Effects of gypsum application on grain yield and methane emissions in rice paddies: a global meta-analysis
-
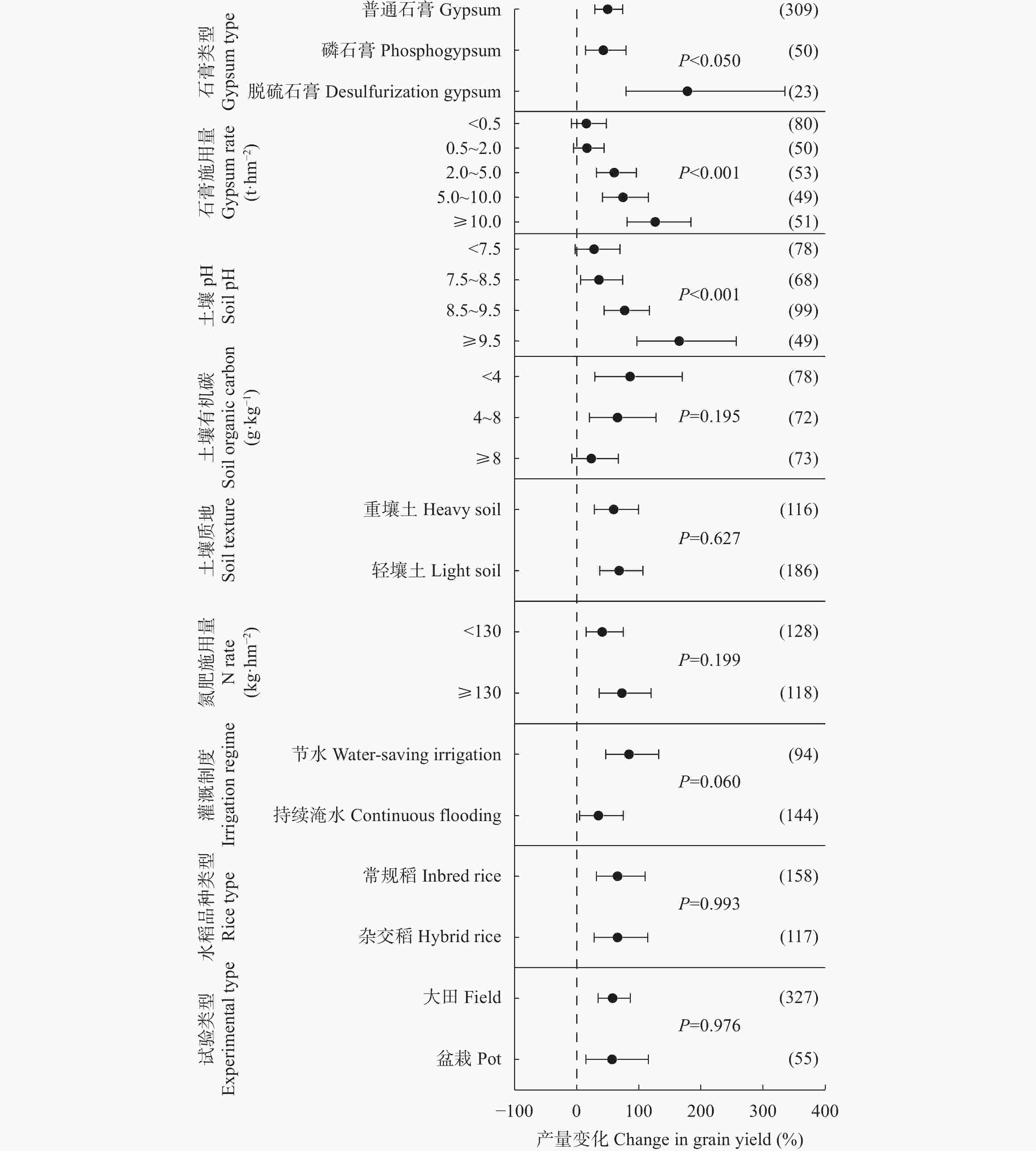
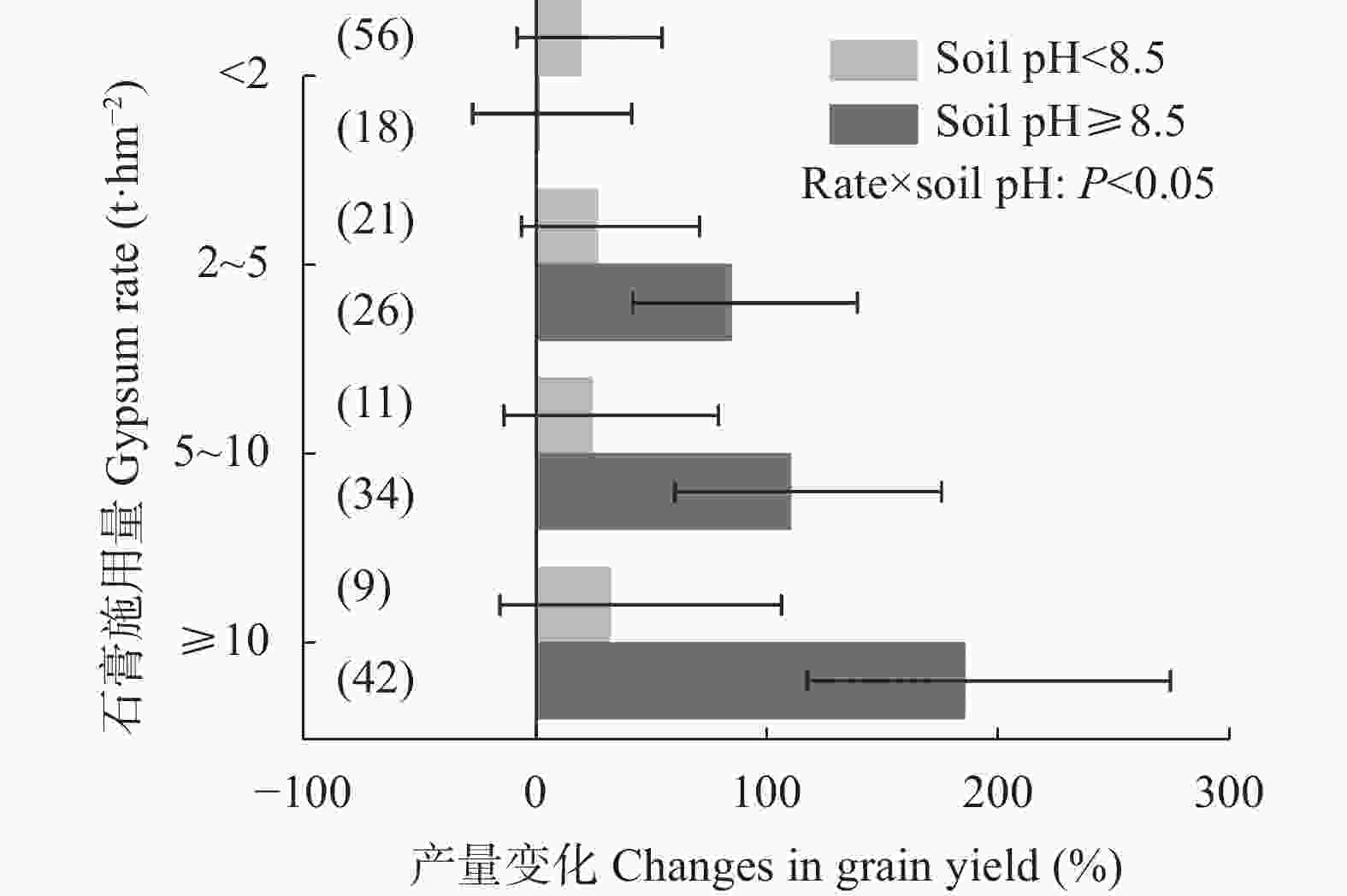
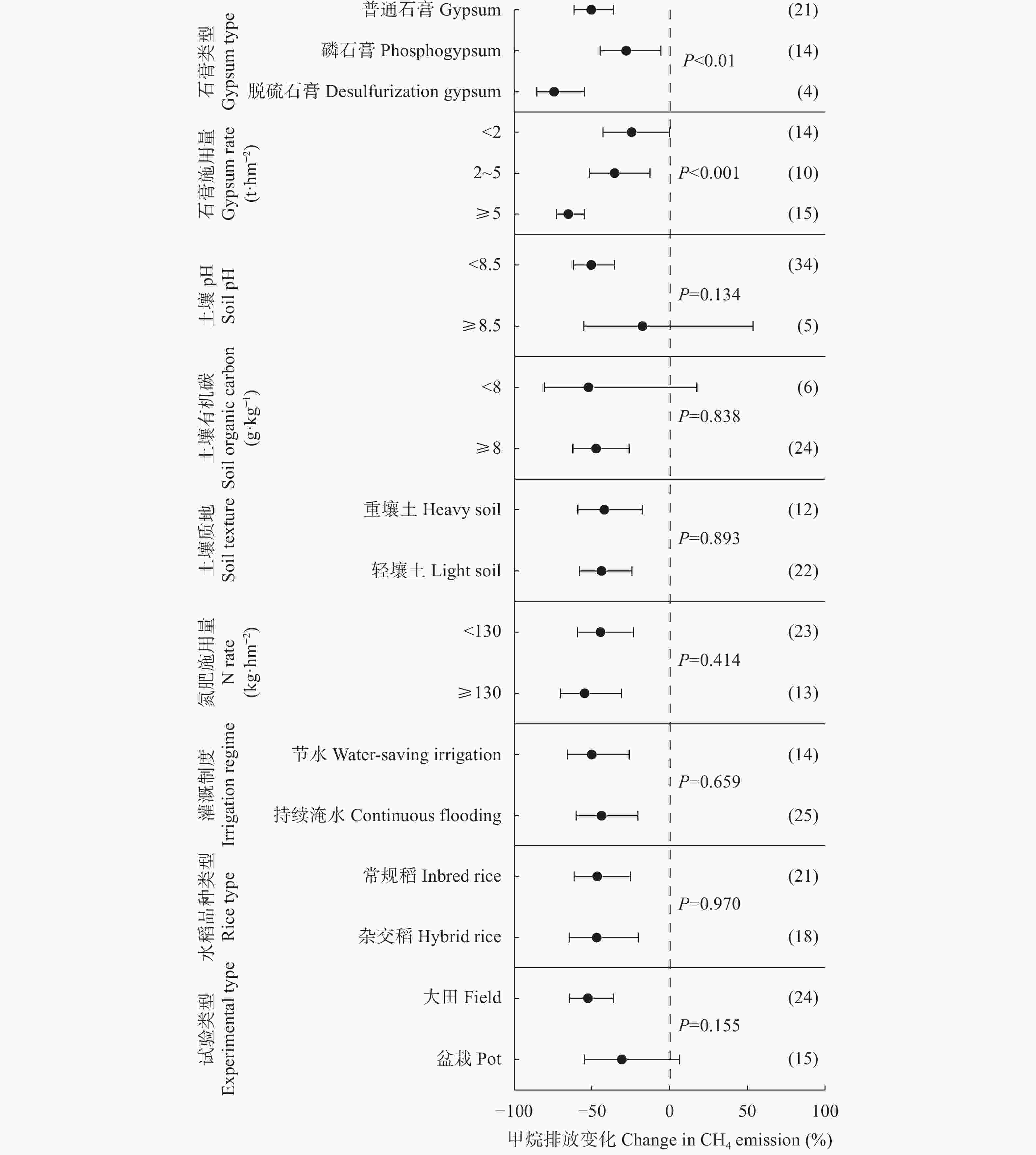
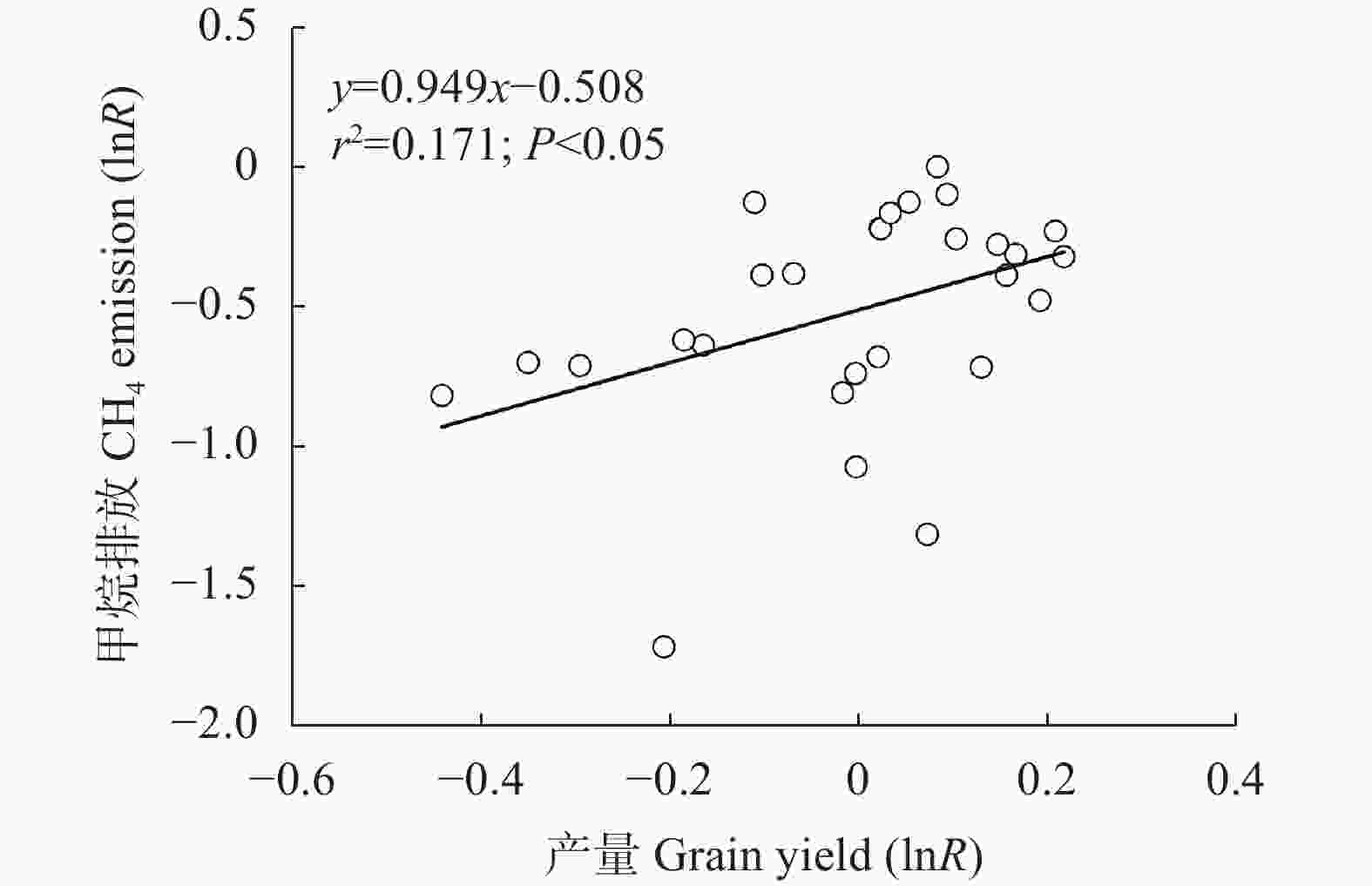
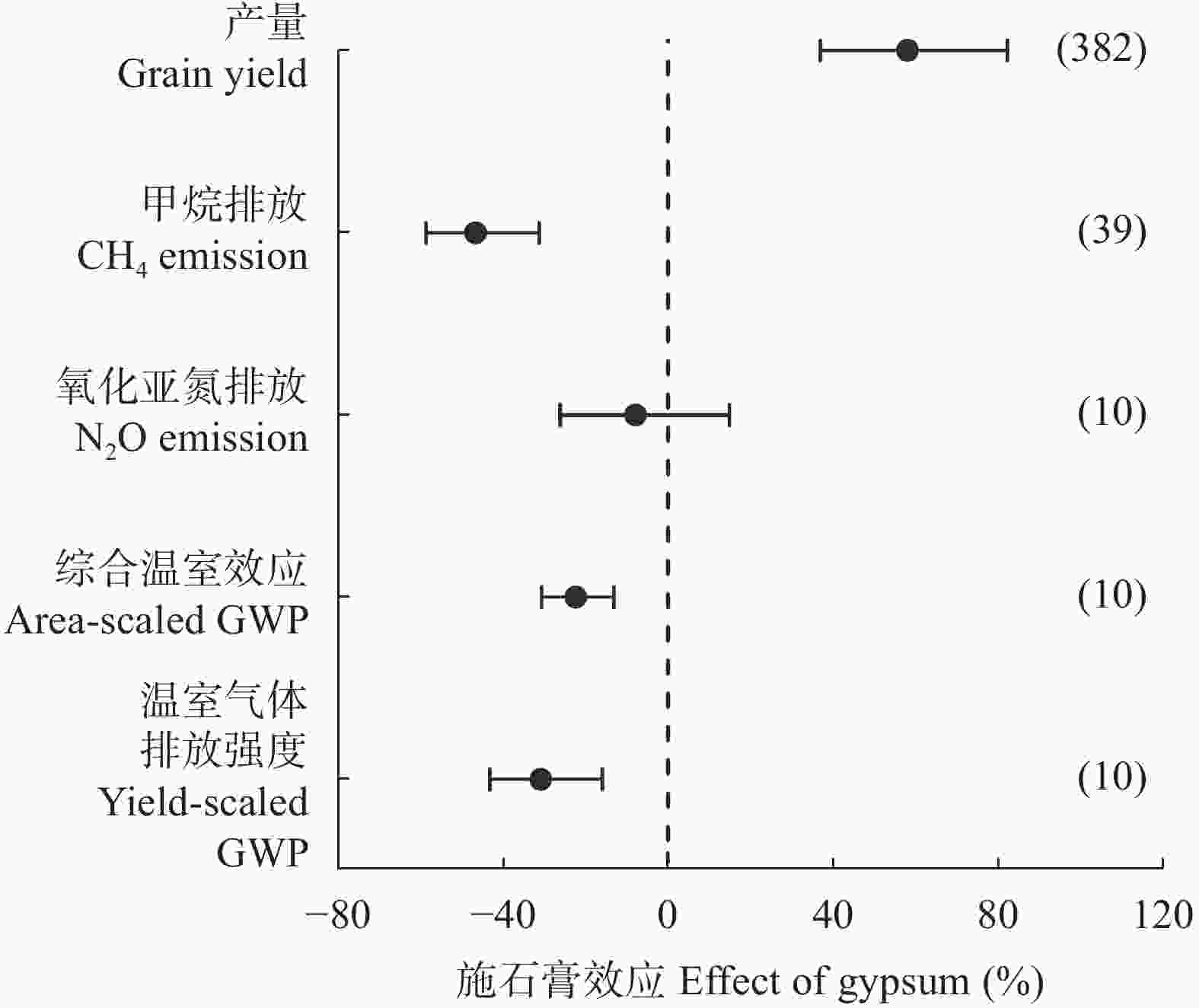
摘要: 石膏是一种常见的稻田土壤改良剂, 施石膏对水稻产量和稻田温室气体排放影响的荟萃分析尚鲜见报道。本研究采用Meta分析方法, 探究施石膏对水稻产量和稻田温室气体排放的影响。以不施石膏为对照, 施石膏为处理, 在全球尺度上筛选出了74篇文献, 建立了包含382对水稻产量、39对甲烷(CH4)排放、10对氧化亚氮(N2O)排放、10对综合温室效应(GWP)和10对温室气体排放强度(GHGI)观测值的数据库。针对不同的石膏施用措施(类型和施用量)、基础土壤性状(pH值、有机碳含量和质地)以及稻田管理方式(氮肥施用量、灌溉制度、水稻品种类型和试验类型), 探究施石膏对水稻产量和稻田CH4排放的影响。从总效应来看, 与不施石膏相比, 施石膏显著增加了水稻产量(+58%), 降低了稻田CH4排放(−47%)、GWP(−22%)和GHGI(−31%), 而对N2O排放影响不显著。脱硫石膏对水稻增产和稻田CH4减排的效应显著高于普通石膏和磷石膏。当施用量<2 t·hm−2时, 石膏对水稻产量影响不显著; 当施用量≥2 t·hm−2时, 石膏对水稻的增产效应随石膏施用量的增加而增加。随着土壤pH增加, 施石膏对水稻产量的增幅显著增加。石膏施用量和土壤pH对水稻产量存在显著的互作效应。在土壤pH<8.5条件下, 施石膏对水稻产量影响不显著; 在土壤pH≥8.5条件下, 水稻产量随着石膏施用量的增加而增加。稻田CH4减排效应随石膏施用量的增加而显著增加。综上, 施石膏显著提高了水稻产量, 同时降低了稻田温室气体排放, 本研究结果可为评估施石膏对全球水稻丰产和缓解气候变暖提供数据支撑。Abstract: Gypsum is a widely recommended soil amendment for rice paddies, but a meta-analysis of the responses of rice yield and greenhouse gas emissions to gypsum application has less been reported. In this study, a global meta-analysis was conducted to quantify the effects of gypsum application on rice yield and greenhouse gas emissions. The dataset was collected from 74 studies involving 382 pairs of rice yield observations, 39 pairs of methane emission observations, 10 pairs of nitrous oxide emission observations, 10 pairs of area-scaled global warming potential (GWP) observations, and 10 pairs of yield-scaled global warming potential (GHGI) observations, where the absence of gypsum acted as the control and the application of gypsum acted as the treatment. Based on a meta-analysis, the effects of gypsum application on rice yield and paddy CH4 emissions were examined under different gypsum application measures (type and application rate), soil properties (pH, organic carbon content, and texture), and field management methods (N rate, irrigation regime, rice type, and experiment type). Overall, gypsum application significantly increased rice yield (+58%) and reduced CH4 emissions (−47%), GWP (−22%), and GHGI (−31%), but did not affect N2O emissions relative to those without gypsum application. The magnitude of the increase in rice yield and reduction in CH4 emissions of desulfurization gypsum was significantly higher than that of gypsum and phosphogypsum. Applying gypsum increased rice yield at gypsum rates ≥ 2 t·hm−2, while no significant effects were observed at gypsum rates < 2 t·hm−2. The magnitude of the increase in gypsum application-induced rice yield increased with increasing soil pH. The gypsum rate and soil pH showed a positive interactive effect, whereby the increase in rice yield increased with the gypsum rate in the initial soils with pH ≥ 8.5 but remained stable at soil pH < 8.5. Gypsum application induced a reduction in CH4 emissions with increasing gypsum application rate. Our results indicate that gypsum application could increase rice yield and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, providing a theoretical basis for evaluating the effects of gypsum application on high rice yield and mitigating global warming.
-
Key words:
- Gypsum /
- Paddy field /
- Yield /
- Methane /
- Meta-analysis
-
图 1 施石膏对水稻产量、CH4排放、N2O排放、综合温室效应和温室气体排放强度的总效应
括号内的数字表示观测值数, 误差线表示95%的置信区间, GWP表示全球增温潜势。Number in the parenthese is the number of observations of each category. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. GWP is global warming potential.
Figure 1. Overall effects of gypsum application on grain yield, CH4 emissions, N2O emissions, area-scaled global warming potential (GWP), and yield-scaled GWP in rice paddies
-
[1] IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working GroupⅠ to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 423–552 [2] LINQUIST B, GROENIGEN K J, ADVIENTO-BORBE M A, et al. An agronomic assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from major cereal crops[J]. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18(1): 194−209 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02502.x [3] ALEXANDRATOS N, BRUINSMA J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: the 2012 Revision[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2012: 65–71 [4] ZHANG P, BING X, JIAO L, et al. Amelioration effects of coastal saline-alkali soil by ball-milled red phosphorus-loaded biochar[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133904 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133904 [5] REICHENAUER T G, PANAMULLA S, SUBASINGHE S, et al. Soil amendments and cultivar selection can improve rice yield in salt-influenced (tsunami-affected) paddy fields in Sri Lanka[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2009, 31(5): 573−579 doi: 10.1007/s10653-009-9253-6 [6] MEL V C, BADO V B, NDIAYE S, et al. Suitable management options to improve the productivity of rice cultivars under salinity stress[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2019, 65(8): 1093−1106 doi: 10.1080/03650340.2018.1552785 [7] WANG S J, CHEN Q, LI Y, et al. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2017, 121: 82−92 doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.04.005 [8] WANG Y G, WANG Z F, LIANG F, et al. Application of flue gas desulfurization gypsum improves multiple functions of saline-sodic soils across China[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 277: 130345 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130345 [9] LINDAU C W, WICKERSHAM P, DELAUNE R D, et al. Methane and nitrous oxide evolution and 15N and 226Ra uptake as affected by application of gypsum and phosphogypsum to Louisiana rice[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 1998, 68(1): 165−173 [10] 李佳, 张宇, 孙丽英, 等. 不同改良剂对滨海盐土区稻田综合温室效应的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 164−171 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0683LI J, ZHANG Y, SUN L Y, et al. Effects of different ameliorant on global warming potentials of coastal saline paddy field[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(11): 164−171 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0683 [11] THEINT E E, BELLINGRATH-KIMURA S D, OO A Z, et al. Influence of gypsum amendment on methane emission from paddy soil affected by saline irrigation water[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2016, 3: 79 [12] BASAK N, SHEORAN P, SHARMA R, et al. Gypsum and pressmud amelioration improve soil organic carbon storage and stability in sodic agroecosystems[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(15): 4430−4444 [13] SUN L Y, MA Y C, LIU Y L, et al. The combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer, humic acid, and gypsum on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from a coastal saline rice field[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(19): 19502−19511 doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05363-z [14] WANG W Q, ZENG C S, SARDANS J, et al. Industrial and agricultural wastes decreased greenhouse-gas emissions and increased rice grain yield in a subtropical paddy field[J]. Experimental Agriculture, 2018, 54(4): 623−640 doi: 10.1017/S001447971700031X [15] JIANG Y, LIAO P, VAN GESTEL N, et al. Lime application lowers the global warming potential of a double rice cropping system[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 325: 1−8 doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.03.034 [16] 王强盛. 稻田种养结合循环农业温室气体排放的调控与机制[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(5): 633−642WANG Q S. Regulation and mechanism of greenhouse gas emissions of circular agriculture ecosystem of planting and breeding in paddy[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(5): 633−642 [17] ZHAO D D, WANG Z C, YANG F, et al. Amendments to saline-sodic soils showed long-term effects on improving growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e8726 doi: 10.7717/peerj.8726 [18] GHAFOOR A, MURTAZA G, AHMAD B, et al. Evaluation of amelioration treatments and economic aspects of using saline-sodic water for rice and wheat production on salt-affected soils under arid land conditions[J]. Irrigation and Drainage: The Journal of the International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage, 2008, 57(4): 424−434 [19] MURTAZA G, GHAFOOR A, OWENS G, et al. Environmental and economic benefits of saline-sodic soil reclamation using low-quality water and soil amendments in conjunction with a rice-wheat cropping system[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2009, 195(2): 124−136 doi: 10.1111/j.1439-037X.2008.00350.x [20] AUGUSTO L, BAKKER M R, MEREDIEU C. Wood ash applications to temperate forest ecosystems — potential benefits and drawbacks[J]. Plant and Soil, 2008, 306(1): 181−198 [21] LIAO P, SUN Y N, ZHU X C, et al. Identifying agronomic practices with higher yield and lower global warming potential in rice paddies: a global meta-analysis[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2021, 322: 107663 [22] JIANG Y, CARRIJO D, HUANG S, et al. Water management to mitigate the global warming potential of rice systems: a global meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 234: 47−54 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.02.010 [23] 刘宇锋, 李伏生. 灌溉方式与施肥水平对超级稻光合生理的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(4): 416−425LIU Y F, LI F S. Effect of irrigation method and fertilization dose on photosynthetic physiology of super rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(4): 416−425 [24] LIAO P, HUANG S, ZENG Y J, et al. Liming increases yield and reduces grain cadmium concentration in rice paddies: a meta-analysis[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 465(1): 157−169 [25] DE GRAAFF M A, VAN GROENIGEN K J, SIX J, et al. Interactions between plant growth and soil nutrient cycling under elevated CO2: a meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2006, 12(11): 2077−2091 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01240.x [26] HEDGES L V, GUREVITCH J, CURTIS P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80(4): 1150−1156 doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1150:TMAORR]2.0.CO;2 [27] 廖萍, 孟轶, 翁文安, 等. 杂交稻对产量和氮素利用率影响的荟萃分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(8): 1546−1556LIAO P, MENG Y, WENG W A, et al. Effects of hybrid rice on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency: a meta-analysis[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(8): 1546−1556 [28] SANTOS P D D, CAVALCANTE L F, GHEYI H R, et al. Saline-sodic soil treated with gypsum, organic sources and leaching for successive cultivation of sunflower and rice[J]. Revista Brasileira De Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 2019, 23(12): 891−898 [29] WU G Q, WANG S M. Calcium regulates K+/Na+ homeostasis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under saline conditions[J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2012, 58(3): 121−127 doi: 10.17221/374/2011-PSE [30] SAQIB A I, AHMED K, QADIR G, et al. Enhancing the solubility and reclamation efficiency of gypsum with H2SO4[J]. Cercetari Agronomice in Moldova, 2019, 52(2): 128−140 doi: 10.2478/cerce-2019-0013 [31] HELMY A M, SHABAN K A, EL-GALAD M A. Effect of gypsum and sulphur application in amelioration of saline soil and enhancing rice productivity[J]. Journal of Soil Sciences and Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 4(10): 1037−1051 doi: 10.21608/jssae.2013.52497 [32] 王增蓁. 火电厂脱硫石膏资源化研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2013: 15–22WANG Z Z. Study on resourse utilization of FGD gypsum in power plant[D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University, 2013: 15–22 [33] KORALEGEDARA N H, PINTO P X, DIONYSIOU D D, et al. Recent advances in flue gas desulfurization gypsum processes and applications — A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 251: 109572 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109572 [34] SHAH A L, ISLAM M R, HAQUE M M, et al. Efficacy of major nutrients in rice production[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Agricultural Research, 2008, 33(4): 639−645 [35] 肖国举, 罗成科, 白海波, 等. 脱硫石膏改良碱化土壤种植水稻施用量研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(6): 2376−2380 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.06.068XIAO G J, LUO C K, BAI H B, et al. Research on the amount of desulfurized gypsum from the coal-burning power plant applied to improve the alkalized soil for paddy rice[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(6): 2376−2380 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.06.068 [36] SINGH Y, SINGH R, SHARMA D. Determination of time frame for substitution of salt-tolerant varieties of rice (Oryza sativa) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) through crop diversification in sodic soils[J]. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 80(10): 6−11 [37] LIU M, LIANG Z W, MA H Y, et al. Responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and yield to phosphogypsum amendment in saline-sodic soils of North-East China[J]. Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 2010, 8(2): 827−833 [38] YAN F Y, WEI H M, DING Y F, et al. Melatonin enhances Na+/K+ homeostasis in rice seedlings under salt stress through increasing the root H+-pump activity and Na+/K+ transporters sensitivity to ROS/RNS[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2021, 182: 104328 doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104328 [39] QADIR A A, MURTAZA G, ZIA-UR-REHMAN M, et al. Application of gypsum or sulfuric acid improves physiological traits and nutritional status of rice in calcareous saline-sodic soils[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2022, 22(2): 1846−1858 doi: 10.1007/s42729-022-00776-1 [40] WANG J M, YANG P L. Potential flue gas desulfurization gypsum utilization in agriculture: a comprehensive review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 82: 1969−1978 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.07.029 [41] 胡翔宇, 向秋洁, 木志坚. 脱硫石膏对稻田CH4释放及其功能微生物种群的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3894−3900HU X Y, XIANG Q J, MU Z J. Effects of gypsum on CH4 emission and functional microbial communities in paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3894−3900 [42] GAUCI V, MATTHEWS E, DISE N, et al. Sulfur pollution suppression of the wetland methane source in the 20th and 21st centuries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2004, 101(34): 12583−12587 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404412101 [43] SANGKERDSUB S, RICKE S C. Ecology and characteristics of methanogenic Archaea in animals and humans[J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2014, 40(2): 97−116 doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.763220 [44] 江家彬, 祝贞科, 林森, 等. 针铁矿吸附态和包裹态有机碳在稻田土壤中的矿化及其激发效应[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(6): 1530−1539 doi: 10.11766/trxb202005050215JIANG J B, ZHU Z K, LIN S, et al. Mineralization of goethite-adsorbed and -encapsulated organic carbon and its priming effect in paddy soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(6): 1530−1539 doi: 10.11766/trxb202005050215 [45] LIAO P, SUN Y N, JIANG Y, et al. Hybrid rice produces a higher yield and emits less methane[J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2019, 65(11): 549−555 doi: 10.17221/330/2019-PSE [46] JIANG Y, TIAN Y L, SUN Y N, et al. Effect of rice panicle size on paddy field CH4 emissions[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2016, 52(3): 389−399 doi: 10.1007/s00374-015-1084-2 [47] DENIER VAN DER GON H A, BODEGOM P M, WASSMANN R, et al. Sulfate-containing amendments to reduce methane emissions from rice fields: mechanisms, effectiveness and costs[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2001, 6(1): 71−89 doi: 10.1023/A:1011380916490 [48] LIU G, YU H Y, MA J, et al. Effects of straw incorporation along with microbial inoculant on methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice fields[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 518: 209−216 [49] 王飞, 李清华, 何春梅, 等. 稻秸-有机肥联合还田对黄泥田水稻产能与化肥替代的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(12): 2024−2033 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210267WANG F, LI Q H, HE C M, et al. Combined return of rice straw and organic fertilizer to yellow-mud paddy soil to improve the rice productivity and substitute chemical fertilizers[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(12): 2024−2033 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210267 [50] VAN DER GON H A C D, NEUE H U. Impact of gypsum application on the methane emission from a wetland rice field[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1994, 8(2): 127−134 doi: 10.1029/94GB00386 [51] CHOUDHARY O P, GHUMAN B S, BIJAY-SINGH, et al. Effects of long-term use of sodic water irrigation, amendments and crop residues on soil properties and crop yields in rice-wheat cropping system in a calcareous soil[J]. Field Crops Research, 2011, 121(3): 363−372 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.01.004 [52] ALI M A, LEE C H, KIM P J. Effect of Phospho-gypsum on reduction of methane emission from rice paddy soil[J]. Korean Journal of Environmental Agriculture, 2007, 26(2): 131−140 doi: 10.5338/KJEA.2007.26.2.131 [53] MORALES C L, TRAVESET A. A meta-analysis of impacts of alien vs. native plants on pollinator visitation and reproductive success of co-flowering native plants[J]. Ecology Letters, 2009, 12(7): 716−728 doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01319.x -





 下载:
下载: