-
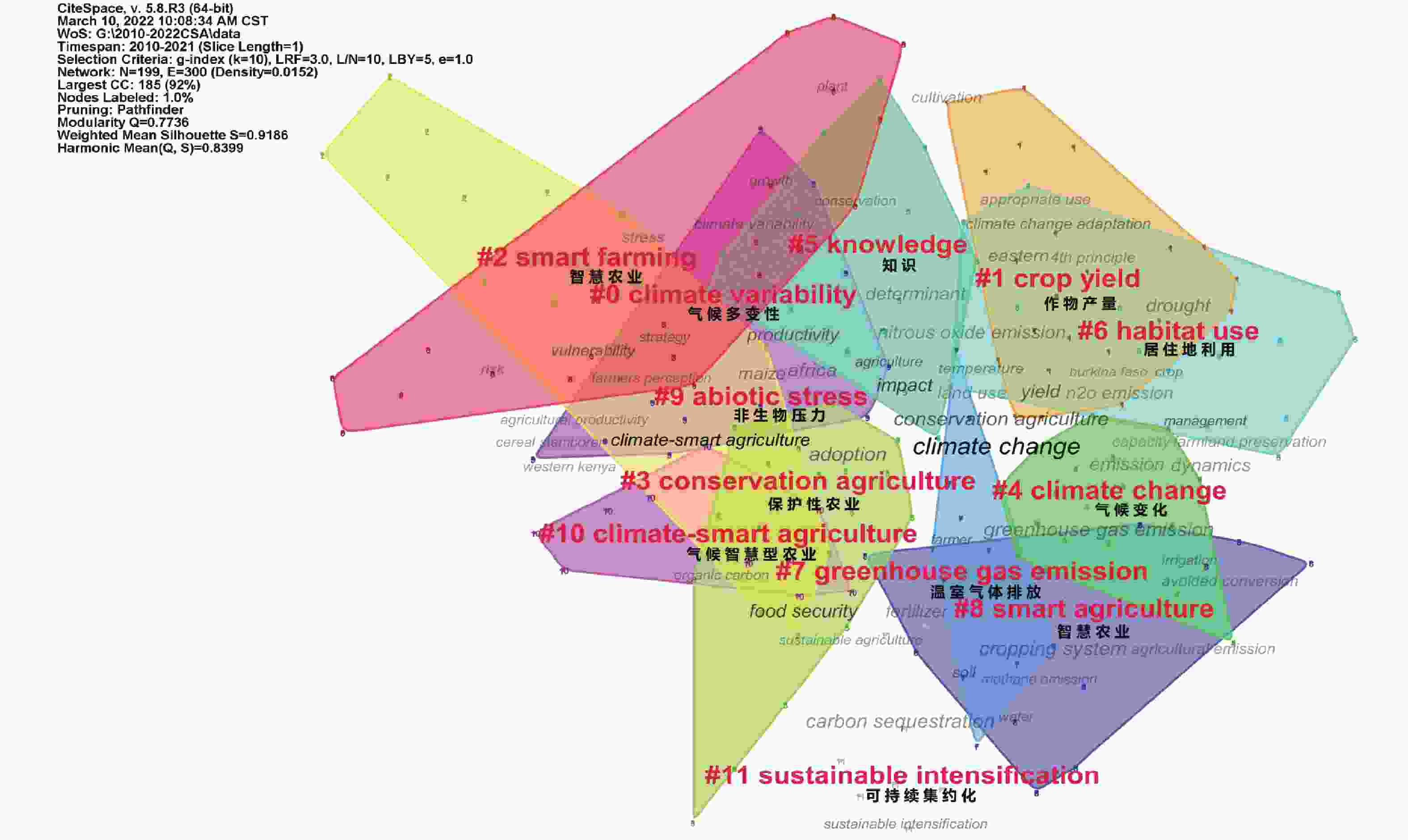
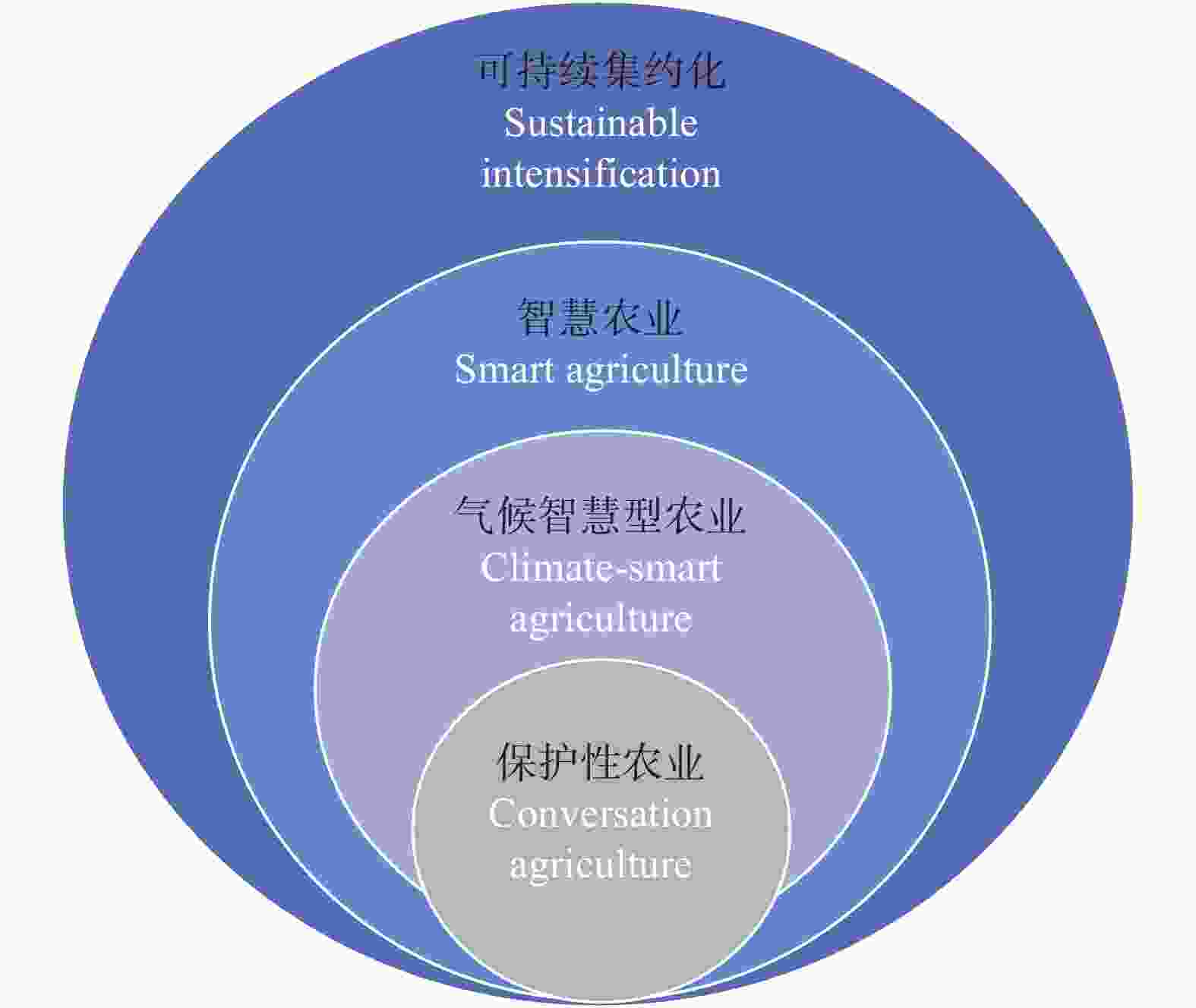
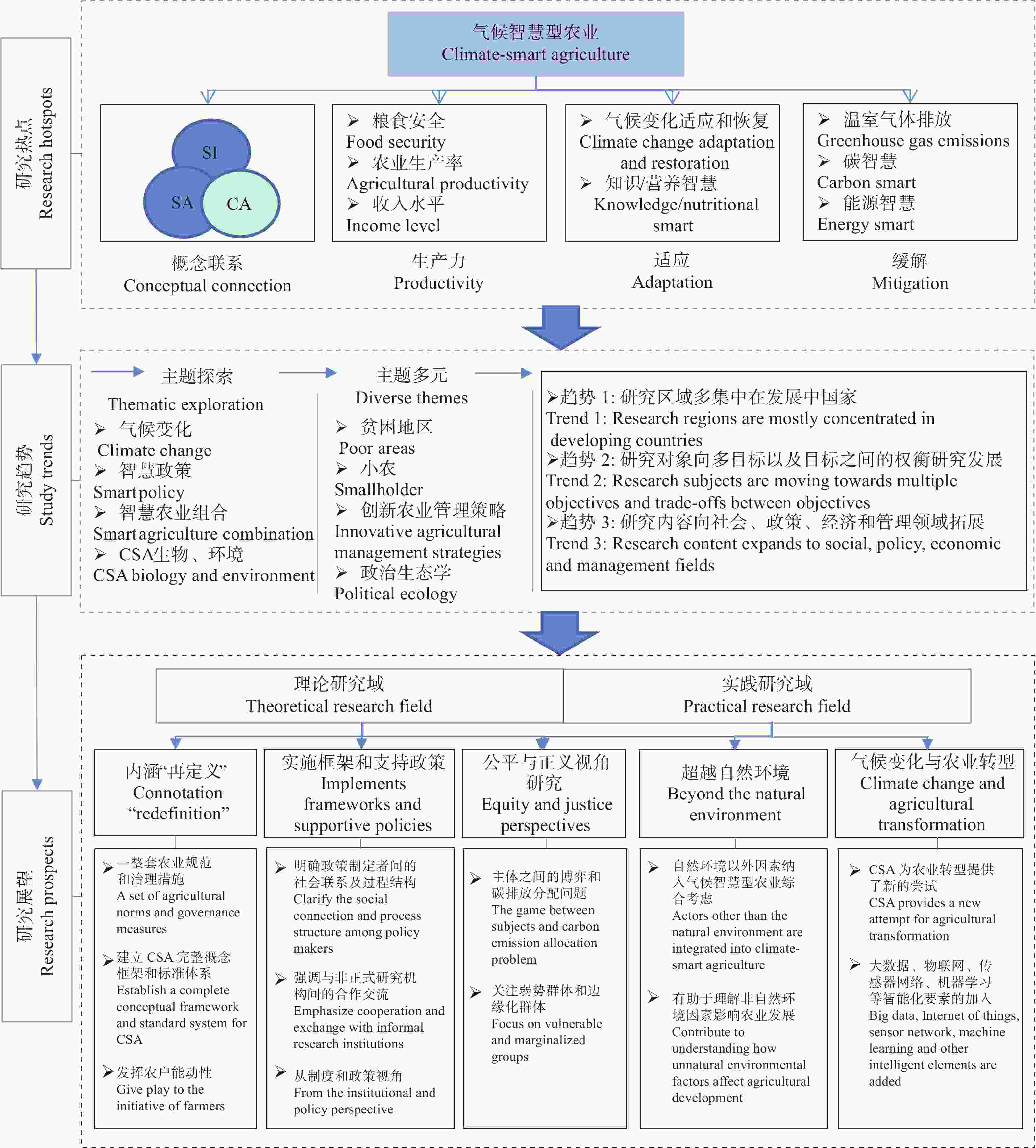
摘要: 气候智慧型农业(climate-smart agriculture, CSA)作为应对气候变化和粮食安全双挑战的高潜力农业系统解决方案, 一经提出就受到了国际各界的高度重视, 而中国的CSA研究项目进展缓慢, 且尚未引起学术界的广泛关注。本研究借助CiteSpace (5.8.R3)软件, 选取Web of Science核心数据集, 对2010—2021年的国际CSA研究文献进行分析, 梳理了国外研究热点与趋势变化, 并提出新的展望思考, 为我国CSA发展提供理论和实践支撑。研究结果表明: 1) CSA已形成多维度平衡农业与气候变化的完整概念框架; 2) CSA与可持续集约化、智慧农业、保护性农业等研究交织融合发展, 研究热点围绕着生产力、适应、缓解这“3个支柱”展开; 3) CSA研究趋势有泛化倾向, 表现在研究区域转向发展中国家, 研究对象注重多目标, 研究内容涉及多领域。最后, 对CSA的未来研究趋势进行展望, 将更关注其内涵探索、实施框架制定、脆弱群体需求、跨学科合作和农业转型等方面。此外, 本文强调, CSA作为应对气候变化的农业发展新模式, 其理论框架和实践技术对中国农业转型具有理论和实践的双重意义, 其在中国的应用与适应发展是一个亟待开拓探究和富有挑战的领域。Abstract: Climate-smart agriculture (CSA), a high-potential agricultural system solution to the dual challenges of climate change and food security, received great attention from researchers worldwide as soon as it was proposed. However, the progress of CSA research projects in China is slow and has not attracted widespread attention from the academic community. Using the CiteSpace (5.8. R3) software, this study selected the core data set of the Web of Science to analyze the international CSA research literatures from 2010 to 2021, sorted out foreign research hotspots and trends, and put forward new outlooks to provide theoretical and practical support for the development of CSA in China. The research results were as follows: 1) CSA had formed a complete conceptual framework for balancing agriculture and climate change in multiple dimensions. 2) CSA and sustainable intensification, smart agriculture (smart farming), conservation agriculture, and other researches were intertwined and developed, and research hotspots revolved around “three pillars”: productivity, adaptation, and mitigation. 3) The trend of CSA research tended to be generalized, and the research areas covered developing countries, research objects focused on multiple goals, and research content covered multiple fields. Finally, according to future research trends, CSA was predicted to pay more attention to its connotation exploration, implementation framework formulation, vulnerable group needs, interdisciplinary cooperation, and agricultural transformation. In addition, this study emphasizes that as a new model of agricultural development in response to climate change, the theoretical framework and practical technologies of CSA have both theoretical and practical significance for agricultural transformation in China, and its application and adaptive development in China is an area that needs to be urgently investigated.
-
Key words:
- Climate change /
- Climate-smart agriculture /
- Three Pillars /
- CiteSpace
-
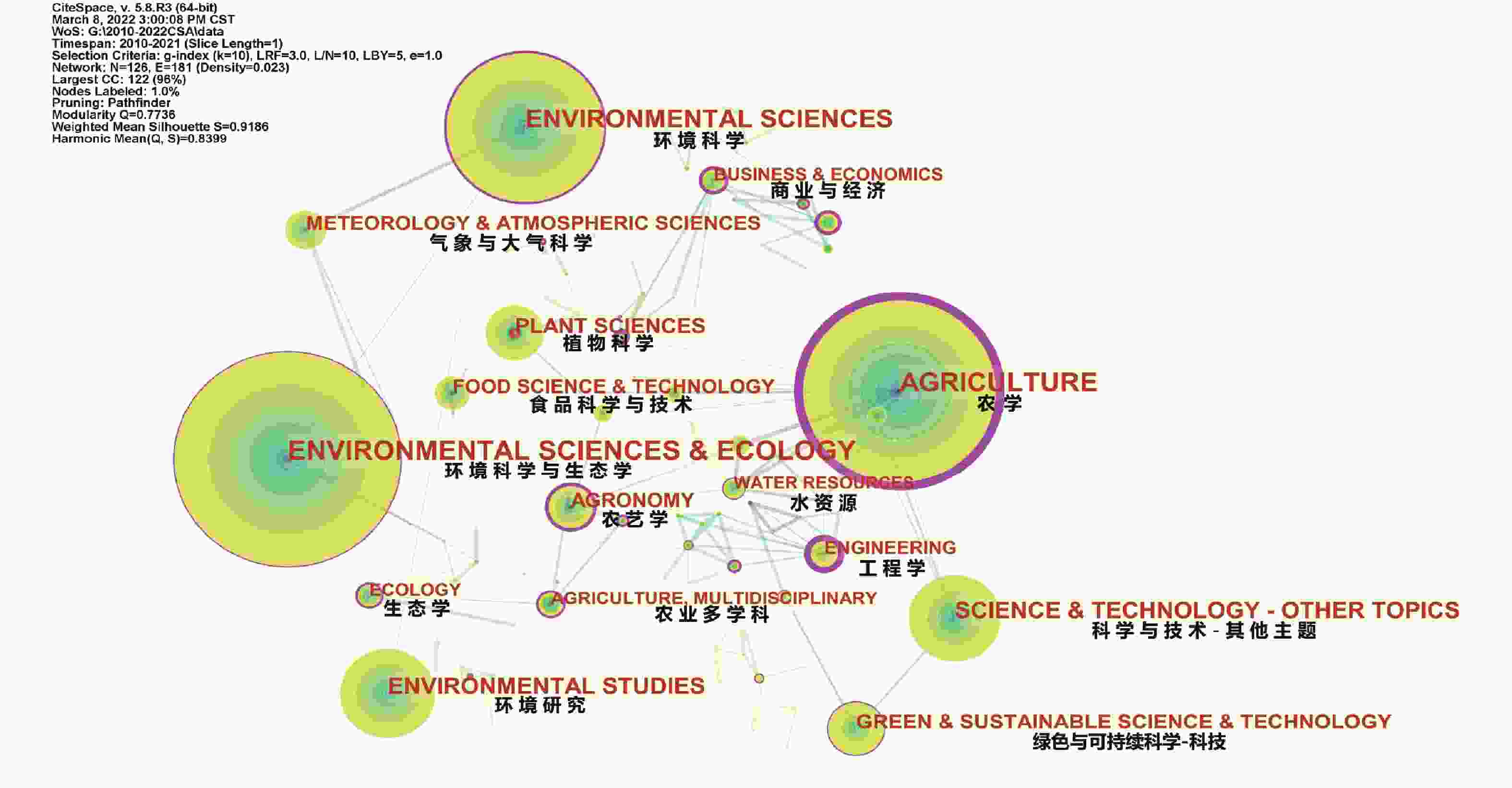
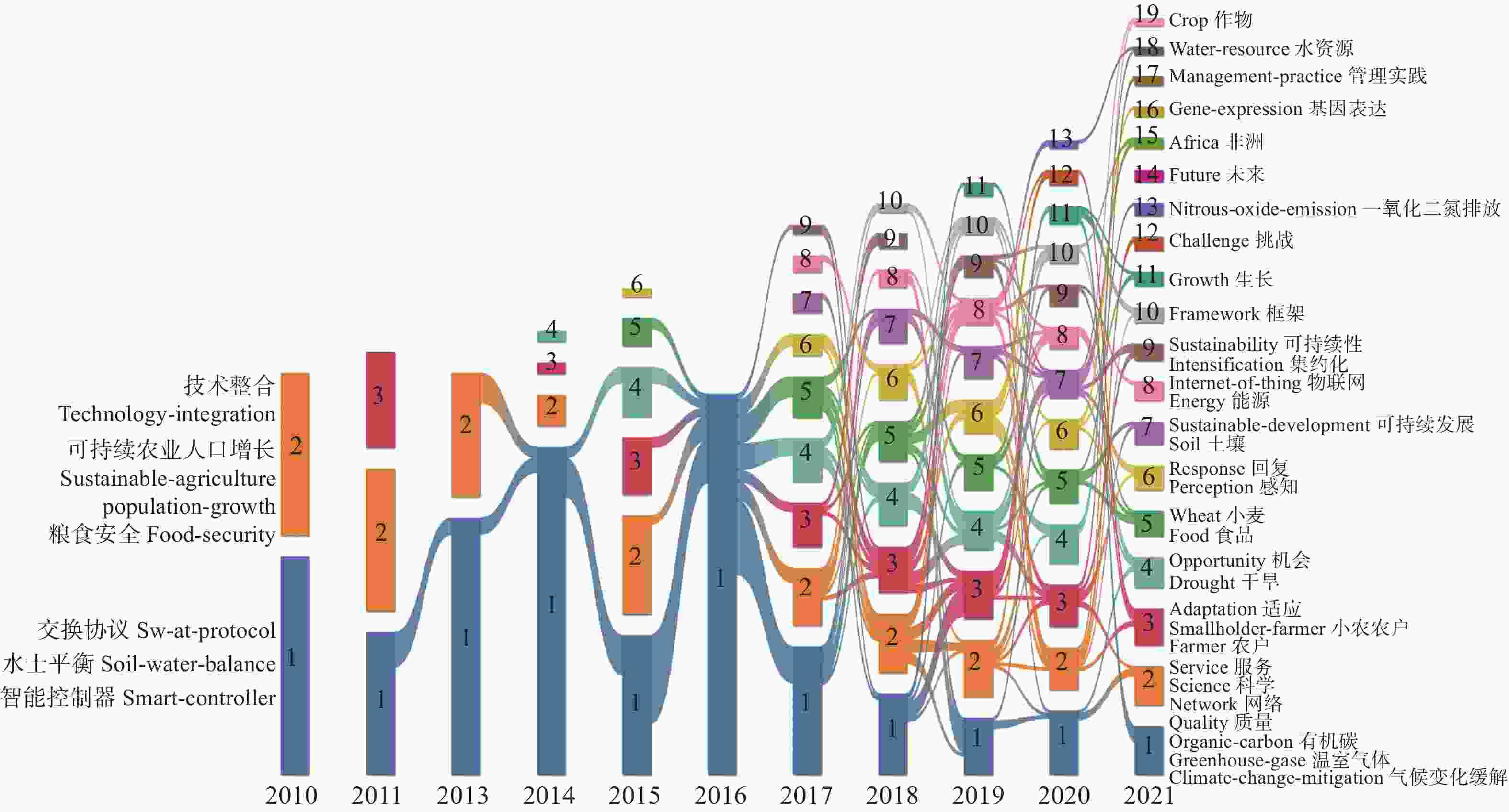
表 1 Web of Science数据库中气候智慧型农业研究排名前5位学科分布情况
Table 1. Distribution of top 5 subjects in climate-smart agriculture (CSA) research ranking in Web of Science database
序号
Serial number学科领域
Academic area学科类别
Subject category频率
Frequency中心性
Centrality1 环境科学与生态学 Environmental sciences and ecology 理学 Science 297 0.16 2 农学 Agriculture 农学 Agronomy 253 1.22 3 环境科学 Environment sciences 理学 Science 209 0.24 4 环境研究 Environment studies 理学 Science 128 0.06 5 科学与技术-其他主题 Science and technology-other topics 理学 Science 123 0.09 -
[1] AKINBAMI J F K. Renewable energy resources and technologies in Nigeria: present situation, future prospects and policy framework[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2001, 6(2): 155−182 doi: 10.1023/A:1011387516838 [2] WHEELER T, VON BRAUN J. Climate change impacts on global food security[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6145): 508−513 doi: 10.1126/science.1239402 [3] NKEMELANG T, NEW M, ZAROUG M. Temperature and precipitation extremes under current, 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ global warming above pre-industrial levels over Botswana, and implications for climate change vulnerability[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2018, 13(6): 065016 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aac2f8 [4] SCHLEUSSNER C F, LISSNER T K, FISCHER E M, et al. Differential climate impacts for policy-relevant limits to global warming: The case of 1.5 ℃ and 2 ℃[J]. Earth System Dynamics Discussions, 2015, 6(2): 2447−2505 [5] MAKATE C. Effective scaling of climate smart agriculture innovations in African smallholder agriculture: a review of approaches, policy and institutional strategy needs[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2019, 96: 37−51 [6] CARTER M R, LITTLE P D, MOGUES T, et al. Poverty traps and natural disasters in Ethiopia and Honduras[J]. World Development, 2007, 35(5): 835−856 doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2006.09.010 [7] TAYLOR M. Climate-smart agriculture: what is it good for?[J]. The Journal of Peasant Studies, 2018, 45(1): 89−107 doi: 10.1080/03066150.2017.1312355 [8] DAS S, GWON H S, KHAN M I, et al. Taxonomic and functional responses of soil microbial communities to slag-based fertilizer amendment in rice cropping systems[J]. Environment International, 2019, 127: 531−539 doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.012 [9] DE NIJS P J, BERRY N J, WELLS G J, et al. Quantification of biophysical adaptation benefits from Climate-Smart Agriculture using a Bayesian Belief Network[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6682 [10] ADGER W N, ARNELL N W, TOMPKINS E L. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2005, 15(2): 77−86 doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.12.005 [11] VERMEULEN S J, CAMPBELL B M, INGRAM J S I. Climate change and food systems[J]. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2012, 37: 195−222 doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-020411-130608 [12] THORNTON P K, WHITBREAD A, BAEDEKER T, et al. A framework for priority-setting in climate smart agriculture research[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2018, 167: 161−175 doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2018.09.009 [13] MANALO J A IV, BALMEO K P, BERTO J C, et al. Integrating climate-smart rice agriculture into secondary-level curriculum: lessons from three high schools in the Philippines[J]. SpringerPlus, 2016, 5(1): 1592 doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-3238-6 [14] HASAN M K, DESIERE S, D’HAESE M, et al. Impact of climate-smart agriculture adoption on the food security of coastal farmers in Bangladesh[J]. Food Security, 2018, 10(4): 1073−1088 doi: 10.1007/s12571-018-0824-1 [15] 杭晓宁, 罗佳, 张鹏程, 等. 西南地区发展气候智慧型农业的对策建议[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 8−15 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0617HANG X N, LUO J, ZHANG P C, et al. Countermeasures on developing climate-smart agriculture in Southwest China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 8−15 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0617 [16] 王一杰, 管大海, 王全辉, 等. 气候智慧型农业在我国的实践探索[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(10): 43−50WANG Y J, GUAN D H, WANG Q H, et al. The practical exploration of climate-smart agriculture in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(10): 43−50 [17] 陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究, 2015, 33(2): 242−253 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2053.2015.02.009CHEN Y, CHEN C M, LIU Z Y, et al. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains[J]. Studies in Science of Science, 2015, 33(2): 242−253 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2053.2015.02.009 [18] KERRI L S, AMANDA K H, BLOOM A J. Climate-smart agriculture global research agenda: scientific basis for action[J]. Agriculture and Food Security, 2014, 3(11): 1−39 [19] PRETTY J, BHARUCHA Z P. Integrated pest management for sustainable intensification of agriculture in Asia and Africa[J]. Insects, 2015, 6(1): 152−182 doi: 10.3390/insects6010152 [20] PETERSEN B, SNAPP S. What is sustainable intensification? Views from experts[J]. Land Use Policy, 2015, 46: 1−10 doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.02.002 [21] VANLAUWE B, COYNE D, GOCKOWSKI J, et al. Sustainable intensification and the African smallholder farmer[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 2014, 8: 15−22 doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2014.06.001 [22] 曹冰雪, 李瑾, 冯献, 等. 我国智慧农业的发展现状、路径与对策建议[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2021, 42(5): 785−794 doi: 10.13872/j.1000-0275.2021.0091CAO B X, LI J, FENG X, et al. Development status, path, and countermeasures of smart agriculture in China[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2021, 42(5): 785−794 doi: 10.13872/j.1000-0275.2021.0091 [23] MIZIK T. Climate-smart agriculture on small-scale farms: a systematic literature review[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(6): 1096 doi: 10.3390/agronomy11061096 [24] MAKATE C, MAKATE M, MANGO N, et al. Increasing resilience of smallholder farmers to climate change through multiple adoption of proven climate-smart agriculture innovations. Lessons from Southern Africa[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 231: 858−868 [25] THIERFELDER C, CHIVENGE P, MUPANGWA W, et al. How climate-smart is conservation agriculture (CA)? — its potential to deliver on adaptation, mitigation and productivity on smallholder farms in southern Africa[J]. Food Security, 2017, 9(3): 537−560 doi: 10.1007/s12571-017-0665-3 [26] JOHANSEN C, HAQUE M E, BELL R W, et al. Conservation agriculture for small holder rainfed farming: opportunities and constraints of new mechanized seeding systems[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 132: 18−32 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.026 [27] FINDLATER K M, KANDLIKAR M, SATTERFIELD T. Misunderstanding conservation agriculture: challenges in promoting, monitoring and evaluating sustainable farming[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2019, 100: 47−54 [28] KASSAM A, FRIEDRICH T, SHAXSON F, et al. The spread of Conservation Agriculture: justification, sustainability and uptake[J]. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability, 2009, 7(4): 292−320 doi: 10.3763/ijas.2009.0477 [29] GARRITY D P, AKINNIFESI F K, AJAYI O C, et al. Evergreen agriculture: a robust approach to sustainable food security in Africa[J]. Food Security, 2010, 2(3): 197−214 doi: 10.1007/s12571-010-0070-7 [30] VAN WIJK M T, MERBOLD L, HAMMOND J, et al. Improving assessments of the three pillars of climate smart agriculture: current achievements and ideas for the future[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2020, 4: 558483 doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.558483 [31] 彭文龙, 吕晓, 辛宗斐, 等. 国际可持续集约化发展经验及其对中国耕地保护的启示[J]. 中国土地科学, 2020, 34(4): 18−25PENG W L, LYU X, XIN Z F, et al. International experience of sustainable intensification and its implications for the protection of cultivated land in China[J]. China Land Science, 2020, 34(4): 18−25 [32] PRETTY J, BHARUCHA Z P. Sustainable intensification in agricultural systems[J]. Annals of Botany, 2014, 114(8): 1571−1596 doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu205 [33] KLEIN R J T, SCHIPPER E L F, DESSAI S. Integrating mitigation and adaptation into climate and development policy: three research questions[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2005, 8(6): 579−588 [34] 宋臻, 史兴民. 雨养农业区农户的气候变化适应行为及影响因素路径分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(3): 461−473 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.011SONG Z, SHI X M. Path analysis of influencing factors of farmers’ adaptive behaviors to climate change in the rain-fed agricultural areas[J]. Progress in Geography, 2020, 39(3): 461−473 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.011 [35] 李红莉, 张俊飚, 张露, 等. 气候变化认知对农户适应性耕作行为的影响−基于湖北省“十县千户”的田野调查[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2021, 42(2): 236−248LI H L, ZHANG J B, ZHANG L, et al. Cognition of farmers’ climate change and its impact on adaptable tillage behavior — based on a thousand households’ field survey in ten counties of Hubei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2021, 42(2): 236−248 [36] SENYOLO M P, LONG T B, BLOK V, et al. How the characteristics of innovations impact their adoption: An exploration of climate-smart agricultural innovations in South Africa[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 172: 3825−3840 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.019 [37] HARVEY C A, CHACÓN M, DONATTI C I, et al. Climate-smart landscapes: opportunities and challenges for integrating adaptation and mitigation in tropical agriculture[J]. Conservation Letters, 2014, 7(2): 77−90 doi: 10.1111/conl.12066 [38] HARIHARAN V K, MITTAL S, RAY M, et al. Does climate-smart village approach influence gender equality in farming households? A case of two contrasting ecologies in India[J]. Climatic Change, 2018(1/2): 1−14 [39] PAUSTIAN K, LEHMANN J, OGLE S, et al. Climate-smart soils[J]. Nature, 2016, 532(7597): 49−57 doi: 10.1038/nature17174 [40] SMITH P. Soils and climate change[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 2012, 4(5): 539−544 doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2012.06.005 [41] 王军, 谭金凯. 气候变化背景下中国沿海地区灾害风险研究与应对思考[J]. 地理科学进展, 2021, 40(5): 870−882 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.013WANG J, TAN J K. Understanding the climate change and disaster risks in coastal areas of China to develop coping strategies[J]. Progress in Geography, 2021, 40(5): 870−882 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.013 [42] BAGLEY J E, MILLER J, BERNACCHI C J. Biophysical impacts of climate-smart agriculture in the Midwest United States[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015, 38(9): 1913−1930 [43] KHATRI-CHHETRI A, AGGARWAL P K, JOSHI P K, et al. Farmers’ prioritization of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) technologies[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2017, 151: 184−191 doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2016.10.005 [44] AGGARWAL P K, JARVIS A, CAMPBELL B M, et al. The climate-smart village approach: framework of an integrative strategy for scaling up adaptation options in agriculture[J]. Ecology and Society, 2018, 23(1): 14 doi: 10.5751/ES-09844-230114 [45] VERNOOY R, BOURONCLE C, ROQUE V S, et al. Sustainable territories adapted to the climate: insights from a new university course designed and delivered in Guatemala[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(12): 4978 doi: 10.3390/su12124978 [46] BACHELET D, JOHNSON B R, BRIDGHAM S D, et al. Climate change impacts on western Pacific northwest prairies and savannas[J]. Northwest Science, 2011, 85(2): 411−429 doi: 10.3955/046.085.0224 [47] KLERKX L, HALL A, LEEUWIS C. Strengthening agricultural innovation capacity: are innovation brokers the answer?[J]. International Journal of Agricultural Resources, Governance and Ecology, 2009, 8(5/6): 409 doi: 10.1504/IJARGE.2009.032643 [48] 梁志会, 张露, 张俊飚, 等. 小农发展气候智慧型农业的效率与成本改进: 倡导农地流转还是发展社会服务?[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(5): 1164−1175LIANG Z H, ZHANG L, ZHANG J B, et al. Improving efficiency and costs in developing climate-smart agriculture by smallholder farmers: enhancing land transfer or socialization services?[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(5): 1164−1175 [49] CHANDRA A, SHMELEV S. The relevance of political ecology perspectives for smallholder Climate-Smart Agriculture: a review[J]. Journal of Political Ecology, 2017, 24(1): 821−842 [50] CHANDRA A, MCNAMARA K E, DARGUSCH P. Climate-smart agriculture: perspectives and framings[J]. Climate Policy, 2018, 18(4): 526−541 doi: 10.1080/14693062.2017.1316968 [51] DOUXCHAMPS S, WIJK M T, SILVESTRI S, et al. Linking agricultural adaptation strategies, food security and vulnerability: evidence from West Africa[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2016, 16(5): 1305−1317 doi: 10.1007/s10113-015-0838-6 [52] AKROFI-ATITIANTI F, SPERANZA C I, BOCKEL L, et al. Assessing climate smart agriculture and its determinants of practice in Ghana: a case of the cocoa production system[J]. Land, 2018, 7(1): 30 doi: 10.3390/land7010030 [53] PARTEY S T, ZOUGMORÉ R B, OUÉDRAOGO M, et al. Developing climate-smart agriculture to face climate variability in West Africa: challenges and lessons learnt[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 187: 285−295 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.199 [54] ARYAL J P, RAHUT D B, MAHARJAN S, et al. Factors affecting the adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India[J]. Natural Resources Forum, 2018, 42(3): 141−158 doi: 10.1111/1477-8947.12152 [55] LOPEZ-RIDAURA S, FRELAT R, VAN WIJK M T, et al. Climate smart agriculture, farm household typologies and food security: an ex-ante assessment from eastern India[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2018, 159: 57−68 doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.09.007 [56] JAT H S, DATTA A, CHOUDHARY M, et al. Climate smart agriculture practices improve soil organic carbon pools, biological properties and crop productivity in cereal-based systems of North-West India[J]. CATENA, 2019, 181: 104059 doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.05.005 [57] HO T T, SHIMADA K. The effects of climate smart agriculture and climate change adaptation on the technical efficiency of rice farming— An empirical study in the Mekong delta of Vietnam[J]. Agriculture, 2019, 9(5): 99 doi: 10.3390/agriculture9050099 [58] TRAN N L D, RAÑOLA R F, SANDER B O, et al. Determinants of adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in rice production in Vietnam[J]. International Journal of Climate Change Strategies and Management, 2020, 12(2): 238−256 [59] MUTENJE M J, FARNWORTH C R, STIRLING C, et al. A cost-benefit analysis of climate-smart agriculture options in Southern Africa: balancing gender and technology[J]. Ecological Economics, 2019, 163: 126−137 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.05.013 [60] ABEGUNDE V O, SIBANDA M, OBI A. Determinants of the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by small-scale farming households in King Cetshwayo District municipality, South Africa[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 12(1): 195 doi: 10.3390/su12010195 [61] ZERSSA G, FEYSSA D, KIM D G, et al. Challenges of smallholder farming in Ethiopia and opportunities by adopting climate-smart agriculture[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(3): 192 doi: 10.3390/agriculture11030192 [62] LONG T B, BLOK V, CONINX I. Barriers to the adoption and diffusion of technological innovations for climate-smart agriculture in Europe: evidence from the Netherlands, France, Switzerland and Italy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112: 9−21 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.044 [63] LIPPER L, THORNTON P, CAMPBELL B M, et al. Climate-smart agriculture for food security[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014, 4(12): 1068−1072 doi: 10.1038/nclimate2437 [64] ALEXANDER S. What climate-smart agriculture means to members of the Global Alliance for climate-smart agriculture[J]. Future of Food: Journal on Food, Agriculture and Society, 2019, 7(1): 21−30 [65] KARLSSON L, NAESS L O, NIGHTINGALE A, et al. ‘Triple wins’ or ‘triple faults’? Analysing the equity implications of policy discourses on climate-smart agriculture (CSA)[J]. The Journal of Peasant Studies, 2018, 45(1): 150−174 doi: 10.1080/03066150.2017.1351433 [66] NYANG'AU J O, MOHAMED J H, MANGO N, et al. Smallholder farmers’ perception of climate change and adoption of climate smart agriculture practices in Masaba South Sub-county, Kisii, Kenya[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(4): e6789 [67] NEUFELDT H, JAHN M, CAMPBELL B M, et al. Beyond climate-smart agriculture: toward safe operating spaces for global food systems[J]. Agriculture & Food Security, 2013(2): 1−6 [68] ADHIKARI S. Drought impact and adaptation strategies in the mid-hill farming system of western Nepal[J]. Environments, 2018, 5(9): 101 doi: 10.3390/environments5090101 [69] SAJ S, TORQUEBIAU E, HAINZELIN E, et al. The way forward: an agroecological perspective for Climate-Smart Agriculture[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 250: 20−24 [70] RAILE E D, YOUNG L M, SARR A, et al. Political will and public will for climate-smart agriculture in Senegal: opportunities for agricultural transformation[J]. Journal of Agribusiness in Developing and Emerging Economies, 2019, 9(1): 44−62 doi: 10.1108/JADEE-01-2018-0003 [71] ROSENZWEIG C, TUBIELLO F N. Adaptation and mitigation strategies in agriculture: an analysis of potential synergies[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2007, 12(5): 855−873 doi: 10.1007/s11027-007-9103-8 [72] SMITH P, OLESEN J E. Synergies between the mitigation of, and adaptation to, climate change in agriculture[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 2010, 148(5): 543−552 doi: 10.1017/S0021859610000341 [73] AMADU F O, MCNAMARA P E, MILLER D C. Understanding the adoption of climate-smart agriculture: a farm-level typology with empirical evidence from southern Malawi[J]. World Development, 2020, 126: 104692 doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104692 [74] SENYOLO M P, LONG T B, OMTA O. Enhancing the adoption of climate-smart technologies using publicprivate partnerships: lessons from the WEMA case in South Africa[J]. International Food and Agribusiness Management Review, 2021, 24(5): 755−776 doi: 10.22434/IFAMR2019.0197 [75] BROWN B, LLEWELLYN R, NUBERG I. Global learnings to inform the local adaptation of conservation agriculture in Eastern and Southern Africa[J]. Global Food Security, 2018, 17: 213−220 doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2017.10.002 [76] KURGAT B K, LAMANNA C, KIMARO A, et al. Adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in Tanzania[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2020, 4: 55 doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.00055 [77] KANGOGO D, DENTONI D, BIJMAN J. Adoption of climate-smart agriculture among smallholder farmers: does farmer entrepreneurship matter?[J]. Land Use Policy, 2021, 109: 105666 doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105666 [78] TOTIN E, SEGNON A, SCHUT M, et al. Institutional perspectives of climate-smart agriculture: a systematic literature review[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(6): 1990 doi: 10.3390/su10061990 [79] IKEME J. Equity, environmental justice and sustainability: incomplete approaches in climate change politics[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2003, 13(3): 195−206 doi: 10.1016/S0959-3780(03)00047-5 [80] GOLI I, NAJAFABADI M O, LASHGARARA F. Where are we standing and where should we be going? gender and climate change adaptation behavior[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics, 2020, 33(2): 187−218 doi: 10.1007/s10806-020-09822-3 [81] BURNHAM M, MA Z. Climate change adaptation: factors influencing Chinese smallholder farmers’ perceived self-efficacy and adaptation intent[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2017, 17(1): 171−186 doi: 10.1007/s10113-016-0975-6 [82] ZAMASIYA B, NYIKAHADZOI K, MUKAMURI B B. Factors influencing smallholder farmers’ behavioural intention towards adaptation to climate change in transitional climatic zones: a case study of Hwedza District in Zimbabwe[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 198: 233−239 [83] LUU T D. Factors influencing farmers’ adoption of climate-smart agriculture in rice production in Vietnam’s Mekong delta[J]. Asian Journal of Agriculture and Development, 2020, 17(1): 109−124 doi: 10.37801/ajad2020.17.1.7 [84] SHARIF M Z, DI N Y, LIU F L. Monitoring honeybees (Apis Spp.) (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in climate-smart agriculture: a review[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2021: 1−15 [85] RAO N H. Big data and climate smart agriculture-status and implications for agricultural research and innovation in India[J]. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy, 2018, 84(3): 640−652 [86] 徐云帆, 黄贤金. 国外地理学对公共卫生问题的研究与启示[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(9): 2638−2656 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020201058XU Y F, HUANG X J. Progress and prospects of geography in public health: a review of literature abroad[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(9): 2638−2656 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020201058 [87] MITARITONNA C, RAGOT L. After Covid-19, will seasonal migrant agricultural workers in Europe be replaced by rotots?[J]. CEPII Policy Brief, 2020: 33 -






 下载:
下载: