Spatio-temporal variation in and the driving factors of desert vegetation in Xinjiang
-
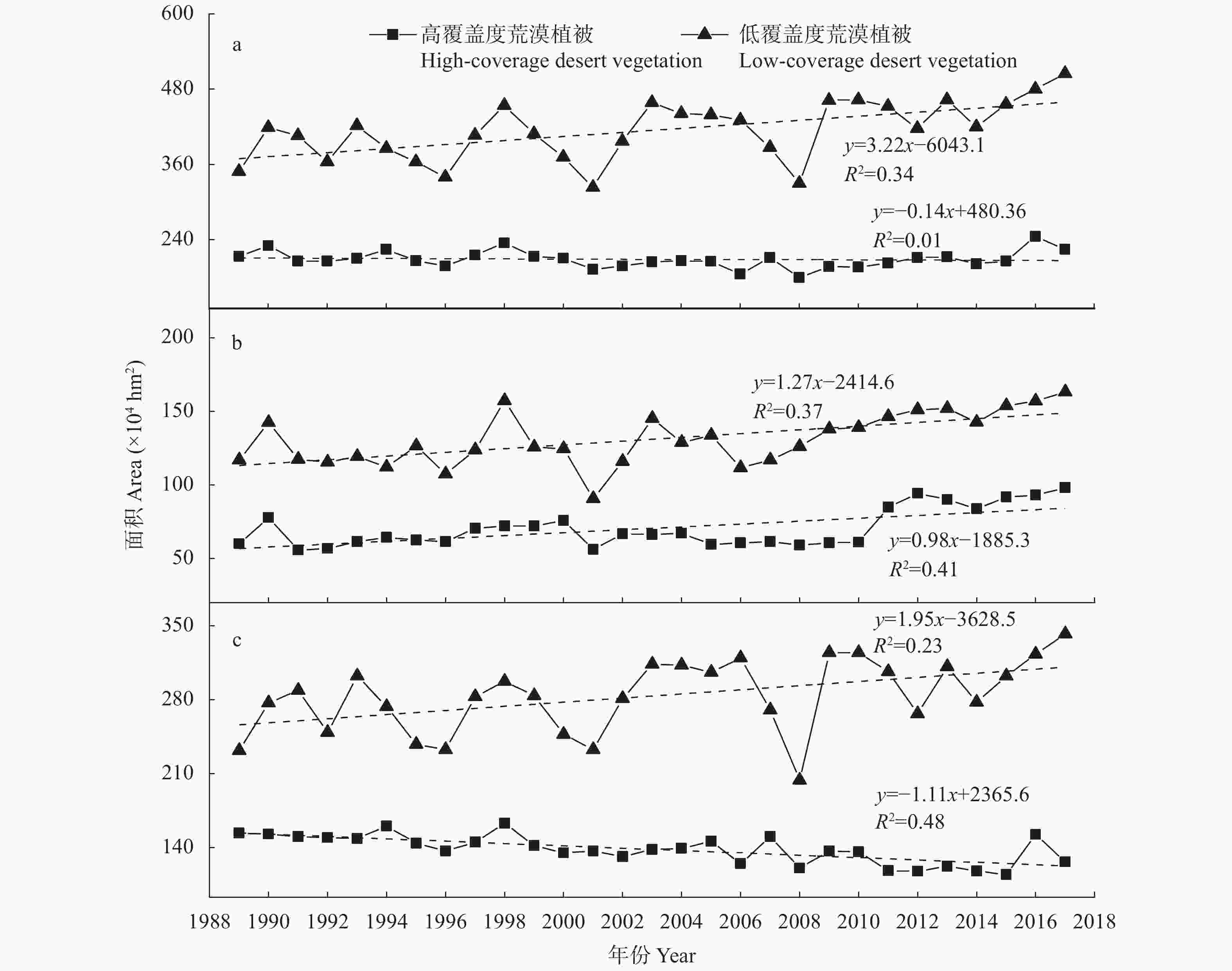
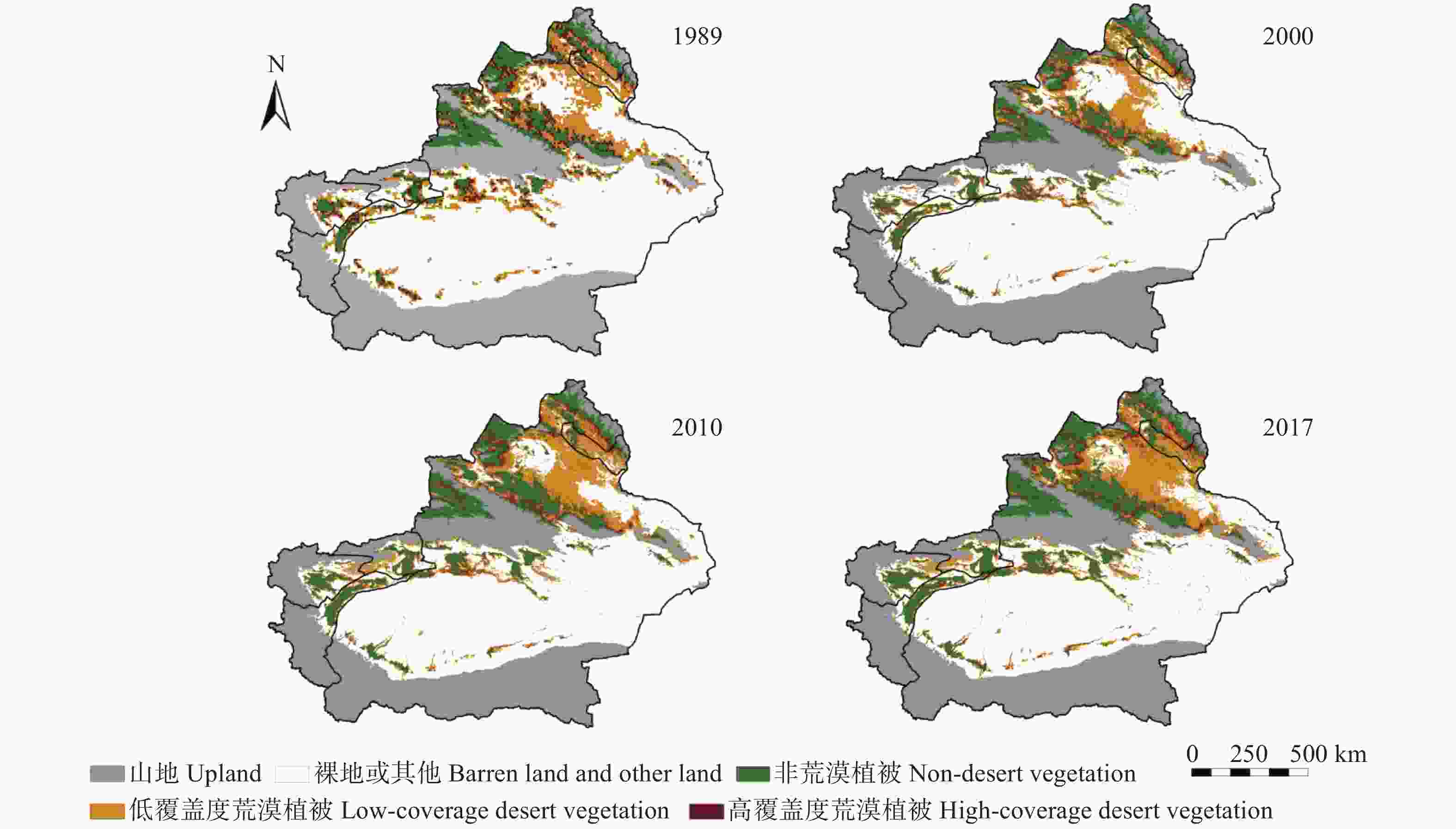
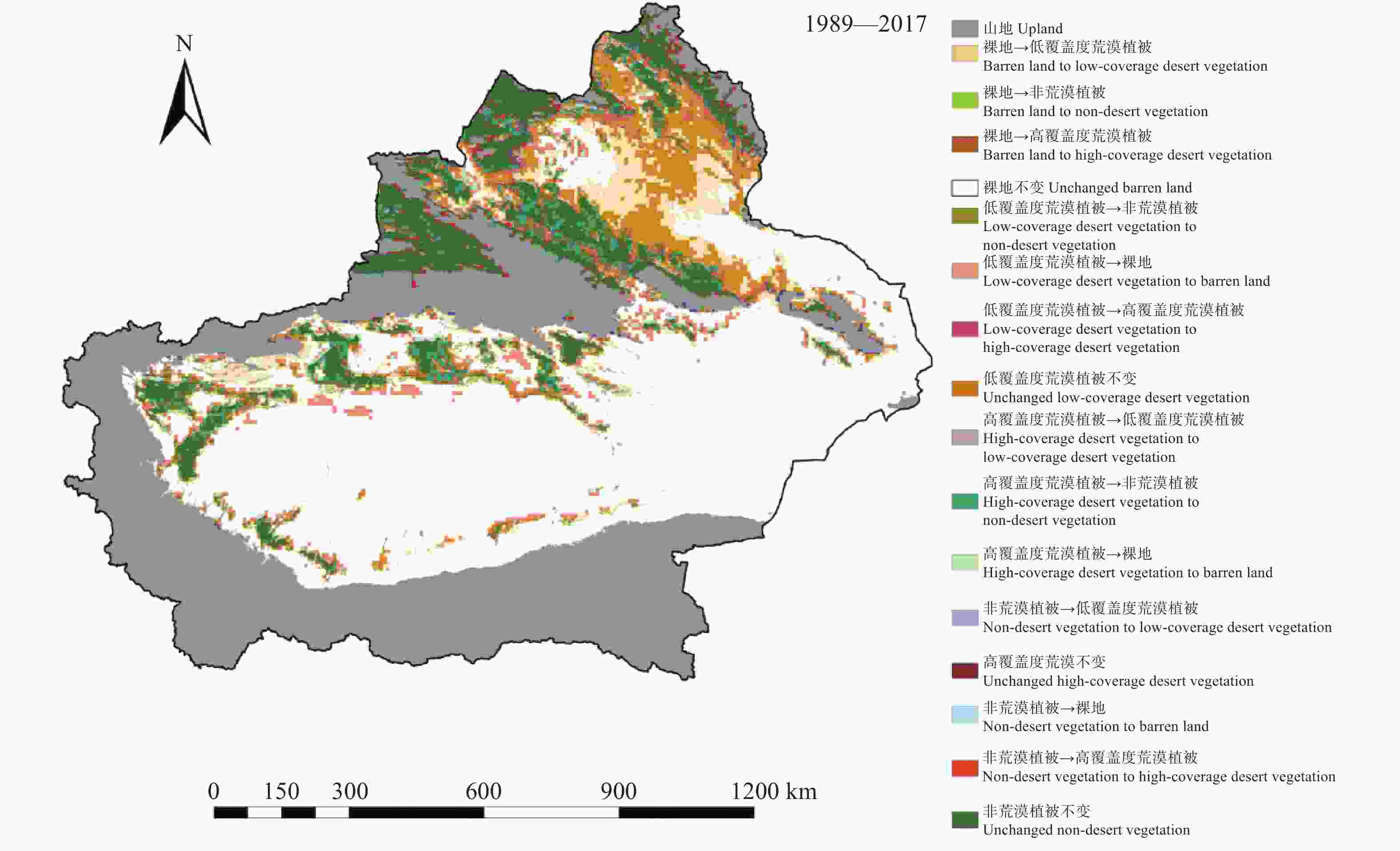
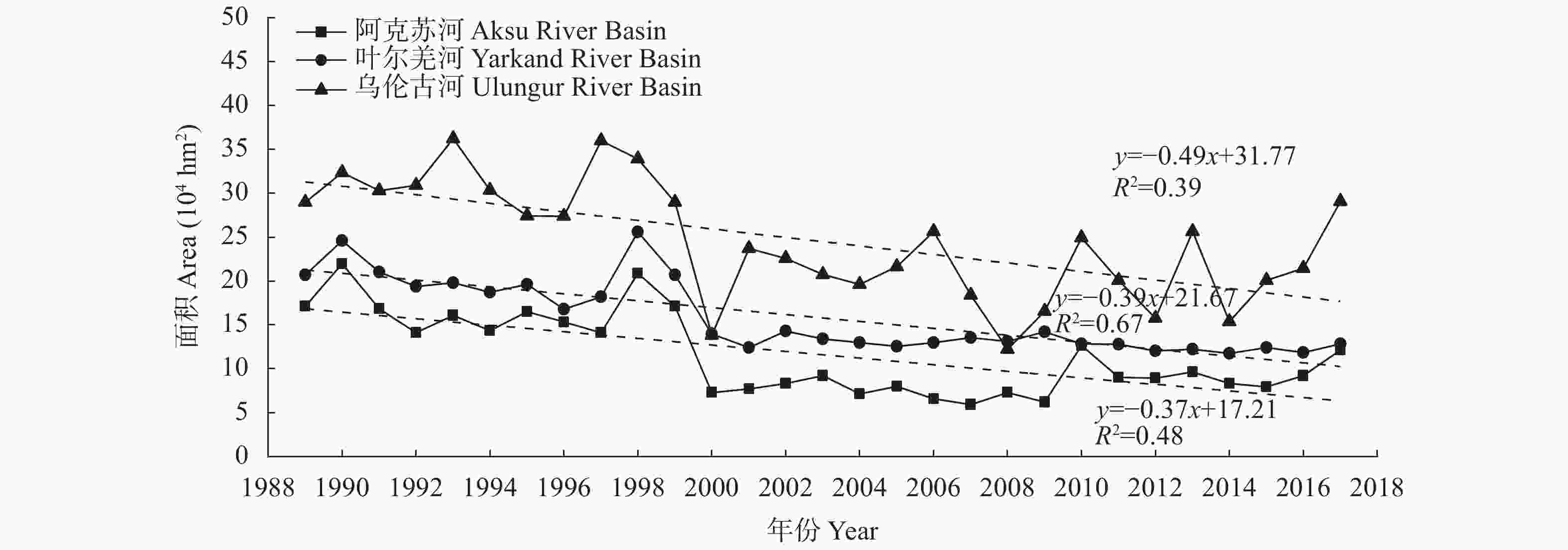
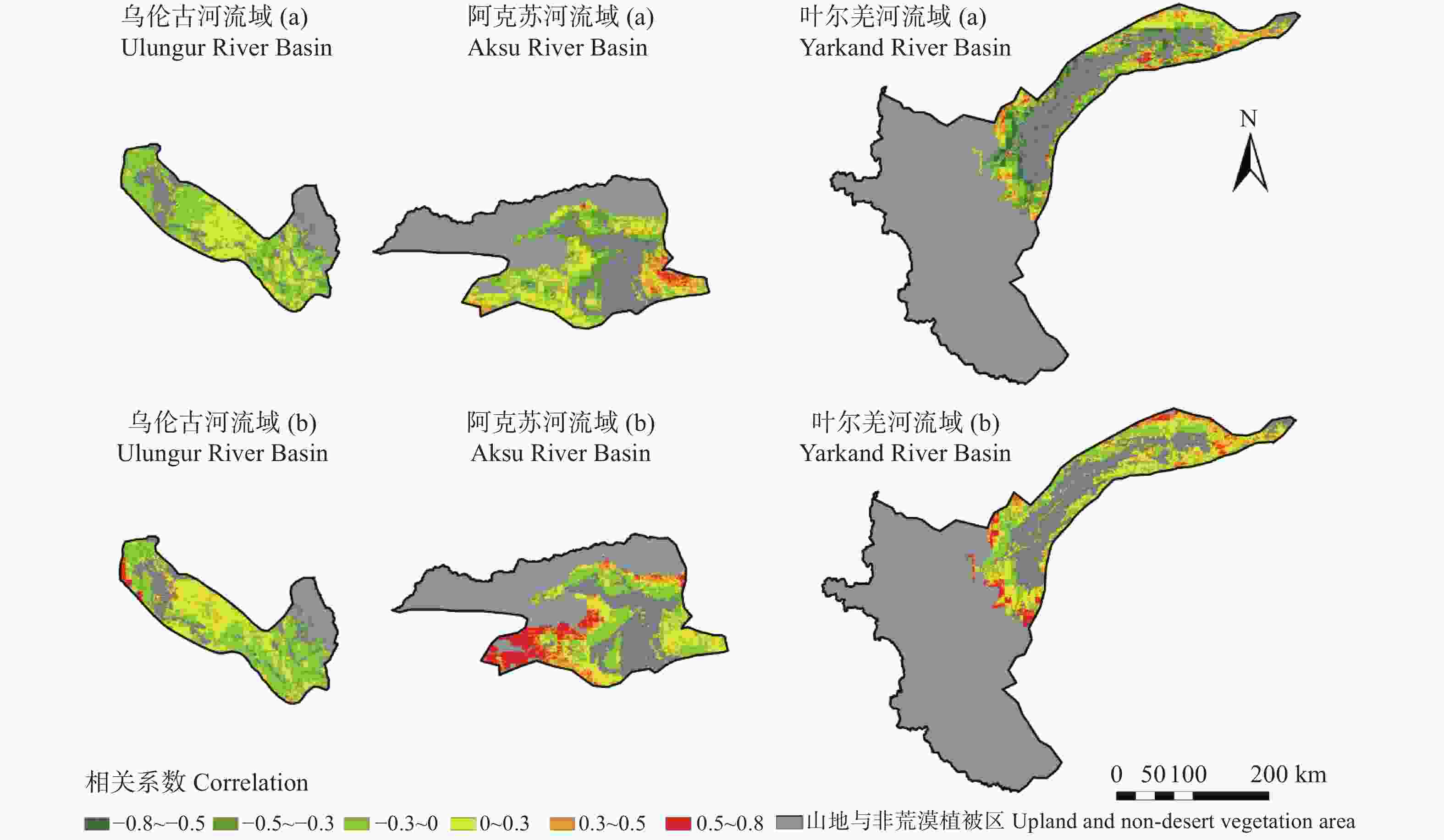
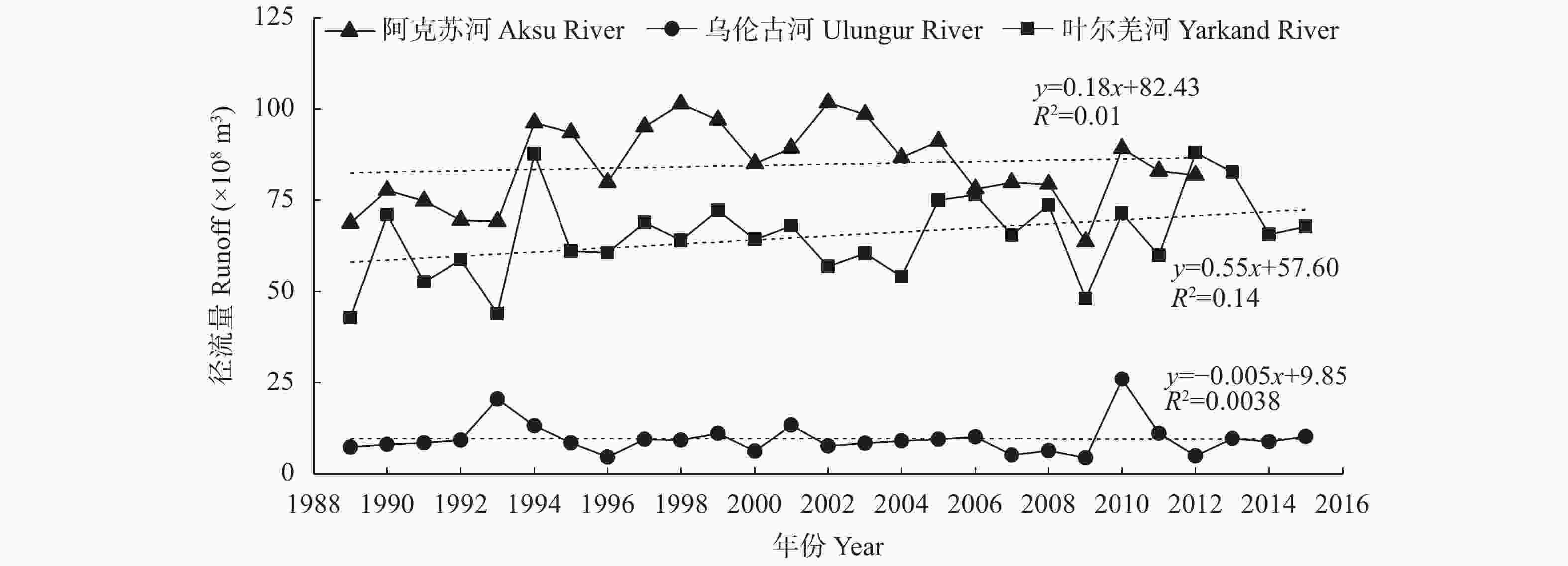
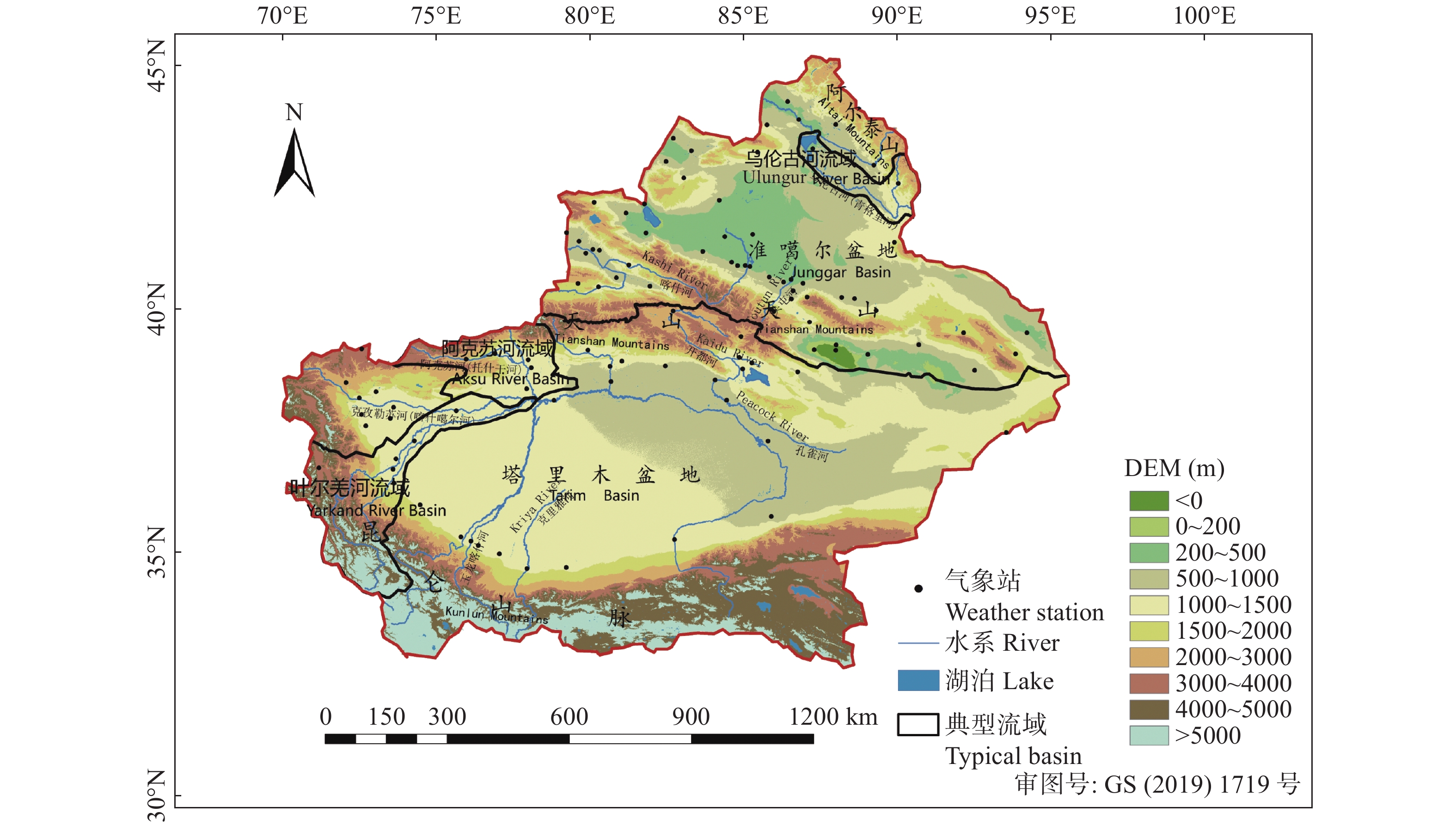
摘要: 荒漠植被是干旱半干旱生态系统重要的组成部分, 在维护生态系统平衡方面发挥着重要的作用。及时准确地监测新疆荒漠植被的时空分布变化, 对资源可持续利用及生态恢复具有重要应用价值。本研究基于AVHRR-NDVI和MOD13A2-NDVI数据集计算了新疆1989—2017年植被覆盖度, 通过对植被覆盖度划分阈值提取计算了荒漠植被的分布及面积, 并分析了其时空变化特征。通过土地利用转移矩阵计算新疆荒漠植被与非荒漠植被、裸地类型的转化情况。利用相关系数分析法定量分析了乌伦古河、叶尔羌河及阿克苏河3个典型流域影响荒漠植被演变的驱动因素。结果表明: 1989—2017年, 新疆荒漠植被总面积呈显著增加趋势, 线性增长率为3.09万hm2∙a−1。低覆盖度荒漠植被面积呈显著增加趋势, 线性增长率为3.22万hm2∙a−1; 高覆盖度荒漠植被面积基本不变。植被转化中, 高、低荒漠植被间转化面积50.85万hm2, 非荒漠植被类型转变为荒漠植被341.24万hm2, 荒漠植被转变为非荒漠植被类型191.25万hm2。通过对典型流域的研究分析得出降水是影响荒漠植被演变最主要的因素, 其次是径流量和政策因素, 气温对于荒漠植被的影响存在区域性差异。Abstract: Desert vegetation is an important part of arid and semi-arid ecosystems in Xinjiang and plays a key role in the maintenance of ecosystem balance. Timely and accurate monitoring of the temporal and spatial distribution of desert vegetation is important for the sustainable utilization of the resources and ecological restoration. Based on remote sensing technology combined with two Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) products (AVHRR-NDVI and MOD13A2-NDVI), the area of desert vegetation in Xinjiang from 1989 to 2017 was estimated. The temporal and spatial characteristics of desert vegetation in three typical river basins (Ulungur River Basin, Aksu River Basin, and Yarkand River Basin) were analyzed, and the relationships between desert vegetation and the climate factors, runoff changes, and policy factors were discussed. The NDVI products were used to calculate the vegetation coverage ( fc), and the distribution and area of desert vegetation were determined according to the threshold of vegetation coverage. Desert vegetation was determined within the fc threshold range of 0.1–0.35, where 0.1–0.25 indicates low-coverage desert vegetation and 0.25–0.35 indicates high-coverage desert vegetation. The transformation between desert vegetation and other vegetation types was calculated using the land use transfer matrix to explore the evolution and transformation of desert vegetation in Xinjiang from 1989 to 2017. The driving factors of desert vegetation evolution in the three typical river basins were analyzed using correlation analysis. The results showed that the total area of desert vegetation in Xinjiang significantly increased from 1989 to 2017 at a rate of 30 900 hm2∙a−1. The area of low-coverage desert vegetation significantly increased at a rate of 32 200 hm2∙a−1; whereas the area of high-coverage desert vegetation did not vary, with a multi-year average value of 2 087 100 hm2. The area of desert vegetation in northern Xinjiang increased slightly, accounting for 67% of the total area of desert vegetation. This was mainly due to an increase in low-coverage desert vegetation. The area of high-coverage desert vegetation in northern Xinjiang slighly decreased. The desert vegetation area in southern Xinjiang significantly increased. During vegetation transformation, 508 500 hm2 of desert vegetation transformed from high to low desert vegetation, 3.4124 million hm2 of non-desert vegetation types transformed into desert vegetation, and 1.9125 million hm2 of desert vegetation transformed into non-desert vegetation types. This study of typical river basins showed that the area of desert vegetation increased with increasing precipitation. Precipitation was the most important factor affecting the evolution of desert vegetation, followed by runoff and policy factors. The influence of air temperature on desert vegetation varied across regions, and the area of desert vegetation near water increased with increasing temperature.
-
Key words:
- Xinjiang /
- Desert vegetation /
- Desert vegetation evolution /
- Coverage rate /
- Ecological system
-
表 1 1989—2017年新疆不同植被类型间转化情况
Table 1. Conversion among different vegetation types in Xinjiang from 1989 to 2017
104 hm2 转化类型 Conversion type 面积 Area 转化类型 Conversion type 面积 Area 非荒漠植被不变
Unchanged non-desert vegetation1372.10 高覆盖度荒漠植被→非荒漠植被
High-coverage desert vegetation to non-desert vegetation58.97 非荒漠植被→裸地
Non-desert vegetation to barren land40.11 高覆盖度荒漠植被不变
Unchanged high-coverage desert vegetation90.16 非荒漠植被→低覆盖度荒漠植被
Non-desert vegetation to low-coverage desert vegetation24.02 高覆盖度荒漠植被→低覆盖度荒漠植被
High-coverage desert vegetation to low-coverage desert vegetation24.90 非荒漠植被→高覆盖度荒漠植被
Non-desert vegetation to high-coverage desert vegetation66.86 高覆盖度荒漠植被→裸地
High-coverage desert vegetation to barren land54.76 低覆盖度荒漠植被→非荒漠植被
Low-coverage desert vegetation to non-desert vegetation36.11 裸地-低覆盖度荒漠植被
Barren land to low-coverage desert vegetation210.25 低覆盖度荒漠植被不变
Unchanged low-coverage desert vegetation242.84 裸地不变
Unchanged barren land8167.30 低覆盖度荒漠植被→裸地
Low-coverage desert vegetation to barren land41.41 裸地→高覆盖度荒漠植被
Barren land to high-coverage desert vegetation40.11 低覆盖度荒漠→高覆盖度荒漠植被
Low-coverage desert vegetation to high-coverage desert vegetation25.95 裸地→非荒漠植被
Barren land to non-desert vegetation111.27 -
[1] 龙雨涛, 李雪娇, 李铭, 等. 浅析不同植被在防风固沙方面发挥的生态效应[J]. 农业与技术, 2015, 35(17): 76−77LONG Y T, LI X J, LI M, et al. Ecological effects of different vegetations on windbreak and sand fixation[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2015, 35(17): 76−77 [2] 杨慧, 张龙儒. 分析不同植被在防风固沙方面发挥的生态效应[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2018, 29(16): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2018.16.010YANG H, ZHANG L R. Ecological effects of different vegetation types in terms of windbreak and sand fixation[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2018, 29(16): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2018.16.010 [3] 于惠, 吴玉锋, 金毅, 等. 河西干旱区植被覆盖度时空格局分析[J]. 草业科学, 2019, 36(3): 623−631YU H, WU Y F, JIN Y, et al. Analysis of the spatio-temporal patterns of vegetation fractional coverage in the Hexi arid area[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(3): 623−631 [4] 彭佳忆, 王新军, 朱磊, 等. 基于无人机影像的荒漠地表类型信息提取[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(3): 771−780PENG J Y, WANG X J, ZHU L, et al. Information extraction of desert surface types based on UAV image[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(3): 771−780 [5] 高永平, 康茂东, 何明珠, 等. 基于无人机可见光波段对荒漠植被覆盖度提取的研究−以沙坡头地区为例[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 54(6): 770−775GAO Y P, KANG M D, HE M Z, et al. Extraction of desert vegetation coverage based on visible light band information of unmanned aerial vehicle: a case study of Shapotou region[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Sciences, 2018, 54(6): 770−775 [6] 吕利利. 基于光谱微分法的荒漠稀疏植被提取及变化分析——以疏勒河流域走廊平原地区为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018LYU L L. Sparse vegetation extraction and change analysis based on spectral differentiation — An example in the Shule River basin plain[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018 [7] 钱育蓉, 于炯, 贾振红, 等. 新疆典型荒漠草地的高光谱特征提取和分析研究[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 157−166 doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130119QIAN Y R, YU J, JIA Z H, et al. Extraction and analysis of hyper-spectral data from typical desert grassland in Xinjiang[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(1): 157−166 doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130119 [8] 何鸿杰. 基于旋转森林算法的荒漠区植被信息提取: 以毛乌素沙地为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019HE H J. Vegetation information extraction in desert areas based on rotation forest algorithm: a case study of Mu Us sandy land[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019 [9] 周丹, 沈彦俊, 陈亚宁, 等. 西北干旱区荒漠植被生态需水量估算[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(3): 670−680ZHOU D, SHEN Y J, CHEN Y N, et al. Estimation of ecological water requirement of desert vegetation in the arid region of Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(3): 670−680 [10] 高志海, 李增元, 魏怀东, 等. 干旱地区植被指数(VI)的适宜性研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(2): 243−248 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.02.015GAO Z H, LI Z Y, WEI H D, et al. Study on the suitability of vegetation indices (VI) in arid area[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2006, 26(2): 243−248 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.02.015 [11] 郭玉川, 何英, 李霞. 基于MODIS的干旱区植被覆盖度反演及植被指数优选[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2011, 23(2): 115−118GUO Y C, HE Y, LI X. Remote sensing inversion of vegetation coverage and optimization of vegetation index based on MODIS data in arid area[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2011, 23(2): 115−118 [12] 拉巴, 扎西欧珠, 白玛央宗, 等. 基于MODIS数据的西藏荒漠化遥感监测研究[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2019, 42(4): 39−46LABA, ZHAXIOUZHU, BAIMAYANGZONG, et al. Study on remote sensing monitoring of desertification in Tibet based on MODIS data[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 42(4): 39−46 [13] 赵霞, 谭琨, 方精云. 1982—2006年新疆植被活动的年际变化及其季节差异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2011, 28(1): 10−16 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1148.2011.00010ZHAO X, TAN K, FANG J Y. NDVI-based interannual and seasonal variations of vegetation activity in Xinjiang during the period of 1982−2006[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2011, 28(1): 10−16 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1148.2011.00010 [14] 赵鹏, 陈桃, 王茜, 等. 气候变化和人类活动对新疆草地生态系统NPP影响的定量分析[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2020, 37(1): 51−62 doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2020.01.007ZHAO P, CHEN T, WANG Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of the impact of climate change and human activities on grassland ecosystem NPP in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 37(1): 51−62 doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2020.01.007 [15] 沈永平. 新疆水资源的特点及问题[J]. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3): 263SHEN Y P. Characteristics and problems of Xinjiang water resources[J]. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 2002, 24(3): 263 [16] 王智, 师庆三, 王涛, 等. 1982—2006年新疆山地-绿洲-荒漠系统植被覆盖变化时空特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(4): 609−618 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.04.007WANG Z, SHI Q S, WANG T, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics of vegetation cover change in mountain-oasis-desert system of Xinjiang from 1982 to 2006[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011, 26(4): 609−618 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.04.007 [17] 杨发相, 李生宇, 岳健, 等. 新疆荒漠类型特征及其保护利用[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(1): 12−19YANG F X, LI S Y, YUE J, et al. Characteristics of desert types and their protection and utilization in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2019, 42(1): 12−19 [18] 蒋霞. 西北干旱区多种植物地理分布与气候的相关性及其可能潜在分布预测[D]. Beijing: 中国科学院研究生院, 2003JIANG X. Relationship between climate and geographic distribution of some plant species and prediction of species potential distribution in the arid land, northwest China[D]: Beijing: Graduate University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003 [19] 柏玲. 气候变化对天山南坡典型流域径流过程的影响——以开都河与阿克苏河为例[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2016BAI L. Climate change and its impacts on runoff process for typical river basin in the southern slopes of Tianshan mountains—Cases in the Kaidu River and Aksu River basins[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2016 [20] 李智超. 1954—2015年新疆叶尔羌河径流变化特征[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(S1): 68−70LI Z C. Runoff variation characteristics of Yarkant River in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region from 1954 to 2015[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(S1): 68−70 [21] 何兵, 高凡, 唐小雨, 等. 基于滑动Copula函数的新疆干旱内陆河流水文气象要素变异关系诊断[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(1): 155−161HE B, GAO F, TANG X Y, et al. Diagnosis of variation of the relationship between hydrological and meteorological elements in arid rnland rivers of Xinjiang based on the sliding Copula function[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(1): 155−161 [22] 林年丰, 汤洁. 中国干旱半干旱区的环境演变与荒漠化的成因[J]. 地理科学, 2001, 21(1): 24−29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.01.005LIN N F, TANG J. Study on the environmental evolution and the causes of desertification in arid and semiarid regions in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2001, 21(1): 24−29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.01.005 [23] 刁维杰, 赵勇, 翟家齐, 等. 1987—2017年民勤绿洲面积时空演变规律及驱动因素解析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(10): 106−113DIAO W J, ZHAO Y, ZHAI J Q, et al. Temporal spatial evolution and driving force analysis of Minqin Oasis during 1987−2017[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(10): 106−113 [24] 陈雪华. 北疆区域植被覆盖变化及其与气象因子的关系[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆师范大学, 2012CHEN X H. Vegetation cover variation and its relation with meteorological factors in northern part of Xinjiang[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2012 [25] 蒲云锦, 韩春光. 新疆植被指数与气象因子关系分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2010, 4(5): 44−47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0799.2010.05.011PU Y J, HAN C G. Relationships of MODIS vegetation index and meteorological factors in Xinjiang[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2010, 4(5): 44−47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0799.2010.05.011 [26] 徐满厚, 薛娴. 气候变暖对高寒地区植物生长与物候影响分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2013, 27(3): 137−141XU M H, XUE X. Analysis on the effects of climate warming on growth and phenology of alpine plants[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2013, 27(3): 137−141 [27] DANG H S, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG K R, et al. Climate-growth relationships of subalpine fir (Abies fargesii) across the altitudinal range in the Shennongjia Mountains, central China[J]. Climatic Change, 2013, 117(4): 903−917 doi: 10.1007/s10584-012-0611-5 [28] 张琴琴, 马英莲. 塔克拉玛干沙漠及其绿洲时空变化研究[J]. 地理空间信息, 2019, 17(5): 53−55, 5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2019.05.014ZHANG Q Q, MA Y L. Research on spatio-temporal changes of the Taklimkan Desert and its oasis[J]. Geospatial Information, 2019, 17(5): 53−55, 5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2019.05.014 [29] 潘光耀, 穆桂金, 岳健, 等. 2001—2010年策勒绿洲−沙漠过渡带的变化及其成因[J]. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(1): 169−175PAN G Y, MU G J, YUE J, et al. Change of the oasis-desert ecotone and its causes in Qira County during the period of 2001− 2010[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(1): 169−175 [30] 刘翔. 携手防沙止漠 共护绿水青山[EB/OL]. 新疆日报. [2020-06-18]. https://www.chinanews.com/gn/2020/06-17/9214893.shtmlLIU X. Hand in hand to prevent sand and desert and protect green waters and mountains[EB/OL]. Xinjiang Daily. [2020-06-18]. http://wap.xjdaily.com/xjrb/20200618/157285.html [31] 宋燕. 生态文明建设要严守三条红线[EB/OL]. 新华网. [2018-06-20]. http://www.xinhuanet.com/2018-06/20/c_1123009773.htmSONG Y. The construction of ecological civilization must strictly observe the three red lines[EB/OL]. Xinhuanet. [2018-06-20]. http://www.xinhuanet.com/2018-06/20/c_1123009773.htm [32] 古丽·加帕尔, 陈曦, 包安明. 干旱区荒漠稀疏植被覆盖度提取及尺度扩展效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(12): 2925−2934GULI·JIAPAER, CHEN X, BAO A M. Coverage extraction and up-scaling of sparse desert vegetation in arid area[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(12): 2925−2934 [33] 李向婷, 白洁, 李光录, 等. 新疆荒漠稀疏植被覆盖度信息遥感提取方法比较[J]. 干旱区地理, 2013, 36(3): 502−511LI X T, BAI J, LI G L, et al. Comparison of methods based on MODIS for estimating sparse vegetation fraction across desert in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2013, 36(3): 502−511 [34] 孙红雨, 王长耀, 牛铮, 等. 中国地表植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子关系−基于NOAA时间序列数据分析[J]. 遥感学报, 1998, 2(3): 204−210 doi: 10.11834/jrs.19980309SUN H Y, WANG C Y, NIU Z, et al. Analysis of the vegetation cover change and the relationship between NDVI and environmental factors by using NOAA time series data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 2(3): 204−210 doi: 10.11834/jrs.19980309 [35] 张生军, 王涛, 王天明, 等. 新疆不同植被NDVI的变化及其与气候因子的关系[J]. 草业科学, 2009, 26(5): 26−31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2009.05.005ZHANG S J, WANG T, WANG T M, et al. The variations in NDVI of different vegetation types in Xinjiang and its relation to climate factors[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(5): 26−31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2009.05.005 [36] 马有绚. 干旱半干旱地区植被指数与气候的关系[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016MA Y X. The relationship between vegetation index and climate factors in arid and semi-arid[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016 -






 下载:
下载: