ENSO events impacts to Shandong apple production Ⅱ: changes of agricultural meteorological disasters under different ENSO scenarios and affected to apple yield
-
摘要: 苹果作为山东优势果品之一, 其生产受农业气象灾害影响较大。探究在ENSO事件下山东农业气象灾害演变规律及其对山东苹果产量的影响, 对指导当地苹果生产具有重大意义。本文基于山东1991—2019年逐日气象观测数据、地市级苹果种植统计数据及ENSO事件数据, 利用数理统计分析和ArcGIS空间表达, 得出以下结论1) 1991−2019年不同ESNO年型下农业气象灾害发生情况区域差异显著。6—8月果实膨大期厄尔尼诺年干旱灾害发生较为频繁, 共计78次, 干旱频率最高约50%; 中性年雨涝灾害较为严重, 高达60次。鲁西、鲁中等热量资源充足地区, 干旱发生较为频繁; 鲁南降水资源较为充沛地区, 雨涝灾害发生频繁。鲁东、胶东半岛等地3—5月苹果花期极端低温灾害发生较为频繁, 发生日数约7~9 d·a−1, 频率约为60%—100%。鲁西等地是6—8月苹果果实膨大期高温热害的高发区, 发生天数11~15 d·a−1。2)不同ESNO年型下, 干旱与厄尔尼诺年呈正相关, 与拉尼娜年呈负相关。3—10月苹果可生长期厄尔尼诺年南方涛动指数与雨涝呈正相关相关, 拉尼娜年、中性年南方涛动指数与雨涝呈负相关。3—5月苹果花期低温灾害与厄尔尼诺年南方涛动指数呈负相关; 与拉尼娜年、中性年南方涛动指数呈正相关。3) 3—10月苹果可生长期, 厄尔尼诺年, 胶东半岛地区干旱加剧, 导致苹果减产率上升; 中性年, 雨涝灾害, 也使得苹果减产减收影响加重。6—8月苹果果实膨大期, 拉尼娜年、中性年下, 鲁西地区干旱与苹果减产率呈正相关; 中性年, 山东大部分地区雨涝与苹果减产率呈正相关。厄尔尼诺年苹果减产率受极端低温灾害影响较小, 高温热害影响较大; 拉尼娜年、中性年山东大部分地区低温冷害、冻害天数增加, 导致苹果减产率上升, 风险加大。苹果生产中, 谨防厄尔尼诺年高温、干旱, 拉尼娜年、中性年应预防低温、雨涝灾害对苹果产量、品质的损害, 确保苹果产业而健康可持续的生产。Abstract: Apple is one of the dominant fruits in Shandong province, which production is greatly affected by agricultural meteorological disasters. It is of great significance to explore the evolution characteristic of agrometeorological disasters and influence on local apple production under extreme climate events. In this study, based on the daily meteorological data, prefectural and municipal apple production statistical data and monthly ENSO events data from 1991 to 2019 in Shandong, using mathematical statistics analysis and ArcGIS spatial expression, we analyzed the study aims. The results showed that: 1) there are significant regional differences of agrometeorological disasters under different ENSO years during 1991 to 2019. During the period of fruit expansion from June to August, drought occurred frequently in El Nino years with 78 times and the highest frequency of drought was about 50%. In Neutral years, the flooding disaster is relatively serious, up to 60 times. Drought occurs frequently in areas with sufficient heat resources, such as Western and Central of Shandong. Rainfall and waterlogging disasters occur frequently in areas with abundant rainfall resources in Southern Shandong. In Eastern Shandong and Jiaodong Peninsula, the extreme low temperature disaster occurred frequently during apple flowering period from March to May. The number of low temperature days is about 7-9 d·a−1, which frequency is about 60%−100%. In Western Shandong Province and other places are the high incidence areas about high temperature heat disaster during apple fruit expansion period from June to August, with the occurrence days of 11-15 d·a−1. 2) Under different ESNO events, drought is positively correlated with El Nino years, while is negatively correlated in La Nina years. During apple growth period from March to October, there is a positive correlation between the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) and rainfall in El Nino years, while it is a negative correlation between the SOI and rain waterlogging in La Nina and Neutral years. Low temperature disasters are negatively correlated with the SOI in El Nino years, while are positively correlated with SOI in La Nina years and Neutral years during apple flowering period from March to May. 3) During March to October, the drought in Jiaodong Peninsula has intensified leading to the increase of apple yield reduction rate in El Nino years; the impact on rain and waterlogging of apple yield and income is also aggravated in Neutral years. In La Nina years and Neutral years, drought in Western Shandong was positively correlated with apple yield reduction rate; while in neutral years, the rainfall in most areas of Shandong is positively related to the reduction rate of apple yield during apple expansion period from June to August. In El Nino years, the reduction rate of apple yield is less affected by extreme low temperature disasters, but more affected by high temperature heat damage. The number of days of low temperature increased in most areas of Shandong under La Nina and Neutral years, which led to the reduction rate of apple yield and risk increase. Beware of high temperature and drought in ENSO event, we should prevent the damage of low temperature, rain and waterlogging to apple yield and quality, and ensure the healthy and sustainable production of apple industry.
-
Key words:
- Apple yield /
- Shandong /
- ENSO events /
- Drought and flood disaster /
- Extreme temperature
-
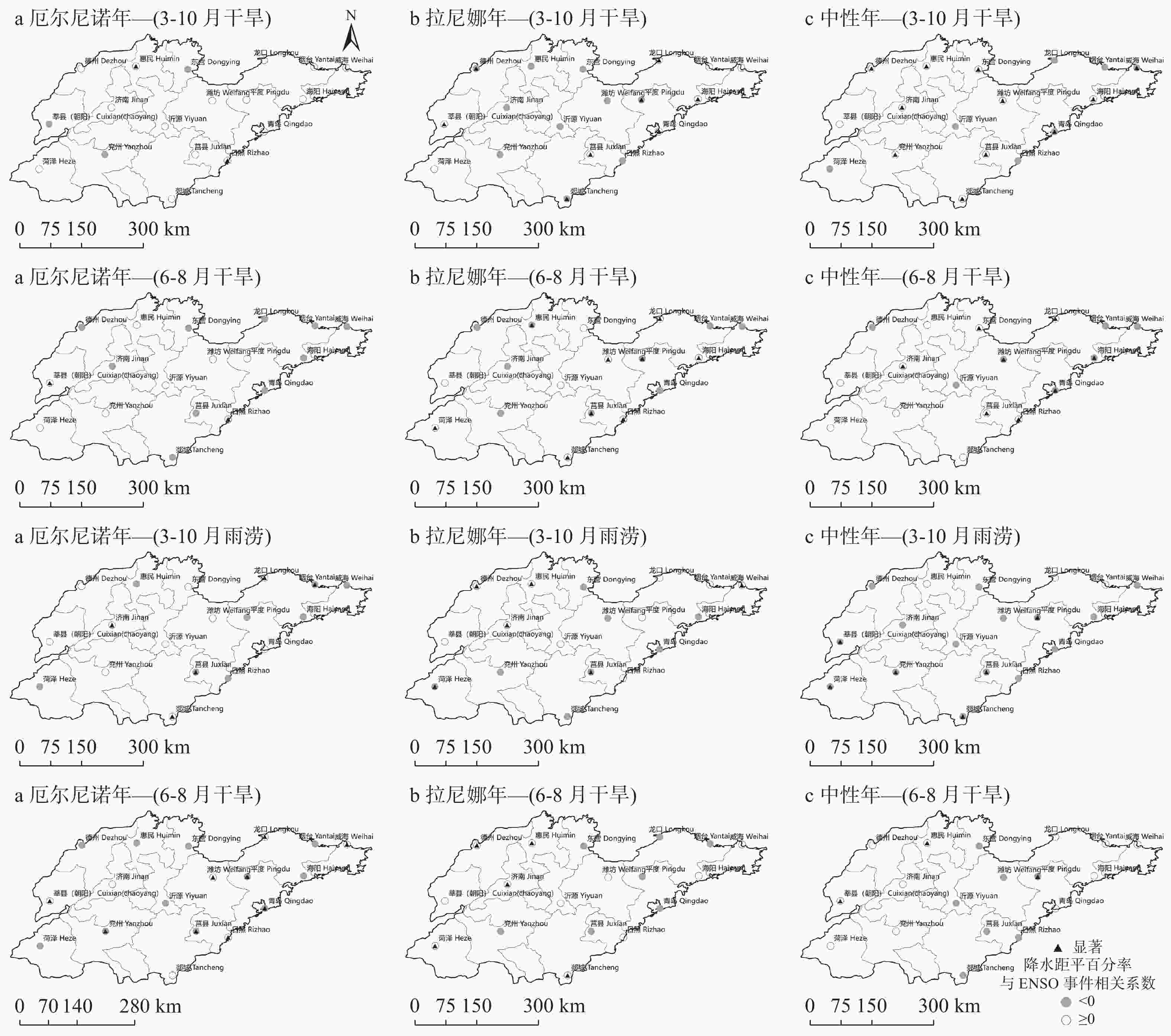
图 8 1991—2019年不同ENSO年型下旱涝灾害与ENSO事件南方涛动指数相关性的空间分布(从上至下: 3—10月干旱、6—8月干旱、3—10月雨涝、6—8月雨涝)
Figure 8. Spatial distribution of correlation between drought and flood disasters and ENSO events in different ENSO years from 1991 to 2019 (from top to bottom: drought in March-October ,drought in June-August, flood in March-October, flood in June-August)
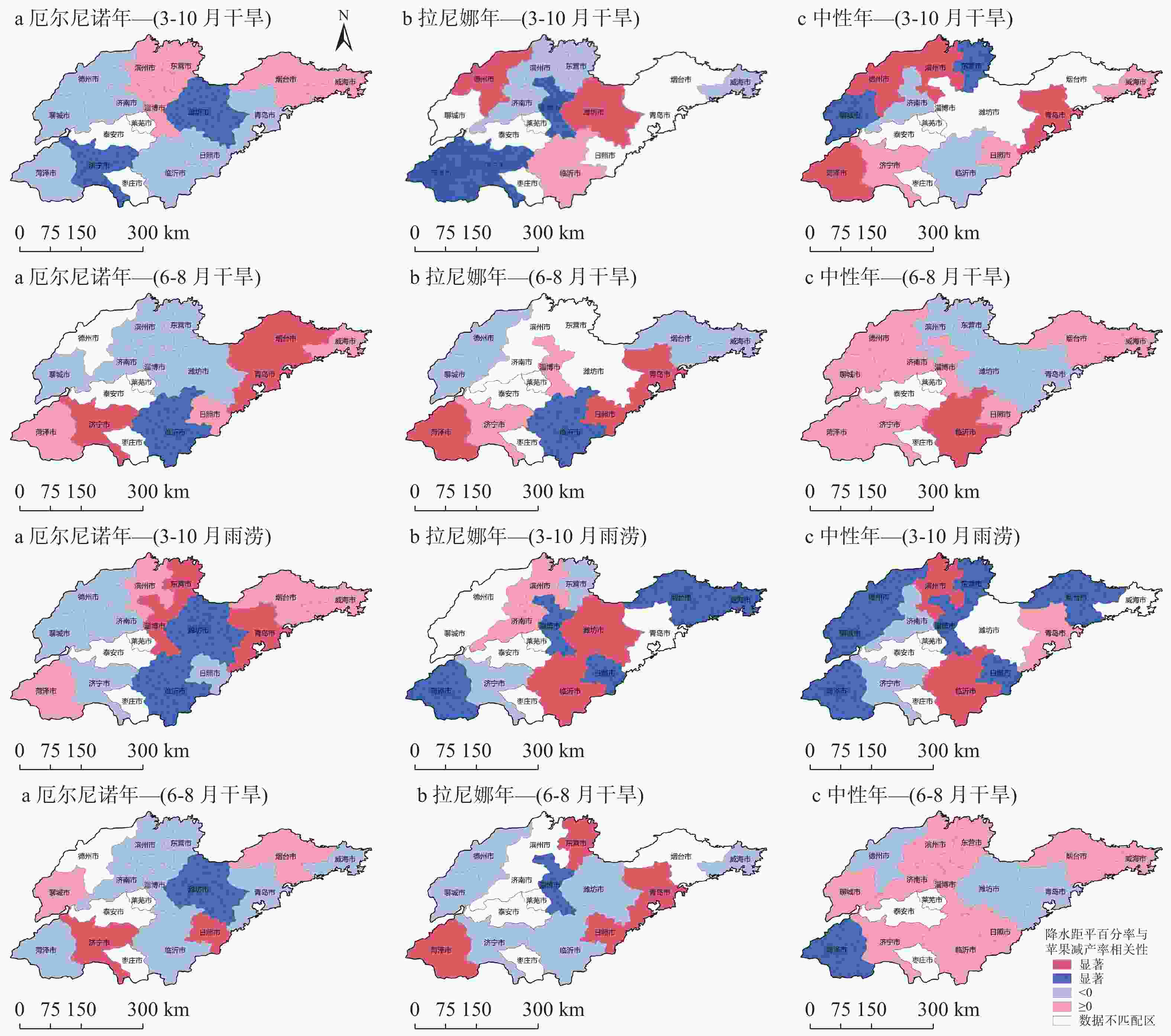
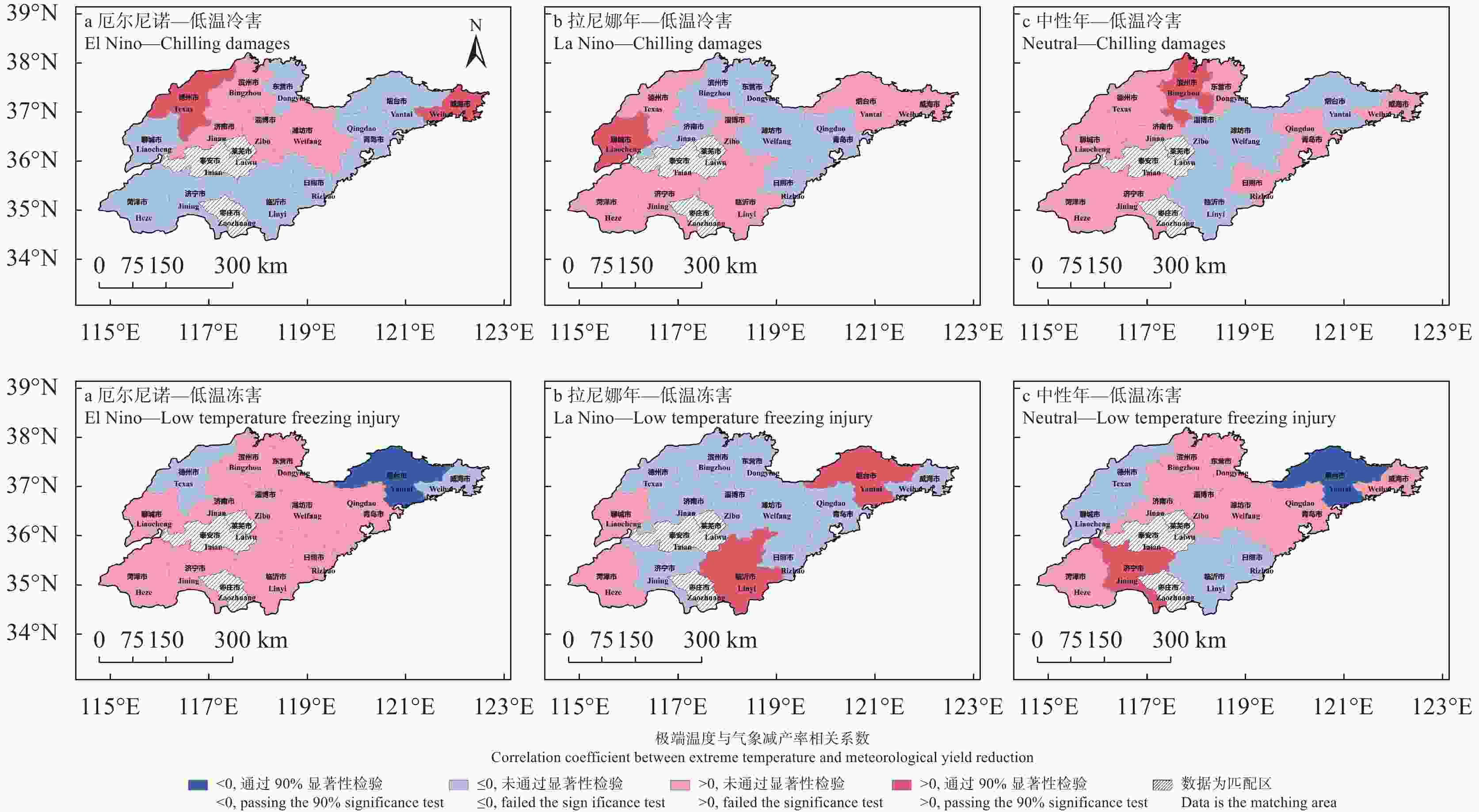
图 11 1991—2019年不同ENSO年型下旱涝灾害与苹果减产率相关性的空间分布(从上至下: 3—10月干旱、3—10月雨涝、6—8月干旱、6—8月雨涝)
Figure 11. Spatial distribution of correlation between drought and flood disasters and apple yield reduction rate under different ENSO years during 1991−2019 (from top to bottom: drought in March-October, drought in June-August, flood in March-October, flood in June-August)
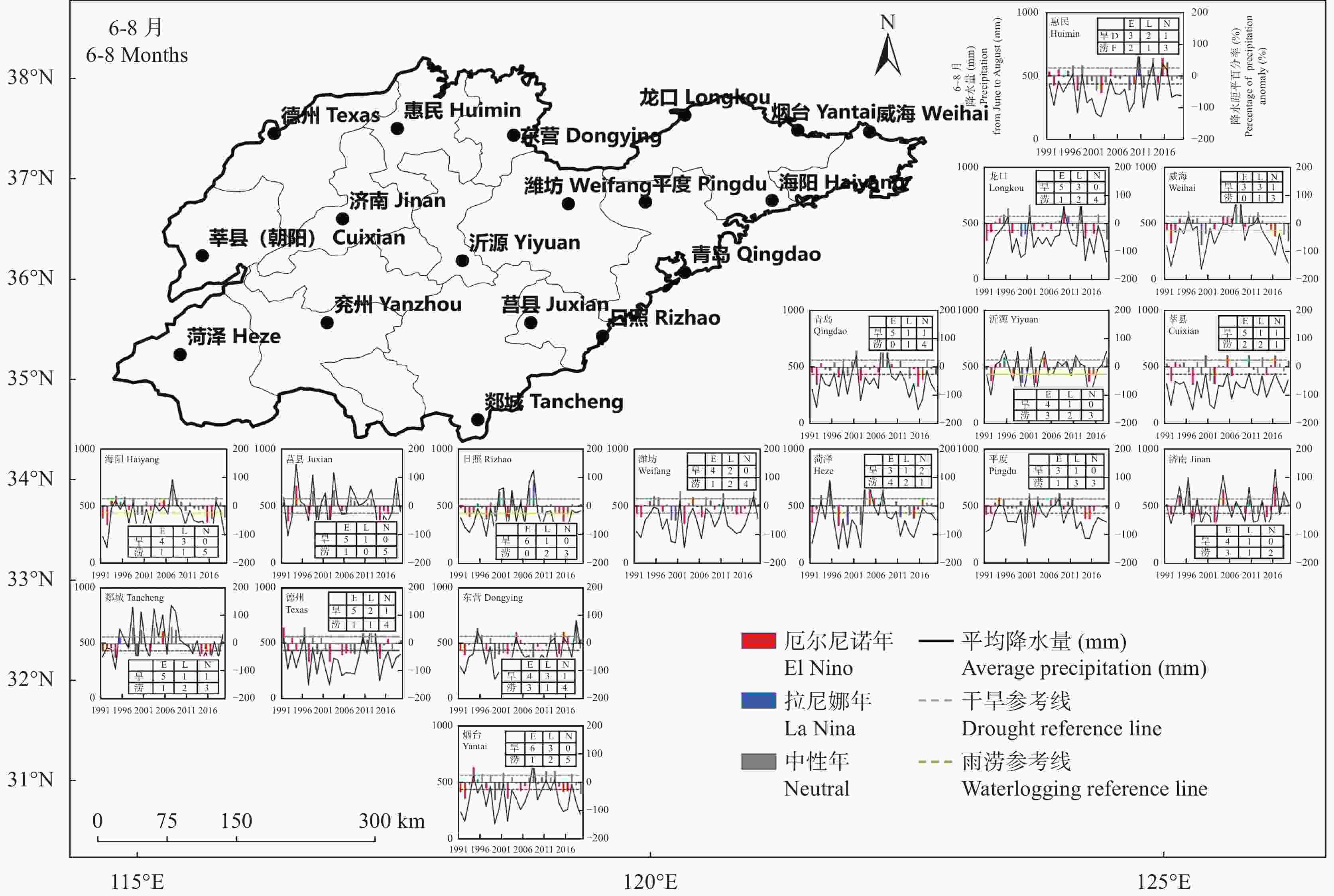
表 1 1991—2019年ENSO事件不同年型的统计[25-26]
Table 1. Classification of different ENSO events from 1991 to 2019
ENSO 年份 Years 总计 Total 厄尔尼诺年 El Nino years 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1997, 2002, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2009, 2014, 2015, 2016 13年 13 years 中性年 Neutral years 1996, 1998, 2001, 2003, 2007, 2012, 2013, 2017, 2018 9年 9 Years 拉尼娜年 La Nina years 1995, 1999, 2000, 2008, 2010, 2011, 2019 7年 7 Years 表 2 根据降水距平百分率划分旱涝等级
Table 2. Drought and flood grades according to the percentage of precipitation anomaly
等级 Level 季节 Season 年 Year 重涝 Heavy waterlogging $ Pa\geqslant 80\text{%} $ $ Pa\geqslant 45\text{%} $ 大涝 Flooding $ 80\text{%} > Pa\geqslant 50\text{%} $ $ 45\text{%} > Pa\geqslant 30\text{%} $ 偏涝 Partial waterlogging $ 50\text{%} > Pa > 25\text{%} $ $ 30\text{%} > Pa > 15\text{%} $ 正常 Normal $ 25\text{%}\geqslant Pa\geqslant -25\text{%} $ $ 15\text{%}\geqslant Pa\geqslant -15\text{%} $ 偏旱 Partial drought $ -25\text{%} > Pa > -50\text{%} $ $ -15\text{%} > Pa > -30\text{%} $ 大旱 Drought $ -50\text{%}\geqslant Pa > -80\text{%} $ $ -30\text{%}\geqslant Pa > -45\text{%} $ 重旱 Heavy drought $ -80\mathrm{\text{%}}\geqslant \mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ $ -45\mathrm{\text{%}}\geqslant \mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 表 3 以旱涝站次比划分区域灾害影响范围
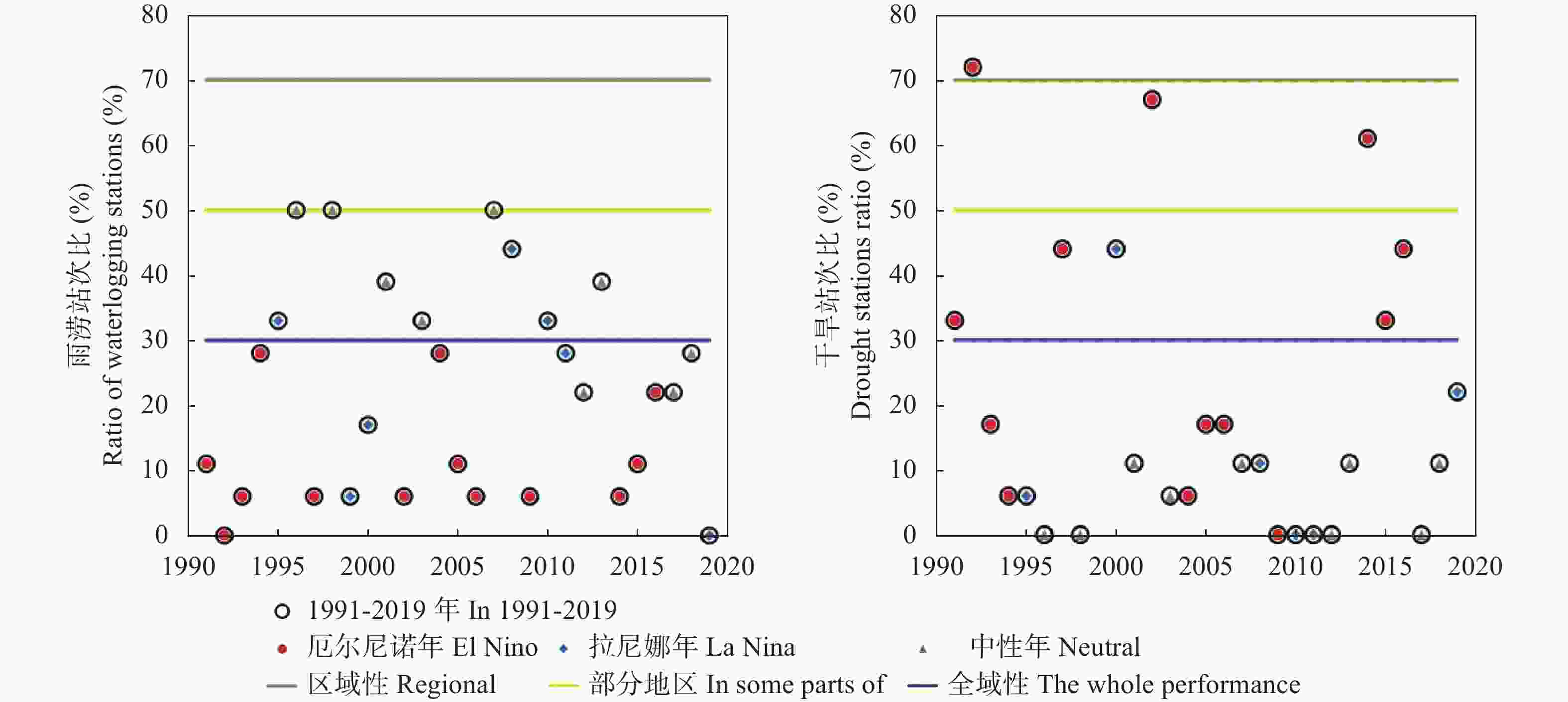
Table 3. The influence area of regional disasters by the stations ratio of drought and flood
旱涝站次比 Drought / flood station ratio 影响范围 Affected region Pj≥70% 全域性干旱(雨涝) Drought (flooding) in the whole region 70%>Pj≥50% 区域性干旱(雨涝) Regional drought (flooding) 50%>Pj≥30% 部分地区干旱(雨涝) Drought (flooding) in the most part of study region 30%>Pj≥10% 局部地区干旱(雨涝) Drought (flooding) in the local region Pj<10% 全域无明显干旱(雨涝)发生 Not occurred drought (flooding) 表 4 山东苹果极端温度指标
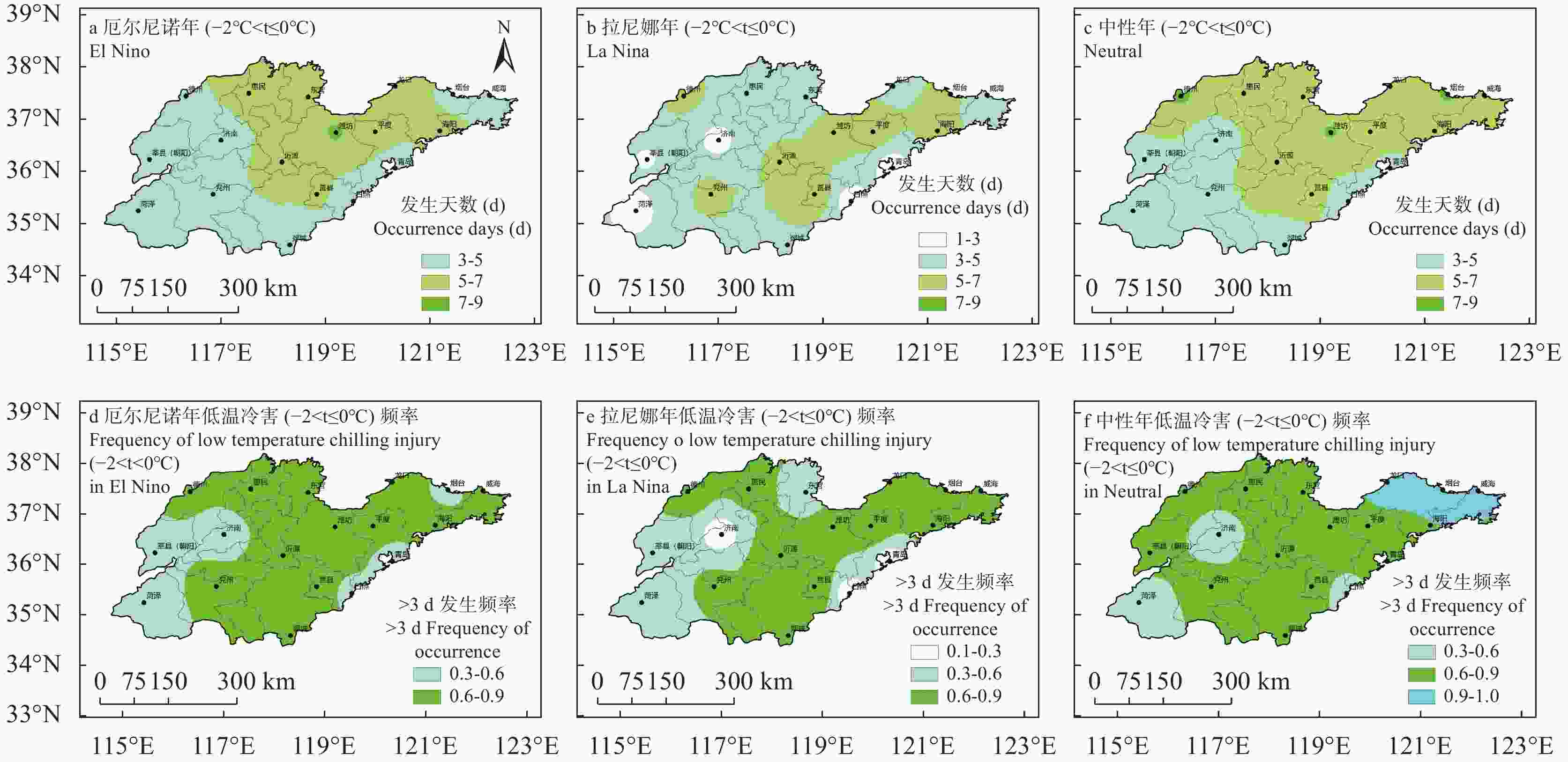
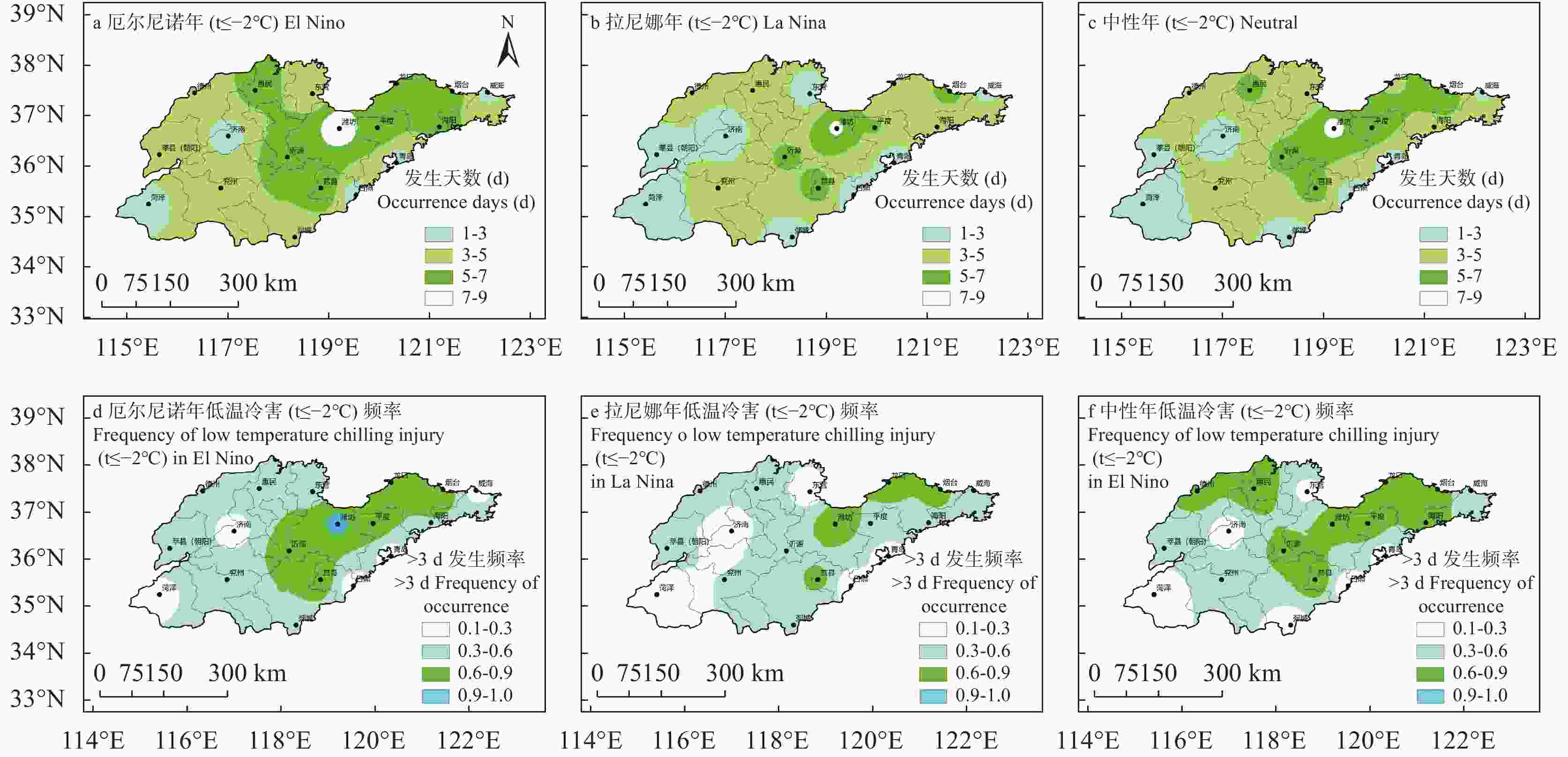
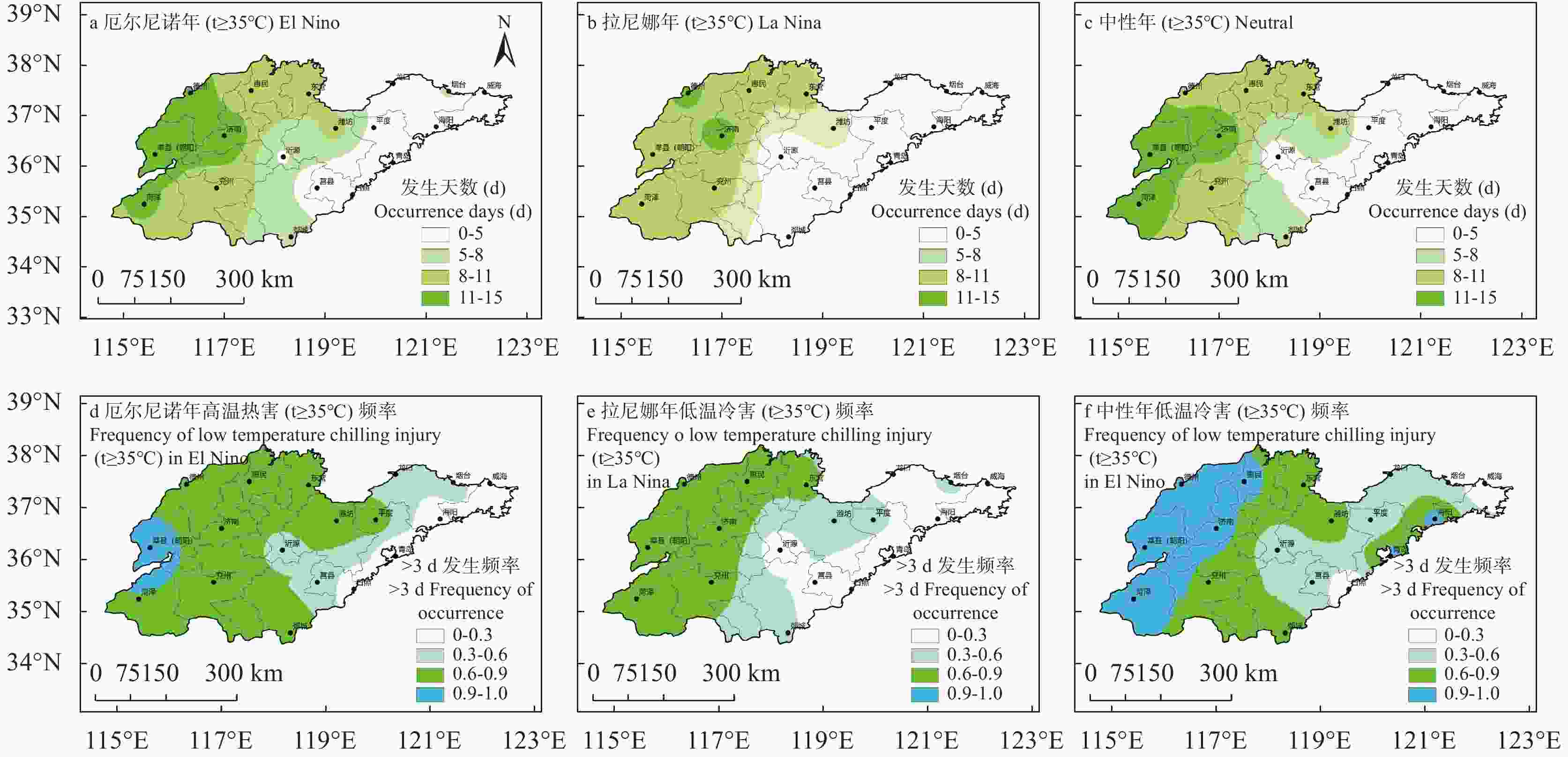
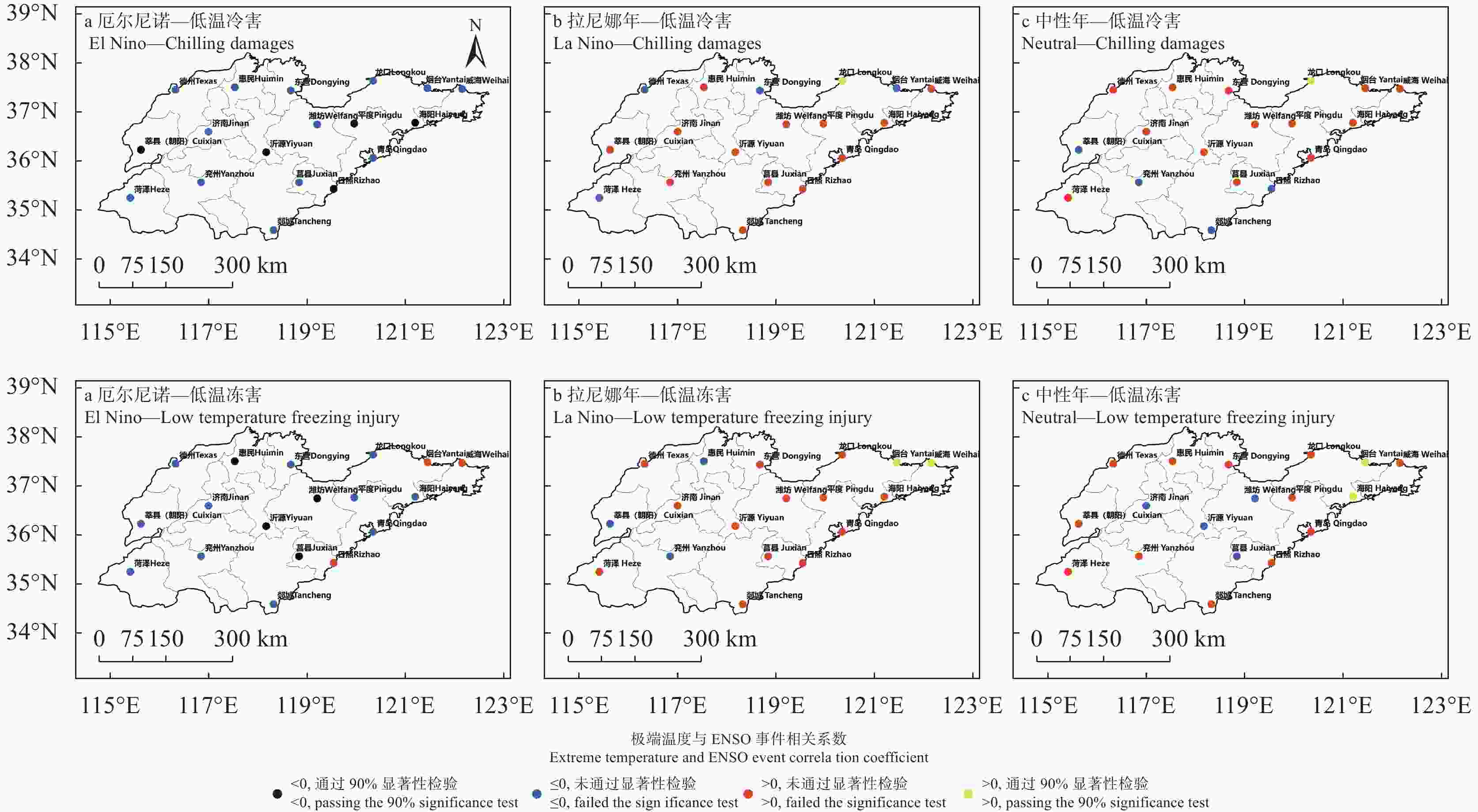
Table 4. Extreme temperature index of apple in Shandong
灾害类型
Agro - Disasters研究时段
The research period灾害种类
Types指标
Indicators极端低温
Extreme low temperature3-5月苹果开花期
Apple flowering period from March to May低温冷害
Chilling damages−2 ℃<$ {t}_{min} $≤0 ℃ 低温冻害
Low temperature freezing$ {t}_{min} $≤−2 ℃ 极端高温
Extreme heat6-8月果实膨大期
Fruit enlargement period from June to August高温热害
High temperature$ {t}_{max} $≥35 ℃ -
[1] 郑小华. 陕西苹果产业与气象条件关系研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2006ZHENG X H. Research on the relations between apple products and meteorological conditions in Shannxi Province[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2006 [2] 徐泽华, 韩美. 山东省干旱时空分布特征及其与ENSO的相关性[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(8): 1236−1248XU Z H, HAN M. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of drought in Shandong Province and it relationship with ENSO[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(8): 1236−1248 [3] 郑冬晓, 杨晓光. ENSO对全球及中国农业气象灾害和粮食产量影响研究进展[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2014, 37(4): 90−101ZHENG D X, YANG X G. Advances on effect of ENSO on agro-meteorological disasters and crop yields of the world and China[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 37(4): 90−101 [4] 王璐璐, 延军平, 韩晓敏. 环渤海地区旱涝灾害与太阳黑子活动、ENSO关系的统计研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 55(1): 123−130WANG L L, YAN J P, HAN X M. Statistical study of the relationship between the drought and flood over circum-Bohai-region and the Sunspot activity and ENSO[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2016, 55(1): 123−130 [5] 郭飞燕, 毕玮, 郭飞龙, 等. 山东气候年际变化特征及其与ENSO的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(3): 465−474GUO F Y, BI W, GUO F L, et al. Interannual climate variabillity in Shandong and its relationship with ENSO[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(3): 465−474 [6] 马露, 杨东, 曾婷. 1961—2012年山东省气候变化特征及其与ENSO的关系[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(16): 241−249 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb14120192MA L, YANG D, ZENG T. Climate change and its relationship with ENSO of Shandong Province from 1961 to 2012[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(16): 241−249 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb14120192 [7] 初军玲, 宋华丽. 文登区气候变化与厄尔尼诺/拉尼娜的关系[J]. 农技服务, 2017, 34(12): 79−80CHU J L, SONG H L. Relationship between climate change and El Niño/La Niña in Wendeng District[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 2017, 34(12): 79−80 [8] 奚秀芬, 郑世芳. 厄尼诺现象与山东旱涝的关系[J]. 山东气象, 1988, 8(4): 18−21,34XI X F, ZHENG S F. Relationship between El Niño phenomenon and drought and flood in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Shandong Meteorology, 1988, 8(4): 18−21,34 [9] 张克新, 董小刚, 廖空太, 等. 1960—2017年黄河流域极端气温的季节变化特征及其与ENSO的相关性分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(2): 185−192ZHANG K X, DONG X G, LIAO K T, et al. Characteristics of seasonal changes in extreme temperature and their relativity with ENSO in the Yellow River Basin from 1960 to 2017[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(2): 185−192 [10] 苗正伟, 李娜, 路梅, 等. 1961—2017年京津冀地区极端气温指数时空变化分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(3): 369−380MIAO Z W, LI N, LU M, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of extreme temperature in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2017[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2019, 55(3): 369−380 [11] 周丹. 1961—2013年华北地区气象干旱时空变化及其成因分析[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2015ZHOU D. Spatio-temporal changes and the cause analysis of meteorological drought in North China from 1961 to 2013[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2015 [12] 程雪, 孙爽, 张方亮, 等. 我国北方地区苹果干旱时空分布特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 63−73 doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200106CHENG X, SUN S, ZHANG F L, et al. Spatial and temporal distributions of apple drought in Northern China[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2020, 31(1): 63−73 doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200106 [13] 杨建莹, 霍治国, 王培娟, 等. 中国北方苹果干旱等级指标构建及危险性评价[J]. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(1): 25−37YANG J Y, HUO Z G, WANG P J, et al. Evaluation index construction and hazard risk assessment on apple drought in Northern China[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2021, 32(1): 25−37 [14] 李星敏, 柏秦凤, 朱琳. 气候变化对陕西苹果生长适宜性影响[J]. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22(2): 241−248 doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110213LI X M, BAI Q F, ZHU L. The influence of climate change on suitability of Shaanxi apple growth[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2011, 22(2): 241−248 doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110213 [15] 刘璐, 闫亮, 李红梅. 陕西省降水对苹果产量的影响分析[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2010, 56(5): 40−43LIU L, YAN L, LI H M. Analysis on the influence of precipitation on apple yield in Shaanxi Province[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 56(5): 40−43 [16] 马丽君. 苹果坐果率低的原因及应对措施[J]. 果树实用技术与信息, 2020(10): 4−5MA L J. Causes and countermeasures of low fruit setting rate of apple[J]. Practical Technology and Information of Fruit Trees, 2020(10): 4−5 [17] 程婷婷, 王猛. 北京市延庆地区苹果种植气象条件及灾害分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2019(14): 100−101 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2019.14.060CHENG T T, WANG M. Analysis on meteorological conditions and disasters of apple planting in Yanqing area of Beijing City[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(14): 100−101 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2019.14.060 [18] 张雯. 苹果花期冻害研究进展[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2021, 67(11): 103−107ZHANG W. Advance of research in apple freezing injury at flowering stage[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 67(11): 103−107 [19] 周军伟. 苹果低温冻害气象指数保险产品设计研究——以山东省栖霞市苹果低温冻害为例[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2014ZHOU J W. Product design of apple low temperature freezing injury index insurance—Shandong Qixia City as an example[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2014 [20] 李普越. 苹果树高温落果预防技术[J]. 河北果树, 2005(4): 36LI P Y. Prevention techniques of high temperature fruit drop of apple trees[J]. Hebei Fruits, 2005(4): 36 [21] 李艳莉, 刘映宁, 李美荣, 等. 陕西果树高温热害气象特征分析[C]//中国气象学会2007年年会生态气象业务建设与农业气象灾害预警分会场论文集. 广州, 2007: 981–989 [22] 魏丽欣, 张良玉, 赵春雷, 等. 河北省苹果膨大期高温热害和气候适宜性分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2019, 42(4): 10−15WEI L X, ZHANG L Y, ZHAO C L, et al. Analysis on high temperature heat damage and climate suitability of apple in swelling period in Hebei Province[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 42(4): 10−15 [23] 高菊红. 基于GIS的山东省苹果花期冻害风险分析与区划[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2014GAO J H. Analysis and regionalization of apple flowering cold injury risk based on GIS in shanddong Province[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2014 [24] 山东省统计局. 山东统计年鉴(1991—2019)[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 1991—2019Shandong Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Shandong Statistical Yearbook 1992[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 1991—2019 [25] 国家气候中心. ENSO监测、分析和预测系统[DB/OL]. 中国气象局, http://cmdp.ncc-cma.netNational Climate Center. ENSO monitoring, analysis and prediction system [DB/OL]. China Meteorological Administration, http://cmdp.ncc-cma.net [26] 邹德全, 邹承立, 田洪进, 等. 1960—2019年遵义市降水对2类ENSO的响应特征[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020(24): 167−171 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2020.24.068ZOU D Q, ZOU C L, TIAN H J, et al. Response characteristics of precipitation in Zunyi City from 1960 to 2019 to two kinds of ENSO[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(24): 167−171 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2020.24.068 [27] 李世奎, 朱佳满, 周远明, 等. 我国苹果种植区划研究[J]. 山西果树, 1985(4): 2−7,2LI S K, ZHU J M, ZHOU Y M, et al. Study on apple planting division in China[J]. Shanxi Fruits, 1985(4): 2−7,2 [28] 屈振江, 周广胜. 中国富士苹果种植气候适宜区的年代际变化[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(23): 7551−7561QU Z J, ZHOU G S. Dynamics of decadal changes in the distribution of cultivation regions with climate suitable for the Fuji apple in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(23): 7551−7561 [29] 郭珊珊. 苹果品质评价和气候区划进展分析[J]. 农村 农业 农民(B版), 2020(9): 55−56GUO S S. Evaluation of apple quality and progress analysis of climate division[J]. Country Agriculture Farmers (B), 2020(9): 55−56 [30] 屈振江, 周广胜. 中国富士苹果种植的气候适宜性研究[J]. 气象学报, 2016, 74(3): 479−490 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2016.027QU Z J, ZHOU G S. Climate suitability for potential Fuji apple cultivation in China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2016, 74(3): 479−490 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2016.027 [31] 张光伦. 苹果生态适宜条件与四川阿坝州苹果生态适宜性研究[J]. 果树科学, 1987, 4(3): 10−16ZHANG G L. Studies on the ecological optimum conditions of apple and its ecological suitability in Aba, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 1987, 4(3): 10−16 [32] 魏钦平, 张继祥, 毛志泉, 等. 苹果优质生产的最适气象因子和气候区划[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(5): 713−716 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.05.014WEI Q P, ZHANG J X, MAO Z Q, et al. Optimum meteorological factors and climate divisions of apple for good quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(5): 713−716 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.05.014 [33] 马露, 杨东, 钱大文. ENSO事件对山东省区域降水量及干旱指数的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(6): 666−673 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.06.002MA L, YANG D, QIAN D W. Impact of ENSO event on precipitation and drought index in Shandong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(6): 666−673 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.06.002 [34] 刘佳. 山东省气象干旱时空变化分析及农业气象干旱风险评估[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2019LIU J. Research on spatiotemporal variation of meteorological drought in Shandong Province and risk assessment of agricultural drought[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2019 [35] 任建成, 张婷婷. 基于标准化降水指数的山东省近45年旱涝演变特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(2): 149−154,162REN J C, ZHANG T T. Evolution characteristics of drought and flood in Shandong Province in recent 45 years based on standardized precipitation index[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(2): 149−154,162 [36] 马露, 杨东, 钱大文. ENSO事件对山东省区域降水量及干旱指数的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(6): 666−673MA L, YANG D, QIAN D W. Impact of ENSO event on precipitation and drought index in Shandong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(6): 666−673 [37] 柏秦凤, 霍治国, 王景红, 等. 中国主要果树气象灾害指标研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2019, 36(9): 1229−1243BAI Q F, HUO Z G, WANG J H, et al. Progress in research on meteorological disaster indicators of major fruit trees in China[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2019, 36(9): 1229−1243 [38] 张永红, 葛徽衍, 郭建茂. 苹果花期低温冻害风险区划与评估[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2013, 59(4): 61−63,109ZHANG Y H, GE H Y, GUO J M. Risk zoning and evaluation of low temperature freezing injury in apple flowering period[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 59(4): 61−63,109 [39] 李健, 刘映宁, 李美荣, 等. 陕西果树花期低温冻害特征及防御对策[J]. 气象科技, 2008, 36(3): 318−322LI J, LIU Y N, LI M R, et al. Low temperature and freezing injury to fruit trees at bloom stage in Shaanxi and countermeasures[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2008, 36(3): 318−322 [40] 李心怡, 张祎, 赵艳霞, 等. 主要作物产量分离方法比较[J]. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 74−82LI X Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y X, et al. Comparative study on main crop yield separation methods[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2020, 31(1): 74−82 [41] 李健, 刘映宁, 李美荣, 等. 陕西果树花期低温冻害特征及防御对策[J]. 气象科技, 2008, 36(3): 318−322LI J, LIU Y N, LI M R, et al. Low temperature and freezing injury to fruit trees at bloom stage in Shaanxi and countermeasures[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2008, 36(3): 318−322 [42] 焦文慧, 张勃, 马彬, 等. 近58 a中国北方地区极端气温时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(5): 1220−1230JIAO W H, ZHANG B, MA B, et al. Temporal and spatial changes of extreme temperature and its influencing factors in Northern China in recent 58 years[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(5): 1220−1230 [43] 刘玄, 唐培军, 吴同帅, 等. 山东省极端气候指数变化特征研究[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2022(2): 40−50LIU X, TANG P J, WU T S, et al. Study on the characteristics of extreme climate indices in Shandong Province[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2022(2): 40−50 [44] 董旭光, 周强, 刘焕彬, 等. 山东夏季极端热事件变化特征分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2020, 40(3): 60−76DONG X G, ZHOU Q, LIU H B, et al. Analysis on spatio-temporal characteristics of summer extreme hot events in Shandong from 1961 to 2019[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 2020, 40(3): 60−76 [45] 姜德娟, 李志, 王昆. 1961—2008年山东省极端温度事件时空特征分析[J]. 科技导报, 2011, 29(1): 30−35JIANG D J, LI Z, WANG K. Temporal and spatial characteristics of extreme temperature events over Shandong Province during 1961—2008[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2011, 29(1): 30−35 [46] CUI C, LIU Y, LIU B C, et al. ENSO events impacts on apple production in Shandong Ⅰ: a study of changes in apple climatic resources and yields under different scenarios[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(10): 1659−1674 -





 下载:
下载: