Effect of seedling size on the medicinal properties of Codonopsis pilosula under organic cultivation
-
摘要: 生态栽培是中药材产业发展的必然趋势。党参种苗大小参差不齐, 为了探明种苗大小对其成药特性的影响, 将种苗分为大苗(BS)、中苗(MS)、小苗(SS)和特小苗(SLS), 并进行全程有机肥栽培, 系统比较各级种苗的成药产量特性。结果表明, 不同大小种苗返青后阶段性异速生长趋势明显, 种苗越大返青越早, 前期长势越强中后期减弱越明显, 侧根数显著增加, 根显著伸长, 根含水量高, 发病率越高; 而种苗越小返青率越低, 但返青株抗病性越强, 成活率越高, 前期长势弱但中后期加快。不同大小种苗的成药株个体和群体的产量差异并不显著, 平均鲜药材产量MS组最高(8225.1 kg·hm–2), SS组次之(8125.0 kg·hm–2), 较BS组分别提高23.4%和21.9%, 较SLS组分别提高45.2%和43.4%; 平均干药材产量SS组最高(2938.1 kg·hm–2), MS组次之(2681.1 kg·hm–2), 较BS组分别提高37.8%和25.7%, 较SLS组分别提高53.6%和40.1%。各级种苗成药根发病率差异性虽不显著, 但发病程度差异性极显著, MS和BS的病情指数分别为4.66%和2.93%, 均较SLS (1.32%)和SS (0.97%)极显著增大(P<0.01)。综评指数排序为SS (0.734)>SLS (0.636)>MS (0.409)>BS (0.282)。这说明有机栽培党参药材产出性能并不随种苗增大而提高, 党参种苗可塑性强, 在成药期建植策略不同, 研究结果打破了对党参种苗选留的传统认知, 建议生产上不盲目追求大苗, 轻易淘汰特小苗, 特小苗可适当增加移栽密度和生态防鸟虫提高返青率, 大苗可适当降低移栽密度或搭架提高返青株成活率, 有效提高党参的生态有机栽培成效。Abstract: Ecological organic cultivation is an increasing trend in the industrialized development of traditional Chinese medicine. The medicinal properties of Codonopsis pilosula vary with seedling size. To explore the effects of seedling size on medicinal formation in organic cultivated C. pilosula, seedlings were categorized as big (BS), middle (MS), small (SS), and slender (SLS) seedlings and transplanted under full organic conditions to comparatively evaluate the yield and medicinal characteristics of the medicinal roots. The results showed that the seedling sizes had an allometric growth pattern. After transplantation, bigger seedlings showed earlier regreening, greater growth at the early stages and weaker growth at the later stages with significant increases in lateral roots number, and higher water content of roots, and higher disease incidence. The smaller seedlings showed later regreening, faster growth at the mid and later stages with increased diameter, less root water content and lower disease incidence. These differences led to non-significant differences in the single root weight and total medicinal yield. The average fresh medicinal yields of MS (8225.1 kg·hm–2) and SS (8125.0 kg·hm–2) were the highest and second highest, respectively, increasing by 23.4% and 21.9% compared with the BS group and by 45.2% and 43.4% compared with the SLS group. The average dry medicinal yield of SS (2938.1 kg·hm–2) and MS (2681.1 kg·hm–2) was the highest and second highest, increasing by 37.8% and 25.7% compared with the BS group and by 53.6% and 40.1% compared with the SLS group, respectively. Among the four seedling sizes, the root disease incidence did not significantly differ, ranked as BS (6.4%) > MS (5.6%) > SS (3.9%)> SLS (3.6%). However, the disease severity showed significant differences, and the disease indices for MS and BS were 4.66% and 2.93%, respectively, both of which were significantly higher than those for SLS (1.32%) and SS (0.97%). The comprehensive evaluation indices were SS (0.734) > SLS (0.636) > MS (0.409) > BS (0.282). In summary, yield did not increase with seedling size largening. Plant seedlings have strong plasticity and manifest various strategies for establishment during the medicinal formation period. These results challenge the traditional selection and retention practices for plant seedlings, suggesting that the big seedlings should not be blindly chosen and that the slender seedlings should not be eliminated during production. Slender plants should be cultivated by increasing the transplantation density and controlling pests and birds to improve the regreening rate, whereas larger seedlings should be cultivated by decreasing the density. Together, these practices could improve the effectiveness of C. pilosula organic cultivation.
-
Key words:
- Codonopsis pilosula /
- Seedling size /
- Organic cultivation /
- Medicinal yield /
- Disease resistance
-
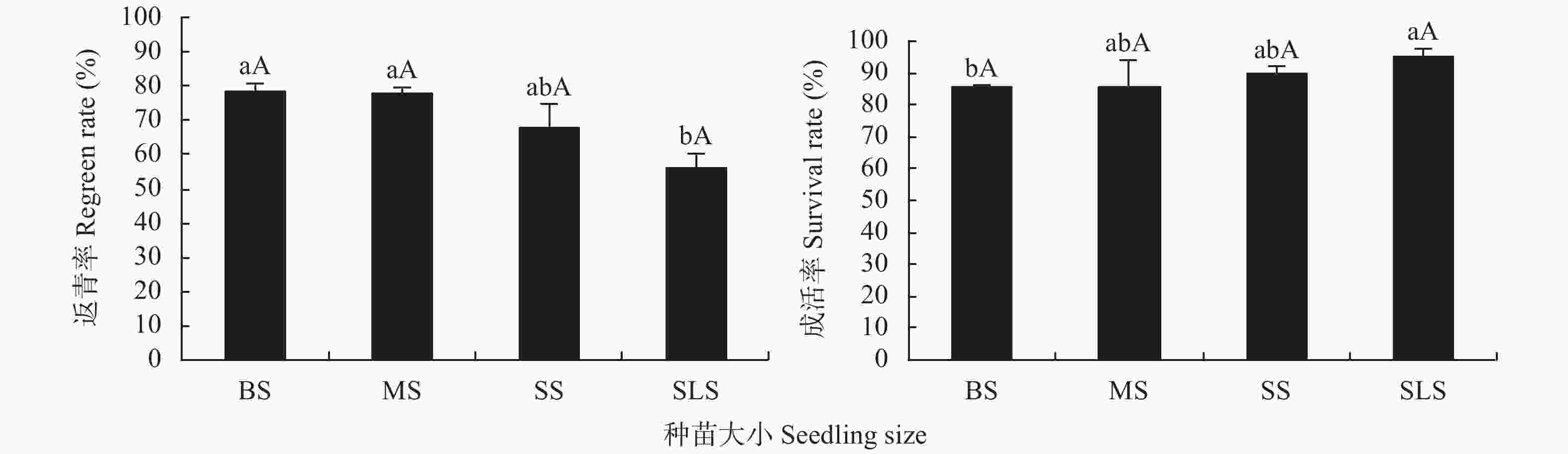
图 2 种苗大小对党参返青率与返青后成活率的影响
BS: 大苗; MS: 中苗; SS: 小苗; SLS: 特小苗。不同小写字母表示不同种苗大小在P<0.05水平差异显著。BS: big seedlings; MS: middle seedlings; SS: small seedlings; SLS: slender seedlings. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different seedling sizes at P<0.05.
Figure 2. Effect of seedling size on the regreening rate and survival rate of Codonopsis pilosula
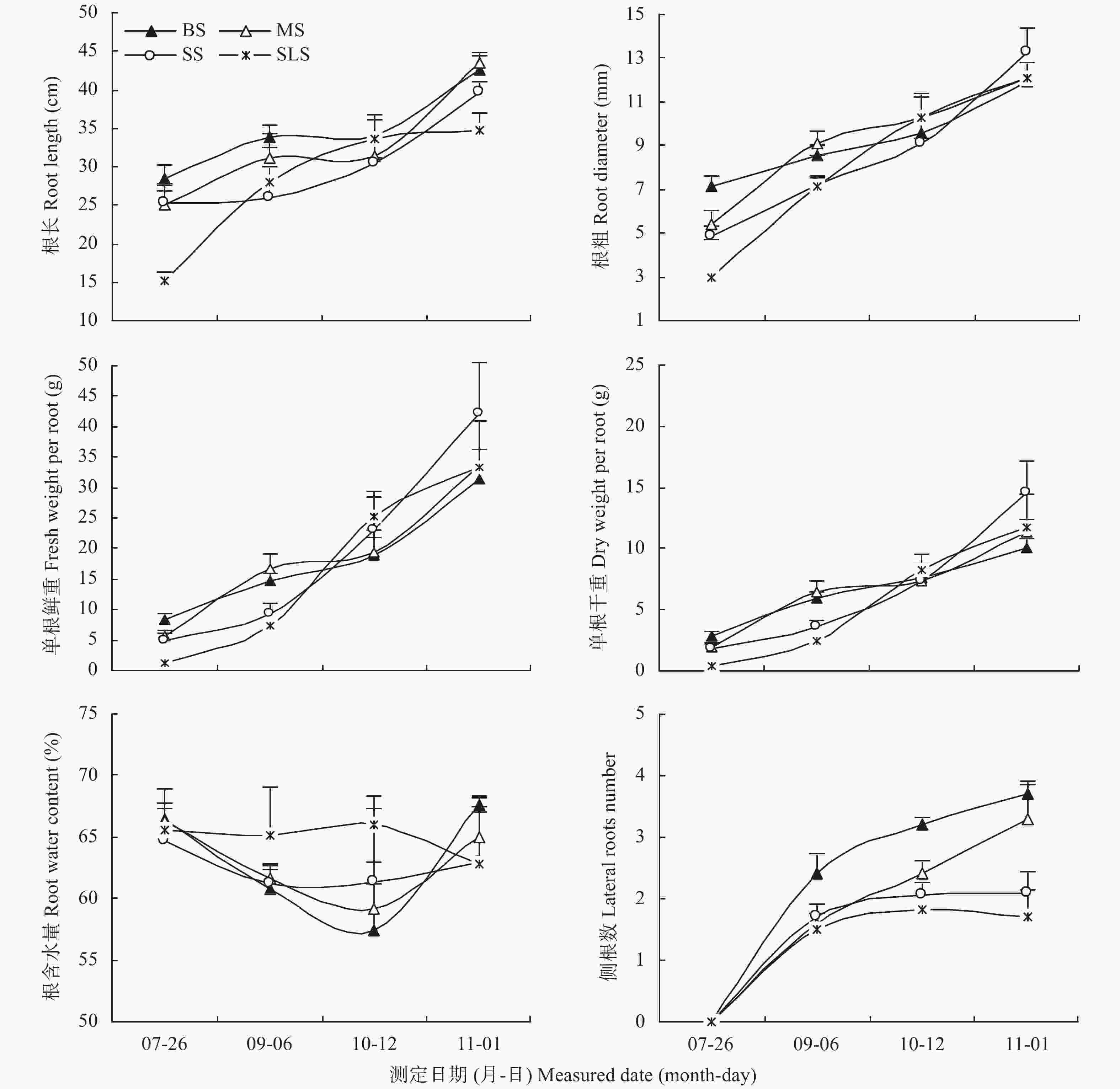
图 3 种苗大小对党参根形态性状和含水量动态变化的影响
BS: 大苗; MS: 中苗; SS: 小苗; SLS: 特小苗。图中数据为每个种苗组10株的平均值±标准误。BS: big seedlings; MS: middle seedlings; SS: small seedlings; SLS: slender seedlings. The data were the means±S.E. for 10 plants in each seedling group.
Figure 3. Effect of seedling size on dynamic changes of root morphology character and water content of Codonopsis pilosula
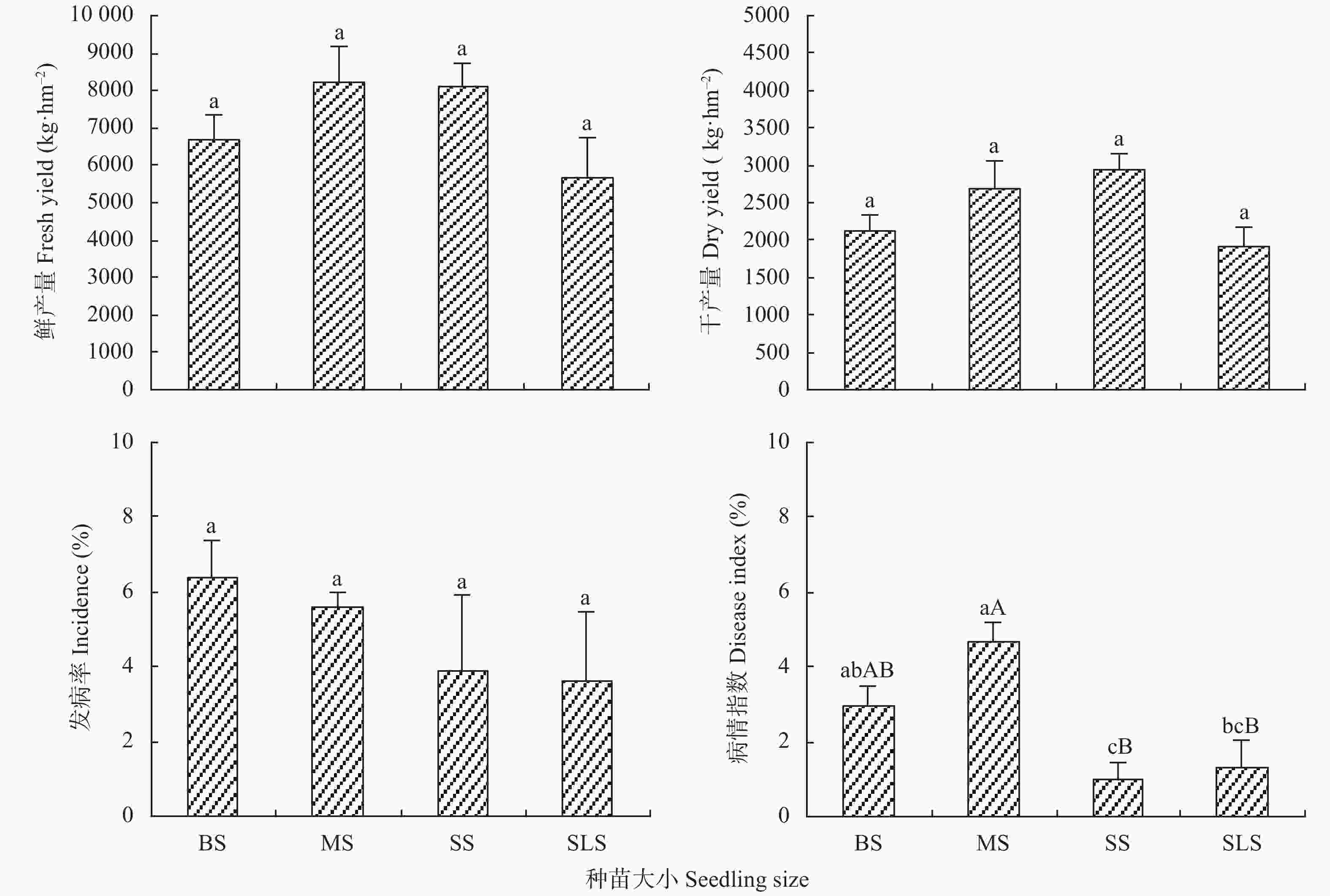
图 4 种苗大小对党参药材根产量和抗病性的影响
BS: 大苗; MS: 中苗; SS: 小苗; SLS: 特小苗。不同小写字母表示不同处理在 P<0.05 水平差异显著, 不同大写字母表示不同处理在 P<0.01 水 平差异极显著。BS: big seedlings; MS: middle seedlings; SS: small seedlings; SLS: slender seedlings. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05; Different capital letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.01.
Figure 4. Effect of seedling size on the medicinal yield and disease resistance of Codonopsis pilosula
表 1 供试‘甘党1号’党参种苗大小分级标准
Table 1. Grading criterion of seedling sizes for the tested Codonopsis pilosula ‘Gandang No.1’
种苗大小 Seedling size 分级标准 Grading criterion 根长
Root length (cm)根粗
Root diameter (mm)单苗鲜重
Fresh weight of single seedling (g)大苗 Big seedlings (BS) ≥25.0 ≥4.50 ≥2.00 中苗 Middle seedlings (MS) 21.0~25.0 3.50~4.50 1.00~2.00 小苗 Small seedlings (SS) 14.0~21.0 1.95~3.50 0.25~1.00 特小苗 Slender seedlings (SLS) <14.0 <1.95 <0.25 表 2 种苗大小对党参药材根产量性状的影响
Table 2. Effect of seedling size on yield characters of Codonopsis pilosula medicinal roots
种苗大小
Seedling size根长
Root length
(cm)根粗
Root diameter
(mm)侧根数
Lateral roots
number单根鲜重
Fresh weight
per root (g)单根干重
Dry weight
per root (g)根含水量
Root water
content (%)折干率
Dry rate (%)大苗 Big seedlings (BS) 44.03±1.72aA 12.64±0.79a 3.20±0.70a 35.27±3.47a 11.25±1.01a 67.99±0.43a 31.92±0.43a 中苗 Middle seedlings (MS) 42.11±1.90aA 12.61±0.62a 2.40±0.78a 36.49±4.97a 11.61±1.67a 67.55±2.50a 31.82±2.50a 小苗 Small seedlings (SS) 38.00±1.50bB 12.61±0.71a 2.07±0.06a 40.60±4.32a 14.22±1.95a 63.78±2.01a 34.95±2.01a 特小苗 Slender seedlings (SLS) 36.43±1.63bB 12.88±0.95a 1.80±0.81a 41.84±9.44a 14.06±3.69a 63.30±7.87a 33.76±4.75a 表中数据为2019年11月1日党参采挖期3个重复小区共30株的平均数±标准差。The data in the table are the means ±S.D. of 30 roots with 3 replicates in the harvest on Nov. 1, 2019. 表 3 党参药材根产量因子及抗病性的相关性分析
Table 3. Relation of medicinal yield factors and disease resistance of Codonopsis pilosula medicinal roots
指标
Index根长
Root length根粗
Root diameter侧根数
Lateral
roots number单根鲜重
Fresh weight
per root单根干重
Dry weight
per root根含水量
Root water
content返青率
Regreening
rate成活率
Survival
rate发病率
Incidence
rate病情指数
Disease
index鲜药材
产量
Fresh yield根粗
Root diameter0.017 侧根数
Lateral roots number0.550 −0.148 单根鲜重
Fresh weight per root−0.419 0.807** −0.194 单根干重
Single dry root weight−0.573 0.654* −0.128 0.909** 根含水量
Root water content0.615* 0.149 0.155 −0.005 −0.379 返青率
Regreening rate0.822** 0.038 0.501 −0.335 −0.413 0.488 成活率
Survival rate−0.214 −0.221 −0.130 −0.081 −0.009 −0.266 −0.411 发病率
Incidence rate0.642* 0.339 0.365 0.100 −0.180 0.700* 0.681* −0.267 病情指数
Disease index0.695* −0.023 0.377 −0.240 −0.464 0.603* 0.587* −0.237 0.666* 鲜药产量
Fresh yield0.365 −0.033 0.062 0.028 −0.057 0.454 0.351 0.056 0.223 0.364 干药产量
Dry yield0.174 −0.027 0.076 0.119 0.156 0.159 0.214 0.124 0.027 0.166 0.940** 生长指标为各小区10株的平均数, 3个重复, 4个等级, n=12。*表示在P<0.05相关显著, **表示在P<0.01相关极显著。R0.05, 10=0.576, R0.01, 10=0.708。The growth indicators are the mean of 10 plants, 3 replicates and 4 seedling grades. * and ** indicate significant and extremely relation at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. R0.05, 10=0.576, R0.01, 10=0.708. 表 4 基于主成分分析的党参产量因子和抗病性指标负荷量和权重
Table 4. Capacities and weights of yield factors and disease resistance indicators of Codonopsis pilosula based on principal components analysis
性状指标 Indicator 负荷量 Load 权重值 Weight value 1 2 3 根长 Root length 0.922 −0.022 −0.068 0.0911 根粗 Root diameter −0.103 0.876 −0.299 0.0688 侧根数 Lateral roots number 0.529 −0.045 −0.134 0.0577 单根鲜重 Single fresh root weight −0.409 0.894 −0.051 0.0893 单根干重 Single dry root weight −0.605 0.734 0.038 0.0987 根含水量 Root water content 0.737 0.278 −0.029 0.0860 返青率 Regreening rate 0.865 0.079 −0.108 0.0904 成活率 Survival rate −0.304 −0.267 0.463 0.0611 发病率 Incidence rate 0.743 0.407 −0.293 0.1038 病情指数 Disease index 0.824 0.066 −0.049 0.0835 鲜产量 Fresh yield 0.482 0.308 0.807 0.0934 干产量 Dry yield 0.261 0.325 0.882 0.0762 特征根 Eigenvalues 4.589 2.631 1.860 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) 38.238 21.924 15.498 75.661 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) 38.238 60.163 75.661 表 5 基于有机栽培党参产量因子和抗病性隶属度的种苗大小综合评价
Table 5. Comprehensive evaluation for different size of seedlings based on membership function value of yield factors and disease resistance of organic cultivated Codonopsis pilosula
性状指标 Character indicator 大苗 Big seedlings 中苗 Middle seedlings 小苗 Small seedlings 特小苗 Slender seedlings 根长 Root length 0.0911 0.0681 0.0188 0.0000 根粗 Root diameter 0.0085 0.0000 0.0009 0.0688 侧根数 Lateral roots number 0.0000 0.0338 0.0479 0.0577 单根鲜重 Fresh weight per root 0.0000 0.0166 0.0725 0.0893 单根干重 Dry weight per root 0.0000 0.0119 0.0987 0.0933 根含水量 Root water content 0.0000 0.0081 0.0773 0.0860 返青率 Regreening rate 0.0904 0.0884 0.0491 0.0000 成活率 Survival rate 0.0000 0.0015 0.0254 0.0611 发病率 Incidence rate 0.0000 0.0300 0.0940 0.1038 病情指数 Disease index 0.0392 0.0000 0.0835 0.0756 鲜产量 Fresh yield 0.0365 0.0934 0.0897 0.0000 干产量 Dry yield 0.0163 0.0571 0.0762 0.0000 综合指数 Comprehensive index 0.2820 0.4089 0.7340 0.6356 排名 Rank 4 3 1 2 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典 (2020年版) [S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 293−294Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020)[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 293−294 [2] LIANG L, HE Z, YU H, et al. Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in Codonopsis pilosula based on transcriptome sequence data[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 1362 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58328-5 [3] ZHENG T, CHENG L Z, YAN Y M, et al. Two new triterpenoids from the roots of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(2): 383 doi: 10.3390/molecules23020383 [4] YANG D D, CHEN Y, GUO F X, et al. Comparative analysis of chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of leaves, leaf tea and root from Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 142: 111844 doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111844 [5] 杨扶德, 罗文蓉, 崔治家, 等. 白条党参种苗的等级划分标准研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(2): 452−454YANG F D, LUO W R, CUI Z J, et al. Codonopsis pilosula seedlings grading standards[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(2): 452−454 [6] 王洁, 邓长泉, 石磊, 等. 党参的现代研究进展[J]. 中国医药指南, 2011, 9(31): 279−281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2011.31.221WANG J, DENG C Q, SHI L, et al. Modern Research Progress of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Guide of China Medicine, 2011, 9(31): 279−281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2011.31.221 [7] 李成义, 刘书斌, 李硕, 等. 甘肃党参栽培现状调查分析[J]. 中国现代中药, 2016, 18(1): 102−105LI C Y, LIU S B, LI S, et al. Investigation and analysis of status cultivation of Gansu Codonopsis radix[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2016, 18(1): 102−105 [8] 蔡子平, 王宏霞, 王国祥, 等. 不同育苗模式对甘肃渭源党参种苗质量的影响[J]. 中药材, 2017, 40(4): 779−781CAI Z P, WANG H X, WANG G X, et al. Effects of different seedling cultivation patterns on seedling quality of Codonopsis pilosula in Weiyuan, Gansu[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017, 40(4): 779−781 [9] 赵亚兰, 陈垣, 郭凤霞, 等. 冬播和春播育苗对党参苗栽产量和质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 139−148 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014437ZHAO Y L, CHEN Y, GUO F X, et al. Effects of sowing time on yield and quality of Codonopsis pilosula seedlings[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(10): 139−148 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014437 [10] 李瑞杰, 陈垣, 郭凤霞, 等. 素花党参种苗质量分级标准研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(20): 3041−3046LI R J, CHEN Y, GUO F X, et al. Studies on classification criteria of Codonopsis pilosula var. modesta seedlings in southern of Gansu[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012, 37(20): 3041−3046 [11] 高石曼, 刘久石, 孙恬, 等. 不同栽培措施对党参药材化学质量的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2016, 41(20): 3753−3760GAO S M, LIU J S, SUN T, et al. Influence of different cultivation measures on chemical quality of Codonopsis Radix[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(20): 3753−3760 [12] 靳鹏博, 胡佳栋, 毛歌, 等. 栽培密度对党参产量和次生代谢物含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 164−172 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017165JIN P B, HU J D, MAO G, et al. Effects of planting density on yield and secondary metabolite content of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(3): 164−172 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017165 [13] 韩凤波, 奚广生. 不同采收期对轮叶党参有效成分含量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2014, (1): 154−156HAN F B, XI G S. Effect of different harvest time on the effective component content of Codonopsis lanceolata[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2014, (1): 154−156 [14] 胡佳栋, 武子丁, 刘子哲, 等. 党参氮磷钾施肥效应与最优施肥量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(9): 1615−1622 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18369HU J D, WU Z D, LIU Z Z, et al. Effects and optimum rate of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization for Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(9): 1615−1622 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18369 [15] 段琦梅, 梁宗锁, 杨东风, 等. 党参质量评价体系的建立及不同产地党参质量差异性分析[J]. 中草药, 2012, 43(5): 995−999DUAN Q M, LIANG Z S, YANG D F, et al. Establishment of quality evaluation system and difference analysis on roots of Codonopsis pilosula from different habitats[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2012, 43(5): 995−999 [16] 王惠珍, 连中学, 陆国弟, 等. 党参种苗等级与药材产量及质量的关系[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2016, 41(21): 3950−3955WANG H Z, LIAN Z X, LU G D, et al. Relationship between seedling grade of Codonopsis pilosula and yield and quality of medicinal materials[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(21): 3950−3955 [17] 肖婉君, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 等. 施用有机肥对当归药材性状、产量及抗病性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 189−199 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2020166XIAO W J, GUO F X, CHEN Y, et al. Effect of organic fertilizer application on the medicinal character, yield and disease resistance of Angelica sinensis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 189−199 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2020166 [18] DEGUINE J P, ATIAMA-NURBEL T, VANHUFFEL L, et al. Recent advances in organic cultivation of chayote (Sechium edule) in Reunion Island[J]. Organic Agriculture, 2020, 10(2): 135−143 doi: 10.1007/s13165-019-00255-5 [19] URS N, WANG-MULLER Q Y, HELGA W, 等. 生态农业和有机农业的创新[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(3): 423−430URS N, WANG-MULLER Q Y, HELGA W, et al. Innovation in agroecological and organic farming systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(3): 423−430 [20] 武高林, 杜国祯. 植物种子大小与幼苗生长策略研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(1): 191−197WU G L, DU G Z. Relationships between seed size and seedling growth strategy of herbaceous plant: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(1): 191−197 [21] HOWE H F, RICHTER W M. Effects of seed size on seedling size in Virola surinamensis; a within and between tree analysis[J]. Oecologia, 1982, 53(3): 347−351 doi: 10.1007/BF00389011 [22] 何春雨, 张延红, 蔺海明. 不同栽植密度和施肥量下党参生物量变化动态及其效应研究[J]. 中药材, 2005, 28(9): 6−9HE C Y, ZHANG Y H, LIN H M. Study on biomass dynamic changes of Codnopsis pilosula under the planting density and fertilizing amount[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2005, 28(9): 6−9 [23] 杨莉梅, 宋振华, 王富胜, 等. 陇中白条党参成药期生长规律研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 2017, 19(8): 1162−1164YANG L M, SONG Z H, WANG F S, et al. Study on growth regularity of Codonopsis pilosula during medicine formation period in middle region of Gansu Province[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2017, 19(8): 1162−1164 [24] 肖淑贤, 王旭峰, 李军, 等. 种苗等级和密度对潞党参产量和商品质量的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(1): 73−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2020.01.19XIAO S X, WANG X F, LI J, et al. Effects of different seedling grades and density on yield and commodity quality of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(1): 73−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2020.01.19 -






 下载:
下载: