-
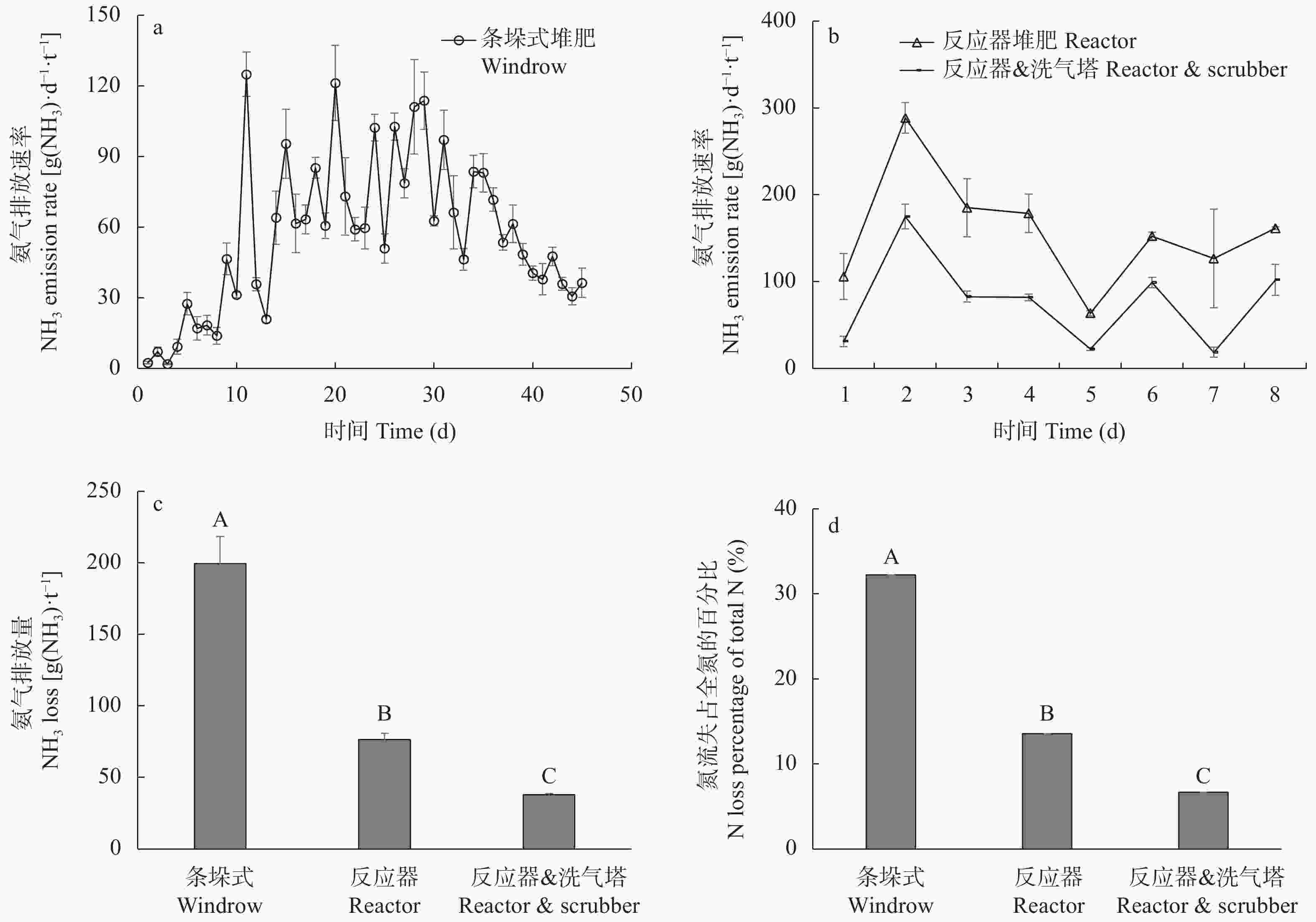
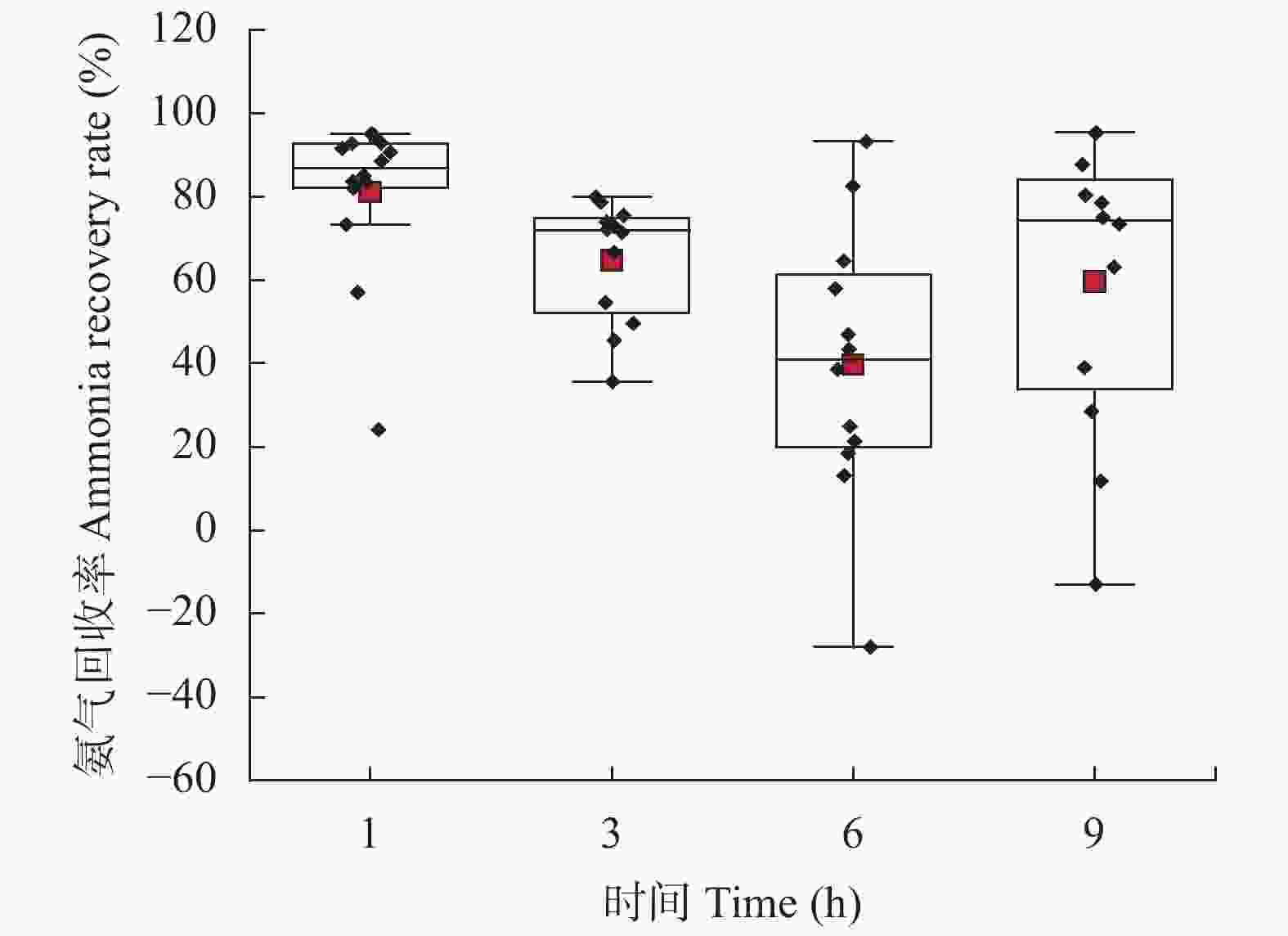
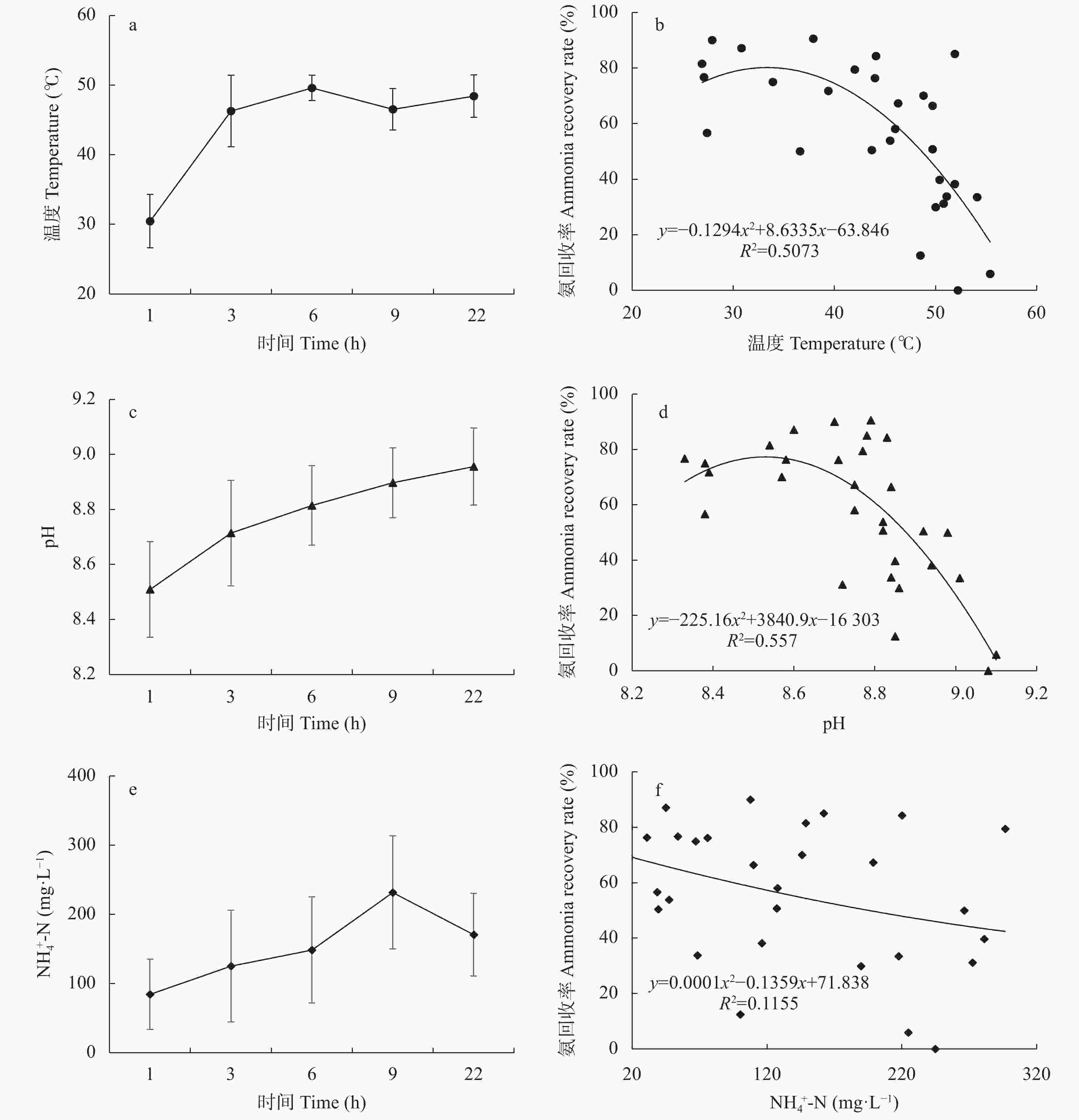
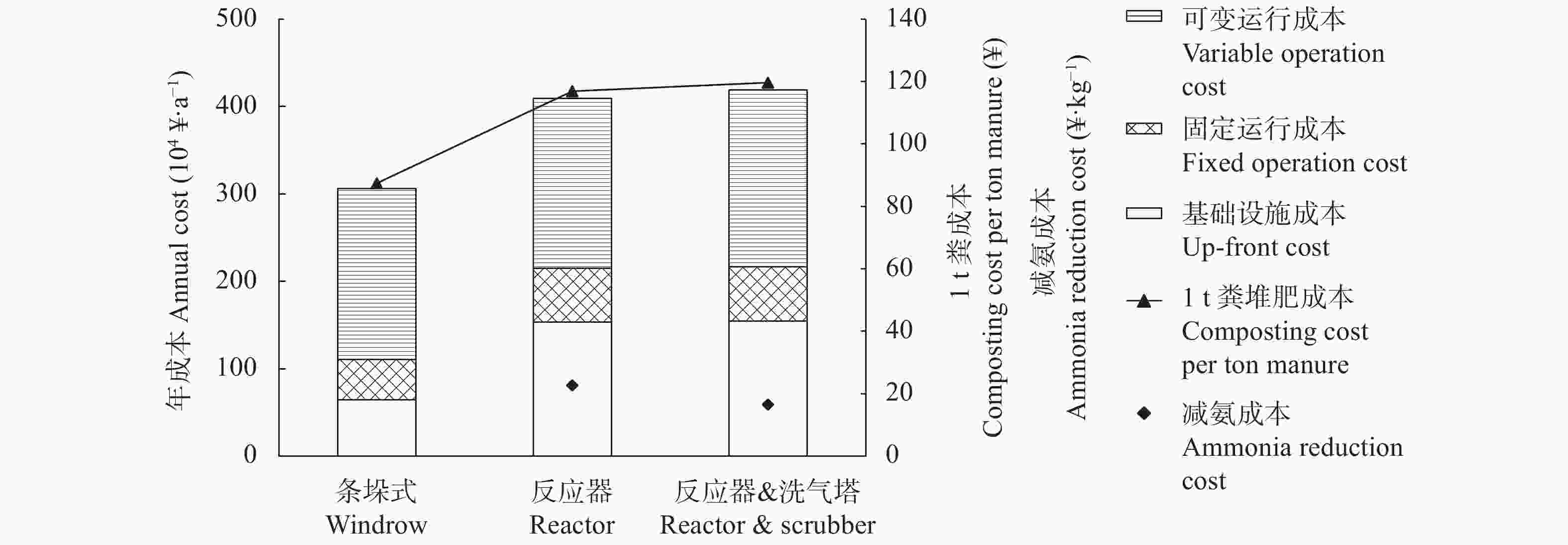
摘要: 堆肥是将粪尿肥料化处理循环利用于土壤的重要技术, 但堆肥过程中约有50%的氮素以氨气形态挥发, 不仅降低了堆肥产品的养分价值, 更诱发了雾霾天气发生, 严重污染大气环境。因此, 减少堆肥过程的氨排放对于提高有机肥品质、降低堆肥过程产生的环境影响具有重要意义。针对实际生产中不同堆肥技术氨排放量不明, 氨减排潜力及经济效益缺乏的问题, 本研究通过生产规模试验, 定量分析了条垛式堆肥和密闭反应器堆肥过程中的氨排放量、氨回收效率及其影响因素, 并对不同堆肥技术进行了经济效益分析。结果表明, 与条垛式堆肥相比, 密闭反应器堆肥可减少氨挥发61.1% (P<0.01), 结合氨气洗涤回收技术(洗气塔)可实现82.3% (P<0.01)的氨减排; 氨气回收效率随吸收时间显著降低, 吸收液温度和铵根离子浓度是影响氨回收效率的关键因素。密闭反应器堆肥技术粪便处理成本(116.9元∙t–1)高于传统条垛式堆肥处理成本(87.4元∙t–1); 然而, 以条垛式堆肥为对照, 密闭反应器堆肥及反应器结合洗气塔技术每减少1 kg氨气的成本为22.0元和16.5元, 低于欧盟氨减排成本。综上所述, 密闭反应器堆肥可显著降低堆肥过程中的氨挥发, 与洗气塔结合使用可将堆肥过程中排放的大部分氨气进行回收, 是一种高效、可行且具有较大氨减排潜力的堆肥技术。Abstract: Composting is an important way to recycle manure into soil as an organic fertilizer or conditioner. However, approximately 50% of the total nitrogen in manure is lost in the form of ammonia during composting, and this loss has an environmental impact on human health. Therefore, to reduce ammonia emission during the composting process to improve the quality of organic fertilizer and reduce its impact on the environment, this study intends to explore a composting method with low ammonia emissions, economy, and high efficiency. In this study, we used quantitative data from full-scale composting systems (windrow composting and reactor composting) in an industrial sheep farm to compare the ammonia emissions from traditional windrow composting and reactor composting, and quantitatively analyzed the ammonia recovery efficiency and influencing factors of gaseous scrubbers, as well as the economic benefits of windrow composting, reactor composting, and reactor composting combined with scrubbers. The results showed that windrow composting and reactor composting emitted 193 g NH3 and 75 g NH3 for 1 ton dry compost materials, respectively. Compared with traditional windrow composting, reactor composting reduced ammonia emissions by 61.1% (P<0.01), which was further increased to 82.3% (P<0.01) when the reactor was composted with a gaseous scrubber. The ammonia recovery rate decreased with an increase in the absorption time. The result showed that ammonia recovery rate of the scrubber was 82.0% (P<0.05) when the solution was fresh and gradually decreased to 39.8% (P<0.05) after 5 h. In addition, the ammonia recovery rate was significantly influenced by the temperature and NH4+-N concentration of the absorption solution. For instance, the ammonia recovery rate decreased from approximately 80% to 20% when the temperature of the solution increased from 30 ℃ to 40 ℃ to 50 ℃. In terms of the cost of composting, reactor composting needed 116.9 Yuan per ton of manure, which was higher than that of traditional windrow composting (87.4 Yuan per ton of manure). The ammonia reduction costs of reactor composting and the scrubber were 22.0 Yuan per kg NH3 and 16.5 Yuan per kg NH3, respectively, when compared with windrow composting, which was lower than the value of the European Union. In addition, reactor composting had a higher efficiency than windrow composting, with composting cycles of 8 and 45 days for reactor composting and windrow composting, respectively. In conclusion, reactor composting can significantly reduce ammonia emissions, and most of the ammonia can be recovered when combined with a gaseous scrubber. The pH, NH4+-N concentration, and temperature of the scrubber solution significantly affected the ammonia recovery rate. Improving the ammonia recovery rate and operational stability of the gas washing tower is a direction for future research to develop ammonia emission reduction technology. Consequently, reactor composting combined with a gaseous scrubber is recommended, which is an efficient and feasible composting technology with great potential for reducing ammonia emission.
-
Key words:
- Livestock manure /
- Reactor composting /
- Windrow composting /
- Ammonia mitigation /
- Ammonia emission
-
表 1 堆肥原料的理化性质(以干重计, n=3)
Table 1. Physico-chemical characters of raw materials for compost (dry matter, n=3)
样品
Sample含水率
Moisture (%)pH 全氮
Total nitrogen (g∙kg–1)全磷
Total phosphorus (g∙kg–1)全钾
Total potassium (g∙kg–1)羊粪 Sheep manure 73.89±0.01 8.49±0.09 21.39±0.18 32.96±0.17 76.18±1.48 蘑菇渣 Mushroom residue 62.99±0.01 5.20±0.02 19.72±0.02 10.30±0.03 8.86±0.05 混合物料
Mixed material条垛式 Windrow 71.68±0.02 8.48±0.04 21.03±0.27 25.92±0.21 55.34±0.44 反应器 Reactor 64.53±0.02 8.48±0.02 21.40±0.66 29.55±0.46 60.28±0.70 表 2 不同堆肥技术成本投入1)
Table 2. Cost of different technical implementation treatments1)
¥·a−1 项目 Category 条垛式
Windrow反应器
Reactor反应器&洗气塔
Reactor & scrubber基础设施成本
Up-front cost土地租赁2) Land use2) 2.3×104 612.5 765.8 基建3) Infrastructure3) 5.4×105 1.6×103 2.0×103 基础设备4) Equipment4) 8.6×104 1.5×107 1.5×107 固定运行成本
Fixed operation cost基建 Infrastructure 4.3×105 0.1×104 0.2×104 基础设备 Equipment 3.4×104 6.1×105 6.2×105 可变运行成本
Variable operation cost电力5) Electric5) 2.5×103 7.2×105 8.0×105 辅料费 Mushroom residue 8.8×105 8.8×105 8.8×105 人工费 Labor 3.5×105 3.5×105 3.5×105 基础设备燃油费 Fuel 7.0×105 — — 1) 2种堆肥方式经济投入在每年处理35 000 t羊粪的基础上进行核算; 2)土地租赁=土地面积×土地价格; 3)基建=基建投入/基建服务年限(20年); 4)基础设备=设备投入/设备服务年限(10年); 5)电力=耗电量×电力价格(0.5元∙kWh–1)。1) Based on 35 000 t of sheep manure per year to calculate the cost of windrow composting and reactor composting; 2) Land use=land area×land price; 3) Infrastructure=infrastructure input/service life (20 years); 4) Equipment=equipment input/ service life (10 years); 5) Electric=electric consumption×electric price (0.5 ¥∙kWh–1). -
[1] CHADWICK D, JIA W, TONG Y A, et al. Improving manure nutrient management towards sustainable agricultural intensification in China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2015, 209: 34−46 [2] PERGOLA M, PERSIANI A, PALESE A M, et al. Composting: the way for a sustainable agriculture[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 123: 744−750 doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.10.016 [3] JIANG T, MA X G, YANG J, et al. Effect of different struvite crystallization methods on gaseous emission and the comprehensive comparison during the composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 217: 219−226 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.046 [4] WANG G H, ZHANG R Y, GOMEZ M E, et al. Persistent sulfate formation from London fog to Chinese haze[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(48): 13630−13635 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616540113 [5] WU Y Y, GU B J, ERISMAN J W, et al. PM2.5 pollution is substantially affected by ammonia emissions in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218: 86−94 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.027 [6] PAULOT F, JACOB D J, PINDER R W, et al. Ammonia emissions in the United States, European Union, and China derived by high-resolution inversion of ammonium wet deposition data: interpretation with a new agricultural emissions inventory (MASAGE_NH3)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(7): 4343−4364 doi: 10.1002/2013JD021130 [7] SUTTON M A, HOWARD C M, ERISMAN J W, et al. The European Nitrogen Assessment (Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives)[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511976988 [8] NDEGWA P M, HRISTOV A N, AROGO J, et al. A review of ammonia emission mitigation techniques for concentrated animal feeding operations[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2008, 100(4): 453−469 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.05.010 [9] STEVENS C J, DISE N B, MOUNTFORD J O, et al. Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5665): 1876−1879 doi: 10.1126/science.1094678 [10] 李艳霞, 王敏健, 王菊思, 等. 固体废弃物的堆肥化处理技术[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2000(4): 39−45LI Y X, WANG M J, WANG J S, et al. The technology of municipal solid wastes composting[J]. Technigues and Equipment for Enviropollcont, 2000(4): 39−45 [11] LIU Z L, WANG X, WANG F H, et al. The progress of composting technologies from static heap to intelligent reactor: benefits and limitations[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 270: 122328 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122328 [12] 刘泽龙, 王选, 曹玉博, 等. 立式筒仓反应器堆肥技术工艺优化研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(12): 1979−1989LIU Z L, WANG X, CAO Y B, et al. Optimization of composting technology for vertical silo reactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(12): 1979−1989 [13] 曹玉博, 张陆, 王选, 等. 畜禽废弃物堆肥氨气与温室气体协同减排研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 923−932 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0104CAO Y B, ZHANG L, WANG X, et al. Synergistic mitigation of ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions during livestock waste composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 923−932 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0104 [14] ZHANG N N, BAI Z H, WINIWARTER W, et al. Reducing ammonia emissions from dairy cattle production via cost-effective manure management techniques in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(20): 11840−11848 [15] KRIS N G, VALDEHUESA G M, NISOLA S L, et al. Removal of odorous compounds emitted from a food-waste composting facility in Korea using a pilot-scale scrubber[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 2018. DOI: 10.1080/10934529.2018.1474586 [16] LARA J S, HADLOCON R B, MANUZON, et al. Development and evaluation of a full-scale spray scrubber for ammonia recovery and production of nitrogen fertilizer at poultry facilities[J]. Environmental Technology, 2015, 36(4): 405−416 [17] 魏宗强, 李吉进, 邹国元, 等. 不同覆盖措施对鸡粪堆肥氨挥发的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2009, 23(6): 108−111 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.06.025WEI Z Q, LI J J, ZOU G Y, et al. Influence of different cover materials on NH3 volatilization from chicken manure composting[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(6): 108−111 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.06.025 [18] 李星. C50堆肥反应器的研究设计[D]. 北京: 中国农业机械化科学研究院, 2015LI X. Research and design of C50 compost bioreactor[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Mechanization Sciences, 2015 [19] JEONG K H, KIM J K, RAVINDRAN B, et al. Evaluation of pilot-scale in-vessel composting for Hanwoo manure management[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 201−206 [20] TORRETTA V, SCHIAVON M, CARUSON P, et al. Air Pollution XXVII[M]. UK: WIT Press, 2019: 287−296 [21] HADLOCON L J S, MANUZON R B, ZHAO L Y. Development and evaluation of a full-scale spray scrubber for ammonia recovery and production of nitrogen fertilizer at poultry facilities[J]. Environmental Technology, 2015, 36(1/2/3/4): 405−416 [22] VALDEHUESA K N G, NISOLA G M, LEE S P, et al. Removal of odorous compounds emitted from a food-waste composting facility in Korea using a pilot-scale scrubber[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2018, 53(12): 1094−1101 doi: 10.1080/10934529.2018.1474586 [23] WANG X, BAI Z, YAO Y, et al. Composting with negative pressure aeration for the mitigation of ammonia emissions and global warming potential[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 195(SEP.10): 448−457 [24] LARNEY F J, OLSON A F. Windrow temperatures and chemical properties during active and passive aeration composting of beef cattle feedlot manure[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 86(5): 783−797 doi: 10.4141/S06-031 [25] HAO X Y, CHANG C, LARNEY F J. Carbon, nitrogen balances and greenhouse gas emission during cattle feedlot manure composting[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(1): 37−44 doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.3700 [26] CHEN T L, CHEN L H, LIN Y J, et al. Advanced ammonia nitrogen removal and recovery technology using electrokinetic and stripping process towards a sustainable nitrogen cycle: a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 309: 127369 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127369 [27] YANG K, QIN M H. The application of cation exchange membranes in electrochemical systems for ammonia recovery from wastewater[J]. Membranes, 2021, 11(7): 494 doi: 10.3390/membranes11070494 [28] GU B J, ZHANG L, VAN DINGENEN R, et al. Abating ammonia is more cost-effective than nitrogen oxides for mitigating PM2.5 air pollution[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6568): 758−762 doi: 10.1126/science.abf8623 [29] GIANNADAKI D, GIANNAKIS E, POZZER A, et al. Estimating health and economic benefits of reductions in air pollution from agriculture[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622/623: 1304−1316 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.064 [30] 刘泽龙. 畜禽废弃物反应器堆肥技术及其通气方式优化研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020LIU Z L. Study on reactor composting technology of livestock waste and the optimization of composting reactor aeration method[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 [31] KLIMONT Z, WINIWARTER W. Integrated Ammonia Abatement– Modelling of Emission Control Potentials and Costs in GAINS[R]. IIASA Interim Report IR-11-027, Laxenburg, Austria: IIASA, 2020 [32] WANG H D, ZHAO Z Q, WINIWARTER W, et al. Strategies to reduce ammonia emissions from livestock and their cost-benefit analysis: a case study of Sheyang County[J]. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex: 1987), 2021, 290: 118045 -





 下载:
下载: