Effects of optimized fertilization on yield, nutrient balance, and eco-environmental benefits in wheat-maize rotation system
-
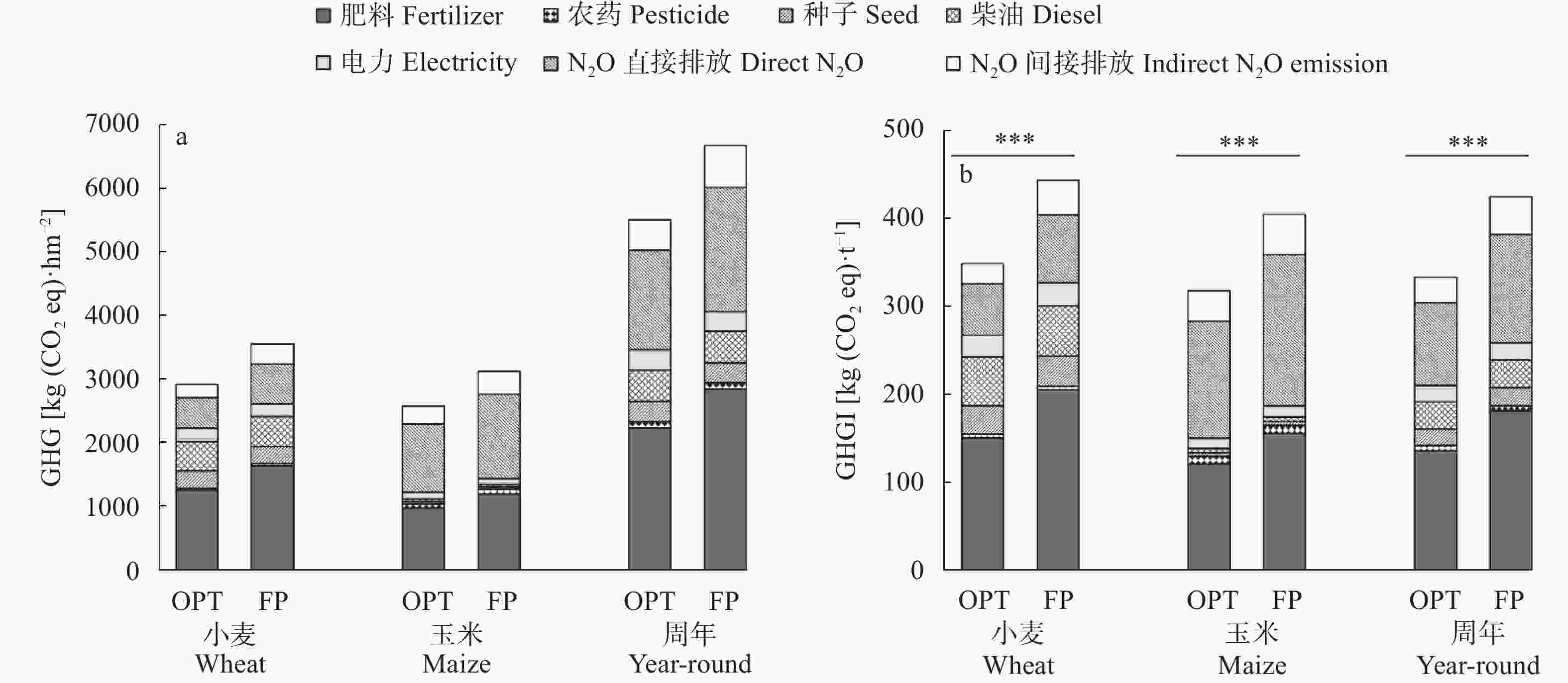
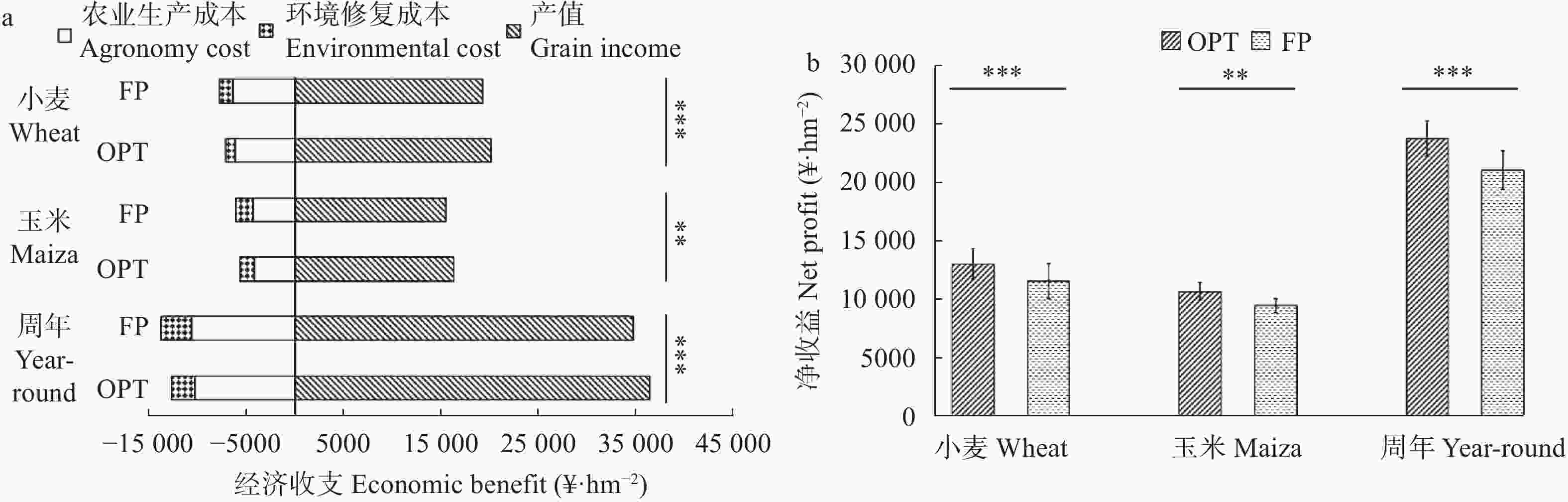
摘要: 小麦-玉米轮作是华北平原主要的种植模式, 对保障我国粮食安全起着关键作用。本文系统研究了不施肥(CK)、优化施肥(OPT)和农户习惯施肥(FP)方式连续8年对小麦-玉米轮作体系产量、养分平衡、温室气体排放和经济效益的影响。结果表明, 小麦季、玉米季和周年轮作中, OPT较FP产量分别提高4.3%、5.3%和4.8%; 氮肥偏生产力分别提高39.1%、31.7%和35.9%; 磷肥偏生产力分别提高39.1%、40.4%和39.8%; 钾肥偏生产力分别降低47.8%、47.3%和47.6%; 温室气体排放量分别降低21.7%、21.1%和21.4%; 温室气体排放强度分别降低27.0%、27.5%和27.3%; 净收益分别提高11.2%、11.4%和11.3%, 农业生产成本分别降低3.7%、2.1%和3.1%, 环境修复成本分别降低28.4%、17.3%和22.1%。周年轮作中, OPT较FP氮素盈余量降低105 kg·hm−2 (46.3%); 磷素盈余量降低48 kg·hm−2 (53.3%); 钾素从亏缺1 kg·hm−2变为盈余59 kg·hm−2, 满足了作物生长需求。连续8年, OPT较FP土壤有机质含量提高5.3%, 速效钾提高12.3%, 有效磷降低27.8%。综上所述, 与农户习惯施肥(FP)相比, 优化施肥(OPT)具有高产、高收益以及环境友好的优势, 为华北平原小麦-玉米轮作体系高效绿色生产提供了科学依据。Abstract: The wheat-maize rotation system in the North China Plain is the main planting pattern that plays a key role in ensuring food security in China. An 8-year positioning experiment with a randomized block design was performed, comprising three treatments: no-fertilizer application control (CK), optimized fertilizer (OPT), and farmers’ practices (FP). The experiments analyzed the effects of OPT and FP on the yield, nutrient balance, greenhouse gas emissions, and economic benefits of the wheat-maize rotation system. The results showed that the yields of OPT increased by 4.3%, 5.3%, and 4.8% compared to FP in wheat, maize, and year-round rotation, respectively. Accordingly, the partial factor productivity of N increased by 39.1%, 31.7%, and 35.9%, respectively. The partial factor productivity of P increased by 39.1%, 40.4%, and 39.8%, respectively. The partial factor productivity of K was reduced by 47.8%, 47.3%, and 47.6%, respectively. The greenhouse gas emissions were reduced by 21.7%, 21.1%, and 21.4%, respectively. The greenhouse gas emission intensity was reduced by 27.0%, 27.5%, and 27.3%. Net profits increased by 11.2%, 11.4%, and 11.3%, respectively. Agronomy costs were reduced by 3.7%, 2.1%, and 3.1%, respectively. The environmental costs were reduced by 28.4%, 17.3%, and 22.1%, respectively. Compared with the FP treatment, the year-round OPT treatment reduced the surplus of nitrogen by decrement of 105 kg·hm−2, i.e., 46.3%. The surplus phosphorus was reduced by 48 kg·hm−2 i.e., 53.3%. The surplus of K of OPT and FP was 59 kg·hm−2 and −1 kg·hm−2, respectively. OPT met the requirements of crop growth better than FP. At the end of 8 years of wheat-maize rotation, the soil organic matter content in OPT treatment increased by 5.3% compared to that in FP. Compared to that of FP, available K increased and P reduced by 12.3% and 27.8%, respectively. In conclusion, compared with FP treatment, OPT treatment has the advantages of high yield, high profit, and environmental friendliness. Therefore, this study provides a scientific basis for the efficient and green product.
-
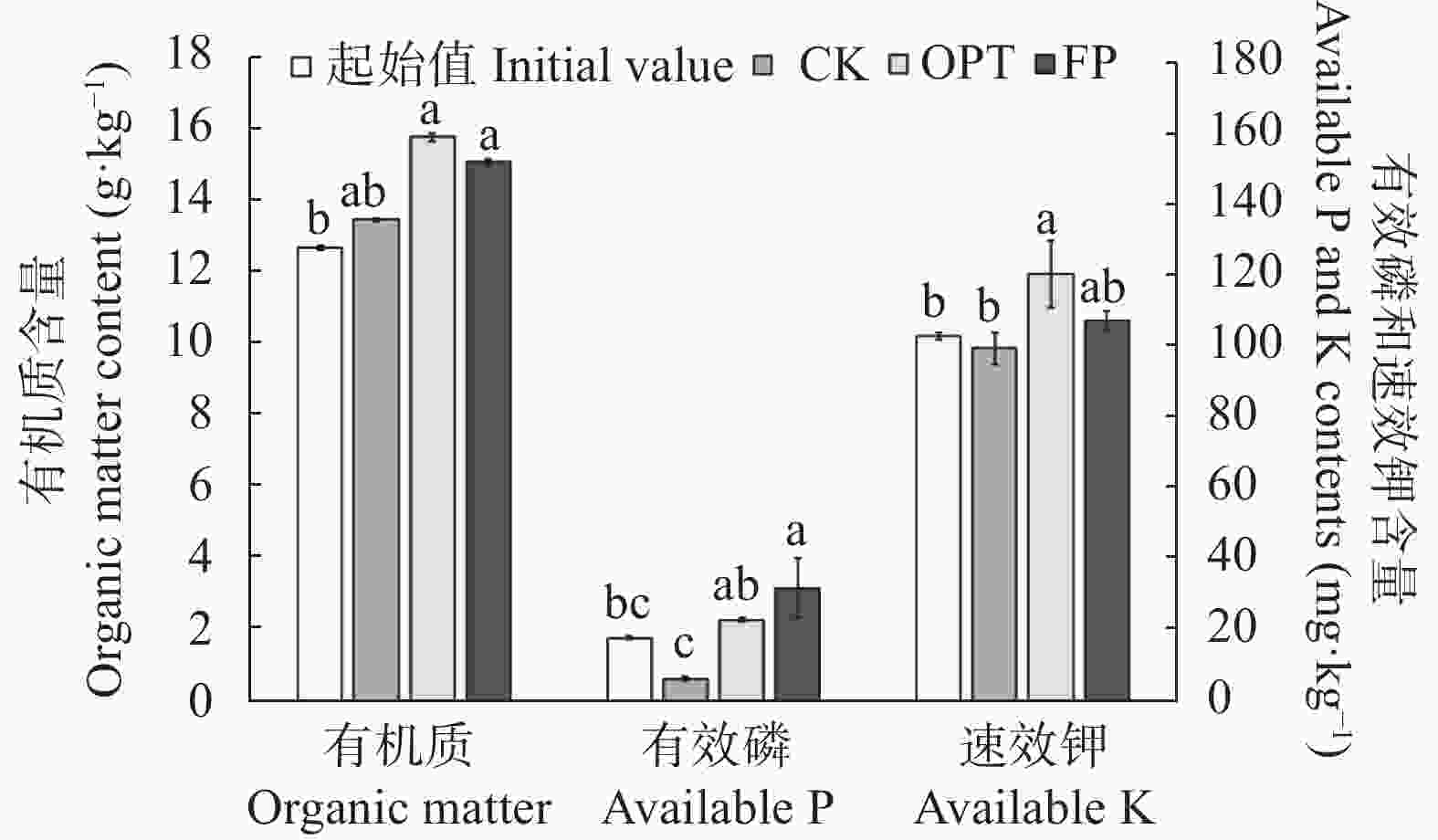
图 2 不同施肥处理下的小麦-玉米轮作体系的土壤养分含量
不同小写字母表示各处理及起始值间差异显著(P<0.05)。CK、OPT和FP为试验结束时不同处理的数值。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences among treatments and experimental initial value (P<0.05). CK, OPT and FP represent the values of treatment CK, OPT and FP at the end of experiment.
Figure 2. Soil nutrients contents of wheat-maize rotation system under different treatments
表 1 不同处理的施肥量
Table 1. Fertilization rates of the different treatments
处理
Treatment小麦 Wheat 玉米 Maize N P2O5 K2O N P2O5 K2O kg·hm−2 表 2 投入农业生产资料及氮损失的碳排放系数
Table 2. Carbon emission factors of different agricultural materials input and nitrogen loss
项目
Item碳排放系数 Carbon emission factor 数据来源
Data source小麦 Wheat 玉米 Maize 氮肥 Nitrogen fertilizer 4.96 kg(CO2 eq)·kg−1 [17] 磷肥 Phosphorus fertilizer 1.14 kg(CO2 eq)·kg−1 [17] 钾肥 Potassium fertilizer 0.66 kg(CO2 eq)·kg−1 [17] 种子 Seed 1.22 kg(CO2 eq)·kg−1 [17] 农药 Pesticide 6.58 kg(CO2 eq)·kg−1 [17] 柴油 Diesel oil 3.44 kg(CO2 eq)·L−1 [17] 电力 Electricity 0.92 kg(CO2 eq)·kW·h−1 [17] NH3挥发 NH3 volatilization 2.69+0.069×N1) 7.98+0.099×N [18] NO3−淋溶 NO3− leaching 3.63×e0.0080×N 10.7×e0.0060×N [18] N2O直接排放 N2O directly emissions 0.50×e0.0032×N 0.99×e0.0047×N [18] N2O间接排放 N2O indirectly emissions 1%×NH3-N2)+1.1%×NO3−-N3) 1%×NH3-N +1.1%×NO3−-N [19] 1) N: 氮肥施用量; 2) NH3-N: NH3挥发; 3) NO3−-N: NO3−淋溶。1) N: application amount of nitrogen; 2) NH3-N: NH3 volatilization; 3) NO3−-N: NO3− leaching. 表 3 不同施肥处理下的小麦-玉米轮作体系的产量及其稳定性
Table 3. Yields and yield stability of wheat-maize rotation system under different treatments
年份
Year处理
Treatment产量 Yield (kg·hm−2) 产量稳定性指数 Stability index 产量可持续性指数 Sustainable yield index 小麦
Wheat玉米
Maize周年
Year-round小麦
Wheat玉米
Maize周年
Year-round小麦
Wheat玉米
Maize周年
Year-round2013—2014 CK 7045±496b 6702±835b 13 747±1059b 0.14 0.25 0.15 0.76 0.64 0.74 OPT 8613±163a 8669±320a 17 282±379a 0.04 0.07 0.04 0.92 0.84 0.91 FP 7969±314ab 8073±385ab 16 042±80a 0.08 0.10 0.01 0.87 0.80 0.98 2014—2015 CK 5558±127b 6608±392c 12 165±471c 0.05 0.12 0.08 0.92 0.81 0.86 OPT 7795±296a 9455±299a 17 251±541a 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.84 0.86 0.86 FP 7530±106a 8184±362b 15 714±376b 0.03 0.09 0.05 0.93 0.82 0.91 2015—2016 CK 3301±278b 5690±333b 8992±600b 0.17 0.12 0.13 0.70 0.81 0.81 OPT 10 357±292a 7940±286a 18 297±434a 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.91 0.86 0.91 FP 10 302±285a 7523±377a 17 825±578a 0.06 0.10 0.06 0.89 0.93 0.88 2016—2017 CK 3272±122b 6179±427b 9450±462b 0.07 0.14 0.10 0.86 0.74 0.81 OPT 7729±417a 7631±278a 15 360±632a 0.11 0.07 0.08 0.79 0.84 0.82 FP 7332±241a 7113±353ab 14 446±544a 0.07 0.10 0.08 0.88 0.82 0.89 2017—2018 CK 2981±174c 6724±332a 9705±487b 0.12 0.10 0.10 0.79 0.85 0.85 OPT 6590±122a 7579±246a 14 169±240a 0.04 0.07 0.03 0.94 0.89 0.93 FP 5841±241b 7559±317a 13 401±367a 0.08 0.08 0.05 0.85 0.84 0.88 2018—2019 CK 3005±532b 7188±532a 10 193±522b 0.35 0.15 0.10 0.45 0.70 0.80 OPT 8031±483a 7356±388a 15 388±542a 0.12 0.11 0.07 0.78 0.83 0.84 FP 7663±160a 7195±417a 14 858±390a 0.04 0.12 0.05 0.91 0.79 0.92 2019—2020 CK 3297±438b 8036±433a 11 334±590b 0.27 0.11 0.10 0.55 0.79 0.81 OPT 8541±232a 9024±249a 17 565±468a 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.90 0.88 0.90 FP 8484±101a 9000±224a 17 484±201a 0.02 0.05 0.02 0.96 0.91 0.96 2020—2021 CK 3998±149b 7138±229a 11 137±308b 0.07 0.06 0.06 0.83 0.86 0.90 OPT 9370±326a 7609±188a 16 979±328a 0.07 0.05 0.04 0.86 0.90 0.92 FP 9111±242a 7312±316a 16 424±295a 0.05 0.09 0.04 0.90 0.83 0.92 年均
AverageCK 4057±268b 6783±188b 10 840±325b 0.16±0.03a 0.13±0.03a 0.10±0.01a 0.73±0.06b 0.78±0.03b 0.82±0.02b OPT 8378±214a 8158±159a 16 536±275a 0.07±0.01b 0.07±0.01b 0.05±0.01b 0.87±0.02a 0.86±0.01a 0.89±0.01a FP 8029±232a 7745±152a 15 774±280a 0.05±0.01b 0.09±0.01b 0.05±0.01b 0.90±0.01a 0.84±0.02a 0.92±0.01a 同列不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences among treatments for the same year (P<0.05). 表 4 不同施肥处理下的小麦-玉米轮作体系的偏生产力
Table 4. Partial factor productivity of wheat-maize rotation system under different treatments
年份
Year处理
Treatment氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial factor productivity 磷肥偏生产力 Phosphate partial factor productivity 钾肥偏生产力 Potassium partial factor productivity 小麦
WheatP>T 玉米
MaizeP>T 周年
Year-roundP>T 小麦
WheatP>T 玉米
MaizeP>T 周年
Year-roundP>T 小麦
WheatP>T 玉米
MaizeP>T 周年
Year-roundP>T kg·kg−1 P>T为OPT和FP处理的配对法t检验结果。P>T is the probability of a significance of difference between OPT and FP based on paired t-test. -
[1] GAO F, LI B, REN B Z, et al. Effects of residue management strategies on greenhouse gases and yield under double cropping of winter wheat and summer maize[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 687: 1138−1146 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.146 [2] ZHANG Y T, WANG H Y, LEI Q L, et al. Optimizing the nitrogen application rate for maize and wheat based on yield and environment on the Northern China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618: 1173−1183 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.183 [3] CUI Z L, YUE S C, WANG G L, et al. In-season root-zone N management for mitigating greenhouse gas emission and reactive N losses in intensive wheat production[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(11): 6015−6022 [4] MA Q, YU W T, JIANG C M, et al. The influences of mineral fertilization and crop sequence on sustainability of corn production in northeastern China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2012, 158: 110−117 [5] SCHRODER J, ZHANG H L, GIRMA K, et al. Soil acidification from long‐term use of nitrogen fertilizers on winter wheat[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2011, 75: 957−964 doi: 10.2136/sssaj2010.0187 [6] 王乐政, 华方静, 曹鹏鹏, 等. 氮磷钾配施对红小豆干物质积累、产量和效益的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(10): 2058−2067 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.10.2058WANG L Z, HUA F J, CAO P P, et al. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium combined application on dry matter accumulation, yield and economic benefits of adzuki bean[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(10): 2058−2067 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.10.2058 [7] 黄晓萌, 刘晓燕, 串丽敏, 等. 优化施肥下长江流域冬小麦产量及肥料增产效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(17): 3541−3552 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.17.011HUANG X M, LIU X Y, CHUAN L M, et al. Effects of yield and fertilization on yield increase of winter wheat in Yangtze valley under optimized fertilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(17): 3541−3552 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.17.011 [8] 包菡, 傅建伟, 张雷, 等. 不同施肥方式对玉米产量和农田氮磷淋溶流失的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2021, 49(4): 57−61 doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2021.04.09BAO H, FU J W, ZHANG L, et al. The effects of different fertilization methods on maize yield and nitrogen and phosphorus leaching loss in farmland[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2021, 49(4): 57−61 doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2021.04.09 [9] 庞津雯, 王钰皓, 刘畅, 等. 不同施肥量对旱作沟垄集雨种植农田土壤水分及玉米产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(5): 826−836 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.20510PANG J W, WANG Y H, LIU C, et al. Effects of fertilization on soil moisture and maize yield in rainfed farmland with ridge mulching-furrow planting system[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(5): 826−836 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.20510 [10] 赵营, 周涛, 郭鑫年, 等. 优化施肥对春小麦产量、氮素利用及氮平衡的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2011, 29(6): 119−124ZHAO Y, ZHOU T, GUO X N, et al. Effect of optimum fertilization on spring wheat yield, N utilization and apparent N balance[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2011, 29(6): 119−124 [11] JIANG Z H, ZHONG Y M, YANG J P, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer rates on carbon footprint and ecosystem service of carbon sequestration in rice production[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 670: 210−217 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.188 [12] BHANDARI M, MA Y, MEN M X, et al. Response of winter wheat yield and soil N2O emission to nitrogen fertilizer reduction and nitrapyrin application in North China Plain[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2020, 51(4): 554−565 doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1718687 [13] 蔡闻佳, 惠婧璇, 赵梦真, 等. 温室气体减排的健康协同效应: 综述与展望[J]. 城市与环境研究, 2019, 6(1): 76−94CAI W J, HUI J X, ZHAO M Z, et al. Ancillary health impacts of GHG mitigation: a review of the current status and future prospects[J]. Urban and Environmental Studies, 2019, 6(1): 76−94 [14] 吴良泉, 武良, 崔振岭, 等. 中国小麦区域氮磷钾肥推荐用量及肥料配方研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(11): 30−40 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2019.11.04WU L Q, WU L, CUI Z L, et al. Optimal regional nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium rates recommendations and special fertilizer formulae study for wheat in China[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2019, 24(11): 30−40 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2019.11.04 [15] 吴良泉, 武良, 崔振岭, 等. 中国玉米区域氮磷钾肥推荐用量及肥料配方研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(4): 802−817 doi: 10.11766/trxb201409230480WU L Q, WU L, CUI Z L, et al. Basic NPK fertilizer recommendation and fertilizer formula for maize production regions in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(4): 802−817 doi: 10.11766/trxb201409230480 [16] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 30–34, 81–83, 106–108, 264–270BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Third version. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 30–34, 81–83, 106–108, 264–270 [17] HUANG S H, DING W C, JIA L L, et al. Cutting environmental footprints of maize systems in China through Nutrient Expert Management[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 282: 111956 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111956 [18] CUI Z L, ZHANG H Y, CHEN X P, et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers[J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7696): 363−366 doi: 10.1038/nature25785 [19] IPCC. 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories[R]. Japan: Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, 2019: Volume 4, chapter 11 [20] HUANG S H, HE P, JIA L L, et al. Improving nitrogen use efficiency and reducing environmental cost with long-term nutrient expert management in a summer maize-winter wheat rotation system[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2021, 213: 105117 [21] 马红梅, 曹寒冰, 谢英荷, 等. 晋南黄土旱塬小麦养分投入与化肥减施经济环境效应评价[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(13): 2804−2817 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.13.010MA H M, CAO H B, XIE Y H, et al. Evaluation on fertilizer application and its economic-environmental benefits associated with fertilizer reduction potential for dryland wheat in loess plateau of southern Shanxi Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(13): 2804−2817 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.13.010 [22] 王丹丹, 李岚涛, 韩本高, 等. 养分专家系统推荐施肥对冬小麦产量、养分转运及肥料利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(11): 1692−1702WANG D D, LI L T, HAN B G, et al. Effects of Nutrient Expert Recommended Fertilization on winter wheat yield, nutrient accumulation, transportation, and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(11): 1692−1702 [23] 牛新胜, 张宏彦. 华北平原冬小麦-夏玉米生产肥料管理现状分析[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2010(5): 1−4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2239.2010.05.001NIU X S, ZHANG H Y. Analysis on current situation of fertilizer management of winter wheat-summer maize in Northern China Plain[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2010(5): 1−4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2239.2010.05.001 [24] 河北省2021年度气候公报[EB/OL]. 河北省气象局, [2022-01-17]. http://he.cma.gov.cn/qxfw/qhfx/qhgb/202201/t20220117_4427650.htmlHebei Province 2021 annual climate bulletin [EB/OL]. Hebei Meteorological Service, [2022-1-17]. http://he.cma.gov.cn/qxfw/qhfx/qhgb/202201/t20220117_4427650.html [25] 河北省2016年度气候公报[EB/OL]. 河北省气象局, [2017-01-13]. http://he.cma.gov.cn/qxfw/qhfx/qhgb/201904/t20190403_272044.htmlHebei Province 2016 annual climate bulletin [EB/OL]. Hebei Meteorological Service, [2017-01-13]. http://he.cma.gov.cn/qxfw/qhfx/qhgb/201904/t20190403_272044.html [26] 门明新, 李新旺, 许皞. 长期施肥对华北平原潮土作物产量及稳定性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(8): 2339−2346 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.08.017MEN M X, LI X W, XU H. Effects of long-term fertilization on crop yields and stability[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(8): 2339−2346 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.08.017 [27] 刘艳妮, 马臣, 于昕阳, 等. 基于不同降水年型渭北旱塬小麦–土壤系统氮素表观平衡的氮肥用量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(3): 569−578 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.17374LIU Y N, MA C, YU X Y, et al. Nitrogen application rate for keeping nitrogen balance in wheat–soil system in Weibei rainfed areas under different rainfall years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(3): 569−578 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.17374 [28] 王乐. 长期施肥下华北土壤化学肥力指标和作物产量演变及影响因素分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020: 23–26WANG L. Analysis of soil chemical fertility index and crop yield evolution and influencing factors in North China under long-term fertilization[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020: 23–26 [29] ZHANG Q S, LI T Y, YIN Y L, et al. Targeting hotspots to achieve sustainable nitrogen management in China’s smallholder-dominated cereal production[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(3): 557 doi: 10.3390/agronomy11030557 [30] CHEN X P, CUI Z L, FAN M S, et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 486−489 doi: 10.1038/nature13609 [31] 巨晓棠, 谷保静. 氮素管理的指标[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(2): 281−296 doi: 10.11766/trxb201609150320JU X T, GU B J. Indexes of nitrogen management[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(2): 281−296 doi: 10.11766/trxb201609150320 [32] 张珂珂, 郭斗斗, 宋晓, 等. 长期不同施肥下潮土磷素演变特征及其对磷盈亏的响应[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(1): 112−121 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20543ZHANG K K, GUO D D, SONG X, et al. Evolution characteristics of soil phosphorus and its response to soil phosphorus balance in fluvo-aquic soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(1): 112−121 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20543 [33] 贾良良, 韩宝文, 刘孟朝, 等. 河北省潮土长期定位施钾和秸秆还田对农田土壤钾素状况的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2014, 29(5): 207−212 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2014.05.035JIA L L, HAN B W, LIU M C, et al. The effects of long term K fertilization and straw recycling on soil K status in fluvo-aquic soil of Hebei Province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2014, 29(5): 207−212 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2014.05.035 [34] 习斌. 典型农田土壤磷素环境阈值研究——以南方水旱轮作和北方小麦玉米轮作为例[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014: 63XI B. Study on the environment threshold of soil Olsen-P in farmland — Case of southern paddy-upland rotation and northern wheat and maize rotation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014: 63 [35] 李秋梅, 陈新平, 张福锁, 等. 冬小麦-夏玉米轮作体系中磷钾平衡的研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, 8(2): 152−156 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2002.02.004LI Q M, CHEN X P, ZHANG F S, et al. Study on balance of phosphorus and potassium in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system[J]. Plant Natrition and Fertilizen Science, 2002, 8(2): 152−156 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2002.02.004 [36] 贾良良, 黄少辉, 刘克桐, 等. 太行山前平原农田基础地力对夏玉米产量的影响及培肥目标[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(3): 340−346 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20117JIA L L, HUANG S H, LIU K T, et al. Effect of inherent soil fertility on summer maize yield and the goal of improving basic soil fertility in the Taihang Mountain pediment plain[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(3): 340−346 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20117 [37] 葛玮健, 常艳丽, 刘俊梅, 等. 土娄土区长期施肥对小麦-玉米轮作体系钾素平衡与钾库容量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(3): 629−636 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11347GE W J, CHANG Y L, LIU J M, et al. Potassium balance and pool as influenced by long-term fertilization under continuous winter wheat-summer maize cropping system in a manural loess soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(3): 629−636 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11347 [38] NELSON R, HELLWINCKEL C, BRANDT C, et al. Energy use and carbon dioxide emissions from cropland production in the United States, 1990–2004[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2009, 38(2): 418−425 doi: 10.2134/jeq2008.0262 [39] HILLIER J, WHITTAKER C, DAILEY G, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions from four bioenergy crops in England and Wales: integrating spatial estimates of yield and soil carbon balance in life cycle analyses[J]. GCB-Bioenergy, 2009, 1(4): 267−281 [40] CHEN H X, LIU J J, ZHANG A F, et al. Effects of straw and plastic film mulching on greenhouse gas emissions in Loess Plateau, China: a field study of 2 consecutive wheat-maize rotation cycles[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 579: 814−824 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.022 [41] HE G, WANG Z H, LI S X, et al. Plastic mulch: Tradeoffs between productivity and greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 172: 1311−1318 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.269 [42] ZHAN A, ZOU C Q, YE Y L, et al. Estimating on-farm wheat yield response to potassium and potassium uptake requirement in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2016, 191: 13−19 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.04.001 [43] 王良, 刘元元, 钱欣, 等. 单季麦秸还田促进小麦-玉米周年碳效率和经济效益协同提高[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(2): 350−364 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.02.010WANG L, LIU Y Y, QIAN X, et al. The single season wheat straw returning to promote the synergistic improvement of carbon efficiency and economic benefit in wheat-maize double cropping system[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(2): 350−364 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.02.010 [44] XIA L L, TI C P, LI B L, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and reactive nitrogen releases during the life-cycles of staple food production in China and their mitigation potential[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 556: 116−125 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.204 [45] JU X T, XING G X, CHEN X P, et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(9): 3041−3046 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813417106 -






 下载:
下载: