Effect of intercropping on balancing effect of absorption and desorption characteristics of phosphorus in red soil
-
摘要: 磷素的吸附和解吸特性对土壤磷素迁移及其环境效应具有重要影响, 过量磷肥施入易造成土壤磷素固定和流失, 但合理间作可促进磷素吸收利用, 减少固定, 研究间作和不同施磷量条件下红壤磷素吸附解吸特性的平衡效应对促进红壤磷的高效利用, 兼顾环境效应具有重要意义。本研究采取2因素裂区区组试验, 主因素为种植模式, 分别为与玉米||大豆(IM)、单作玉米(MM); 副因素为施磷水平, 分别为P0 [0 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2]、P60 [60 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2]、P90 [90 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2]、P120 [120 kg(P2O5)∙hm−2] 4个施磷水平, 通过田间试验, 研究间作和施磷量对红壤磷素吸附解吸平衡效应的影响; 应用结构方程模型(SEM)和邻接树法(ABT)定量分析间作和施磷水平对磷吸附和解吸的相对贡献, 揭示间作影响红壤磷素吸附解吸的关键因子。结果表明: 1) Langmuir 等温吸附方程最适合红壤对磷的吸附特征拟合, 土壤磷吸附量随平衡溶液磷浓度的增加呈先增加再趋于饱和的趋势, 土壤磷吸附量随施磷量的增加逐渐降低。2)种植模式和施磷水平以及交互作用极显著(P<0.01)影响红壤磷素的吸附量和解吸量。间作处理较单作磷素吸附量和解吸量分别增加22.9%和9.2%(P<0.05); 不同施磷水平下, 间作磷吸附量较单作显著增加13.0%、19.4%、41.5%和23.9% (P<0.05); 磷解吸量在P0和P60处理间作较单作显著增加90.2%和194.4% (P<0.05), 而在P90和P120处理间作较单作减少52.1%和34.1% (P<0.05)。3)不同种植模式与施磷水平下, 土壤磷吸附量与土壤pH、有机质、树脂磷、有效磷、全磷以及磷吸附饱和度呈极显著负相关(P<0.01), 与游离氧化铁、游离氧化铝和磷吸持指数呈极显著正相关(P<0.01), 土壤磷解吸量与标准需磷量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。红壤磷素的吸附和解吸主要受pH、有机质和游离氧化铁的影响, 间作通过改变土壤的pH、有机质和游离氧化铁含量影响红壤磷吸附量和解吸量。玉米||大豆间作具有较好的土壤磷缓冲能力, 低磷水平下促进磷素大量解吸供植物吸收利用, 高磷水平下促进磷素吸附有效减缓磷素的损失。Abstract: The migration and environment effect of phosphorus in soil are affected by its’ adsorption and desorption. Although the excessive application of phosphorus fertilizer causes phosphorus fixation and loss, reasonable intercropping promotes the absorption and utilization and decreases fixation of phosphorus. This study investigated the adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in red soil under intercropping and phosphorus application, it is signicant for promoting the efficient utilization of red soil phosphorus and balancing environmental effects. In this study, a two-factor split-plot block experiment was adopted through field trials, in which the first factor was the planting pattern, namely maize||soybean intercropping and maize monoculture; the second factor was phosphorus application levels: P0 (0), P60 [60 kg (P2O5)·hm−2], P90 [90 kg (P2O5)·hm−2], and P120 [120 kg (P2O5)·hm−2]. This study aimed to explore the effects of intercropping and application of phosphorus on the adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in red soil, and to quantitatively analyze the relative contribution of intercropping and phosphorus application to phosphorus adsorption and desorption by using the structural equation model, and to reveal the key intercropping effect factors on the adsorption/desorption of phosphorus in red soil by using the aggregated boosted tree methods. Results showed that: 1) the Langmuir isothermal adsorption equation was most suitable for fitting phosphorus adsorption in red soil. The adsorption amount of soil phosphorus increased first and then tended toward saturation with the increase in phosphorus concentration in the equilibrium solution, while the adsorption amount of phosphorus decreased gradually with the increase in phosphorus application. 2) Phosphorus adsorption and desorption in red soil were significantly affected by planting pattern, phosphorus application, and the interaction between planting pattern and application of phosphorus (P<0.01). Compared with monoculture, the maize||soybean intercropping increased the adsorption and desorption of phosphorus by 22.9% and 9.2%, respectively (P<0.05). Under four application rates of phosphorus, compared with monoculture, the adsorption of phosphorus in intercropping increased significantly by 13.0%, 19.4%, 41.5%, and 23.9% (P<0.05), respectively. The desorption of phosphorus increased significantly by 90.2% and 194.4% in P0 and P60 intercropping (P<0.05), but decreased by 52.1% and 34.1% in P90 and P120 intercropping, respectively (P<0.05). 3) Under different planting patterns and phosphorus application levels, the adsorption of soil phosphorus had a significant negative correlation with soil pH, organic matter, resin phosphorus, available phosphorus, total phosphorus, and degree of phosphorus saturation (P<0.01), and a significant positive correlation with free iron oxide, free alumina, and phosphate sorption index (P<0.01). However, the desorption of phosphorus from red soil had a significant negative correlation with a standard phosphorus requirement (P<0.01). The adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in the red soil were mainly affected by pH, organic matter, and free iron oxide. Intercropping of maize and soybean changed soil pH and contents of organic matter and free iron oxide, resulting in differences in the phosphorus adsorption and desorption from that of maize monoculture in red soil, improving the soil phosphorus buffering capacity. At a low phosphorus level, intercropping can accelerate a large amount of phosphorus desorption for plants to absorb and utilize; at high phosphorus levels, intercropping can promote phosphorus adsorption and effectively slow down the loss of phosphorus.
-
Key words:
- Phosphorus /
- Adsorption /
- Desorption /
- Intercropping of maize and soybean /
- Phosphorus application level /
- Red soil
-
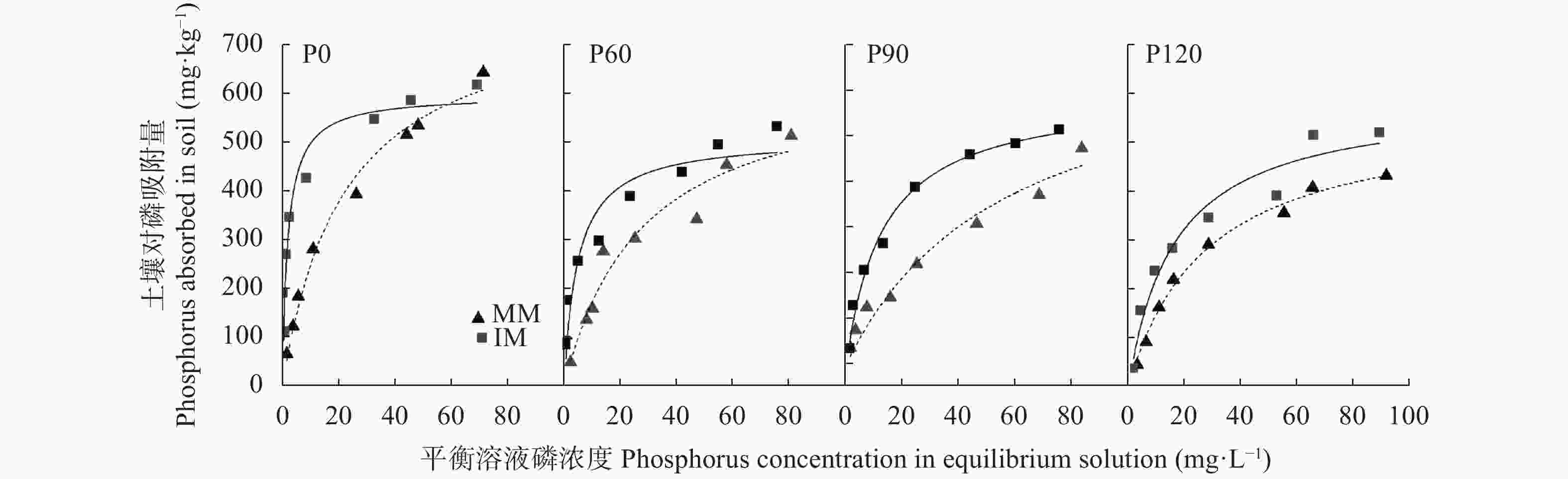
图 2 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷等温吸附曲线
P0为不施磷, P60为低施磷量[60 kg(P2O5)·hm−2], P90为常规施磷肥[90 kg(P2O5)·hm−2], P120为高施磷量[120 kg(P2O5)·hm−2]。
Figure 2. Adsorption isotherms of phosphorus in soil of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
P0 is no phosphorus fertilizer, P60 is low-level phosphorus fertilizer [60 kg(P2O5)·hm−2], P90 is conventional phosphorus fertilizer [90 kg(P2O5)·hm−2], P120 is high-level phosphorus fertilizer [120 kg(P2O5)·hm−2].
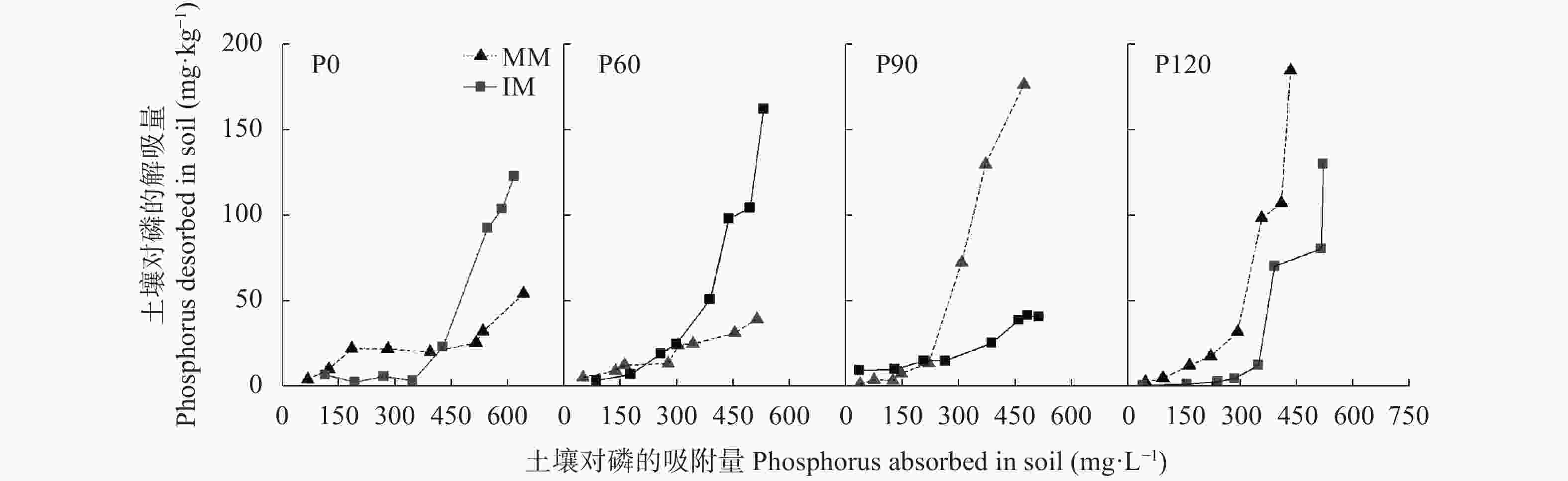
图 3 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷等温解吸曲线
P0、P60、P90、P120说明见图2的图注。
Figure 3. Isothermal desorption curves of phosphorus in soil of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
Description of P0, P60, P90, P120 are shown in the note of Figure 2.
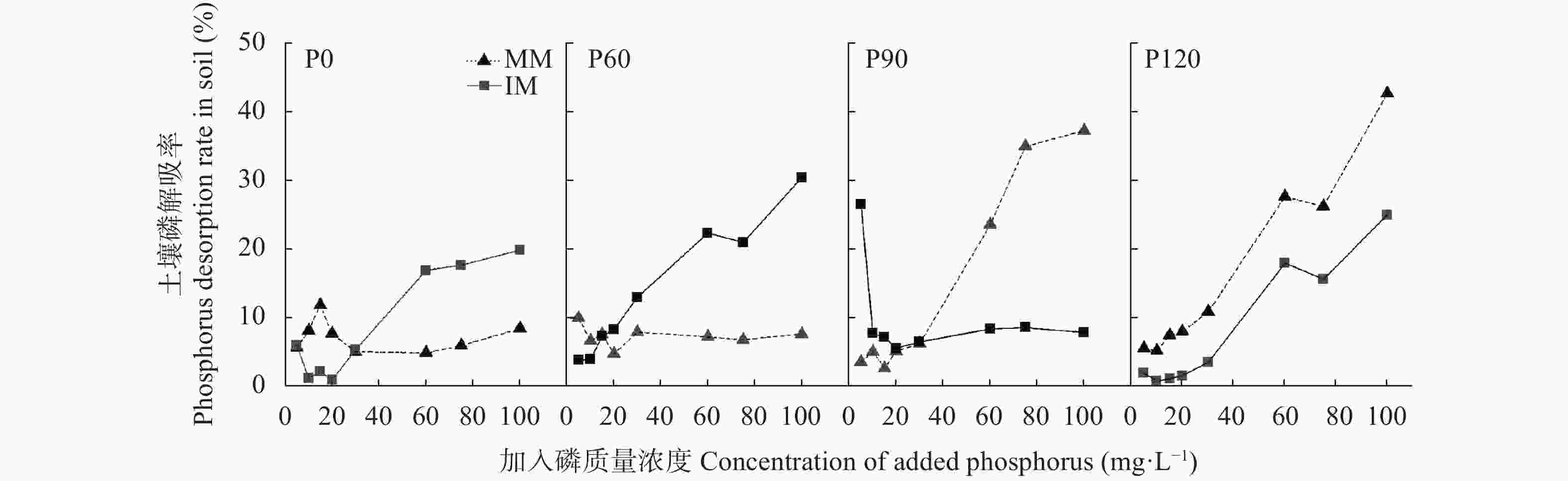
图 4 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷解吸率变化特征
P0、P60、P90、P120说明见图2的图注。
Figure 4. Characteristics of desorption rates of soil phosphorus of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
Description of P0, P60, P90, P120 are shown in the note of Figure 2.
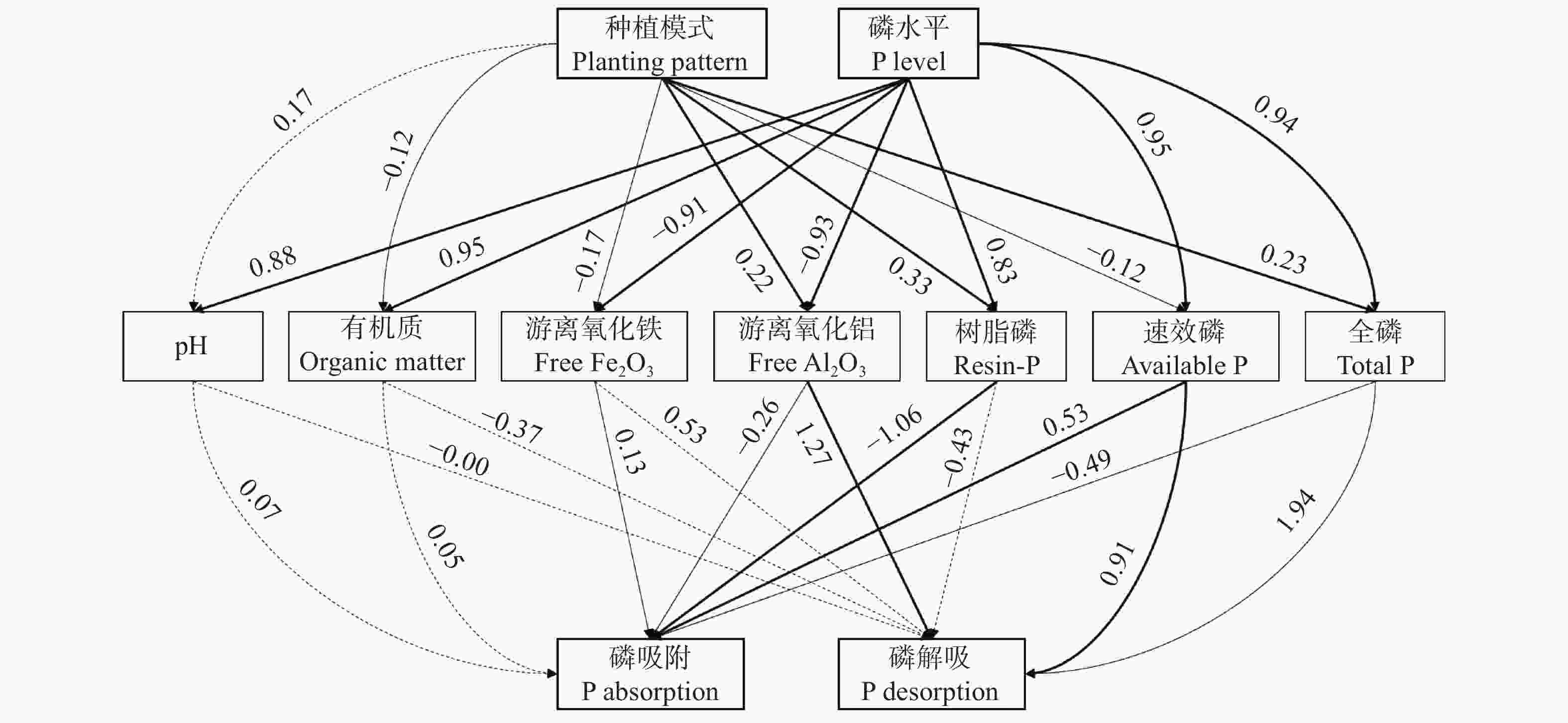
图 5 结构模型方程分析不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作和玉米单作土壤性质与磷吸附和解吸附的因果关系
细实线、粗实线和虚线箭头表示显著(P<0.05)、极显著(P<0.01)和不显著(P>0.05)路径, χ2 =57.70, Df.=17, P<0.01。The thin lines, thick lines, and dotted arrows indicate significant (P<0.05), very significant (P<0.01), and no significant (P>0.05) path. χ2 =57.70, Df.=17, P<0.01.
Figure 5. Structural equation model analysis of causal relationships among soil properties and phosphorus (P) adsorption, desorption of maize-soybean intercropping and maize monoculture systems under different phosphorus levels
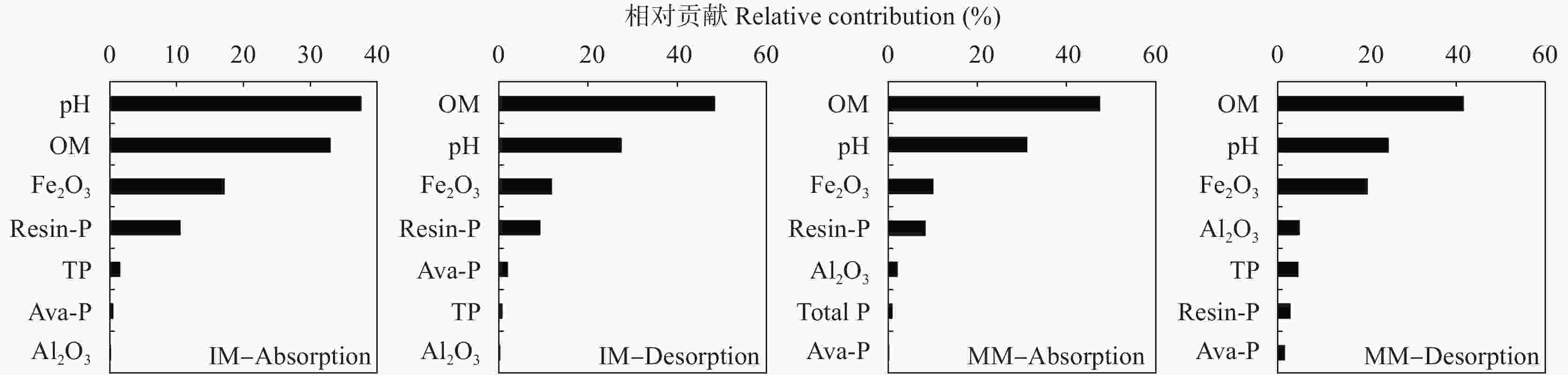
图 6 基于邻接树法分析玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)土壤因子对磷吸附(Absorption)和解吸(Desorption)的相对作用
OM为有机质, Fe2O3为游离氧化铁, Resin-P为树脂磷, TP为全磷, Ava-P为速效磷, Al2O3为游离氧化铝。OM is organic matter, Fe2O3 is free Fe2O3, Resin-P is resin phosphorus, TP is total phosphorus, Ava-P is available phosphorus, Al2O3 is free Al2O3.
Figure 6. Aggregated boosted tree (ABT) analysis for relative importance of soil chemical properties for phosphorus absorption and desorption of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems
表 1 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷等温吸附方程
Table 1. Equations of adsorption isotherms of phosphorus (P) in soil of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
处理
TreatmentLangmuir 方程 Langmuir equation Freundlich 方程 Freundlich equation Temkin 方程 Temkin equation C/Q=C/Qm+1/K1×Qm R2 Q=K2×C1/n R2 Q=a+K3lnC R2 P0 IM C/Q=0.001 30C+0.025 29 0.990** Q=233.560C0.239 0.932* Q=227.585+92.4259lnC 0.948* MM C/Q=0.001 60C+0.004 295 0.990** Q=73.682C0.511 0.993** Q=−58.744+151.8457lnC 0.971** P60 IM C/Q=0.001 60C+0.022 52 0.940* Q=146.870C0.299 0.981** Q=132.150+85.2624lnC 0.966** MM C/Q=0.001 85C+0.010 81 0.980** Q=54.640C0.511 0.945* Q=−102.068+130.4687lnC 0.935* P90 IM C/Q=0.001 66C+0.023 42 0.990** Q=91.126C0.413 0.963** Q=4.501+116.5802lnC 0.988** MM C/Q=0.001 70C+0.022 94 0.990** Q=31.421C0.600 0.986** Q=−48.210+97.3087lnC 0.883* P120 IM C/Q=0.001 73C+0.053 17 0.990** Q=81.520C0.421 0.952** Q=−33.856+119.6437lnC 0.970** MM C/Q=0.001 67C+0.029 91 0.960** Q=48.804C0.497 0.962** Q=−114.631+120.6803lnC 0.991** P0、P60、P90、P120说明见图2的图注。C为平衡溶液磷浓度, Q为土壤对磷吸附量, Qm为磷最大吸附量, K1为吸附亲和力常数, K2、K3为吸附容量指标, 1/n、a为吸附强度系数。Description of P0, P60, P90, P120 are shown in the note of Figure 2. C is phosphorus content at equilibrium solution; Q is phosphorus adsorbed capacity; Qm is phosphorus maximum adsorbed capacity; K1 is adsorption affinity constant; K2 and K3 are adsorption capacity indexes; “1/n” and “a” are adsorption strength coefficients. 表 2 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷吸附量及等温吸附参数
Table 2. Soil phosphorus (P) absorption and its isothermal adsorption parameters of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
处理 Treatment 吸附量
Absorption
(mg∙kg−1)最大吸附量
Maximal
adsorption (mg∙kg−1)吸附亲和力常数
Adsorption affinity
constant最大缓冲容量
Maximum buffer
capacity (mg∙kg−1)标准需磷量
Standard P
requirement (mg∙kg−1)磷吸持指数
P sorption
index吸附饱和度
Degree of P
saturation (%)P0 IM 387.68a 768.04a 0.051bc 39.55c 7.75c 18.48ab 0.379f MM 342.98b 626.47b 0.172a 132.85a 43.38a 19.73a 0.455f P60 IM 334.75bc 625.15b 0.071b 44.41c 8.75c 15.25bc 1.528d MM 280.34d 541.67e 0.171a 92.50b 17.91b 13.89cd 1.285e P90 IM 309.90c 601.15bc 0.071b 42.70c 8.42c 14.69c 1.652cd MM 219.06f 588.42bc 0.074b 43.60c 8.58c 11.09e 1.720c P120 IM 310.97c 579.09d 0.032c 18.81d 3.68d 15.46bc 2.229a MM 250.96e 598.97bc 0.056bc 33.43c 6.63cd 12.28de 1.997b 种植模式 Planting pattern (Pp) ** ** ** ** ** ** * 施磷量 P level (P) ** ** ** ** ** ** ** Pp×P ns ** ** ** ** ns ** P0、P60、P90、P120说明见图2的图注。同列数值后不同字母表示处理间差异达P<0.05显著水平; *和**分别表示达P<0.05和P<0.01显著水平, ns表示未达显著水平。Description of P0, P60, P90, P120 are shown in the note of Figure 2. Data followed by different letters in the same column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** denote significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; ns denotes not significant. 表 3 不同施磷水平下玉米||大豆间作(IM)和玉米单作(MM)的土壤磷解吸量及滞后系数
Table 3. Desorption and desorption hysteresis coefficients of phosphorus in soil of maize-soybean intercropping (IM) and maize monoculture (MM) systems under different phosphorus levels
处理
Treatment解吸量
Desorption
(mg·kg−1)解吸率
Desorption
rate (%)滞后系数
Hysteresis
coefficientP0 IM 45.11bc 11.68c 0.88b MM 23.71d 6.95d 0.93a P60 IM 58.72a 17.55b 0.82c MM 19.94d 7.07d 0.93a P90 IM 24.43d 7.86d 0.92a MM 51.04ab 23.45a 0.77d P120 IM 37.82c 12.19c 0.88b MM 57.41a 22.89a 0.77d 种植模式 Planting pattern (Pp) ns ** ** 施磷量 Phosphorus level (P) ** ** ** Pp×P ** ** ** P0、P60、P90、P120说明见图2的图注。同列数值后不同字母表示处理间差异达P<0.05显著水平; *和**分别表示达P<0.05和P<0.01显著水平, ns表示未达显著水平。Description of P0, P60, P90, P120 are shown in the note of Figure 2. Data followed by different letters in the same column are significantly different at P<0.05 level. * and ** denote significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; ns denotes not significant. 表 4 玉米||大豆间作和玉米单作红壤性质与磷吸附解吸特征参数的相关性
Table 4. Relationship between red soil properties and phosphorus (P) sorption-desorption parameters of maize-soybean intercropping and maize monoculture systems
指标
IndexpH 有机质
Organic matter游离氧化铁
Free Fe2O3游离氧化铝
Free Al2O3树脂磷
Resin-Pi有效磷
Olsen-P全磷
Total P标准需磷量
Standard P requirement磷吸持指数
P sorption index吸附饱和度
Degree of P saturation吸附量 Absorption −0.645** −0.609** 0.678** 0.692** −0.886** −0.612** −0.735** 0.212 0.931** −0.645** 解吸量 Desorption 0.232 0.278 −0.121 −0.200 0.189 0.372 0.394 −0.518** −0.276 0.302 **表示极显著相关(P<0.01); *表示显著相关(P<0.05)。** represents significant correlation at P<0.01 level; * represents significant correlation at P<0.05 level. -
[1] 张新明, 李华兴, 刘远金. 磷酸盐在土壤中吸附与解吸研究进展[J]. 土壤与环境, 2001, 10(1): 77−80ZHANG X M, LI H X, LIU Y J. Study progress of phosphate adsorption and desorption in soils[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2001, 10(1): 77−80 [2] 王夏晖, 尹澄清, 颜晓, 等. 流域土壤基质与非点源磷污染物作用的3种模式及其环境意义[J]. 环境科学, 2004, 25(4): 123−128 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2004.04.026WANG X H, YIN C Q, YAN X, et al. Three patterns of interaction between soil and non-point source P-pollutants in agricultural watershed[J]. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(4): 123−128 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2004.04.026 [3] QUESADA C A, LLOYD J, ANDERSON L O, et al. Soils of Amazonia with particular reference to the RAINFOR sites[J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(6): 1415−1440 doi: 10.5194/bg-8-1415-2011 [4] 夏瑶, 娄运生, 杨超光, 等. 几种水稻土对磷的吸附与解吸特性研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(11): 1369−1374 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2002.11.012XIA Y, LOU Y S, YANG C G, et al. Characteristics of phosphate adsorption and desorption in paddy soils[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35(11): 1369−1374 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2002.11.012 [5] 赵庆雷, 王凯荣, 谢小立. 长期有机物循环对红壤稻田土壤磷吸附和解吸特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(1): 355−362 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.01.046ZHAO Q L, WANG K R, XIE X L. Effects of organic nutrient recycling on phosphorus adsorption-desorption characteristics in a reddish paddy rice system[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(1): 355−362 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.01.046 [6] 罗敏, 王旭东. 不同肥力土的土壤颗粒分布及其磷素吸附-解析规律[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2008, 26(6): 106−109LUO M, WANG X D. Distribution of particles size and their phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of Lou soils with different fertility[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2008, 26(6): 106−109 [7] 李寿田, 周健民, 王火焰, 等. 不同土壤磷的固定特征及磷释放量和释放率的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, 40(6): 908−914 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2003.06.016LI S T, ZHOU J M, WANG H Y, et al. Characteristics of fixation and release of phosphorus in three soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003, 40(6): 908−914 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2003.06.016 [8] 来璐, 郝明德, 彭令发. 土壤磷素研究进展[J]. 水土保持研究, 2003, 10(1): 65−67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2003.01.019LAI L, HAO M D, PENG L F. Development of researches on soil phosphorus[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003, 10(1): 65−67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2003.01.019 [9] 李杰, 石元亮, 陈智文. 我国南方红壤磷素研究概况[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(3): 763−768LI J, SHI Y L, CHEN Z W. Research on phosphorus in southern red soils of in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(3): 763−768 [10] ZHANG Y H, HUANG S M, GUO D D, et al. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of different textural fluvo-aquic soils under long-term fertilization[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(3): 1306−1318 doi: 10.1007/s11368-018-2122-0 [11] DEBICKA M, KOCOWICZ A, WEBER J, et al. Organic matter effects on phosphorus sorption in sandy soils[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2016, 62(6): 840−855 doi: 10.1080/03650340.2015.1083981 [12] ARAI Y, SPARKS D L. Phosphate reaction dynamics in soils and soil components: a multiscale approach[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 2007, 94: 135−179 [13] 闫金龙, 吴文丽, 江韬, 等. 土壤组分对磷形态和磷吸附-解吸的影响−基于三峡库区消落带落干期土壤[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(3): 1124−1131 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.03.028YAN J L, WU W L, JIANG T, et al. Effect of organic matter and iron oxides on phosphorus forms and adsorption-desorption on dry-period soils in the water-level-fluctuating zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(3): 1124−1131 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.03.028 [14] 陈波浪, 盛建东, 蒋平安, 等. 不同质地棉田土壤对磷吸附与解吸研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(2): 303−307CHEN B L, SHENG J D, JIANG P A, et al. Study on characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption of cotton field with different soil textures[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(2): 303−307 [15] 韩旭, 吴东洋, 王新刚. 不同土壤对磷的吸附特性研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2011, (20): 285−286 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.20.185HAN X, WU D Y, WANG X G. Study on the adsorption characteristics of phosphorus in different soils[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011, (20): 285−286 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.20.185 [16] 王斌, 刘骅, 李耀辉, 等. 长期施肥条件下灰漠土磷的吸附与解吸特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(4): 726−733WANG B, LIU H, LI Y H, et al. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of gray desert soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(4): 726−733 [17] 杨艳芳, 孔令柱, 郑真, 等. 退耕还湖后湿地土壤对磷的吸附解吸特性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(4): 1063−1068YANG Y F, KONG L Z, ZHENG Z, et al. Characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption of soils from wetlands recovered from farmlands in Caizi Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(4): 1063−1068 [18] 邱亚群, 甘国娟, 刘伟, 等. 不同利用方式土壤中磷的吸附与解吸特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(7): 2757−2762QIU Y Q, GAN G J, LIU W, et al. Characteristics of phosphate adsorption and desorption in soils under different utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(7): 2757−2762 [19] 徐敏, 宋春, 毛璐, 等. 不同土地利用方式下紫色土磷吸附—解吸动力学特征[J]. 水土保持通报, 2015, 35(5): 39−44XU M, SONG C, MAO L, et al. Dynamics of phosphorus adsorption-desorption in purple soil under different land use types[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 35(5): 39−44 [20] 王琼, 展晓莹, 张淑香, 等. 长期不同施肥处理黑土磷的吸附-解吸特征及对土壤性质的响应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(21): 3866−3877 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.21.015WANG Q, ZHAN X Y, ZHANG S X, et al. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics and its response to soil properties of black soil under long-term different fertilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(21): 3866−3877 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.21.015 [21] 李想, 刘艳霞, 刘益仁, 等. 有机无机肥配合对土壤磷素吸附、解吸和迁移特性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2013, 27(2): 253−259 doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2013.02.0253LI X, LIU Y X, LIU Y R, et al. Interactive effects of combined inorganic and organic fertilizers on phosphorous adsorption, desorption and mobility[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 27(2): 253−259 doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2013.02.0253 [22] 李仁英, 吴洪生, 黄利东, 等. 不同来源生物炭对土壤磷吸附解吸的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(6): 1398−1403LI R Y, WU H S, HUANG L D, et al. Effect of biochar of different sources on adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(6): 1398−1403 [23] 彭启超, 刘小华, 罗培宇, 等. 不同原料生物炭对氮、磷、钾的吸附和解吸特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(10): 1763−1772 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18406PENG Q C, LIU X H, LUO P Y, et al. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by biochars from different raw materials[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(10): 1763−1772 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18406 [24] 龚振平, 杜婷婷, 闫超, 等. 玉米秸秆还田及施磷量对黑土磷吸附与解吸特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(22): 161−169 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.22.019GONG Z P, DU T T, YAN C, et al. Effects of corn straw returning and phosphorus application rate on phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of black soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(22): 161−169 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.22.019 [25] XIA H Y, WANG Z G, ZHAO J H, et al. Contribution of interspecific interactions and phosphorus application to sustainable and productive intercropping systems[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 154: 53−64 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2013.07.011 [26] LI X F, WANG C B, ZHANG W P, et al. The role of complementarity and selection effects in P acquisition of intercropping systems[J]. Plant and Soil, 2018, 422(1/2): 479−493 [27] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999: 18, 638LU R K. Soil Argrochemistry Analysis Protocols[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Science and Technology Press, 1999: 18, 638 [28] 夏文建, 冀建华, 刘佳, 等. 长期不同施肥红壤磷素特征和流失风险研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(12): 1876−1886XIA W J, JI J H, LIU J, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil phosphorus characteristics and loss risk of red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(12): 1876−1886 [29] HUANG W L, WEBER W J. A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 10. relationships between desorption, hysteresis, and the chemical characteristics of organic domains[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(9): 2562−2569 [30] 吴明隆. 结构方程模型: AMOS的操作与应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2009WU M L. Structure Equation Model: The Operation and Application of AMOS[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2009 [31] DE'ATH G. Boosted trees for ecological modeling and prediction[J]. Ecology, 2007, 88(1): 243−251 doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2007)88[243:BTFEMA]2.0.CO;2 [32] BALEMI T, NEGISHO K. Management of soil phosphorus and plant adaptation mechanisms to phosphorus stress for sustainable crop production: a review[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2012, 12: 547−562 [33] 曹志洪, 李庆逵. 黄土性土壤对磷的吸附与解吸[J]. 土壤学报, 1988, 25(3): 218−226CAO Z H, LI Q K. Phosphorus sorption and desorption isotherms for some loessial soils of North China Plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1988, 25(3): 218−226 [34] 何振立, 朱祖祥, 袁可能, 等. 土壤对磷的吸持特性及其与土壤供磷指标之间的关系[J]. 土壤学报, 1988, 25(4): 397−404HE Z L, ZHU Z X, YUAN K N, et al. Potential phosphate sorptivity value from Langmuir equation and its application for phosphate fertilizer recommendation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1988, 25(4): 397−404 [35] VU D T, TANG C, ARMSTRONG R D. Changes and availability of P fractions following 65 years of P application to a calcareous soil in a Mediterranean climate[J]. Plant and Soil, 2008, 304(1/2): 21−33 [36] 张海涛, 刘建玲, 廖文华, 等. 磷肥和有机肥对不同磷水平土壤磷吸附-解吸的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(2): 284−290 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2008.02.013ZHANG H T, LIU J L, LIAO W H, et al. Effect of phosphate fertilizer and manure on properties of phosphorus sorption and desorption in soils with different phosphorus levels[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(2): 284−290 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2008.02.013 [37] BARROW N J, DEBNATH A. Effect of phosphate status on the sorption and desorption properties of some soils of northern India[J]. Plant and Soil, 2014, 378(1/2): 383−395 [38] WANG L Q, LIANG T. Effects of exogenous rare earth elements on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in different types of soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 103: 148−155 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.050 [39] SHARPLEY A N, MCDOWELL R W, KLEINMAN P J A. Phosphorus loss from land to water: integrating agricultural and environmental management[J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237(2): 287−307 doi: 10.1023/A:1013335814593 [40] 张鑫, 谷会岩, 陈祥伟. 择伐干扰对小兴安岭阔叶红松林土壤磷吸附解吸的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(1): 11−17ZHANG X, GU H Y, CHEN X W. Effects of selective cutting disturbance on soil phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a Korean pine and broad-leaved mixed forest in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(1): 11−17 [41] VARINDERPAL-SINGH, DHILLON N S, BRAR B S. Influence of long-term use of fertilizers and farmyard manure on the adsorption-desorption behaviour and bioavailability of phosphorus in soils[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2006, 75(1/2/3): 67−78 [42] LI M, HOU Y L, ZHU B. Phosphorus sorption-desorption by purple soils of China in relation to their properties[J]. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 2007, 45(3): 182−189 doi: 10.1071/SR06135 [43] DJODJIC F, BÖRLING K, BERGSTRÖM L. Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(2): 678−684 doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.6780 [44] 马良, 徐仁扣. pH和添加有机物料对3种酸性土壤中磷吸附-解吸的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2010, 26(6): 596−599 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.06.016MA L, XU R K. Effects of regulation of pH and application of organic material on adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in three types of acid soils[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2010, 26(6): 596−599 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.06.016 [45] 夏汉平, 高子勤. 磷酸盐在土壤中的竞争吸附与解吸机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 1993, 4(1): 89−93 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.01.001XIA H P, GAO Z Q. Mechanisms of competitive adsorption and desorption of phosphate in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1993, 4(1): 89−93 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.01.001 [46] 王而力, 王嗣淇, 徐颖. 沙土不同粒径微团聚体对磷的富集特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(3): 827−834WANG E L, WANG S Q, XU Y. Enrichment characteristics of phosphorus on micro-aggregates in different sizes of sandy soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(3): 827−834 [47] 甘海华, 徐盛荣. 红壤及其有机无机复合体对磷的吸附与解吸规律探讨[J]. 土壤通报, 1994, 25(6): 264−266 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.1994.06.005GAN H H, XU S R. Study on P adsorption-desorption characteristics of red soil and its organo-mineral complexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1994, 25(6): 264−266 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.1994.06.005 -





 下载:
下载: