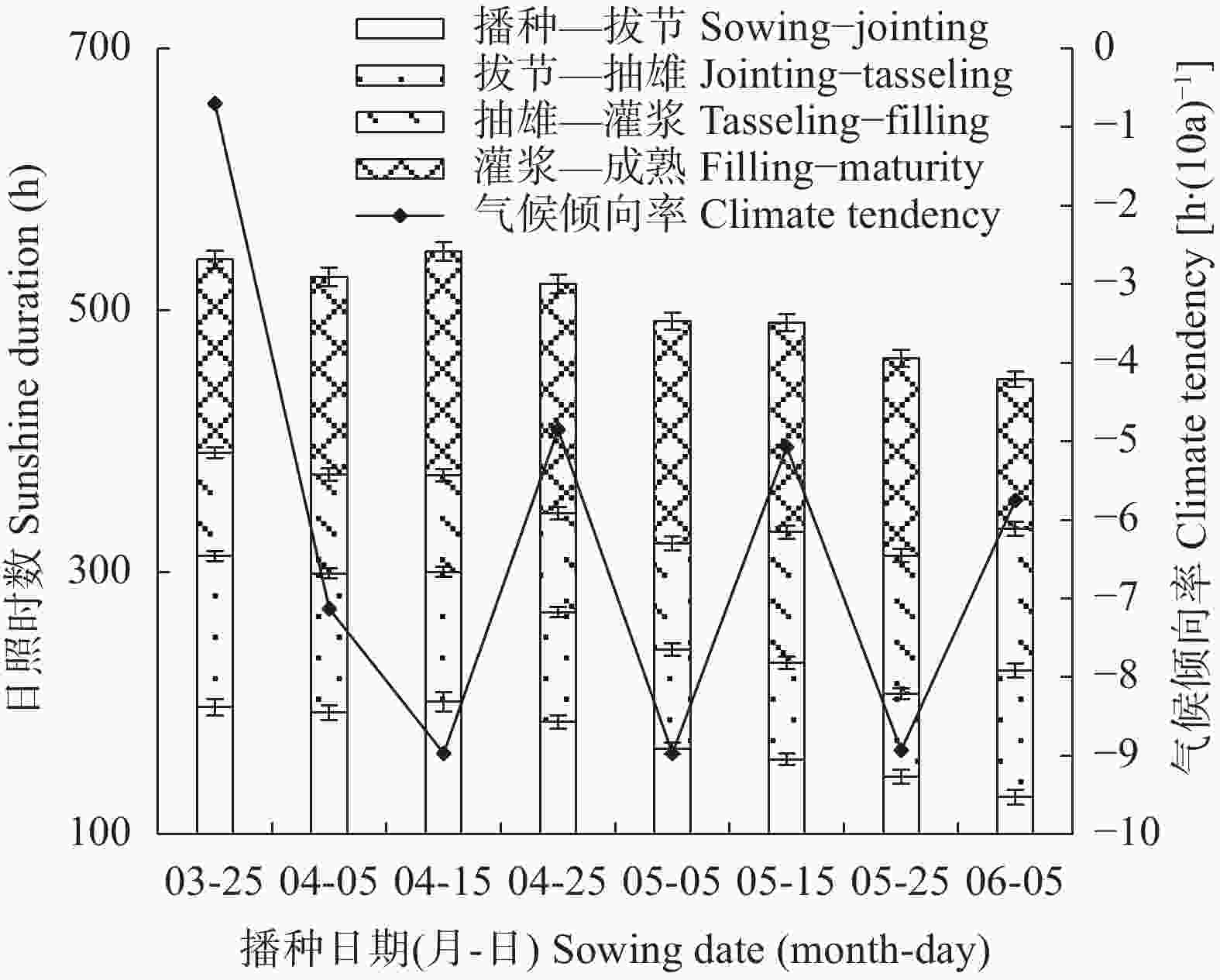
摘要: 川中丘陵区是西南玉米主产区之一, 季节性干旱是该区最主要的农业气象灾害, 研究不同播种时期玉米不同生育阶段气候资源及干旱特征对该区玉米避旱减灾有重大意义。本文以川中丘陵地区的中江为例, 利用1981—2020年四川省中江县气象站地面气象观测资料, 从3月下旬至6月上旬设置8个播期, 分析不同播期玉米生育期主要农业气候资源变化规律, 同时基于作物水分亏缺指数(CWDI)研究不同播期玉米各生育阶段干旱特征, 为川中丘陵区玉米适宜播期选择和生育期内阶段性干旱防御提供科学依据。结果表明: 1)近40年各播期玉米生育期气候资源变化均呈日照时数下降、温度升高、降雨量下降的趋势; 随播期推迟, 日均温、生长度日、高温度日均先升后降, 日照时数随播期推迟呈下降趋势, 而降雨量则随播期推迟呈增加趋势。适当推迟播期, 有利于提高玉米对日照、热量和降水资源的综合利用。2)随播期推迟, 玉米播种—拔节、拔节—抽雄阶段CWDI呈明显降低趋势, 3月下旬播种玉米抽雄—灌浆阶段CWDI明显高于其他播期; 推迟播期可降低玉米生育期水分亏缺的危险。3)不同播期玉米最易受旱生育阶段存在差异, 3月下旬、5月下旬、6月上旬播种玉米在播种—拔节阶段干旱频率最高, 4月上旬—5月中旬播种玉米在拔节—抽雄阶段干旱频率最高。4)各播期玉米各生育阶段干旱强度以轻旱、中旱为主, 重旱次之, 特旱最低; 推迟播期玉米干旱强度由中旱降为轻旱为主, 可降低玉米干旱发生频率, 特别是重旱和特旱发生频率。研究区玉米宜在5月中旬前播种; 玉米在3月下旬、4月上旬播种时, 应注重灌浆期以前的抗旱管理; 4月中旬到5月中旬播种时, 应注重抽雄前的抗旱管理, 同时预防灌浆—成熟阶段的高温风险。Abstract: The hilly area of central Sichuan is one of the main maize-producing areas in Southwest China, where seasonal drought is the main agro-meteorological disaster. It is of great significance to study the climatic resources and drought characteristics of maize at different growing periods with different sowing dates for maize drought avoidance and disaster reduction in this area. Using Zhongjiang County in the hilly area of central Sichuan as an example, based on the surface meteorological observation data of Zhongjiang Meteorological Station from 1981 to 2020, eight sowing dates with 20 days intervals were set from late March to early June to analyze the change laws of main agro-climate resources during maize growth periods under different sowing dates. At the same time, based on the crop water deficit index (CWDI), the drought characteristics of maize at different growth periods under different sowing dates were studied to provide a scientific basis for the selection of suitable sowing dates and the prevention of staged drought during the growth periods of maize in the hilly region of central Sichuan. The results showed that first, over the past 40 years, the changes in climatic resources during the maize growth season of each sowing date showed a trend of decreasing sunshine hours, increasing temperature, and decreasing rainfall. With the delay in sowing date, the daily average temperature, growing degree days, and heat degree days first increased and then decreased, while the sunshine hours gradually decreased and the rainfall gradually increased. Therefore, appropriately delaying the sowing date of maize is beneficial for improving the utilization of sunshine, heat, and rainfall resources. Second, with the delay in sowing date, the CWDI during the maize sowing–jointing and jointing–tasseling periods noticeably decreased, and the CWDI during the tasseling–filling of maize sown on the late-March was significantly higher than that on other sowing dates. Delaying the sowing date can reduce the risk of water deficits during the maize growth periods. Third, there were differences in most susceptible growing period to drought among different sowing dates. Maize sown in late March, late May, and early June had the highest drought frequencies during the sowing–jointing stage, and maize sown from early April to mid-May had the highest drought frequency during the jointing–tasseling stage. Fourth, the drought intensity at each growing period of maize sown in different dates was dominated by light and moderate drought, followed by severe drought, with extreme drought occurring the lowest. When the sowing date was delayed, the maize drought intensity decreased from moderate to mild. Appropriately delaying the sowing date of maize can reduce the frequency of drought, especially the frequency of severe and extreme drought. The proper sowing date of maize in the study area is before mid-May. When maize is sown in late March and early April, attention should be paid to drought resistance management prior to the grain-filling period. When sowing from mid-April to mid-May, attention should be paid to drought resistance management before tasseling to prevent high temperature risks during the filling-maturity stage.
-
Key words:
- Maize /
- Sowing date /
- Crop water deficit index (CWDI) /
- Climatic resources /
- Drought characteristics
-
表 1 不同播期玉米生育阶段
Table 1. Growing stages of maize sown in different dates
播种日期(月-日)
Sowing date (month-day)播种—拔节
Sowing−jointing拔节—抽雄
Jointing−tasseling抽雄—灌浆
Tasseling−filling灌浆—成熟
Filling−maturity03-25 3月下旬—5月上旬
21st Mar. to 10 th May5月中旬—6月上旬
11st May to 10 th Jun.6月中旬—6月下旬
11st Jun. to 30 th Jun.7月上旬—7月下旬
1st Jul. to 31th Jul.04-05 4月上旬—5月中旬
1st Apr. to 20th May5月下旬—6月中旬
21st May to 20th Jun.6月下旬—7月上旬
21st Jun. to 10th Jul.7月中旬—8月上旬
11st Jul. to 10th Aug.04-15 4月中旬—5月下旬
11st Apr. to 31th May6月上旬—6月下旬
1st Jun. to 30th Jun.7月上旬—7月中旬
1st Jul. to 20th Jul.7月下旬—8月中旬
21st Jul. to 20th Aug.04-25 4月下旬—5月下旬
21st Apr. to 31th May6月上旬—6月下旬
1st Jun. to 30th Jun.7月上旬—7月中旬
1st Jul. to 20th Jul.7月下旬—8月中旬
21st Jul. to 20th Aug.05-05 5月上旬—6月上旬
1st May to 10th Jun.6月中旬—7月上旬
11st Jun. to 10th Jul.7月中旬—7月下旬
11st Jul. to 31th Jul.8月上旬—8月下旬
1st Aug. to 31th Aug.05-15 5月中旬—6月上旬
11st May to 10th Jun.6月中旬—7月上旬
11st Jun. to 10th Jul.7月中旬—7月下旬
11st Jul. to 31th Jul.8月上旬—8月下旬
1st Aug. to 31th Aug.05-25 5月下旬—6月中旬
21st May to 20th Jun.6月下旬—7月中旬
21st Jun. to 20th Jul.7月下旬—8月上旬
21st Jul. to 10th Aug.8月中旬—9月上旬
11st Aug. to 10th Sep.06-05 6月上旬—6月下旬
1st Jun. to 30th Jun.7月上旬—7月下旬
1st Jul. to 31th Jul.8月上旬—8月中旬
1st Aug. to 20th Aug.8月下旬—9月中旬
21st Aug. to 20th Sep.表 2 基于作物水分亏缺指数(CWDI)的农业干旱等级
Table 2. Grades of agricultural drought based on crop water deficit index (CWDI)
干旱等级
Drought gradeCWDI (%) 无旱 No drought
轻旱 Light drought
中旱 Moderate drought
重旱 Severe drought
特旱 Excessive droughtCWDI≤35
35<CWDI≤50
50<CWDI≤65
65<CWDI≤80
CWDI>80 -
[1] 贺晋云, 张明军, 王鹏, 等. 近50年西南地区极端干旱气候变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(9): 1179−1190 doi: 10.11821/xb201109003HE J Y, ZHANG M J, WANG P, et al. Climate characteristics of the extreme drought events in Southwest China during recent 50 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(9): 1179−1190 doi: 10.11821/xb201109003 [2] ZHANG L X, ZHOU T J. Drought over east Asia: a review[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28(8): 3375−3399 doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00259.1 [3] 邓绍辉, 罗晓彬. 建国以来四川旱灾特点及其防治[J]. 四川师范大学学报(社会科学版), 2005, 32(3): 125−132DENG S H, LUO X B. Features, prevention and remedy of droughts in Sichuan since 1949[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2005, 32(3): 125−132 [4] 任美锷, 包浩生. 中国自然区域及开发整治[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992REN M E, BAO H S. Natural Areas and Development and Regulation in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992 [5] 许武成, 周旭, 徐邓耀. 近50年川中丘陵区气候变化及与ENSO关系研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2008, 28(1): 52−56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2184.2008.01.009XU W C, ZHOU X, XU D Y. The relationship between climate changes in the hill region of middle Sichuan during last 50 years and ENSO[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 2008, 28(1): 52−56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2184.2008.01.009 [6] 孔凡磊, 谢孟林, 查丽, 等. 川中丘陵区气候变化及其对春玉米生产潜力的影响−以遂宁为例[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(6): 203−209 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2015.06.34KONG F L, XIE M L, ZHA L, et al. Climate variation and its impact on potential productivity of spring maize in Hilly Area of Central Sichuan — A case study of Suining County[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2015, 33(6): 203−209 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2015.06.34 [7] 陈明, 寇雯红, 李玉环, 等. 气候变化对东北地区玉米生产潜力的影响与调控措施模拟−以吉林省为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(3): 821−828CHEN M, KOU W H, LI Y H, et al. Impacts of climate change on maize potential productivity in Northeast China and the simulation of control measures: a case study of Jilin Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(3): 821−828 [8] 靳英华, 周道玮, 秦丽杰. 适应气候变化的吉林省半干旱区玉米播种期[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(10): 2795−2802JIN Y H, ZHOU D W, QIN L J. Sowing date of corn in semiarid region of Jilin Province, Northeast China in adapting to climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(10): 2795−2802 [9] 李潮海, 苏新宏, 谢瑞芝, 等. 超高产栽培条件下夏玉米产量与气候生态条件关系研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2001, 34(3): 311−316 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2001.03.015LI C H, SU X H, XIE R Z, et al. Study on relationship between grain yield of summer corn and climatic ecological condition under super-high-yield cultivation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2001, 34(3): 311−316 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2001.03.015 [10] 豆攀, 李孝东, 孔凡磊, 等. 播期对川中丘区玉米干物质积累与产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(2): 221−229DOU P, LI X D, KONG F L, et al. Effect of sowing date on dry matter accumulation and yield of maize in hilly regions of Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(2): 221−229 [11] HEIM R R Jr. A review of towentieth-century drought indices used in the United States[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2002, 83(8): 1149−1166 doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(2002)083<1149:AROTDI>2.3.CO;2 [12] 薛海丽, 张钦, 唐海萍. 近60 a内蒙古不同草原类型区极端气温和干旱事件特征分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(4): 701−711 doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2018.04.04XUE H L, ZHANG Q, TANG H P. Extreme temperature and drought events in four different grassland areas of Inner Mongoliain in recent 60 years[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(4): 701−711 doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2018.04.04 [13] CHEN H P, SUN J Q. Anthropogenic warming has caused hot droughts more frequently in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 544: 306−318 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.044 [14] 詹存, 梁川, 赵璐. 川中丘陵区季节性干旱时空分布特征及成因分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(21): 82−90, 301 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.21.011ZHAN C, LIANG C, ZHAO L. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and causes analysis of seasonal drought in hilly area of central Sichuan[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(21): 82−90, 301 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.21.011 [15] 刘宗元, 张建平, 罗红霞, 等. 基于农业干旱参考指数的西南地区玉米干旱时空变化分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(2): 105−115LIU Z Y, ZHANG J P, LUO H X, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of maize drought in Southwest of China based on agricultural reference index for drought[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(2): 105−115 [16] 张玉芳, 王锐婷, 陈东东, 等. 利用水分盈亏指数评估四川盆地玉米生育期干旱状况[J]. 中国农业气象, 2011, 32(4): 615−620 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2011.04.022ZHANG Y F, WANG R T, CHEN D D, et al. Evaluation on drought at maize growth stage in Sichuan Basin based on water budget index[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2011, 32(4): 615−620 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2011.04.022 [17] 曹言, 王杰, 李尤亮, 等. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的云南省夏玉米不同生育期干旱时空特征分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(8): 97−106CAO Y, WANG J, LI Y L, et al. The spatial and temporal characteristics of drought during summer maize at different growth stages in Yunnan Province based on crop water deficit index[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(8): 97−106 [18] 李崇瑞, 游松财, 武永峰, 等. 改进作物水分亏缺指数用于东北地区春玉米干旱灾变监测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(21): 175−185 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.21.021LI C R, YOU S C, WU Y F, et al. Improved crop water deficit index for monitoring drought disaster change process of spring maize in the Northeast China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(21): 175−185 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.21.021 [19] 张晓旭, 孙忠富, 郑飞翔, 等. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的黄淮海平原夏玉米全生育期干旱分布特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 2021, 42(6): 495−506 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2021.06.005ZHANG X X, SUN Z F, ZHENG F X, et al. Characteristics of drought distribution for summer maize over whole growth period in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain based on crop water deficit index[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2021, 42(6): 495−506 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2021.06.005 [20] 黄晚华, 杨晓光, 曲辉辉, 等. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的春玉米季节性干旱时空特征分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(8): 28−34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.08.006HUANG W H, YANG X G, QU H H, et al. Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristic on seasonal drought of spring maize based on crop water deficit index[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(8): 28−34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.08.006 [21] 高超, 李学文, 孙艳伟, 等. 淮河流域夏玉米生育阶段需水量及农业干旱时空特征[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(2): 297−309 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83010GAO C, LI X W, SUN Y W, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of water requirement and agricultural drought during summer maize season in Huaihe River Basin[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 297−309 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83010 [22] 薛昌颖, 马志红, 胡程达. 近40a黄淮海地区夏玉米生长季干旱时空特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2016, 25(2): 1−14XUE C Y, MA Z H, HU C D. Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought during summer maize growing season in Huang-Huai-Hai area for recent 40 years[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2016, 25(2): 1−14 [23] 李泽明, 何永坤, 唐余学, 等. 近50年重庆地区玉米干旱时空特征分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2014, 27(1): 363−368LI Z M, HE Y K, TANG Y X, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of maize drought in recent 50a in Chongqing[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 27(1): 363−368 [24] 曹永强, 王怡涵, 冯兴兴, 等. 河北省夏玉米不同生育期干旱时空分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(4): 1−9CAO Y Q, WANG Y H, FENG X X, et al. Spatial and temporal analysis of drought in different growth stages of summer corn in Hebei Province[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(4): 1−9 [25] 何永坤, 唐余学, 范莉, 等. 近50年西南地区玉米干旱变化规律研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(1): 34−42HE Y K, TANG Y X, FAN L, et al. Study on the variation of drought for maize in southwestern China in the recent 50 years[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 38(1): 34−42 [26] 淮贺举, 孙宁, 史磊刚, 等. 东北地区春玉米生育期内气候资源变化特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 98−105HUAI H J, SUN N, SHI L G, et al. Variation characteristics of climate resources during the growth period of spring maize in northeast China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 98−105 [27] 王占彪, 王猛, 尹小刚, 等. 气候变化背景下华北平原夏玉米各生育期水热时空变化特征[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(4): 473−481WANG Z B, WANG M, YIN X G, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of heat and rainfall changes in summer maize season under climate change in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(4): 473−481 [28] 贾建英, 贺楠, 韩兰英, 等. 基于自然灾害风险理论和ArcGIS的西南地区玉米干旱风险分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(4): 152−159 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.04.022JIA J Y, HE N, HAN L Y, et al. Analysis on drought risk of maize in Southwest China based on natural disaster risk theory and ArcGIS[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(4): 152−159 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.04.022 [29] 王明田, 曲辉辉, 杨晓光, 等. 基于降水保证指数的四川省种植制度优化研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(10): 82−92WANG M T, QU H H, YANG X G, et al. Optimized cropping systems based on ensure index of precipitation in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(10): 82−92 [30] 张玉芳, 吴冰洁, 郭斌. 气候变化背景下四川省玉米生育期农业气候资源变化趋势[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(9): 2102−2111ZHANG Y F, WU B J, GUO B. Characteristics of agro-meteorological climate resource during maize growing season under global climate change in Sichuan Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(9): 2102−2111 [31] 周清, 朱保美. 2005年齐河县夏玉米全生育期气象条件分析[J]. 山东气象, 2006, 26(2): 46, 48ZHOU Q, ZHU B M. Analysis of meteorological conditions of the summer corn in Qihe County in 2005[J]. Journal of Shandong Meteorology, 2006, 26(2): 46, 48 [32] 张兵兵, 吕晓, 杨璐, 等. 基于气候变化下的辽西地区春玉米生长发育及产量与水热变化的响应研究[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(23): 41−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2019.23.015ZHANG B B, LYU X, YANG L, et al. Response of spring maize growth, yield and hydrothermal change in western Liaoning Province based on climate change[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 25(23): 41−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2019.23.015 [33] MENG Q F, HOU P, LOBELL D B, et al. The benefits of recent warming for maize production in high latitude China[J]. Climatic Change, 2014, 122(1/2): 341−349 [34] OLESEN J E, BØRGESEN C D, ELSGAARD L, et al. Changes in time of sowing, flowering and maturity of cereals in Europe under climate change[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants Part A, Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure & Risk Assessment, 2012, 29(10): 1527−1542 [35] 张森, 徐开未, 裴丽珍, 等. 川中丘陵区气象因子与玉米倒伏和产量的灰色关联度分析[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2021, 39(5): 666−673, 680ZHANG S, XU K W, PEI L Z, et al. Grey correlation analysis of meteorological factors, maize lodging and yield in the hilly region of central Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2021, 39(5): 666−673, 680 [36] 隋月, 黄晚华, 杨晓光, 等. 气候变化背景下中国南方地区季节性干旱特征与适应Ⅳ. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的玉米干旱时空特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(9): 2590−2598SUI Y, HUANG W H, YANG X G, et al. Characteristics and adaptation of seasonal drought in Southern China under the background of global climate change. Ⅳ. Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought for maize based on crop water deficit index[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(9): 2590−2598 [37] 谈美秀, 王靖, 余卫东, 等. 基于统计和过程模型的河南省夏玉米最适播种期时空分布特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(12): 3670−3678TAN M X, WANG J, YU W D, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of the optimal sowing dates of summer maize based on both statistical and processes models in Henan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(12): 3670−3678 [38] 明博, 朱金城, 陶洪斌, 等. 黑龙港流域玉米不同生育阶段气象因子对产量性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(5): 919−927 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00919MING B, ZHU J C, TAO H B, et al. Effects of meteorological factors at different growth stages on yield traits of maize (Zea mays L.) in Heilonggang basin[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(5): 919−927 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00919 -





 下载:
下载: