Responses of yield traits and grain filling characteristics of maize monoculture to sowing dates and their relationships with meteorological factors
-
摘要: 本文通过研究在限水灌溉条件下, 不同播期对一作玉米产量、产量性状和籽粒灌浆特性的影响及阶段气象因子与产量、产量性状及灌浆参数的相关关系, 探讨了播期对一年一作玉米产量的影响机制, 为低平原区高产高效生产提供了数据支撑。试验采用‘先玉335’和‘郑单958’ 2个玉米品种, 设置5个播期: 5月5日(SD1)、5月20日(SD2)、6月5日(SD3)、6月20日(SD4)和6月30日(SD5)。结果表明: 1)播期对产量影响显著, 且受品种和年型综合影响。随播期的延后, 产量呈现出先增加后降低的趋势, 2年平均以SD1产量最低, SD4产量最高, SD3和SD4间产量差异不显著。SD4产量高的主要原因是穗粒数和百粒重较高。2)通径分析表明, 产量要素对产量的贡献相互影响, 其中对产量的直接作用最大的是百粒重。3)采用Logistic模型研究粒重变化特征(R2>0.98, P<0.01) , 粒重的大小由平均灌浆速率(V)和灌浆持续期(D)的乘积决定, 其中D对粒重的直接贡献最大。4)从气象因子对产量和百粒重的影响来看, 播种到吐丝的日平均气温(TAvsf)越高, 吐丝到成熟的日均温差TRAvfm越大, 产量越高; 吐丝后10 d≥35 ℃的天数(D1fa)越多, 吐丝到成熟的日均气温(TAvfm)越高,产量和百粒重越低; 其中TAvfm对产量和百粒重的直接贡献最大, 且各气象因子对产量和百粒重的作用相互影响。SD1粒重较低的主要原因是TAvfm高、TRAvfm小, 且D1fa的天数多, D较短。SD3和SD4 粒重较高的主要原因是TRAvsf较大, V、D较高。SD5虽然TRAvfm较大, 但因TAvfm较低, 总体D缩短, 最终粒重降低。5)从品种来看, ‘先玉 335’较‘郑单 958’产量高的主要原因是穗粒数和百粒重高, 且‘先玉 335’的V和V×D分别较‘郑单958’高0.19 mg∙grain−1∙d−1、0.73 mg∙grain−1∙d−1。这说明选用产量潜力大、灌浆速率高的品种, 在6月上旬到6月中下旬播种可优化生育期气象要素, 进而提高粒重和产量。Abstract: This paper discussed the influence mechanism of sowing dates on maize yield. Under the condition of limited water irrigation, the effects of different sowing dates on yield, yield traits and grain filling characteristics of maize monoculture and the correlation between meteorological factors at different sowing dates and yield, yield traits and grain filling parameters were studied, which provided data support for high yield and high efficiency production in low plain areas. ‘Xianyu 335’ and ‘Zhengdan 958’ were used in the experiment. Five sowing dates were set: May 5 (SD1), May 20 (SD2), June 5 (SD3), June 20 (SD4) and June 30 (SD5). The results showed that: 1) the yield had significant effect by sowing dates and was affected by variety and climate year. The grain yield increased initially and followed by decrease subsequent decrease with the extension of sowing dates. The two-year-average yield of SD1 was the lowest, and that of SD4 was the highest. The yield difference between SD3 and SD4 was not significant. The high yield of SD4 was mainly due to the high grain number per spike and 100-grain weight. 2) Path analysis showed that the contribution of yield factors to yield affected each other, and the most direct effect on yield was 100-grain weight. 3) The variation characteristics of grain weight described by Logistic Model, the determination coefficient R2 was above 0.98, and the difference was significance at P<0.01.The grain weight is determined by the product of the average grain-filling rate (V) and the grain filling duration (D), and D has the largest direct contribution to the grain weight. 4) From the effect of meteorological factors on yield and yield traits, the higher the daily average temperature from sowing to silking, and the larger the daily temperature difference (TRAvfm) from silking to maturity, the higher the yield. The more days ≥35 ℃ (D1fa) after silking 10 days, the higher the daily average temperature (TAvfm) from silking to maturity, the lower the yield and 100-grain weight. The TAvfm had the largest direct contribution to yield and 100-grain weight, and the effects of various meteorological factors on yield and grain weight were mutually affected. The main reason for the lower grain weight of SD1 was that the accumulated temperature ≥10 ℃ during the whole growth period and the accumulated temperature from sowing to silking ≥10 ℃ were higher, TAvfm was higher, TRAvfm was smaller, and the days of D1fa were more, and D was shorter. SD3 and SD4 had larger TRAvfm, higher V and D, and higher grain weight. Although the sowing date of SD5 was relatively later, the lower TAvfm resulted in the decrease of the accumulated temperature from silking to maturity, and filling stage was shortened, thereby reducing the final grain weight. 5) In terms of varieties, the main reasons for the higher yield of ‘Xianyu 335’ compared with ‘Zhengdan 958’ were the higher grain number per spike and 100-grain weight, and the V and the product V and D of ‘Xianyu 335’ were 0.19 mg·grain−1·d−1 and 0.73 mg·grain−1·d−1 higher than those of ‘Zhengdan 958’, respectively. This showed that selecting varieties with high yield potential and high filling rate, sowing from early June to middle and late June could optimize meteorological factors during growth period, thereby increasing grain weight and yield.
-
表 1 2017年和2018年不同播期对玉米产量和产量性状的影响
Table 1. Effects of sowing date on yield and yield components of different maize varieties in 2017 and 2018
年份
Year品种
Variety播期(月-日)
Sowing date
(month-day)穗粒数
Grain number
per ear百粒重
100-grain
weight (g)有效株数
Effective number of
plants (×104 plant)产量
Yield
(kg·hm−2)2017 先玉 335
Xianyu 33505-05 658.6±13.3a 24.2±0.9c 6.3±0.05c 9506.2±195.6c 05-20 454.9±24.5c 41.3±0.7a 6.5±0.03b 12572.9±112.8a 06-05 524.2±13.7b 36.8±0.5b 6.7±0.00a 12290.0±544.5a 06-20 456.4±9.8c 40.1±0.9a 6.7±0.03a 12159.0±138.3a 06-30 473.0±11.7c 36.3±0.6b 6.6±0.00a 10603.6±230.2b 郑单958
Zhengdan 95805-05 459.0±26.2b 32.8±0.6c 6.5±0.02b 9146.8±285.8b 05-20 540.6±3.6a 34.8±0.8bc 6.7±0.00a 11813.5±265.9a 06-05 523.8±14.7a 35.5±0.2b 6.5±0.03b 12110.5±611.6a 06-20 498.2±23.1ab 38.9±1.0a 6.7±0.01a 11590.9±353.1a 06-30 493.0±10.9ab 33.5±1.0bc 6.6±0.01b 9948.9±301.1b 2018 先玉 335
Xianyu 33505-05 488.9±11.2a 33.5±0.1b 6.4±0.04 9527.7±369.1c 05-20 494.3±18.3a 31.8±0.4b 6.5±0.04bc 10050.8±409.9c 06-05 446.4±17.0b 40.9±0.6a 6.7±0.02a 11222.3±135.7b 06-20 518.1±8.2a 40.2±0.4a 6.6±0.02ab 12917.1±255.6a 06-30 493.9±14.9a 39.9±0.9a 6.1±0.08d 11655.5±42.4b 郑单958
Zhengdan 95805-05 495.5±1.7a 28.3±0.1e 6.5±0.04bc 8510.7±106.5c 05-20 410.2±14.6b 30.0±0.4d 6.5±0.04bc 7676.3±204.3d 06-05 481.3±1.9a 37.3±0.2a 6.7±0.04a 11238.5±115.8a 06-20 510.6±2.2a 35.3±1.0b 6.4±0.00c 11566.6±343.0a 06-30 485.5±13.0ab 32.4±0.2c 6.6±0.02ab 10101.5±260.7b 因素 Factor F值 F value 年际 Year (A) 15.1** 2.6 30.6** 29.6** 播期 Sowing date (B) 6.4** 109.7** 29.9** 58.1** 品种Variety (C) 2.8 78.1** 10.4** 43.3** A×B 9.4** 38.8** 16.0** 27.9** A×C 0.0 44.3** 3.6 7.9** B×C 10.7** 15.9** 18.8** 3.4* A×B×C 21.7** 24.8** 22.6** 1.2 不同小写字母表示该品种值在当年不同播期间的差异显著性。**和*表示P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著性。Different lowercase letters indicate that the value of the variety are significantly different during different sowing periods in the year. ** and * indicate significance at P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively. 表 2 玉米产量三要素与产量的通径分析
Table 2. Path analysis of three factors of yield and yield
因子
Factor相关系数
Correlation coefficient直接系数
Path coefficient间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficient 通过x1 Through x1 通过x2 Through x2 通过x3 Through x3 x1 0.1276 0.5950** −0.4451 −0.0223 x2 0.7968** 1.0267** −0.2578 0.0280 x3 0.2529 0.1033 −0.1288 0.2783 剩余通径系数=0.2826, n=20。x1: 穗粒数, x2: 百粒重, x3: 有效株数。**表示P<0.01。x1, x2 and x3 represent grain number per ear, 100-grain weight, number of effective plants, respectively. The residual path coefficient is 0.2826, n=20. ** indicates significance at the level of P<0.01. 表 3 试验期间对不同玉米品种产量和产量性状影响显著的气象因子状况
Table 3. Status of meteorological factors having a significant impact on yield and yield traits of different maize varieties in 2017 and 2018
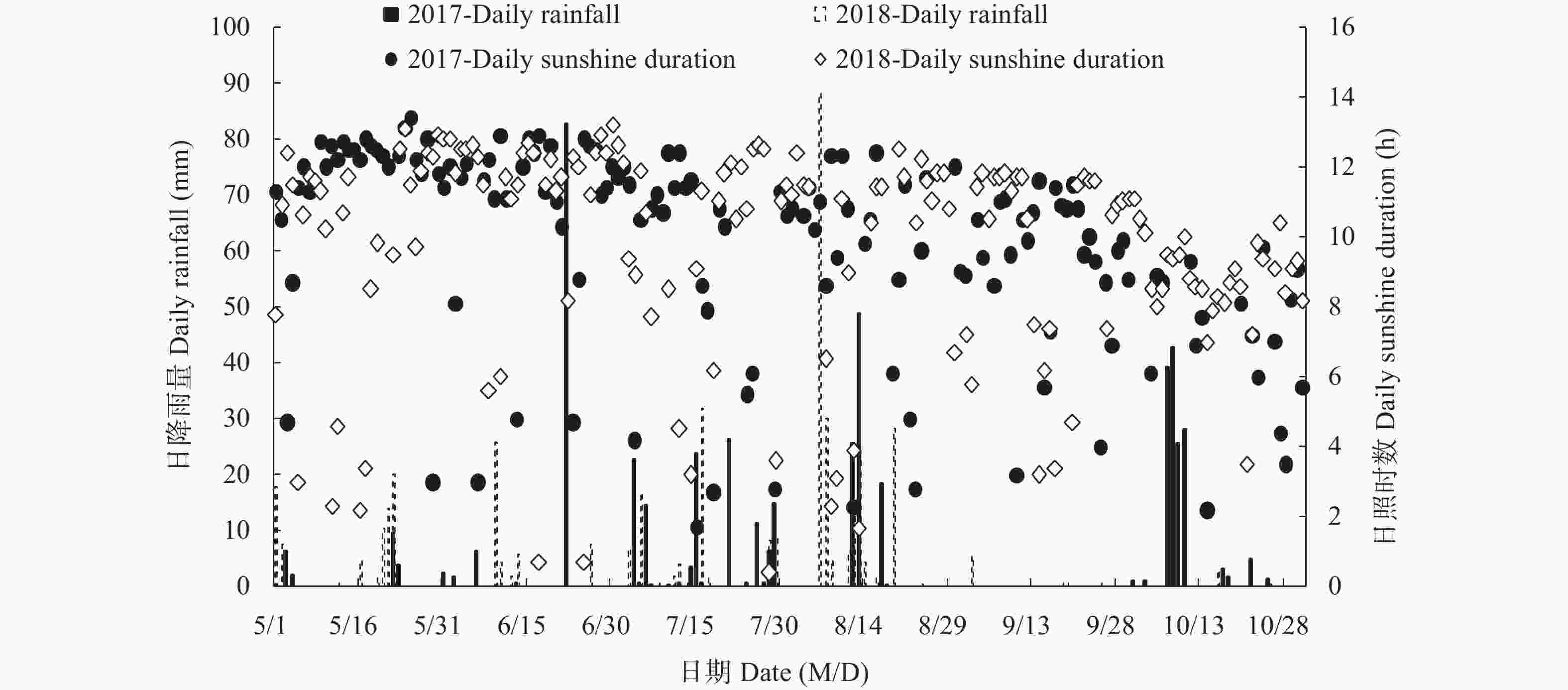
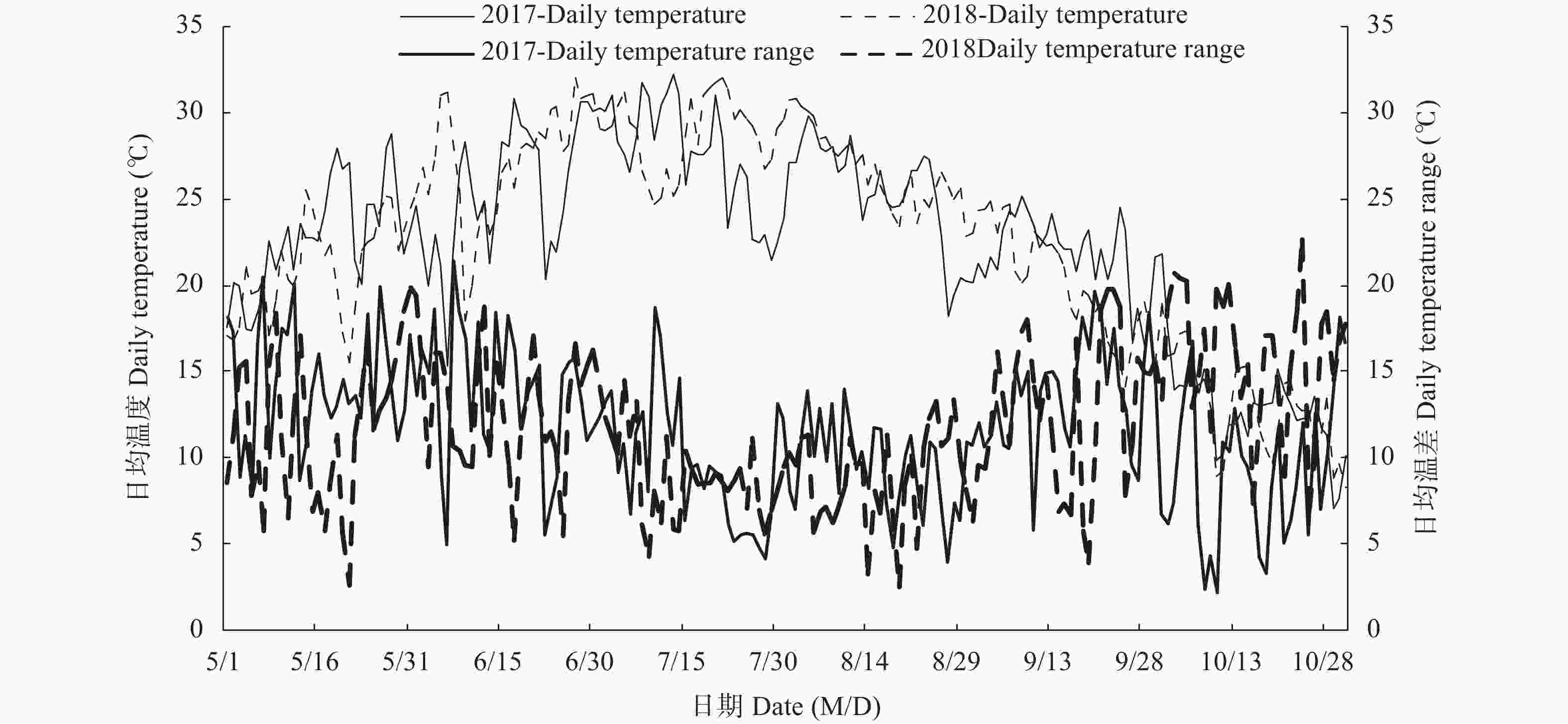
年份 Year 播期(月-日) Sowing date (month-day) 品种 Variety TAvsf (℃) Fsf (mm) TAvfm (℃) TRAvfm (℃) Ssf (h/d) D1fa (d) D2fa (d) 2017 05-05 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 25 146.0 26.0 9.4 10.4 7 7 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 25.1 174.8 25.5 9.5 10.4 6 7 05-20 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 26.3 217.9 24.3 10.6 9.7 1 2 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 26.4 285.1 24.0 10.6 9.7 1 1 06-05 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 26.9 221.0 21.6 11.1 8.3 1 3 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 26.9 122.3 21.0 11.1 8.4 1 2 06-20 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 27.3 156.0 19.5 10.5 8 0 1 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 27.3 128.5 19.3 10.5 8 0 1 06-30 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 27.3 214.1 18.3 10.8 7.5 0 1 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 27.2 284.1 18.3 10.8 7.5 0 1 2018 05-05 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 25 146.0 27.3 8.5 9.6 2 5 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 25 174.8 27.0 8.9 9.6 3 6 05-20 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 26.4 218.0 25.2 10 9.1 6 9 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 26.5 285.1 24.7 10.2 9.2 4 8 06-05 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 28.1 221.0 22.8 11.4 8.9 4 8 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 28.1 123.3 22.7 11.4 9 4 7 06-20 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 29.1 156.0 20.7 12.2 8.6 1 4 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 29.1 128.5 20.3 12.4 8.4 1 3 06-30 先玉 335 Xianyu 335 28.1 214.1 17.5 13.8 7.5 0 0 郑单 958 Zhengdan 958 28.1 284.1 17.5 13.8 7.5 0 0 TAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日平均气温; TAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日平均气温; Fsf: 播种到吐丝的降雨; Ssf: 播种到吐丝的日照; TRAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日均温差; D1fa: 吐丝后10 d≥35℃的天数; D2fa: 吐丝后10 d≥33℃的天数。 *和**表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著性。TAvsf, Fsf and Ssf represent daily average temperature, rainfall and sunshine hours from sowing to silking. TAvfm and TRAvfm represent daily average temperature and daily average temperature difference from silking to maturity, respectively. TAvf1 and TAvf12 represent daily average temperature range from silking to the first and first to second inflections, respectively. D1fa and D2fa represent days of ≥ 35 ℃ and ≥ 33 ℃ 10 days after silking, respectively. * and ** indicate significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. 表 4 气象要素与玉米产量和产量性状的偏相关关系
Table 4. Partial correlation between meteorological factors with yield and yield traits of maize
TAvsf TAvfm Fsf TRAvfm Ssf D1fa D2fa TAvf1 TAvf12 穗粒数 Grain number per ear −0.1897 0.1146 −0.0216 −0.0757 0.2376 0.1934 −0.0484 0.0327 −0.0076 百粒重 100-grain weight 0.6153** −0.4996* 0.4133 0.4570* −0.5160* −0.5691** −0.4187 −0.4580* −0.4516* 有效株数 Number of effective plant 0.1727 −0.1011 −0.0092 −0.1047 −0.1214 −0.1358 −0.0082 −0.0890 0.0178 产量Yield 0.5758** −0.4724* 0.4669* 0.4735** −0.3972 −0.5394* −0.5198* −0.4674* −0.4760* TAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日平均气温; TAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日平均气温; Fsf: 播种到吐丝的降雨; Ssf: 播种到吐丝的日照; TRAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日均温差; D1fa: 吐丝后10 d≥35℃的天数; D2fa: 吐丝后10 d≥33℃的天数。TAvf1和TAv f12分别为吐丝到第1和第1到第2拐点的日平均气温。*和**表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。TAvsf, Fsf and Ssf represent daily average temperature, rainfall and sunshine hours from sowing to sulking, respectively. TAvfm and TRAvfm represent daily average temperature and daily average temperature difference from silking to maturity, respectively. D1fa and D2fa represent days of ≥ 35 ℃ and ≥ 33 ℃ 10 days after silking, respectively. TAvf1 and TAvf12 represent daily average temperature range from silking to the first and first to second inflections, respectively. * and ** indicate significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. 表 5 气象要素与玉米产量的通径分析
Table 5. Path analysis of meteorological factors and yield of maize
因子
Factor相关系数
Correlation
coefficient通径系数
Path coefficient间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficients 通过TAvsf
Through TAvsf通过TAvfm
Through TAvfm通过Fsf
Through Fsf通过TRAvfm
Through TRAvfm通过D1fa
Through D1fa通过D2fa
Through D2fa通过TAvf1
Through TAvf1通过TAvf12
Through TAvf12TAvsf 0.5758** 1.7764 −1.4599 −0.1564 −1.2033 −0.4062 0.9062 −0.6367 0.4618 TAvfm −0.4724* 1.9326 −1.3418 −0.0764 0.8666 0.2744 −1.0633 0.1661 −1.2308 Fsf 0.4669* 0.0872 0.8503 −1.6925 −0.9018 −0.6055 2.0968 −1.2360 0.5592 TRAvfm 0.4735* −1.1025 1.3672 −1.5191 −0.1885 −0.4001 1.2707 −0.7146 0.5560 D1fa −0.5394* 0.3719 −0.8076 1.4260 0.2214 0.7001 −2.3328 1.2697 −0.4001 D2fa −0.5198* −1.4281 −0.5695 1.4388 0.2424 0.7029 0.7375 1.3825 −0.4534 TAv f1 −0.4674* 0.1951 −0.6892 1.6458 0.2461 0.6808 0.6913 −2.3812 −0.5028 TAv f12 −0.4760* −1.3034 −1.1295 1.8250 0.2516 1.1967 0.4921 −1.7643 1.1358 剩余通径系数=0.5483, n=20。TAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日平均气温; TAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日平均气温; Fsf: 播种到吐丝的降雨; TRAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日均温差; D1fa: 吐丝后10 d≥35℃的天数; D2fa: 吐丝后10 d≥33℃的天数; TAvf1: 吐丝到第1拐点的日平均气温; TAv f12:第1到第2拐点的日平均气温。*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。The residual path coefficient is 0.6939, n=20. TAvsf and Fsf represent daily average temperature and rainfall from sowing to silking, respectively. TAvfm and TRAvfm represent daily average temperature and daily average temperature difference from silking to maturity, respectively. D1fa and D2fa represent days of ≥35 ℃ and ≥33 ℃ 10 days after silking, respectively. TAvf1 and TAvf12 represent daily average temperature range from silking to the first and first to second inflections, respectively. *and ** indicate significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. 表 6 气象要素与玉米百粒重的通径分析
Table 6. Path analysis of meteorological factors and 100-grain weight of maize
因子
Factor相关系数
Correlation
coefficient通径系数
Path
coefficient间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficient 通过TAvsf
Through TAvsf通过TAvfm
Through TAvfm通过TRAvfm
Through TRAvfm通过Ssf
Through Ssf通过D1fa
Through D1fa通过TAvf1
Through TAvf1通过TAvf12
Through TAvf12TAvsf 0.6153** 1.2805 −1.0472 −0.4597 −0.5536 0.2358 0.0657 0.1045 TAvfm −0.4996* 1.3863 −0.9673 0.4969 0.1603 −0.3547 −0.3375 −0.8837 TRAvfm 0.4570* −0.6321 1.0380 −1.0897 −0.4712 0.2323 0.0737 0.1258 Ssf −0.5160* 0.1789 −1.0147 1.2425 0.3826 −0.3301 −0.1089 −0.1118 D1fa −0.5691** −0.4807 −0.6131 1.0229 0.2675 0.4682 −0.1309 −0.0905 TAvf1 −0.4580* −0.3963 −0.5233 1.1805 0.2601 0.4736 −0.4013 −0.1138 TAvf12 −0.4516* −0.9359 −0.8575 1.3091 0.4572 0.5005 −0.2857 −0.1171 剩余通径系数=0.5483, n=20。TAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日平均气温; TAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日平均气温; Fsf: 播种到吐丝的降雨; TRAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日均温差; D1fa: 吐丝后10 d≥35℃的天数; D2fa: 吐丝后10 d≥33℃的天数; TAvf1: 吐丝到第1拐点的日平均气温; TAv f12:第1到第2拐点的日平均气温。*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。The residual path coefficient is 0.6939, n=20. TAvsf and Fsf represent daily average temperature and rainfall from sowing to silking, respectively. TAvfm and TRAvfm represent daily average temperature and daily average temperature difference from silking to maturity, respectively. D1fa and D2fa represent days of ≥35 ℃ and ≥33 ℃ 10 days after silking, respectively. TAvf1 and TAvf12 represent daily average temperature range from silking to the first and first to second inflections, respectively. *and ** indicate significance at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. 表 7 不同播期不同品种粒重及粒重变化特征方程
Table 7. Characteristic equation of grain weight and grain weight change of different maize varieties sown at different dates
年份
Year品种
Variety播期(月-日)
Sowing date (month-day)粒重变化特征方程
Grain weight change characteristic equation方程决定系数R2
Coefficient of determination实测粒重
Measured grain weight (mg)2017 先玉335
Xianyu 33505-05 Yt=0.3270/[1+exp(3.0944−0.1123t)] 0.9969** 320.7c 05-20 Yt=0.4033/[1+exp(4.0557−0.1415t)] 0.9962** 396.2a 06-05 Yt=0.3964/[1+exp(2.5405−0.1378t)] 0.9879** 379.2b 06-20 Yt=0.3965/[1+exp(3.7615−0.1365t)] 0.9820** 390.4a 06-30 Yt=0.3928/[1+exp(4.2806−0.1462t)] 0.9900** 388.8ab 郑单958
Zhengdan 95805-05 Yt=0.3138/[1+exp(3.7647−0.1326t)] 0.9970** 307.7d 05-20 Yt=0.3443/[1+exp(3.5721−0.1304t)] 0.9953** 337.9c 06-05 Yt=0.3572/[1+exp(2.6575−0.1399t)] 0.9901** 343.4c 06-20 Yt=0.4264/[1+exp(3.1927−0.0990t)] 0.9830** 429.4a 06-30 Yt=0.3752/[1+exp(3.3797−0.1171t)] 0.9830** 363.0b 2018 先玉335
Xianyu 33505-05 Yt=0.3714/[1+exp(3.4882−0.1419t)] 0.9943** 362.7c 05-20 Yt=0.3424/[1+exp(3.2859−0.1396t)] 0.9968** 335.6d 06-05 Yt=0.4167/[1+exp(3.2712−0.1259t)] 0.9970** 404.8b 06-20 Yt=0.4379/[1+exp(3.6048−0.1150t)] 0.9889** 421.7a 06-30 Yt=0.4187/[1+exp(3.3637−0.1055t)] 0.9897** 407.4b 郑单958
Zhengdan 95805-05 Yt=0.2963/[1+exp(3.1152−0.1285t)] 0.9880** 285.0d 05-20 Yt=0.3059/[1+exp(3.2796−0.1361t)] 0.9886** 293.4d 06-05 Yt=0.4122/[1+exp(3.2118−0.0995t)] 0.9942** 399.8a 06-20 Yt=0.3965/[1+exp(3.4208−0.1198t)] 0.9918** 383.0b 06-30 Yt=0.3373/[1+exp(3.4976−0.1328t)] 0.9986** 331.2c 不同小写字母表示该品种的实测粒重在当年不同播期间差异显著性。**表示P<0.01水平显著。Different lowercase letters indicate the significant difference of measured grain weight of variety in different sowing periods in the year. ** indicates significance at P<0.01. 表 8 不同播期不同玉米品种籽粒灌浆特征参数
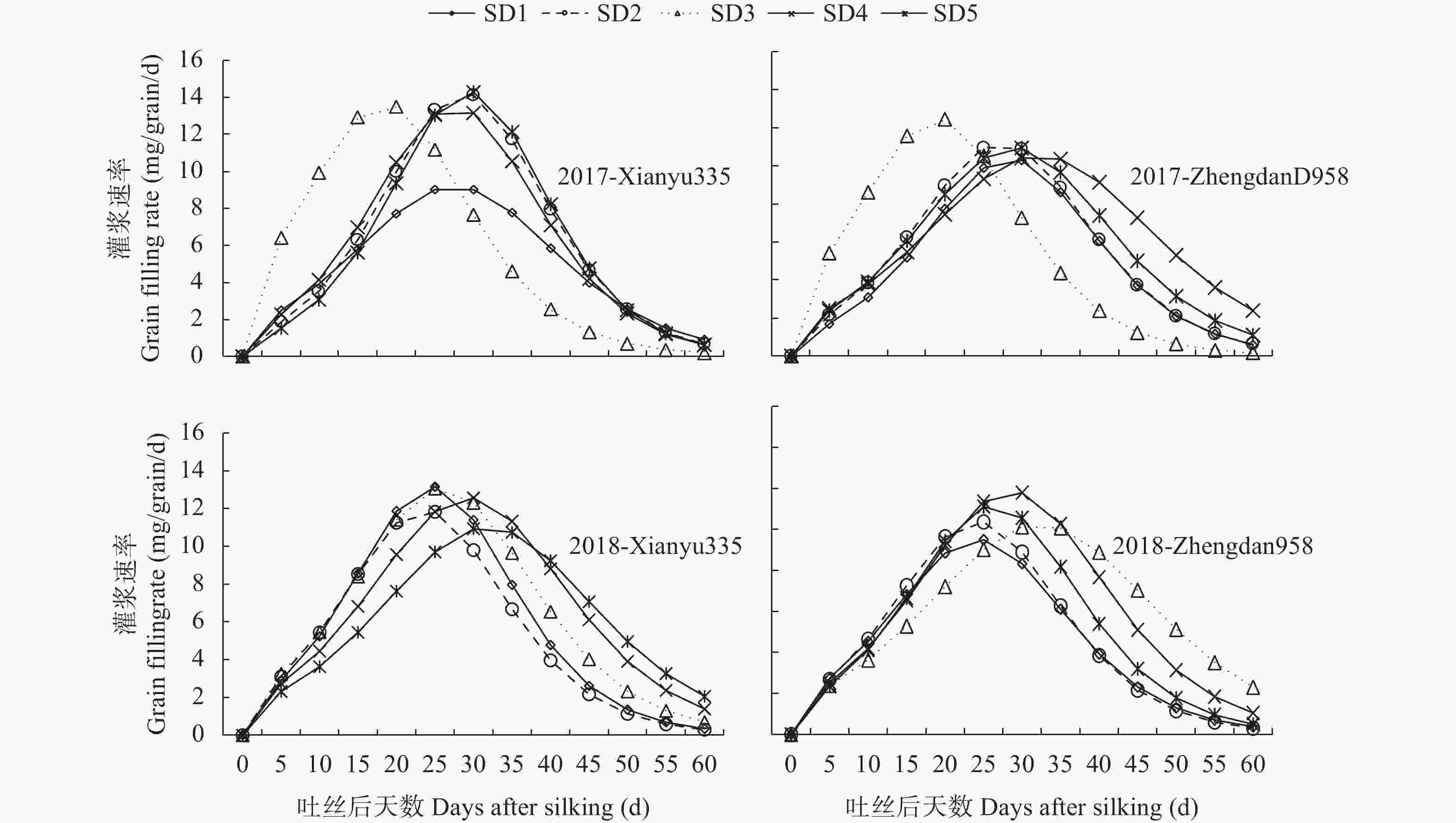
Table 8. Grain filling characteristic parameters of different maize varieties sown at different dates
年份 Year 品种 Variety 播期(月-日) Sowing date (month-day) t1 (d) t2 (d) Vmax (mg∙grain−1∙d−1) V (mg∙grain−1∙d−1) D (d) 2017 先玉335 Xianyu 335 05-05 15.83 39.28 9.18 4.78 68.47 05-20 19.36 37.97 14.27 6.60 61.14 06-05 8.88 27.99 13.66 7.66 51.78 06-20 17.91 37.20 13.53 6.48 61.22 06-30 20.27 38.29 14.36 6.47 60.71 郑单958 Zhengdan 958 05-05 18.46 38.32 10.40 4.98 63.05 05-20 17.30 37.49 11.22 5.50 62.63 06-05 9.58 28.41 12.49 6.89 51.84 06-20 18.95 45.55 10.55 5.42 78.66 06-30 17.62 40.11 10.98 5.51 68.10 2018 先玉335 Xianyu 335 05-05 15.30 33.86 13.18 6.52 56.96 05-20 14.11 32.97 11.95 6.07 56.45 06-05 15.52 36.44 13.12 6.67 62.48 06-20 17.86 40.76 12.59 6.32 69.27 06-30 19.40 44.37 11.04 5.55 75.44 郑单958 Zhengdan 958 05-05 14.00 34.49 9.52 4.94 60.00 05-20 14.42 33.77 10.41 5.29 57.86 06-05 19.05 45.52 10.25 5.25 78.46 06-20 17.56 39.55 11.88 5.93 66.91 06-30 16.42 36.25 11.20 5.54 60.94 t1: 到达第1拐点的时间; t2: 到达第2拐点的时间; Vmax: 最大灌浆速率; V: 平均灌浆速率分别用和表示; D: 灌浆持续期。t1 and t2 represent the time to reach the first and second inflection points, respectively. Vmax and V mean the maximum grain-filling rate and the average grain-filling rate, respectively. D means grain filling duration. 表 9 玉米籽粒灌浆特征参数间和粒重的相关关系
Table 9. Correlation between grain filling characteristic parameters and grain weight of maize
因子 Factor t1 t2 Vmax V D t2 0.8630** Vmax −0.0544 −0.3440 V −0.4171 −0.5365* 0.9035** D 0.7088** 0.99681** −0.4536* −0.5424* 粒重 Grain weight 0.4013 0.4933* 0.5033* 0.4547* 0.4894* t1: 到达第1拐点的时间; t2: 到达第2拐点的时间; Vmax: 最大灌浆速率; V: 平均灌浆速率分别用和表示; D: 灌浆持续期。*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著性。t1 and t2 represent the time to reach the first and second inflection points, respectively. Vmax and V mean the maximum grain-filling rate and the average grain-filling rate, respectively. D means grain filling duration.*and ** indicate significance at the level of P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. 表 10 玉米籽粒灌浆特征参数与粒重的通径分析
Table 10. Path analysis between grain filling characteristic parameters and grain weight of maize
因子
Factors相关系数
Correlation coefficient通径系数
Path coefficients间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficients 通过t2
Through t2通过Vmax
Through Vmax通过V
Through V通过D
Through Dt2 0.4933* −0.5449 −0.2122 −0.2344 1.4847 Vmax 0.5033* 0.6169 0.1874 0.3947 −0.6957 V 0.4547* 0.4368 0.2923 0.5574 −0.8319 D 0.4894* 1.5337 −0.5275 −0.2799 −0.2369 剩余通径系数=0.0946, n=20。t2: 到达第2拐点的时间; Vmax: 最大灌浆速率; V: 平均灌浆速率; D: 灌浆持续期。* 表示P<0.05水平差异显著性。The residual path coefficient=0.0946, n=20. t2 represents the time to reach the first and second inflection points, respectively. Vmax and V mean the maximum grain-filling rate and the average grain-filling rate, respectively. D means grain filling duration. * indicates significance at the level of P<0.05. 表 11 气象因子间及灌浆特征参数和粒重与气象因子间的偏相关关系
Table 11. The partial correlation relationship between meteorological factors, grain filling characteristic parameters, grain weight and meteorological factors
因子 Factor T TAvsm Tsf TAvsf TRAvsf Ssf TAvfm TRAvfm D1fa Tf1Av Tf12Av TAvsm 0.9076** Tsf 0.6867** 0.5448* TAvsf −0.5648** −0.5722** −0.5208* TRAvsf 0.7786** 0.7902** 0.5585* −0.8199** Ssf 0.8016** 0.8388** 0.7459** −0.8300** 0.9330** TAvfm 0.9029** 0.9996** 0.5462* −0.5798** 0.7871** 0.8416** TRAvfm −0.6420** −0.6417** 0.8490** −0.7863** −0.7065** −0.7860** Ffm 0.7580** 0.6817** 0.5319* −0.6367** 0.6113** 0.6215** 0.7183** −0.8457** D1fa 0.5808** 0.7349** −0.5015* 0.6337** 0.7020** 0.7378** −0.4940* Tf1 −0.5257* −0.4804* 0.8536** TAvf1 0.8000** 0.9174** 0.4987* 0.6007** 0.7101** 0.8516 ** −0.4804* 0.8536** 0.5514* Tf12 0.4467* 0.5820** −0.4616* 0.5481* 0.5514* T Avf12 0.8315** 0.8960** -0.7014** 0.7971** 0.7505** 0.5788** −0.8444** 0.6076** 0.7636** −0.3696 t2 −0.4520* −0.3335 −0.5958** 0.3679 −0.3072 −0.3764 −0.3307 0.3029 −0.1107 −0.3350 −0.3696 Vmax −0.1115 −0.1837 −0.1798 0.2426 −0.1628 −0.3021 −0.2332 0.1066 −0.4533* −0.2847 −0.0972 V −0.0026 −0.1110 0.0890 0.2481 −0.1668 −0.2222 −0.2008 0.1224 −0.3986 −0.1639 −0.1132 D −0.4110 −0.3023 −0.4776* 0.3864 −0.3256 −0.3474 −0.3212 0.3201 −0.0687 −0.2711 −0.3935 灌浆粒重 Grain weight −0.4543* −0.4549* −0.4912* 0.6599** −0.5173* −0.6255** −0.5550* 0.4478* −0.5122* −0.4890* −0.5145* T: 全生育期≥10℃的积温; Tsf: 播种到吐丝≥10℃的积温; Tf1: 吐丝到第1拐点≥10℃的积温; Tf12: 第1到第2拐点≥10℃的积温; TAvsm: 播种到成熟的日平均气温; TAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日平均气温; TAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日平均气温; TAvf1: 吐丝到第1拐点的日平均气温; TAvf12: 第1到第2拐点的日平均气温; Ssf: 表示播种到吐丝的日照时数; Ffm: 表示吐丝到成熟的降雨量; TRAvsf: 播种到吐丝的日均温差; TRAvfm: 吐丝到成熟的日均温差; t2: 到达第2拐点的时间; Vmax: 最大灌浆速率; V: 平均灌浆速率分别用和表示; D: 灌浆持续期。*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著性。T and TAvsm represent accumulated temperatures ≥10℃ and daily average temperatures from sowing to maturity, respectively. Tsf, TAvsf, TRAvsf and Ssf represent accumulated temperatures ≥10℃, daily average temperatures, the daily mean temperature difference and sunshine hours from sowing to silking, respectively. TAvfm, TRAvfm and Ffm represent daily average temperature, the daily mean temperature difference and rainfall from silking to maturity, respectively. Tf1 and Tf12 represent accumulated temperatures ≥10℃ from silking to the first inflection point and from the first to the second inflection, respectively. TAvf1 and TAvf12 represent daily average temperatures from silking to the first inflection and from first inflection points to second inflection, respectively. t2 represents the time to reach the first and second inflection points, respectively. Vmax and V mean the maximum grain-filling rate and the average grain-filling rate, respectively. D means grain filling duration. * and ** indicate significance at the level of P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively. -
[1] WANG X, LI X B, FISCHER G, et al. Impact of the changing area sown to winter wheat on crop water footprint in the North China Plain[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 57: 100−109 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.04.023 [2] SHEN Y J, ZHANG Y C, R SCANLON B, et al. Energy/water budgets and productivity of the typical croplands irrigated with groundwater and surface water in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2013, 181: 133−142 doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2013.07.013 [3] PAN Y, YU Z R, HOLST J, et al. Integrated assessment of cropping patterns under different policy scenarios in Quzhou County, North China Plain[J]. Land Use Policy, 2014, 40: 131−139 doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.11.015 [4] 王学, 李秀彬, 辛良杰, 等. 华北地下水超采区冬小麦退耕的生态补偿问题探讨[J]. 地理学报, 2016, 71(5): 829−839 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201605011WANG X, LI X B, XIN L J, et al. Ecological compensation for winter wheat abandonment in groundwater over-exploited areas in the North China Plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2016, 71(5): 829−839 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201605011 [5] FENG Z M, LIU D W, ZHANG Y H. Water requirements and irrigation scheduling of spring maize using GIS and CropWat model in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2007, 17(1): 56−63 doi: 10.1007/s11769-007-0056-3 [6] 刘佳鸿, 何奇瑾, 管玥, 等. 黄淮海北部地区夏玉米稳产高产的播期优选[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(5): 131−138 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.05.016LIU J H, HE Q J, GUAN Y, et al. Suitable sowing date for stable and high yield of summer maize in the northern region of Huang-Huai-Hai, China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(5): 131−138 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.05.016 [7] SUN H Y, ZHANG X Y, CHEN S Y, et al. Effects of harvest and sowing time on the performance of the rotation of winter wheat-summer maize in the North China Plain[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2007, 25(3): 239−247 doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2006.12.003 [8] 罗新兰, 崔佳龙, 蔡福, 等. 播期对玉米生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(5): 14−20 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.05.03LUO X L, CUI J L, CAI F, et al. Effect of sowing date on growth and yield of maize[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(5): 14−20 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.05.03 [9] 李洁, 晋凡生, 张冬梅, 等. 播期对不同熟期玉米品种生育期及产量的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2016, 6(12): 1−7 doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas16090004LI J, JIN F S, ZHANG D M, et al. Effects of sowing dates on growth stage and yield of maize varieties with different maturity periods[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2016, 6(12): 1−7 doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas16090004 [10] 钱春荣, 王荣焕, 赵久然, 等. 不同熟期玉米品种的籽粒灌浆特性及其与温度关系研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(8): 105−114QIAN C R, WANG R H, ZHAO J R, et al. Study on the grain filling characteristics and their relationship with temperature of maize hybrids differing in maturities[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(8): 105−114 [11] 郑洪建, 董树亭, 王空军, 郭玉秋, 胡昌浩, 张吉旺. 生态因素对玉米品种产量影响及调控的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(6): 862−868 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2001.06.029ZHENG H J, DONG S T, WANG K J, et al. Effects of ecological factors on maize (Zea mays L. )yield of different varieties and corresponding regulative measure[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(6): 862−868 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2001.06.029 [12] 刘明, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 等. 播期对春玉米生长发育与产量形成的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(1): 18−23 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2009.00018LIU M, TAO H B, WANG P, et al. Effect of sowing date on growth and yield of spring-maize[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(1): 18−23 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2009.00018 [13] 明博, 朱金城, 陶洪斌, 等. 黑龙港流域玉米不同生育阶段气象因子对产量性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(5): 919−927 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00919MING B, ZHU J C, TAO H B, et al. Effects of meteorological factors at different growth stages on yield traits of maize (Zea mays L. ) in heilonggang basin[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(5): 919−927 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00919 [14] 李言照, 东先旺, 刘光亮, 陶飞. 光温因子对玉米产量及产量构成因素值的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2002, 10(2): 86−89LI Y Z, DONG X W, LIU G L, et al. Effects of light and temperature factors on yield and its components in maize[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2002, 10(2): 86−89 [15] LIU Y E, HOU P, XIE R Z, et al. Spatial adaptabilities of spring maize to variation of climatic conditions[J]. Crop Science, 2013, 53(4): 1693−1703 doi: 10.2135/cropsci2012.12.0688 [16] 王柳, 熊伟, 温小乐, 等. 温度降水等气候因子变化对中国玉米产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(21): 138−146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.21.017WANG L, XIONG W, WEN X L, et al. Effect of climatic factors such as temperature, precipitation on maize production in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(21): 138−146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.21.017 [17] TAO Z Q, CHEN Y Q, LI C, et al. The causes and impacts for heat stress in spring maize during grain filling in the North China Plain—a review[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(12): 2677−2687 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61409-0 [18] ZHOU B Y, YUE Y, SUN X F, et al. Maize kernel weight responses to sowing date-associated variation in weather conditions[J]. The Crop Journal, 2017, 5(1): 43−51 doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2016.07.002 [19] 刘哲, 乔红兴, 赵祖亮, 等. 黄淮海夏播玉米花期高温热害空间分布规律研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(7): 272−279 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.07.039LIU Z, QIAO H X, ZHAO Z L, et al. Spatial distribution of high temperature stress at corn flowering stage in Huang-Huai-Hai plain of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(7): 272−279 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.07.039 [20] 肖荷霞, 陈建忠, 席国成. 黑龙港类型区气象生态因子与夏玉米产量性状关系的研究[J]. 华北农学报, 1999, 14(S1): 126−130XIAO H X, CHEN J Z, XI G C. Relation of ecoclimatic factors with yield properties of summer maize in heilonggang catchment area[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali—Sinica, 1999, 14(S1): 126−130 [21] 李潮海, 苏新宏, 谢瑞芝, 周苏玫, 李登海. 超高产栽培条件下夏玉米产量与气候生态条件关系研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2001, 34(3): 311−316 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2001.03.015LI C H, SU X H, XIE R Z, et al. Study on relationship between grain-yield of summer corn and climatic ecological condition under super-high-yield cultivation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2001, 34(3): 311−316 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2001.03.015 [22] 孙宏勇, 刘小京, 王金涛, 等. 品种和播期对华北春玉米产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(6): 837−846 doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.170786SUN H Y, LIU X J, WANG J T, et al. Effects of sowing date and cultivar on grain yield and water use efficiency of spring maize in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(6): 837−846 doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.170786 [23] 陈传晓, 董志强, 高娇, 等. 不同积温对春玉米灌浆期叶片光合性能的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(6): 1593−1600CHEN C X, DONG Z Q, GAO J, et al. Effects of different accumulated temperature on photosynthetic performances of spring maize varieties during grain-filling period[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(6): 1593−1600 [24] 徐田军, 吕天放, 陈传永, 等. 播期对玉米干物质积累转运和籽粒灌浆特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(6): 112−118 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2016.292XU T J, LV T F, CHEN C Y, et al. Effect of sowing date on maize dry matter accumulation, transformation and grain filling characters[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(6): 112−118 doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2016.292 [25] 韩慧敏, 张磊, 孙淼, 等. 黄淮海不同夏玉米品种生长发育及产量对播期的响应[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(2): 106−114HAN H M, ZHANG L, SUN M, et al. Response of growth, development and yield of different summer maize cultivars to sowing date in Huang-Huai-Hai plain[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(2): 106−114 [26] 张冬梅, 姜春霞, 黄学芳, 等. 早熟区不同熟期玉米品种产量对播期和施肥方式的响应[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(24): 59−66 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050115ZHANG D M, JIANG C X, HUANG X F, et al. Response of yields of different maturity maize varieties to sowing time and fertilization method in early-mature area[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(24): 59−66 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050115 [27] 李清超, 马浪浪, 文琼, 等. 玉米杂交组合产量性状与产量的相关及通径分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(27): 59−62 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050138LI Q C, MA L L, WEN Q, et al. Correlation and path analysis of yield and yield characteristics of maize hybrids[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(27): 59−62 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050138 [28] 向道权, 黄烈健, 曹永国, 戴景瑞. 玉米产量性状主基因-多基因遗传效应的初步研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2001, 16(3): 1−5 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7091.2001.03.001XIANG D Q, HUANG L J, CAO Y G, et al. A preliminary study on genetic effect of maize yield component traits based on major gene and polygene mixed inheritance[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreall—Sinica, 2001, 16(3): 1−5 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7091.2001.03.001 [29] 张秋芝, 郝玉兰, 南张杰, 等. 玉米杂交种的产量比较及主要农艺性状的相关和通径分析[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2005, 20(4): 33−39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2005.04.009ZHANG Q Z, HAO Y L, NAN Z J, et al. Yield performance of maize hybrids and analysis of correlation between yield and agronomic characteristics[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural College, 2005, 20(4): 33−39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2005.04.009 [30] 付晋峰, 王璞. 播期和种植密度对玉米子粒灌浆的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2016, 24(3): 117−122,130FU J F, WANG P. Effects of sowing date and planting density on maize filling[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2016, 24(3): 117−122,130 [31] 徐田军, 吕天放, 陈传永, 等. 播期对玉米干物质积累转运和籽粒灌浆特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(6): 112−118XU T J, LV T F, CHEN C Y, et al. Effect of sowing date on maize dry matter accumulation, transformation and grain filling characters[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(6): 112−118 [32] 江铭诺, 刘朝顺, 高炜. 华北平原夏玉米潜在产量时空演变及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(6): 865−876JIANG M N, LIU C S, GAO W. Analysis of spatial and temporal variation in potential summer maize yield and its response to climate change in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(6): 865−876 [33] 孟林, 刘新建, 邬定荣, 等. 华北平原夏玉米主要生育期对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(4): 375−382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.04.001MENG L, LIU X J, WU D R, et al. Responses of summer maize main phenology to climate change in the North China plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(4): 375−382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.04.001 [34] 马雪晴, 胡琦, 潘学标, 等. 1961—2015年华北平原夏玉米生长季气候年型及其影响分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2019, 40(2): 65−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2019.02.001MA X Q, HU Q, PAN X B, et al. Analysis of annual climate types and its impact on summer maize in the North China plain over the period 1961-2015[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2019, 40(2): 65−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2019.02.001 [35] 孔德胤, 杨松, 陶建光, 等. 播期对河套地区玉米灌浆进度的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(4): 30−35 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18100124KONG D Y, YANG S, TAO J G, et al. Sowing date affects grain filling progress of maize in Hetao area[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(4): 30−35 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18100124 [36] 杜霞, 豆攀, 陈祥, 等. 气象条件对川中丘陵地区玉米生长和产量的影响及播期优化−以中江为例[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 48(3): 257−264 doi: 10.13331/j.cnki.jhau.2022.03.002DU X, DOU P, CHEN X, et al. Effects of meteorological conditions on maize growth and yield in hilly area of central Sichuan and optimization of sowing date: a case study of Zhongjiang, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 48(3): 257−264 doi: 10.13331/j.cnki.jhau.2022.03.002 [37] 刘明, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 等. 播期对春玉米生长发育、产量及水分利用的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2009, 17(2): 108−111LIU M, TAO H B, WANG P, et al. Effects of sowing date on growth, yield formation and water utilization of spring maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2009, 17(2): 108−111 [38] 陶志强, 陈源泉, 李超, 等. 华北低平原不同播种期春玉米的产量表现及其与气象因子的通径分析[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(9): 1628−1634 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01628TAO Z Q, CHEN Y Q, LI C, et al. Path analysis between yield of spring maize and meteorological factors at different sowing times in North China low plain[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(9): 1628−1634 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01628 [39] 魏钟博, 边大红, 杜雄, 等. 黑龙港流域夏玉米生育期降水、需水和干旱时空分布特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(9): 124−133 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.09.014WEI Z B, BIAN D H, DU X, et al. Characteristics of spatial-temporal distribution of precipitation, water requirement and drought for summer maize growth period in Heilonggang Basin[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(9): 124−133 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.09.014 [40] 和骅芸, 胡琦, 潘学标, 等. 气候变化背景下华北平原夏玉米花期高温热害特征及适宜播期分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(1): 1−15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.01.001HE H Y, HU Q, PAN X B, et al. Characteristics of heat damage during flowering period of summer maize and suitable sowing date in North China plain under climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(1): 1−15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.01.001 [41] 任佰朝, 高飞, 魏玉君, 等. 冬小麦–夏玉米周年生产条件下夏玉米的适宜熟期与积温需求特性[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44: 137−143 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00137REN B C, GAO F, WEI Y J, et al. Suitable maturity period and accumulated temperature of summer maize in wheat–maize double cropping system[J]. Acta Agronomic Sinica, 2018, 44: 137−143 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00137 [42] 李文阳, 王长进, 张子学, 等. 不同播期夏玉米籽粒灌浆特性及与主要气象因子的关系[J]. 安徽科技学院学报, 2013, 27(5): 21−26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8772.2013.05.005LI W Y, WANG C J, ZHANG Z X, et al. The relationship between grain filling characteristics of summer maize and main meteorological factors during grain filling under different planting date[J]. Journal of Anhui Science and Technology University, 2013, 27(5): 21−26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8772.2013.05.005 [43] 马冲, 邹仁峰, 苏波, 张健, 陈举林. 不同熟期玉米籽粒灌浆特性的研究[J]. 作物研究, 2000, 14(4): 17−19 doi: 10.16848/j.cnki.issn.1001-5280.2000.04.006MA C, ZOU R F, SU B, et al. Studies on grain filling characteristics of hybrid corn with different growth durations[J]. Crop Research, 2000, 14(4): 17−19 doi: 10.16848/j.cnki.issn.1001-5280.2000.04.006 [44] 盛得昌, 王媛媛, 黄收兵, 等. 高温对玉米植株形态与功能、产量构成及子粒养分的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(5): 86−92 doi: 10.13597/j.cnki.maize.science.20200513SHENG D C, WANG Y Y, HUANG S B, et al. Effects of high temperature on morphology and function, yield components and grain nutrients of maize plants[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(5): 86−92 doi: 10.13597/j.cnki.maize.science.20200513 [45] 刘萍, 徐顺飞, 杜庆平, 等. 播期对夏玉米产量与光合特性的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39(5): 722−729 doi: 10.7685/jnau.201602019LIU P, XU S F, DU Q P, et al. Effects of sowing date on yield and photosynthetic characteristics of summer maize[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016, 39(5): 722−729 doi: 10.7685/jnau.201602019 [46] 王若男, 任伟, 李叶蓓, 等. 灌浆期低温对夏玉米光合性能及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(2): 1−8 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.02.01WANG R N, REN W, LI Y B, et al. Effects of low temperature during grain filling stage on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of summer maize[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(2): 1−8 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.02.01 [47] 高军波, 楚冰洋, 闫军辉, 等. 1960年以来河南省玉米气候生产潜力估算与种植空间优化[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(1): 245−254 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.01.027GAO J B, CHU B Y, YAN J H, et al. Estimation of climate production potential of corn and optimization of planting space in Henan Province from 1960[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(1): 245−254 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.01.027 [48] TAO Z Q, SUI P, CHEN Y Q, et al. Subsoiling and ridge tillage alleviate the high temperature stress in spring maize in the North China plain[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2013, 12(12): 2179−2188 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(13)60347-0 [49] 曹彩云, 党红凯, 郑春莲, 等. 低平原区一季玉米种植产量和水分利用效率对播期的响应研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2020, 43(3): 9−16,22 doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2020.0045CAO C Y, DANG H K, ZHENG C L, et al. Response of sowing date to yield and water use efficiency of one season maize in lowland plain area[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020, 43(3): 9−16,22 doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2020.0045 [50] 徐田军, 吕天放, 赵久然, 等. 玉米生产上3个主推品种光合特性、干物质积累转运及灌浆特性[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(3): 414−422 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00414XU T J, LV T F, ZHAO J R, et al. Photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and translocation, grain filling parameter of three main maize varieties in production[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 414−422 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00414 [51] 付景, 孙宁宁, 刘天学, 等. 穗期高温对玉米子粒灌浆生理及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2019(3): 118−125 doi: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2019.03.019FU J, SUN N N, LIU T X, et al. The effects of high temperature at spike stage on grain-filling physiology and yield of maize[J]. Crops, 2019(3): 118−125 doi: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2019.03.019 [52] 齐琦, 胡凯, 张敖, 等. 高产玉米‘郑单958’和‘先玉335’的灌浆和叶片光合特性的比较[J]. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(9): 1489−1494 doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2015.0125QI Q, HU K, ZHANG A, et al. Comparion of grain filling and leaf photosynthetic characteristics in high yield maize ‘Zhengdan 958' and ‘Xianyu 335'[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2015, 51(9): 1489−1494 doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2015.0125 [53] 赵霞, 穆心愿, 马智艳, 等. 不同玉米杂交种对花期高温、干旱复合胁迫的响应[J]. 河南农业科学, 2017, 46(8): 32−37 doi: 10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2017.08.006ZHAO X, MU X Y, MA Z Y, et al. Response of different maize hybrids to high temperature and drought stresses at flowering stage[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 46(8): 32−37 doi: 10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2017.08.006 -





 下载:
下载: