Effects of different precipitation years on soil nitrate distribution, leaching loss and nitrogen uptake and utilization under drip irrigation of maize
-
摘要: 为寻找满足宁夏地区滴灌条件下不同降水年型间科学施肥模式, 缓解不合理施氮导致的资源浪费、黄河水质下降和地下水污染等问题, 本研究于2018—2020年在宁夏平吉堡农场开展氮梯度试验, 分析不同降水年型下不同施氮处理土壤硝态氮残留和淋溶量以及对滴灌玉米氮素吸收利用和产量的影响。结果表明: 土壤硝态氮含量峰值与降水量密切相关, 丰水年(2018年)硝态氮残留量峰值在40~60 cm土层, 枯水年(2019年和2020年)在20~40 cm土层; 不同降水年型份间土壤硝态氮残留量和淋失量均随施氮量的增加而增加, 且降水量显著影响硝态氮淋失量; 丰水年由降水因素导致的硝态氮淋失量占总淋失量的50.62%, 枯水年占总淋失量的34.82%。回归分析结果表明, 不同降水年型间玉米产量随施氮量呈先上升后下降的趋势, 均在N3处理 (施N量为270 kg∙hm−2)下达最高产量, 且N3处理的产量和吸氮量与N4处理(施N量为360 kg∙hm−2)无显著差异; 丰水年N3的氮肥利用率、氮肥农学利用率和氮肥偏生产力比N4分别提升11.38%、6.16 kg∙kg−1和13.85 kg∙kg−1, 枯水年分别提升12.10%、5.06 kg∙kg−1和15.00 kg∙kg−1。综合考量不同降水年型间0~100 cm土层硝态氮分布特征和硝态氮淋失量及施氮处理下的产量、氮素吸收利用, 推荐宁夏引黄灌区滴灌玉米不同降水年型下施氮量在270 kg∙hm−2时较适宜, 丰水年施氮最大阈值为275.59 kg∙hm−2 , 枯水年施氮最大阈值为320.20 kg∙hm−2。Abstract: In order to improve crop yield, excessive nitrogen application in agricultural production has become increasingly serious in recent years. Excessive nitrogen application leads to increasing accumulation of soil nitrate nitrogen and water pollution, and nitrogen leaching loss varies among different precipitation years. It is of great significance to clarify the scientific fertilization model among different precipitation year types under drip irrigation in Ningxia to alleviate the problems of resource waste, water quality decline of Yellow River and groundwater pollution caused by unreasonable nitrogen application. In this study, a 3-years nitrogen gradient experiment was carried out in Pingjipu Farm, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, with five nitrogen application treatments of 360 kg∙hm−2 (N4), 270 kg∙hm−2 (N3), 180 kg∙hm−2 (N2), 90 kg∙hm−2 (N1), and 0 kg∙hm−2 (N0), to analyze the effects of different nitrogen fertilization treatments on soil nitrate nitrogen residue and leaching amount, as well as on nitrogen absorption, utilization and yield of corn under drip irrigation in rainy and dry years. The results showed that the peak value of soil nitrate nitrogen content was closely related to precipitation, the peak value of nitrate nitrogen residue was at 40-60 cm soil layer in Rainy years (2018 year), and at 20-40 cm soil layer in dry years (2019 year and 2020 year). Different precipitation years soil nitrate nitrogen residue and leaching increased with the increase of nitrogen application, and reached the maximum value under N4 treatment. Precipitation significantly affected nitrate leaching, and in rainy years the nitrate nitrogen leaching loss caused by factors accounted for 50.62% of the total leaching loss, and the dry year accounted for 34.82% of the total leaching loss. The regression analysis results showed that maize yield increased firstly and then decreased with the appropriate amount in different precipitation years. And the maximum yield was found under 270 kg∙hm−2 (N3) in different precipitation years, and the yield and nitrogen uptake under N3 treatment have no difference with 360 kg∙hm−2 (N4). In Rainy and dry years, compared with N4, the utilization rate, agronomic utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer and partial nitrogen fertilizer productivity increased by 11.38%, 6.16 kg∙kg−1, 13.85 kg∙kg−1 and 12.10%, 5.06 kg∙kg−1, 15.00 kg∙kg−1. To sum up, Considering the distribution characteristics of nitrate in 0-100 cm soil layer, the amount of nitrate leaching, and the yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization under nitrogen application in different precipitation years, when the nitrogen application rate was 270 kg∙hm−2, the yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization of maize in rainy and dry years were maintained at a high level, and the amount of nitrate leaching was also within an acceptable range. It is recommended that 270 kg∙hm−2 is the appropriate nitrogen application rate for maize under different precipitation patterns in Ningxia Yellow River irrigation area. The maximum threshold of nitrogen application rate in rainy year is 275.59 kg∙hm−2, and the maximum threshold of nitrogen application rate in dry year is 320.20 kg∙hm−2. The results of this study can provide a theoretical basis for the decision of scientific nitrogen application among different precipitation year types of drip irrigation maize in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and the green and sustainable development of agriculture.
-
Key words:
- Drip irrigation Maize /
- Precipitation /
- Nitrate leaching /
- Nitrogen use /
- Threshold
-
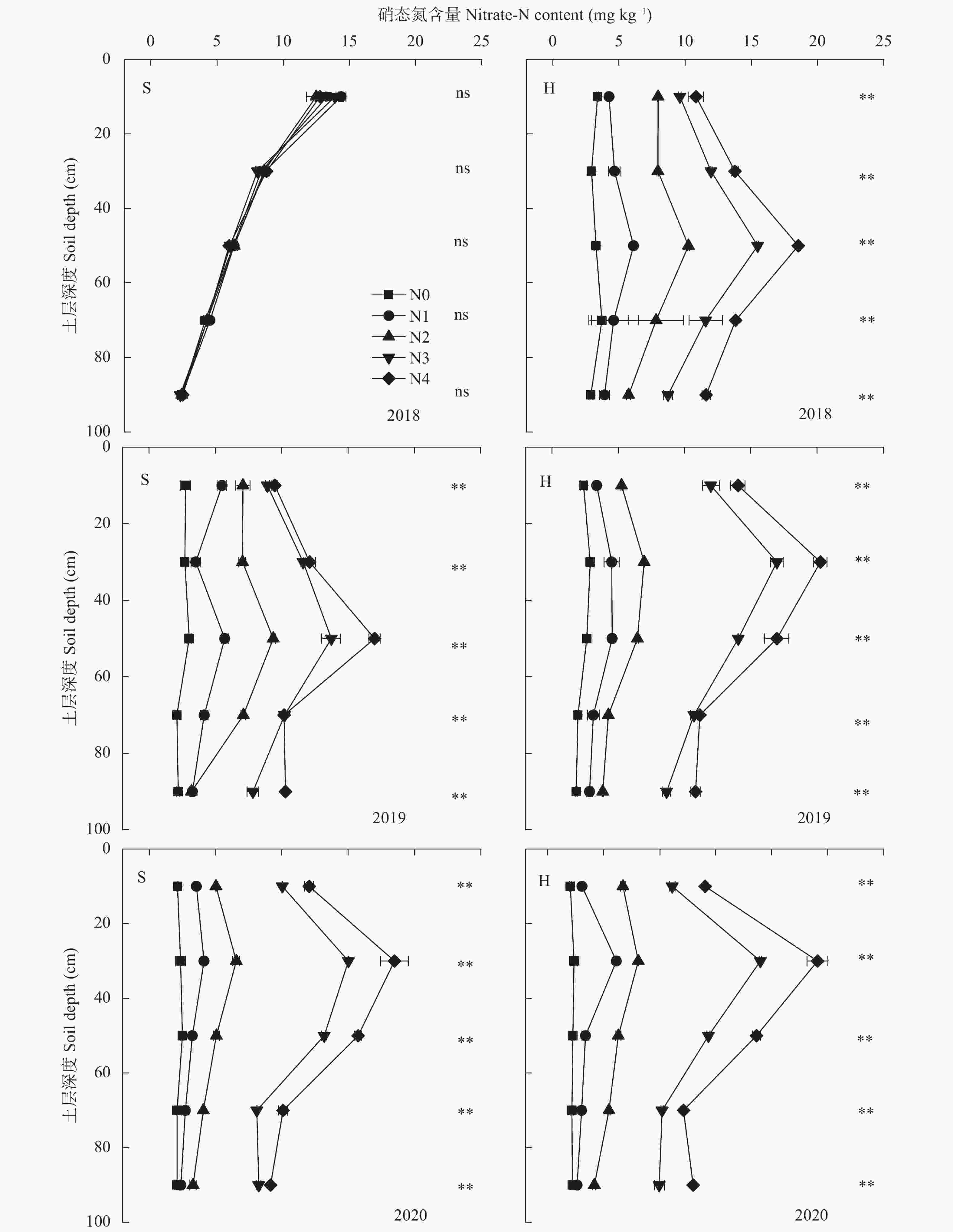
图 2 2018—2020年施氮量对播前(S)和收获后(H) 0~100 cm土层硝态氮分布的影响
N0、N1、N2、N3、N4分别表示施氮量为0 kg∙hm−2、90 kg∙hm−2、180 kg∙hm−2、270 kg∙hm−2、360 kg∙hm−2。“**”表示不同处理间差异极显著(P<0.01), “ns”表示不同处理间差异不显著(P>0.05)。N0, N1, N2, N3 and N4 represent nitrogen application rates of 0 kg∙hm−2, 90 kg∙hm−2, 180 kg∙hm−2, 270 kg∙hm−2 and 360 kg∙hm−2, respectively. “**” mean that the difference between treatments is extremely significant (P<0.01). “ns” means no significant difference among treatments (P>0.05)
Figure 2. Effects of nitrogen application rates on nitrate nitrogen distribution in 0−100 cm soil layer before sowing (S) and after harvest (H) from 2018 to 2020
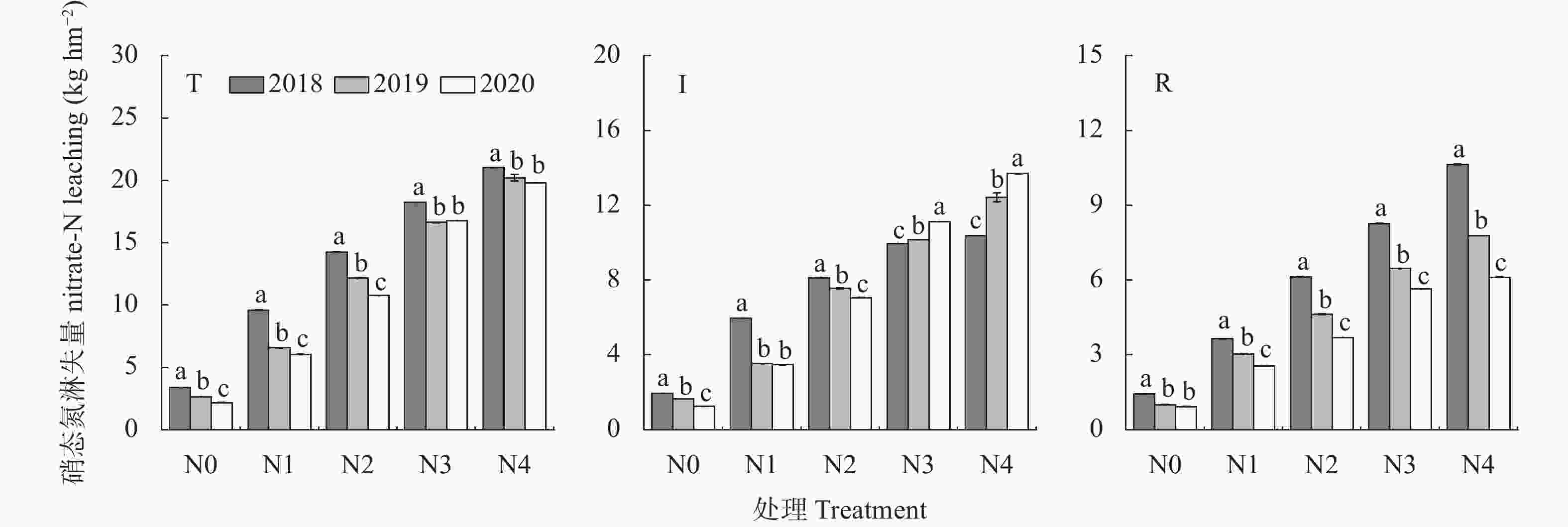
图 3 2018—2020年不同施氮量下玉米生长季(4—9月)农田土壤硝态氮总淋失量(T)、灌溉(I)和降水(R)淋失量
N0、N1、N2、N3、N4分别表示施氮量为0 kg∙hm−2、90 kg∙hm−2、180 kg∙hm−2、270 kg∙hm−2、360 kg∙hm−2。不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P <0.05)。N0, N1, N2, N3 and N4 represent nitrogen application rates of 0 kg∙hm−2, 90 kg∙hm−2, 180 kg∙hm−2, 270 kg∙hm−2 and 360 kg∙hm−2, respectively. Different lowercase letters showed significant difference among treatments (P<0.05).
Figure 3. Total soil nitrate leaching loss (T), irrigation (I) and rainfall leaching loss (R) in maize growing season (April to September) under different nitrogen application treatments from 2018 to 2020
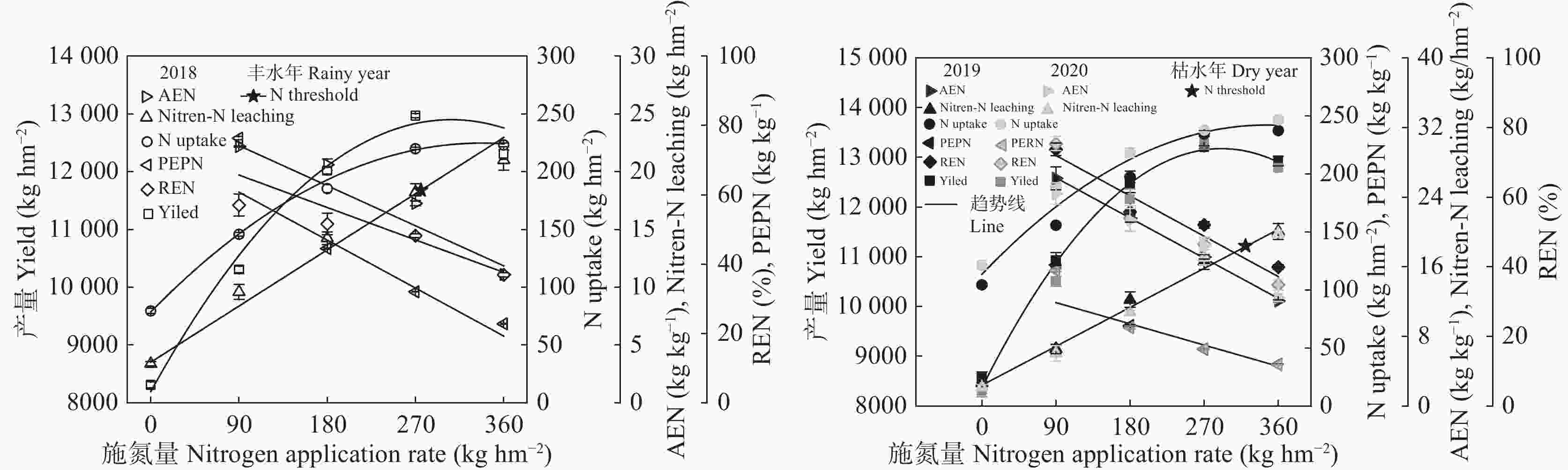
图 4 玉米产量、氮素吸收利用、硝态氮淋失量与施氮量回归分析
REN为氮肥回收利用率; AEN为氮肥农学利用率; PFEN为氮肥偏生产力; N uptake为吸氮量; Nitrate-N leaching为硝态氮淋失量; N Threshold 为硝态氮淋失量阈值; 枯水年回归数据为2019和2020年平均值。 REN is Recovery efficiency of N; AEN is Agronomic efficiency of N; PFEN is Partial-factor productivity of N; N uptake is Nitrogen uptake; Nitrate-N leaching is Nitrate leaching loss; N Threshold is Nitrate leaching threshold; The regression data of water dry years are the average values of 2019 and 2020.
Figure 4. Regression Analysis of maize yield, nitrogen absorption and utilization, Nitrate-N leaching and nitrogen application
表 1 试验地土壤理化性质
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of the test soils
土层
Soil layer
(cm)pH 有机质
Organic matter
(g∙kg−1)全氮
Total N
(g∙kg−1)全磷
Total P
(g∙kg−1)全钾
Total K
(g∙kg−1)碱解氮
Avail N
(mg∙kg−1)速效磷
Avail K
(mg∙kg−1)速效钾
Avail K
(mg∙kg−1)容重
Bulk density
(g∙cm−3)0~20 7.81 12.31 0.78 0.54 3.32 38.03 19.37 101.82 1.31 20~40 7.95 5.46 0.52 0.34 3.45 18.45 17.37 86.45 1.35 40~60 7.98 2.36 0.36 0.26 3.36 12.55 14.36 44.67 1.32 60~80 7.94 1.45 0.23 0.17 3.28 8.36 8.36 27.74 1.29 80~100 7.86 1.52 0.18 0.19 3.24 5.48 4.32 12.36 1.30 表 2 玉米不同生育期各试验处理的肥料(纯N-P-K)施用量
Table 2. Application rates of fertilizers (N-P-K) in each treatment of the test at different growth stages of maize (kg∙hm−2)
处理 Treatment 苗期 Seedling stage 拔节期 Jointing stage 抽雄期 Tasseling stage 灌浆期 Grouting period N0 0-13.8-12 0-62.1-54 0-27.6-24 0-34.5-30 N1 9-13.8-12 40.5-62.1-54 18-27.6-24 22.5-34.5-30 N2 18-13.8-12 81-62.1-54 36-27.6-24 45-34.5-30 N3 27-13.8-12 121.5-62.1-54 54-27.6-24 67.5-34.5-30 N4 36-13.8-12 162-62.1-54 72-27.6-24 90-34.5-30 表 3 2018-2020年滴灌玉米产量、氮素吸收量及利用率
Table 3. Yield, nitrogen uptake and utilization rate of drip irrigation Maize in 2018−2020
年份
Year处理
Treatment产量
Yield
(kg·hm−2)吸氮量
N uptake
(kg·hm−2)氮肥回收率
Recovery efficiency
of N (%)氮肥农学效率
Agronomic efficiency
of N (kg·kg−1)氮肥偏生产力
Partial-factor productivity
of N (kg·kg−1)2018 N0 8309.60±150.89Bd 79.51±2.28Bd N1 10 305.84±156.17Bc 145.87±1.74Bc 57.03±3.17Ba 22.18±0.06Ba 114.51±0.62Ba N2 12 018.66±154.97Bb 185.39±3.51Bb 51.61±3.08Bab 20.61±0.50Ba 66.77±0.31Bb N3 12 969.88±34.21Ba 219.93±1.01Ba 48.20±0.58Bb 17.26±0.20Ab 48.04±0.13Ac N4 12 308.23±192.14Bab 223.16±1.61Ba 36.92±0.57Bc 11.10±0.15Bc 34.19±0.26Bd 2019 N0 8579.71±100.67Ad 104.44±1.58Ad N1 10 934.31±149.99Ac 155.77±1.34Ac 73.73±1.84Aa 26.16±1.30Aa 121.49±1.67Aa N2 12 463.31±176.19Ab 197.35±5.01Ab 55.73±0.95Ab 21.58±0.46Ab 69.24±0.98Ab N3 13 203.78±28.46Aa 234.59±2.36Aa 52.00±0.94Ab 17.13±0.28Ac 48.90±0.10Ac N4 12 925.42±95.03Aab 237.36±1.20Aa 39.90±0.67Ac 12.07±0.14Ad 35.90±0.26Ad 2020 N0 8312.06±131.36Bd 121.36±3.88Ad N1 10 507.22±189.18Ac 189.18±2.09Ac 75.36±2.03Aa 24.39±1.24Aa 116.75±1.09Aa N2 12 156.17±218.39Ab 218.39±4.31Ab 53.91±3.58Ab 21.36±1.31Ab 67.53±1.14Ab N3 13 294.24±237.82aA 237.82±1.52Aa 46.51±1.51Cc 18.45±0.95Ac 49.24±0.46Ac N4 12 786.96±68.09Aab 246.71±1.54Aa 34.82±1.51Bd 12.43±0.45Ad 35.52±0.19Ad 方差分析 ANOVA 降水年型 Rainfall years (R) 37.43** 62.69** 32.70** 21.12** 20.48** 施氮量 N application rate (N) 995.78** 272.79** 159.37** 288.76** 5447.23** R×N 1.62ns 0.70ns 19.51** 3.54* 2.81ns 不同小写字母表示同一年份间不同施氮处理间差异显著(P<0.05), 不同大写字母表示不同年份间同一施氮处理下差异性显著(P<0.05)。“**”表示不同处理间差异极显著(P<0.01), “*”表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05), “ns”表示不同处理间差异不显著(P>0.05)。Different small letters indicated significant differences among different N application treatments in the same year (P<0.05), and different capital letters indicated significant differences under the same N application treatment in different years (P<0.05). “**” mean that the difference between different treatments is extremely significant (P<0.01). “*” mean that significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). “ns” means no significant difference among treatments (P>0.05) 表 4 不同降水年型施氮量(x)与土壤硝态氮淋失量和玉米产量、吸氮量、氮肥利用率的回归方程模型
Table 4. Regression analysis model of nitrogen application rate (x) with soil nitrate-N leaching, maize yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency in different precipitation years
年份 Year 项目 Item (y) 回归方程 Regression equation R2 丰水年 Rainy year 硝态氮淋失量 Nitrate-N leaching y=5.40×10-2x+3.52 0.984** 产量 Yield y=−0.05x2+30.72x+8195.93 0.979** 吸氮量 N uptake y=−1.00×10-3x2+0.87x+78.66 0.997** 氮肥偏生产力 PEPN y=−0.23x+111.93 0.820* 氮肥农学效率 AEN y=−3.90×10-2x+25.73 0.960** 氮肥回收率 REN y=−1.04×10-2x+75.07 0.892** 枯水年 Dry years 硝态氮淋失量 Nitrate-N leaching y=0.050x+2.39 0.997** 产量 Yield y=−5.70×10-2x2+33.07x+8365.58 0.993** 吸氮量 N uptake y=−1.10×10-4x2+0.74x+113.53 0.999** 氮肥偏生产力 PEPN y=−0.21x+107.43 0.804* 氮肥农学效率 AEN y=−5.10×10-2x+30.58 0.983** 氮肥回收率 REN y=−0.13x+83.58 0.958** *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01 -
[1] 王艳丽, 吴鹏年, 李培富, 等. 有机肥配施氮肥对滴灌春玉米产量及土壤肥力状况的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(8): 1230−1237WANG Y L, WU P N, LI P F, et al. Effect of organic fertilizer with nitrogen fertilizer on yield and soil fertility status of drip irrigated spring maize[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1230−1237 [2] 贾彪, 付江鹏. 基于临界氮浓度的宁夏玉米氮吸收与亏缺模型研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(1): 256−263 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.01.028JIA B, FU J P. A model of N uptake and deficit of maize in Ningxia based on critical N concentration[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(1): 256−263 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.01.028 [3] 叶盛嘉, 郑晨萌, 张影, 等. 氮肥减量配施有机肥对豫中地区冬小麦-夏玉米轮作生产力和土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(6): 900−912 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210658YE S J, ZHENG C M, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of N fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer on productivity and soil properties of winter wheat-summer maize rotation in central Henan[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(6): 900−912 doi: 10.12357/cjea.20210658 [4] 孙继颖, 高聚林, 王志刚, 等. 不同类型青贮玉米饲用产量及营养价值对密度调控的响应[J]. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1733−1742SUN J Y, GAO J L, WANG Z G, et al. Response of different types of silage maize forage yield and nutritional value to density regulation[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1733−1742 [5] 李少昆, 赵久然, 董树亭, 等. 中国玉米栽培研究进展与展望[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(11): 1941−1959 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.11.001LI S K, ZHAO J R, DONG S T, et al. Progress and prospects of maize cultivation research in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(11): 1941−1959 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.11.001 [6] ZHANG A P, GAO J, LIU R L, et al. The Comparison of Different Fertilizer Technologies on Nitrogen Leaching Losses and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice Production−Taking Ningxia Irrigation Region as an Example[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2015, 32(2): 175−184 [7] QUAN H, WU L h, DING D Y, et al. Interaction between soil water and fertilizer utilization on maize under plastic mulching in an arid irrigation region of China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2022: 265 [8] 王西娜, 于金铭, 谭军利, 等. 宁夏引黄灌区春小麦氮磷钾需求及化肥减施潜力[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(23): 4891−4903 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.23.014WANG X N, YU J M, TAN J L, et al. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium demand and fertilizer reduction potential of spring wheat in Ningxia Yellow Irrigation Area[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(23): 4891−4903 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.23.014 [9] GUO J J, FAN J L, XIANG Y Z, et al. Coupling effects of irrigation amount and nitrogen fertilizer type on grain yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated maize[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2022: 261 [10] WANG Y S, LIU Y S, LIU R L, et al. Biochar amendment reduces paddy soil nitrogen leaching but increases net global warming potential in Ningxia irrigation[J]. Scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 1592 doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01173-w [11] 章明清, 陈防, 林琼, 等. 施肥对菜园土壤养分淋溶流失浓度的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008(2): 291−299 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2008.02.014ZHANG M Q, CHEN F, LIN Q, et al. Effect of fertilizer application on the concentration of nutrient leaching loss from vegetable gardens[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2008(2): 291−299 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2008.02.014 [12] 郭丽, 史建硕, 王丽英, 等. 滴灌水肥一体化条件下施氮量对夏玉米氮素吸收利用及土壤硝态氮含量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(5): 668−676 doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.170416GUO L, SHI J S, WANG LY, et al. Effect of nitrogen application on nitrogen uptake and utilization and soil nitrate nitrogen content of summer maize under drip irrigation with integrated water and fertilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(5): 668−676 doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.170416 [13] 张学军, 赵营, 陈晓群, 等. 氮肥施用量对设施番茄氮素利用及土壤NO3−_N累积的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2007(9): 3761−3768 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.09.026ZHANG X J, ZHAO Y, CHEN X Q, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on nitrogen utilization and soil NO3-_N accumulation in tomatoes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007(9): 3761−3768 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.09.026 [14] LV H F, LIN S, WANG Y F, et al. Drip fertigation significantly reduces nitrogen leaching in solar greenhouse vegetable production system[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 245: 694−701 [15] WU Y, BIAN S F, LIU Z M, et al. Drip irrigation incorporating water conservation measures: Effects on soil water–nitrogen utilization, root traits and grain production of spring maize in semi-arid areas[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(12): 3127−3142 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63314-7 [16] 李娟娟, 李利敏, 马理辉. 不同滴灌施肥量对沙地玉米氮效率及硝态氮的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(5): 56−63 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19349LI J J, LI L M, MA L H. Effects of different drip irrigation fertilization on N efficiency and nitrate nitrogen in sandy maize[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2020(5): 56−63 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19349 [17] 王素艳, 李欣, 王璠, 等. 宁夏降水资源格局演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3): 733−746 doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.03.15WANG S Y, LI X, WANG P, et al. Characteristics of the evolution of precipitation resource pattern in Ningxia[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3): 733−746 doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.03.15 [18] GUO S L, ZHU H H, DANG T H, et al. Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China[J]. Geoderma, 2012, 189-190: 442−450 doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.06.012 [19] WANG Y, ZHOU M, HOU M, et al. Regulation of nitrogen balance and yield on greenhouse eggplant under biochar addition in Mollisol[J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2022, 68(1) [20] CAMBOURIS A N, ZEBARTH B J, NOLIN M C, et al. Apparent fertilizer nitrogen recovery and residual soil nitrate under continuous potato cropping: Effect of N fertilization rate and timing[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 88(5): 813−825 doi: 10.4141/CJSS07107 [21] 宁芳, 张元红, 温鹏飞, 等. 不同降水状况下旱地玉米生长与产量对施氮量的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(5): 777−791 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83055NING F, ZHANG Y H, WEN P F, et al. Response of dryland maize growth and yield to nitrogen application under different precipitation conditions[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 777−791 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83055 [22] 刘朋召, 王旭敏, 宁芳, 等. 减量施氮对渭北旱地春玉米产量、氮素利用及土壤硝态氮含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2621−2629 doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202008.025LIU P Z, WANG XM, NING F, et al. Effects of reduced N application on yield, N use and soil nitrate-N content of spring maize in Weibei dryland[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2621−2629 doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202008.025 [23] LAI Z L, FAN J L, YANG R, et al. Interactive effects of plant density and nitrogen rate on grain yield, economic benefit, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency of drip-fertigated maize in northwest China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2022: 263 doi: 10.1016/J.AGWAT.2021.107453 [24] WOOD C W, TRACY P W, REEVES D W, et al. Determination of cotton nitrogen status with a handheld chlorophyll meter[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2008, 15(9): 1435−1448 [25] XING H L, ZHOU W B, WANG C, et al. Excessive nitrogen application under moderate soil water deficit decreases photosynthesis, respiration, carbon gain and water use efficiency of maize[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 166: 1065−1075 doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.014 [26] 刘朋召, 周栋, 郭星宇, 等. 不同降雨年型旱地冬小麦水分利用及产量对施氮量的响应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(14): 3065−3076 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.14.012LIU P Z, ZHOU D, GUO X Y, et al. Water use and yield response of dryland winter wheat to N application in different rainfall years[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(14): 3065−3076 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.14.012 [27] 任宁, 汪洋, 王改革, 等. 不同降雨年份控释尿素与普通尿素配施对夏玉米产量、氮素利用及经济效益的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(4): 681−691 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19258REN N, WANG G Y, WANG R, et al. Effects of controlled-release urea and regular urea on yield, nitrogen utilization and economic efficiency of summer corn in different rainfall years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2020, 26(4): 681−691 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19258 [28] 付江鹏, 贾彪, 杨文伟, 等. 基于叶片干物质的滴灌玉米临界氮稀释曲线构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3): 945−952 doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202003.030FU J P, JIA B, YANG W W, et al. Construction of critical nitrogen dilution curve for drip irrigated maize based on leaf dry matter[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(3): 945−952 doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202003.030 [29] 张富仓, 严富来, 范兴科, 等. 滴灌施肥水平对宁夏春玉米产量和水肥利用效率的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(22): 111−120 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.22.014ZHANG F C, YAN F L, FAN X K, et al. Effect of drip irrigation fertilization level on yield and water and fertilizer use efficiency of spring maize in Ningxia[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(22): 111−120 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.22.014 [30] HOSSEIN D, NADER K. Interactive effects of Nitrogen and Drip Irrigation Rates on Root Development of Corn (Zea Mays L.) and Residual Soil Moisture[J]. Gesunde Pflanzen, 2020, 72: 1−15 doi: 10.1007/s10343-019-00495-1 [31] 贾彪, 李振洲, 王锐, 等. 不同施氮量下覆膜滴灌玉米相对根长密度模型研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(9): 266−273JIA B, LI Z Z, WANG R, et al. Modeling the relative root length density of maize under mulch drip irrigation with different N application rates[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(9): 266−273 [32] 郭星宇, 刘朋召, 王瑞, 等. 旱地冬小麦产量、氮肥利用率及土壤氮素平衡对降水年型与施氮量的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(5): 1262−1272 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2022.11034GUO XNY, LIU P Z, WANG R, et al. Response of dryland winter wheat yield, nitrogen fertilizer utilization and soil nitrogen balance to annual pattern of precipitation and nitrogen application[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1262−1272 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2022.11034 [33] 刘艳妮, 马臣, 于昕阳, 等. 基于不同降水年型渭北旱塬小麦–土壤系统氮素表观平衡的氮肥用量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(3): 569−578LIU Y N, MA C, YU X Y, et al. Study on nitrogen fertilizer dosage based on the apparent nitrogen balance of wheat-soil system in Weibei dry plateau with different precipitation year types[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2018, 24(3): 569−578 [34] XU A X, LI L L, XIE J H, et al. Effect of Long-Term Nitrogen Addition on Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Residual Soil Nitrate in a Semiarid Area of the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(5): 1735−1742 doi: 10.3390/su12051735 [35] CUI Z L, ZHANG F S, CHEN X P, et al. On-farm evaluation of an in-season nitrogen management strat-egy based on soil N-min test[J]. Field Crops Res, 2008, 105: 48−55 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2007.07.008 [36] 雒文鹤, 师祖姣, 王旭敏, 等. 节水减氮对土壤硝态氮分布和冬小麦水氮利用效率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(6): 924−936 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.91060LUO W H, SHI Z J, WANG X M, et al. Effects of water conservation and nitrogen reduction on soil nitrate nitrogen distribution and water nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 924−936 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.91060 [37] 张春霞, 文宏达, 刘宏斌, 等. 优化施肥对大棚番茄氮素利用和氮素淋溶的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(5): 1139−1145 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0513ZHANG C X, WEN H D, LIU H B, et al. Effect of optimal fertilization on nitrogen utilization and nitrogen leaching in greenhouse tomato[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(5): 1139−1145 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0513 [38] 戴嘉璐, 李瑞平, 李聪聪, 等. 盐渍化灌区玉米施氮量阈值DNDC模型模拟[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(24): 131−140 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.24.015DAI J L, LI R P, LI C C, et al. Simulation of DNDC model with N application threshold for maize in saline irrigated areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(24): 131−140 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.24.015 [39] 冯浩原, 尹光华, 马宁宁, 等. 不同降水年型地下滴灌追氮对玉米产量的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2021, 39(12): 1250−1256FENG H Y, YIN G H, MA N N, et al. Effect of subsurface drip irrigation on maize yield in different precipitation years[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2021, 39(12): 1250−1256 -





 下载:
下载: