Influence of intercropping Sedum plumbizincicola with Capsicum annum on the migration and availability of soil cadmium
-
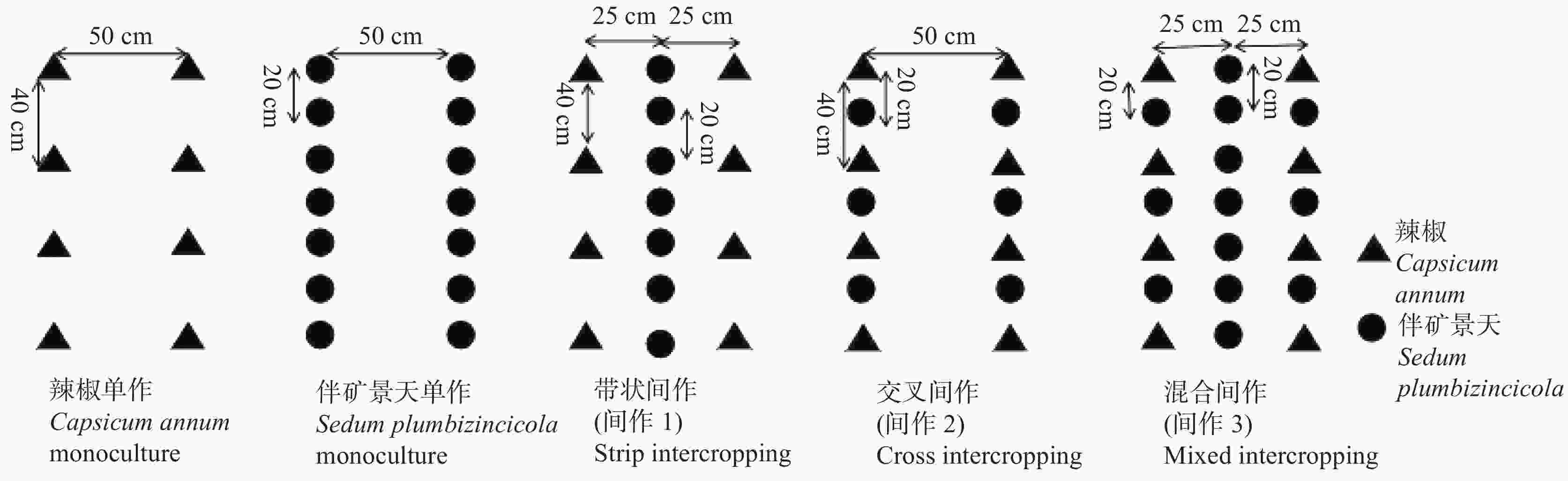
摘要: 为明确伴矿景天间作模式对辣椒植物根系周围土壤镉(Cd)迁移与可利用风险的影响, 于2019年在贵州省遵义市新蒲新区进行田间试验, 设置伴矿景天或辣椒单作、伴矿景天条带式间作辣椒(间作1)、伴矿景天交叉式间作辣椒(间作2)、伴矿景天混合式间作辣椒(间作3)等5种种植模式, 收获期采集辣椒根系周围土壤样品, 测定土壤各形态Cd含量和土壤pH、有机质、全量和有效氮磷钾以及球囊霉素(GRSP)含量。结果表明, 与辣椒单作相比, 间作2和间作3使辣椒根系周围土壤酸溶态Cd显著降低39.6%和41.5% (P<0.05), 可还原态Cd含量显著降低23.9%和29.0% (P<0.05)。同时也降低了土壤Cd迁移和植物可利用风险, 其中间作2和间作3处理土壤Cd迁移性分别降低25.8%和34.2%, 可利用性分别降低11.6%和26.9%。3种伴矿景天间作方式显著提高了土壤易提取球囊霉素含量, 分别提高24.5%、39.9%和40.6% (P<0.05); 间作2和间作3处理显著增加土壤总球囊霉素含量, 分别增加51.7%和86.7% (P<0.05)。冗余分析表明, 土壤环境因子对土壤Cd迁移和可利用风险影响重要性排序为总提取球囊霉素>速效钾>pH>易提取球囊霉素>全钾>全磷>全氮>碱解氮>有效磷>有机质, 土壤总提取球囊霉素、速效钾是影响土壤Cd迁移性和可利用性的关键调控因子。综上所述, 伴矿景天间作措施显著降低了辣椒根系周围土壤Cd迁移和可利用风险, 其中交叉式间作和混合式间作效果优于条带式间作。Abstract: A field experiment was conducted in Xinpu New District, Zunyi City, Guizhou Province, in 2019 to explore the effects of different Sedum plumbizincicola intercropping patterns on the migration and availability of cadmium (Cd) in the soil around the roots of Capsicum annum. Five planting patterns were established: monoculture S. plumbizincicola, monoculture C. annum, stripe intercropping of C. annum with S. plumbizincicola (JZ1), cross intercropping of C. annum with S. plumbizincicola (JZ2), and mixed intercropping of C. annum with S. plumbizincicola (JZ3). Soil samples were collected around the C. annum roots at harvest, and the Cd content, soil pH, organic matter content, and contents of total and available nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and content of glomalin (GRSP) were measured and analyzed. The results showed that, compared to C. annum monoculture, the contents of acid-soluble Cd and reducible Cd in the soil around the C. annum roots effectively decreased by 39.6% and 23.9% in the cross intercropping system with S. plumbizincicola, and 41.5% and 29.0% in mixed intercropping system with S. plumbizincicola, respectively. The risks of soil Cd migration and availability were also reduced. Stripe intercropping C. annum with S. plumbizincicola had no effect on Cd mobility and availability in the soil around the C. annum root system. The Cd migration of the crossing intercropping and mixed intercropping systems decreased by 25.8% and 34.2%, respectively, and the Cd availability decreased by 11.6% and 26.9%, respectively. The stripe, cross and mixed intercropping systems did not affect the contents of Cd in oxidizable and residual states, but significantly increased the content of easily extracted GRSP in the soil by 24.5%, 39.9%, and 40.6%, respectively. Cross intercropping C. annum with S. plumbizincicola and mixed intercropping treatments also significantly increased the total soil GRSP content by 51.7% and 86.7%, respectively. Redundancy analysis showed that the importance of the soil environmental factors on soil Cd migration and availability followed the order: total extracted GRSP > available potassium > pH > easily extractable GRSP > total potassium > total phosphorus > total nitrogen > alkaline hydrolyzed nitrogen > available phosphorus > organic matter. The extractable GRSP and available potassium from the soil were the key regulatory factors affecting soil Cd migration and availability. In summary, intercropping with S. plumbizincicola significantly reduced the risks of Cd migration and availability in the soil around the C. annum roots, and the effects of cross and mixed intercropping were better than that of stripe intercropping. These results provide a theoretical basis for better usage of farmland with low to medium levels of Cd.
-
Key words:
- Intercropping /
- Capsicum annum /
- Sedum plumbizincicola /
- Cadmium /
- Mobility /
- Availability
-
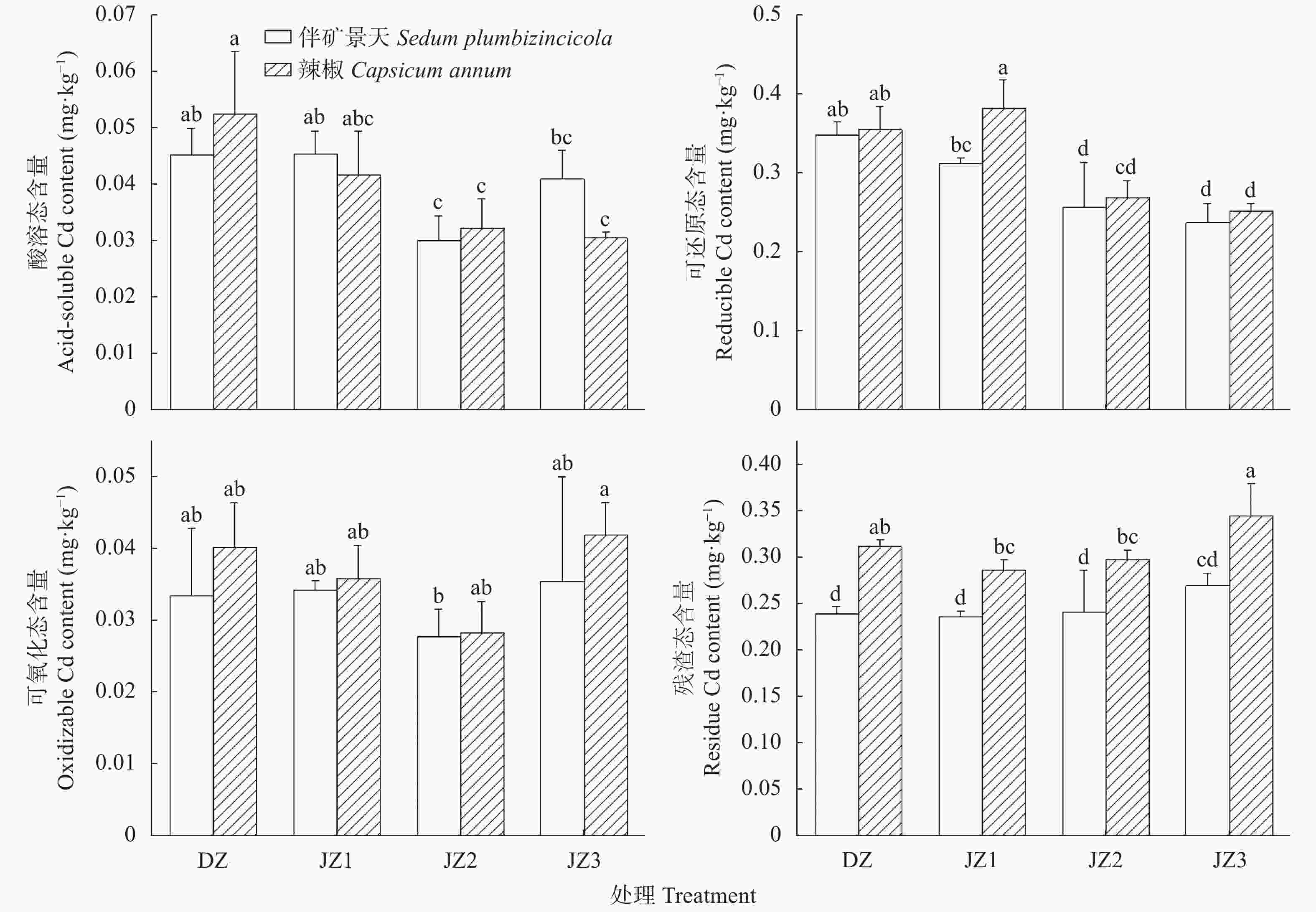
图 2 伴矿景天和辣椒不同种植方式下土壤Cd形态变化
DZ: 单作; JZ1: 带状间作(间作1); JZ2: 交叉间作(间作2); JZ3: 混合间作(间作3)。图中不同小写字母表示同一植物不同种植方式间在P<0.05水平上差异显著。DZ: monoculture; JZ1: stripe intercropping; JZ2: cross intercropping; JZ3: mixed intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different planting patterns for the same plant at P<0.05 level.
Figure 2. Changes of soil Cd forms under different planting patterns of Capsicum annum and Sedum plumbizincicola
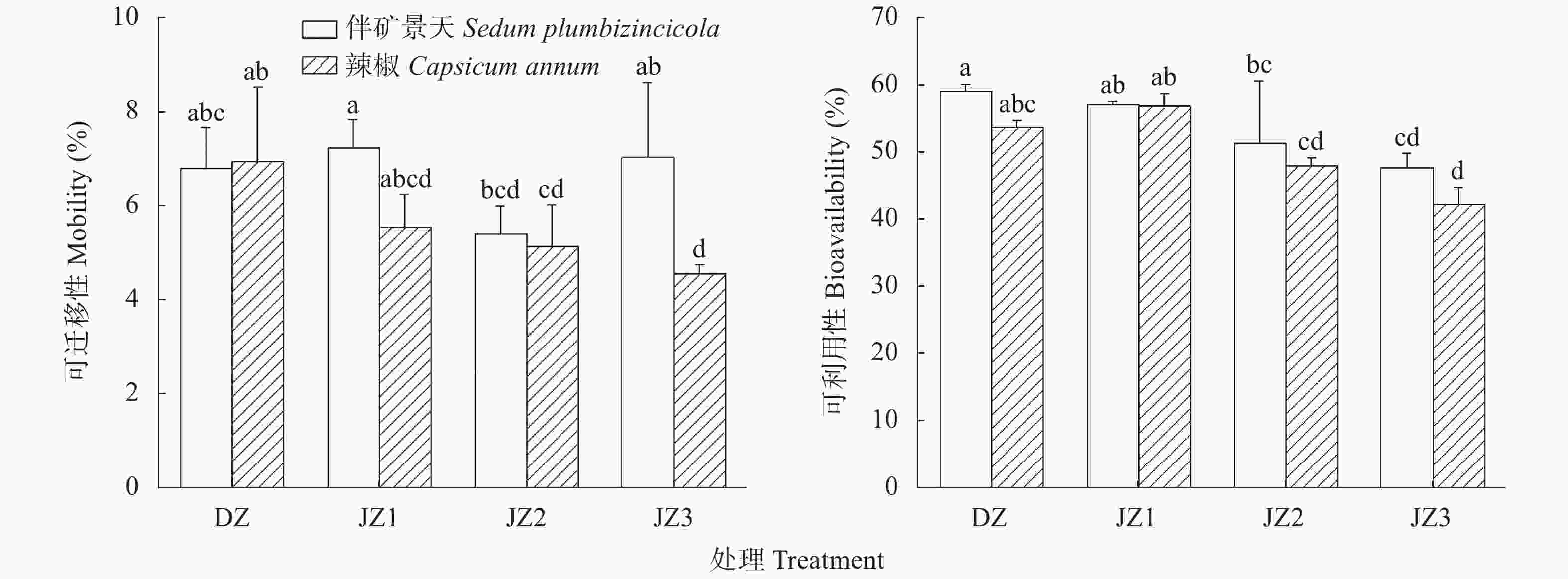
图 3 伴矿景天和辣椒不同种植方式对土壤Cd迁移和Cd可利用的影响
DZ: 单作; JZ1: 带状间作(间作1); JZ2: 交叉间作(间作2); JZ3: 混合间作(间作3)。图中不同小写字母表示不同植物在不同处理间P<0.05水平上差异显著。DZ: monoculture; JZ1: stripe intercropping; JZ2: cross intercropping; JZ3: mixed intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different planting patterns of different plants at P<0.05 level.
Figure 3. Effects of planting patterns of Capsicum annum and Sedum plumbizincicola on the migration and bioavailability of soil Cd
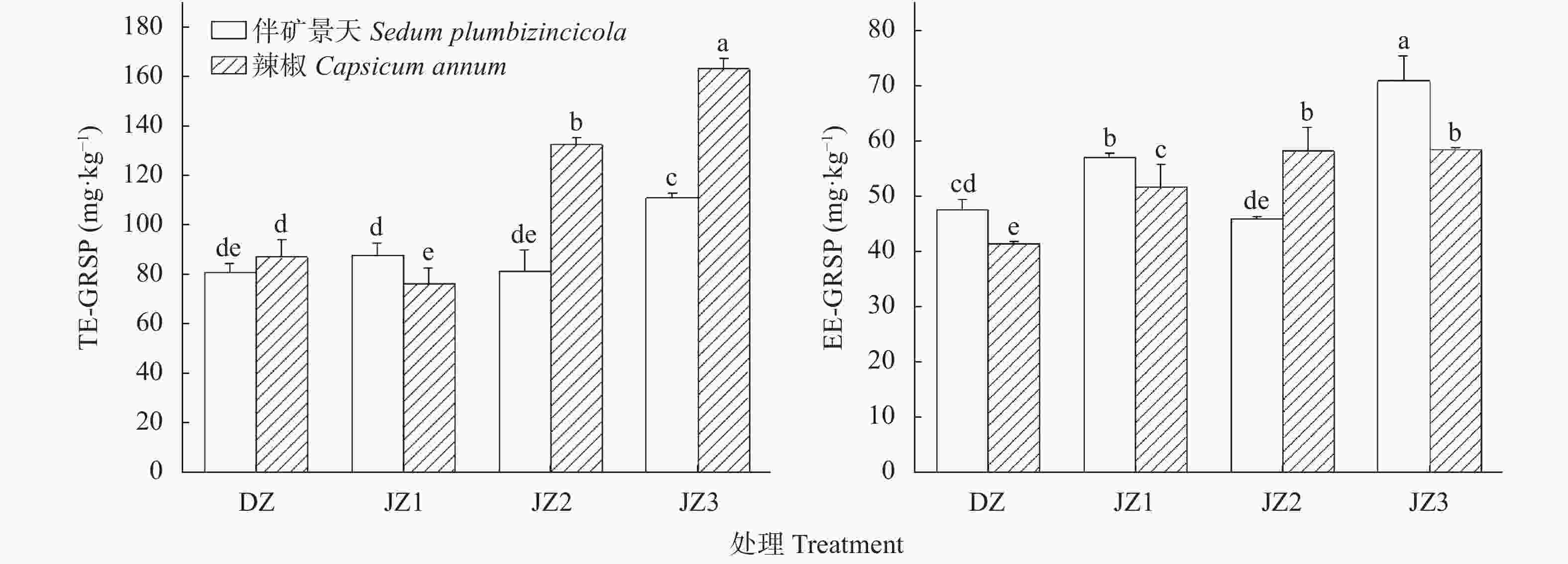
图 4 伴矿景天和辣椒不同种植方式对土壤总提取球囊霉素(TE-GRSP)、易提取球囊霉素(EE-GRSP)相关蛋白含量影响
DZ: 单作; JZ1: 带状间作(间作1); JZ2: 交叉间作(间作2); JZ3: 混合间作(间作3)。图中不同小写字母表示不同植物在不同处理间P<0.05水平上差异显著。DZ: monoculture; JZ1: stripe intercropping; JZ2: cross intercropping; JZ3: mixed intercropping. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different planting patterns of different plants at P<0.05 level.
Figure 4. Effects of planting patterns of Capsicum annum and Sedum plumbizincicola on contents of soil total extraction of globulin (TE-GRSP) and easily extracted globulin (EE-GRSP)
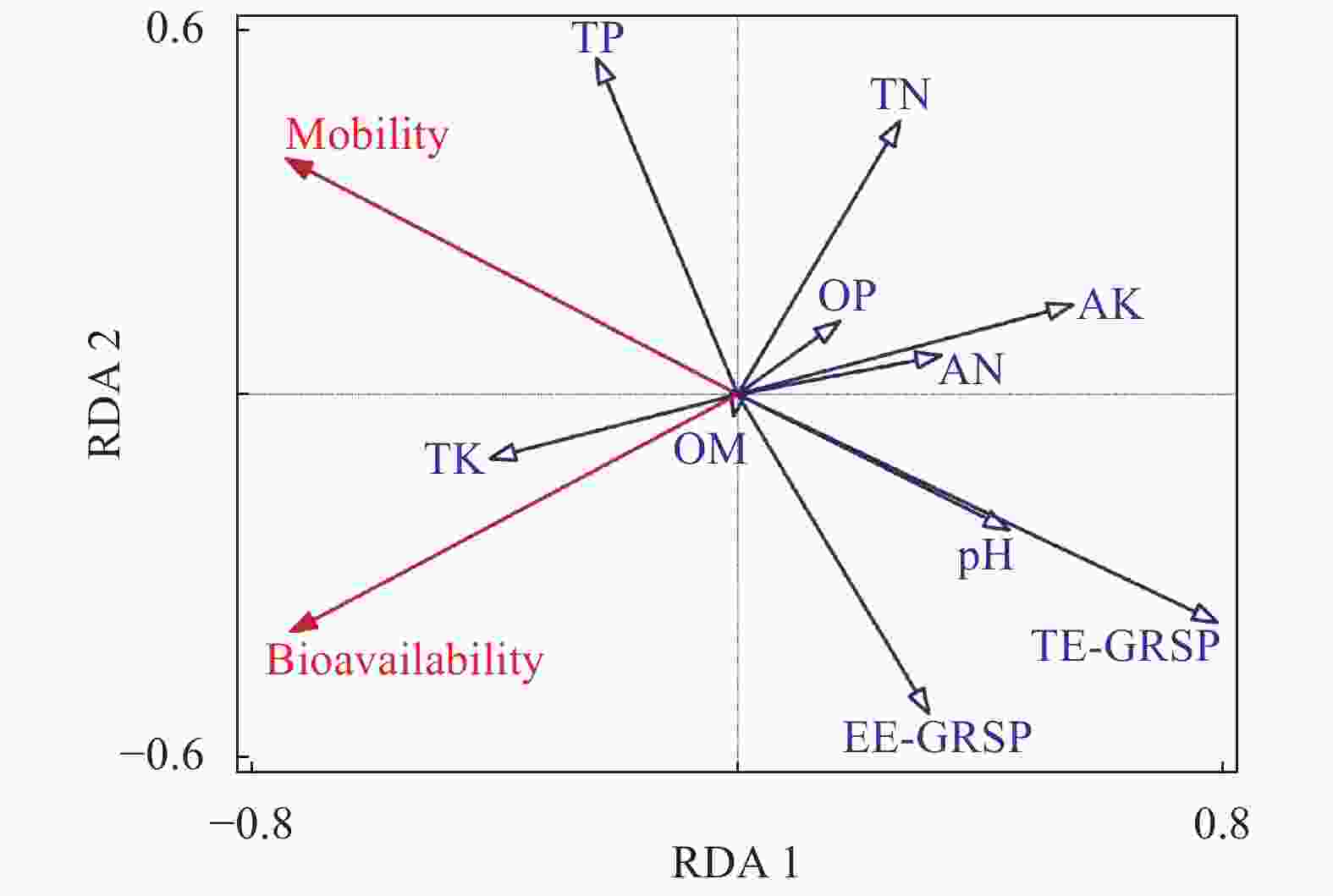
图 5 土壤化学性质、球囊霉素与Cd迁移性、可利用性的冗余度分析
OM: 有机质; TN: 全氮; TP: 全磷; TK: 全钾; AN: 碱解氮; OP: 有效磷; AK: 速效钾; TE-GRSP: 总提取球囊霉素; EE-GRSP: 易提取球囊霉素。OM: organic matter; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium; AN: available nitrogen; OP: Olsen phosphorus; AK: available potassium; TE-GRSP: total extraction of globulin; EE-GRSP: easily extracted globulin.
Figure 5. Redundancy analysis of soil chemical properties and glomalin content and the mobility and availability of Cd
表 1 伴矿景天和辣椒不同种植方式对土壤化学性质的影响
Table 1. Effects of planting patterns of Capsicum annum and Sedum plumbizincicola on soil chemical properties
处理
TreatmentpH 有机质
Organic matter
(g·kg−1)全氮
Total nitrogen (g·kg−1)全磷
Total phosphorus (g·kg−1)全钾
Total potassium (g·kg−1)碱解氮
Available nitrogen (mg·kg−1)有效磷
Olsen phosphorus (mg·kg−1)速效钾
Available potassium (mg·kg−1)单作
SingleS 7.07±0.27a 13.7±1.8ab 0.82±0.01b 0.89±0.01cd 15.1±0.4ab 49.7±2.1c 10.1±0.2d 140±4.0d P 7.69±0.06b 7.7±0.84c 0.54±0.06c 0.78±0.01ef 15.5±1.3a 30.1±2.1d 6.2±0.6e 95±9.0e 间作1
Intercropping 1S 7.66±0.36b 14.4±2.2a 0.76±0.02b 1.10±0.10b 13.7±0.1cd 66.3±9.5a 25.7±0.7a 163±16bcd P 7.63±0.08b 11.0±1.3b 0.97±0.19a 1.20±0.03a 13.9±0.5cd 43.7±5.3c 22.4±0.0b 197±12a 间作2
Intercropping 2S 7.58±0.05b 11.2±0.58b 0.78±0.04b 0.73±0.09f 12.7±0.6de 53.4±5.3bc 10.0±0.0d 152±8.0cd P 7.71±0.06b 14.2±0.32a 0.91±0.09ab 0.96±0.02c 12.3±0.2e 60.0±3.0ab 15.3±0.6c 166±9.0bc 间作3
Intercropping 3S 7.61±0.02b 12.0±0.86b 0.80±0.06b 0.73±0.01f 14.3±0.2bc 47.6±8.4c 14.0±0.6c 180±17ab P 7.71±0.03b 12.7±2.0ab 0.85±0.04ab 0.83±0.01de 13.5±0.8cde 63.7±0.7a 22.5±2.4b 201±20a 间作1: 条带式间作; 间作2: 交叉式间作; 间作3: 混合式间作。S为伴矿景天, P为辣椒。同列数据后不同字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。Intercropping 1: stripe intercropping; Intercropping 2: cross intercropping; Intercropping 3: mixed intercropping. S is Sedum plumbizincicola and P is Capsicum annum. Different letters after mean values in the same column indicate significant differences among different planting patterns of different plants at P<0.05 level. 表 2 土壤Cd迁移性和可利用性与土壤化学性质和球囊霉素含量的冗余分析
Table 2. RDA sequencing results of soil Cd mobility and availability and soil chemical properties and globulin contents
参数 Statistic 第1轴 Axis 1 第2轴 Axis 2 第3轴 Axis 3 第4轴 Axis 4 土壤特征值 Eigenvalues 0.5471 0.1522 0.1701 0.1307 变异的累积解释量 Explained variation (cumulative) 54.71 69.93 86.93 100.00 相关性 Pseudo-canonical correlation 0.8735 0.7334 0.0000 0.0000 累积解释量 Explained fitted variation (cumulative) 78.23 100.00 表 3 土壤化学性质与球囊霉素的显著性检验结果和重要性排序
Table 3. Significance and importance of soil chemical properties and glomalin content
指标
Index重要性排序
Order of importance解释量
Explains (%)F P TE-GRSP 1 36.3 12.6 0.002 AK 2 16.9 4.5 0.024 pH 3 11.7 2.9 0.076 EE-GRSP 4 9.6 2.3 0.12 TK 5 9.3 2.2 0.108 TP 6 7.6 1.8 0.162 TN 7 7.0 1.7 0.216 AN 8 6.2 1.4 0.224 OP 9 1.8 0.4 0.634 OM 10 <0.1 <0.1 0.994 TE-GRSP: 总提取球囊霉素; AK: 速效钾; EE-GRSP: 易提取球囊霉素; TK: 全钾; TP: 全磷; TN: 全氮; AN: 碱解氮; OP: 有效磷; OM: 有机质。TE-GRSP: total extraction of globulin; AK: available potassium; EE-GRSP: easily extracted globulin; TK: total potassium; TP: total phosphorus; TN: total nitrogen; AN: available nitrogen; OP: Olsen phosphorus; OM: organic matter. -
[1] 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2822−2833CHEN W X, LI Q, WANG Z, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in arable land soil of China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2822−2833 [2] HU B F, SHAO S, NI H, et al. Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 114961 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114961 [3] 刘清, 王子健, 汤鸿霄. 重金属形态与生物毒性及生物有效性关系的研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 1996, 17(1): 89−92LIU Q, WANG Z J, TANG H X. Research progress in heavy metal speciation and toxicity and bioavailability of heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 1996, 17(1): 89−92 [4] 韩春梅, 王林山, 巩宗强, 等. 土壤中重金属形态分析及其环境学意义[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(12): 1499−1502 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.12.025HAN C M, WANG L S, GONG Z Q, et al. Chemical forms of soil heavy metals and their environmental significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(12): 1499−1502 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.12.025 [5] 王蕊, 陈明, 陈楠, 等. 基于总量及形态的土壤重金属生态风险评价对比: 以龙岩市适中镇为例[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10): 4348−4359WANG R, CHEN M, CHEN N, et al. Comparison of soil heavy metal ecological risk assessment based on total and form: A case study of Shizhong Town, Longyan City[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4348−4359 [6] 李如忠, 姜艳敏, 潘成荣, 等. 典型有色金属矿山城市小河流沉积物重金属形态分布及风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(3): 1067−1075LI R Z, JIANG Y M, PAN C R, et al. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in stream sediments from a typical nonferrous metals mining city[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(3): 1067−1075 [7] 郭鹏然, 雷永乾, 蔡大川, 等. 广州城市污泥中重金属形态特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(2): 684−691GUO P R, LEI Y Q, CAI D C, et al. Characteristics of speciation and evaluation of ecological risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge of Guangzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(2): 684−691 [8] 王利军, 卢新卫, 雷凯. 宝鸡城市街尘、土壤及河流沉积物重金属形态迁移特征[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 2011, 24(1): 22−26WANG L J, LU X W, LEI K. Speciation and transfer of heavy metals in street dust, soil and river sediment of Baoji City[J]. Urban Environment & Urban Ecology, 2011, 24(1): 22−26 [9] 杨新明, 庄涛, 韩磊, 等. 小清河污灌区农田土壤重金属形态分析及风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 644−652 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051001YANG X M, ZHUANG T, HAN L, et al. Fraction distribution and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the farmland soil from the sewage irrigated area of Xiaoqing River[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 644−652 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051001 [10] 麻冰涓, 王海邻, 李小超, 等. 河南省武陟县大田土壤重金属形态分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(4): 363−367MA B J, WANG H L, LI X C, et al. Fractional distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil, Wuzhi, Henan[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(4): 363−367 [11] 关天霞, 何红波, 张旭东, 等. 土壤中重金属元素形态分析方法及形态分布的影响因素[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(2): 503−512GUAN T X, HE H B, ZHANG X D, et al. The methodology of fractionation analysis and the factors affecting the species of heavy metals in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(2): 503−512 [12] 杨秀敏, 任广萌, 李立新, 等. 土壤pH值对重金属形态的影响及其相关性研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(6): 79−83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2017.06.015YANG X M, REN G M, LI L X, et al. Effect of pH value on heavy metals form of soil and their relationship[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(6): 79−83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2017.06.015 [13] 窦韦强, 安毅, 秦莉, 等. 土壤pH对镉形态影响的研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(3): 439−444DOU W Q, AN Y, QIN L, et al. Advances in effects of soil pH on cadmium form[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(3): 439−444 [14] 刘佳丽, 王祖伟, 张辉. 模拟降水对碱性盐化土壤中镉的淋滤及形态变化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(8): 1974−1978 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.08.037LIU J L, WANG Z W, ZHANG H. Simulated rainfall leaching cadmium and cadmium fraction changes in soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(8): 1974−1978 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.08.037 [15] 罗文贱, 张政勤, 陈勇, 等. 连续解吸中离子强度对可变电荷土壤和高岭石体系pH的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(1): 146−154 doi: 10.11766/trxb201505070152LUO W J, ZHANG Z Q, CHEN Y, et al. Effect of ionic-strength change on the system pH of variable charge soils and kaolinite during successive desorption[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(1): 146−154 doi: 10.11766/trxb201505070152 [16] CAPORALE A G, VIOLANTE A. Chemical processes affecting the mobility of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments[J]. Current Pollution Reports, 2016, 2(1): 15−27 doi: 10.1007/s40726-015-0024-y [17] YU H Y, LIU C P, ZHU J S, et al. Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: The effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 209: 38−45 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.021 [18] 王浩, 章明奎. 有机质积累和酸化对污染土壤重金属释放潜力的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(3): 538−541WANG H, ZHANG M K. Effects of organic matter accumulation and acidification on release potential of heavy metals from polluted soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(3): 538−541 [19] 宋波, 曾炜铨. 土壤有机质对镉污染土壤修复的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2015, 46(4): 1018−1024SONG B, ZENG W Q. Effects of organic matter on the remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil — A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 46(4): 1018−1024 [20] 王建, 周紫燕, 凌婉婷. 球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白的分布及环境功能研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(2): 634−642WANG J, ZHOU Z Y, LING W T. Distribution and environmental function of glomalin-related soil protein: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(2): 634−642 [21] 肖玖军, 邢丹, 毛明明, 等. AM真菌对桑树根围土壤团聚体的影响机制[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(3): 773−782XIAO J J, XING D, MAO M M, et al. Mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal affecting soil aggregates in rhizosphere of mulberry (Morus alba)[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(3): 773−782 [22] GILLESPIE A W, FARRELL R E, WALLEY F L, et al. Glomalin-related soil protein contains non-mycorrhizal-related heat-stable proteins, lipids and humic materials[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(4): 766−777 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.12.010 [23] WU Z P, MCGROUTHER K, HUANG J D, et al. Decomposition and the contribution of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) in heavy metal sequestration: Field experiment[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 68: 283−290 doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.10.010 [24] 仲召亮, 王文杰, 王琼, 等. 松嫩平原农业区土壤理化性质与真菌代谢产物−球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(8): 2274−2280ZHONG Z L, WANG W J, WANG Q, et al. Correlation between soil physicochemical properties and fungi-derived glomalin-related soil proteins in agricultural region of Songnen Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(8): 2274−2280 [25] 能凤娇, 吴龙华, 刘鸿雁, 等. 芹菜与伴矿景天间作对污泥农用锌镉污染土壤化学与微生物性质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5): 1428−1434NENG F J, WU L H, LIU H Y, et al. Effects of intercropping Sedum plumbizincicola and Apium graceolens on the soil chemical and microbiological properties under the contamination of zinc and cadmium from sewage sludge application[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5): 1428−1434 [26] DENG L, LI Z, WANG J, et al. Long-term field phytoextraction of zinc/cadmium contaminated soil by Sedum plumbizincicola under different agronomic strategies[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2016, 18(2): 134−140 doi: 10.1080/15226514.2015.1058328 [27] 唐明灯, 艾绍英, 李盟军, 等. 轮间作对伴矿景天和苋菜生物量及Cd含量的影响[J]. 广东农业科学, 2012, 39(13): 35−37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.13.012TANG M D, AI S Y, LI M J, et al. Effects of interplanting-rotation on growth and Cd concentration of Sedum plumbizincicola and Amaranthus cruetus[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 39(13): 35−37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.13.012 [28] 蔡倩, 孙占祥, 郑家明, 等. 辽西半干旱区玉米大豆间作模式对作物干物质积累分配、产量及土地生产力的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(5): 909−920 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.05.004CAI Q, SUN Z X, ZHENG J M, et al. Effects of corn and soybean intercropping patterns on dry matter accumulation and distribution, yield and land productivity in semiarid areas of western Liaoning[J]. Chinese Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 54(5): 909−920 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.05.004 [29] 邓晓霞, 米艳华, 黎其万, 等. 利用改进的BCR法和Tessier法提取稻田土壤中Pb、Cd的对比研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016, 28(9): 64−68DENG X X, MI Y H, LI Q W, et al. Comparative study on extraction of Pb and Cd from paddy soils by modified BCR method and tessier method[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2016, 28(9): 64−68 [30] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000BAO S D. Agronomic Analysis of Soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000 [31] WRIGHT S F, UPADHYAYA A, BUYER J S. Comparison of N-linked oligosaccharides of glomalin from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soils by capillary electrophoresis[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1998, 30(13): 1853−1857 doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00047-9 [32] TIWARI K K, SINGH N K, PATEL M P, et al. Metal contamination of soil and translocation in vegetables growing under industrial wastewater irrigated agricultural field of Vadodara, Gujarat, India[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011, 74(6): 1670−1677 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.04.029 [33] 张云, 王丹媚, 王孝源, 等. 外源茉莉酸对菊芋镉胁迫下光合特性及镉积累的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2015, 17(4): 1−15ZHANG Y, WANG D M, WANG X Y, et al. Effects of exogenous jasmonic acid on photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium accumulation of Jerusalem artichoke under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 17(4): 1−15 [34] 卢一富, 李真理, 阮心玲, 等. 铅冶炼污染石灰性土壤上冬小麦间作伴矿景天的探讨[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(9): 1686−1692 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.09.009LU Y F, LI Z L, RUAN X L, et al. Preliminary investigation of intercropping of wheat with Cd hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola on calcareous, lead smelting contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(9): 1686−1692 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.09.009 [35] LIANG H M, LIN T H, CHOU J M, et al. Model evaluation of the phytoextraction potential of heavy metal hyperaccumulators and non-hyperaccumulators[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(6): 1945−1952 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.11.052 [36] GOVE B, HUTCHINSON J J, YOUNG S D, et al. Uptake of metals by plants sharing a rhizosphere with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2002, 4(4): 267−281 doi: 10.1080/15226510208500087 [37] 但春凤, 王家豪, 黄莉娟, 等. 玉米/紫花苜蓿间作对土壤化学性质的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2020, (14): 97−102DAN C F, WANG J H, HUANG L J, et al. Effects of corn/alfalfa intercropping on soil chemical properties[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 2020, (14): 97−102 [38] 张艳, 郭书亚, 尚赏, 等. 甘薯/玉米不同间作方式对土壤养分、酶活性及作物产量的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(8): 1234−1238 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2020.08.15ZHANG Y, GUO S Y, SHANG S, et al. Effects of different intercropping methods of sweet potato/corn on soil nutrients, enzyme activity and crop yield[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(8): 1234−1238 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2020.08.15 [39] 姚远, 刘兆新, 刘妍, 等. 花生、玉米不同间作方式对花生生理性状以及产量的影响[J]. 花生学报, 2017, 46(1): 1−7YAO Y, LIU Z X, LIU Y, et al. Effect of different peanut-maize intercropping patterns on peanut growth and yield[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2017, 46(1): 1−7 [40] 逄雅萍, 黄爽, 杨金忠, 等. 生物碳促进水稻土镉吸附并阻滞水分运移[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(11): 107−114PANG Y P, HUANG S, YANG J Z, et al. Promotion of biochar on adsorption of cadmium and retardation on water transport in paddy soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(11): 107−114 [41] MA Y, OLIVEIRA R S, NAI F J, et al. The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 156: 62−69 [42] 骆永明, 吴龙华, 胡鹏杰, 等. 镉锌污染土壤的超积累植物修复研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 9–10LUO Y M, WU L H, HU P J, et al. Phytoremediation of Hyperaccumulation in Soil Contaminated by Cadmium and Zinc Research[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 9–10 [43] 闫仁俊, 韩磊, 赵亚萍, 等. 玉米与龙葵间作模式对植物生长及Cd富集特征的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2162−2171 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0639YAN R J, HAN L, ZHAO Y P, et al. Effects of intercropping modes of Zea mays L. and Solanum nigrum L. on plant growth and Cd enrichment characteristics[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2162−2171 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0639 [44] 焦念元, 宁堂原, 杨萌珂, 等. 玉米花生间作对玉米光合特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(14): 4324−4330 doi: 10.5846/stxb201207311087JIAO N Y, NING T Y, YANG M K, et al. Effects of maize‖peanut intercropping on photosynthetic characters and yield forming of intercropped maize[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(14): 4324−4330 doi: 10.5846/stxb201207311087 [45] 蒙秋霞, 邢虹娟, 白光洁, 等. 瓜菜间作对大樱桃生长和土壤理化性质、微生物区系的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2021, (3): 91−98MENG Q X, XING H J, BAI G J, et al. Intercropping of different vegetables and melons affects sapling growth, soil properties and soil microbial population in cherry orchard[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021, (3): 91−98 [46] 陈国皓, 祖艳群, 湛方栋, 等. 钝化剂处理对玉米与伴矿景天间作下植株生长及镉累积特征的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(9): 2103−2110 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1446CHEN G H, ZU Y Q, ZHAN F D, et al. Effects of passivators on the growth and cadmium accumulation of intercropped maize and Sedum plumbizincicola[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(9): 2103−2110 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1446 [47] 李善家, 王军强, 施志国, 等. 不同基肥处理对玉米土壤酶活性和球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2017, 23(2): 357−363LI S J, WANG J Q, SHI Z G, et al. Effect of different base fertilizer treatments on maize soil enzyme activity and glomalin-related protein[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2017, 23(2): 357−363 [48] NICHOLS K A, WRIGHT S F. Comparison of glomalin and humic acid in eight native us soils[J]. Soil Science, 2005, 170(12): 985−997 doi: 10.1097/01.ss.0000198618.06975.3c [49] CHERN E C, TSAI D W, OGUNSEITAN O A. Deposition of glomalin-related soil protein and sequestered toxic metals into watersheds[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(10): 3566−3572 -





 下载:
下载: