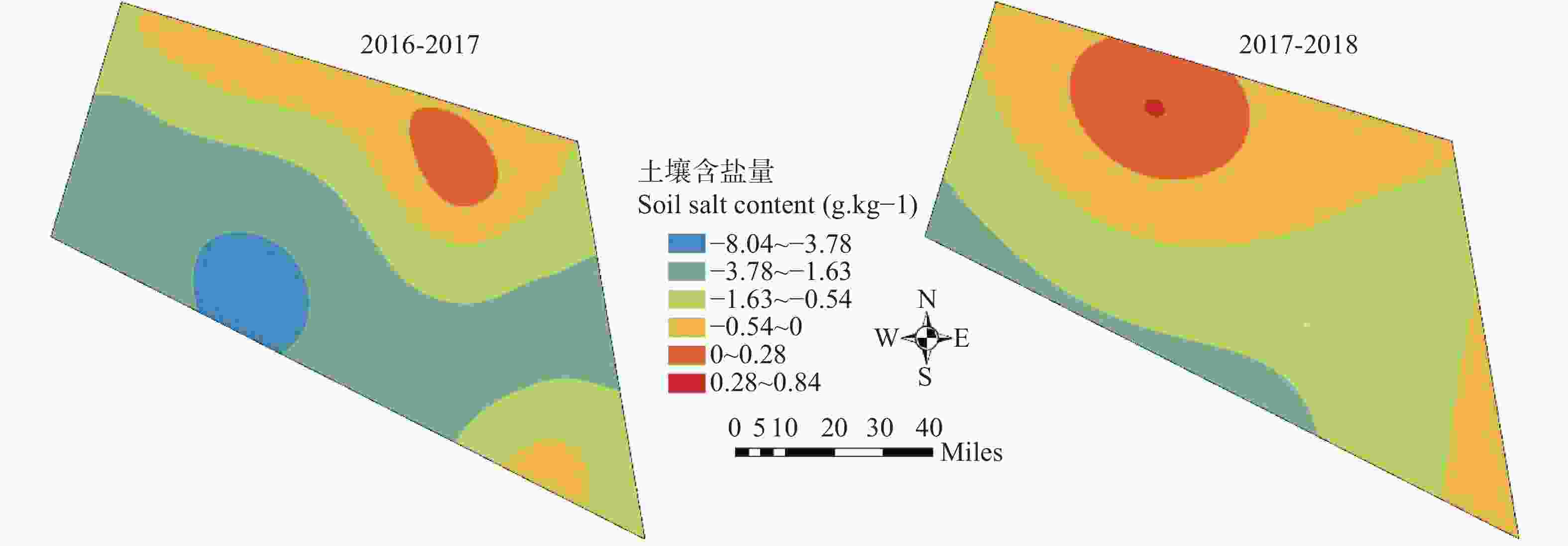
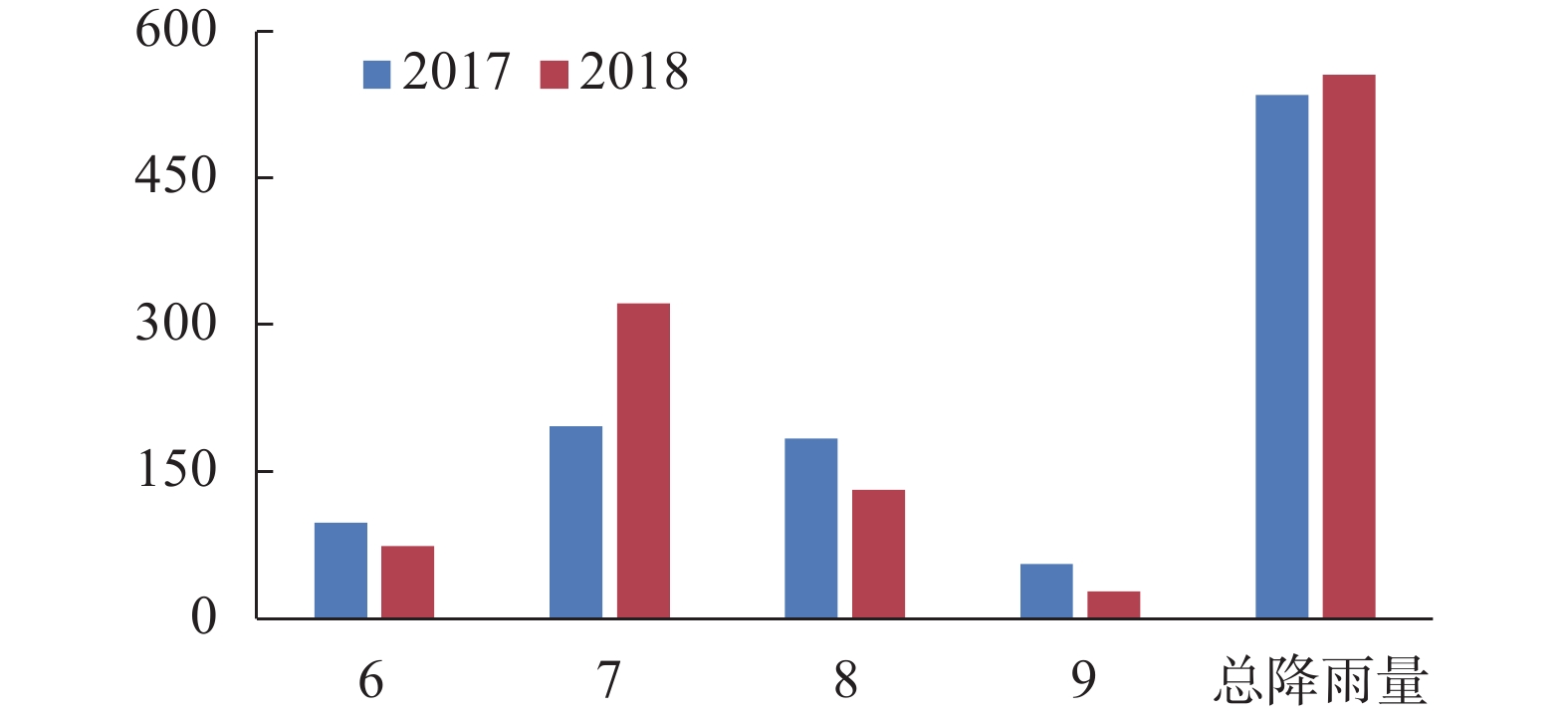
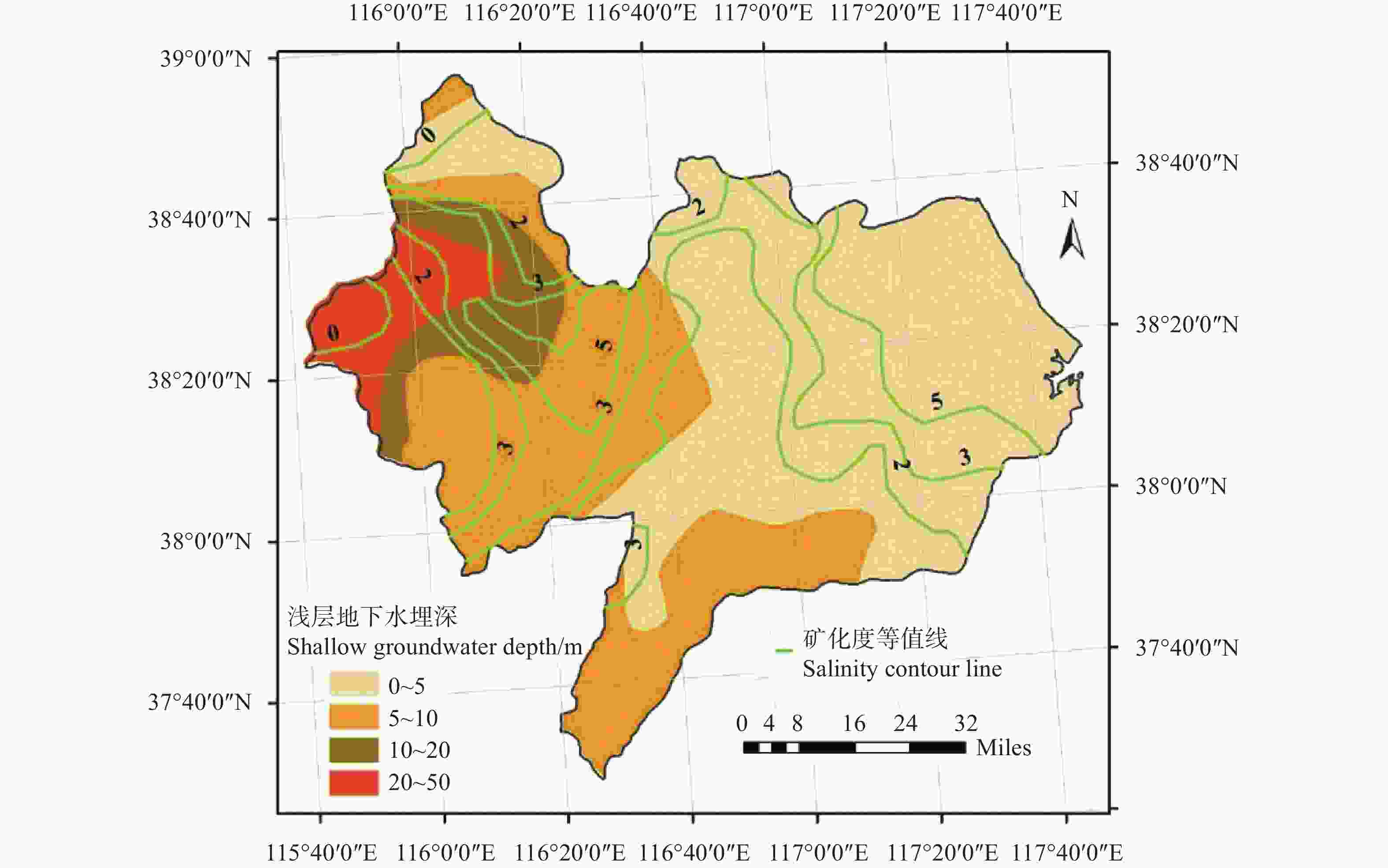
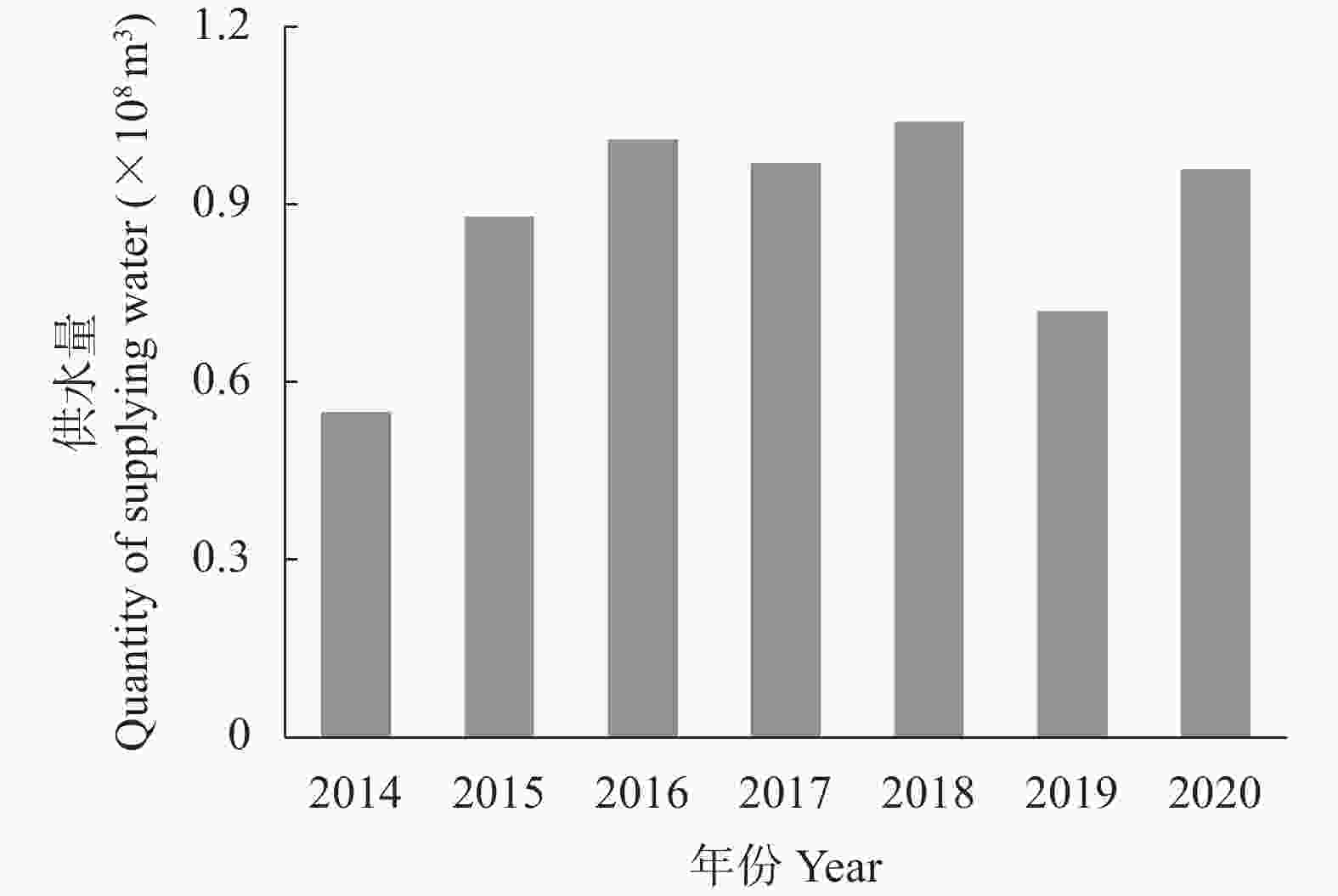
| [1] |
DE FRAITURE C, WICHELNS D. Satisfying future water demands for agriculture[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(4): 502−511 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2009.08.008
|
| [2] |
朱正全, 冯绍元, 王娟, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区农业灌溉资源型节水潜力分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2016(9): 77−80ZHU Z Q, FENG S Y, WANG J, et al. Analysis and estimation on resource-based water-saving potential of agricultural irrigation in Hetao irrigation district of Inner Mongolia[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2016(9): 77−80
|
| [3] |
张喜英, 刘小京, 陈素英, 等. 环渤海低平原农田多水源高效利用机理和技术研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(8): 995−1004ZHANG X Y, LIU X J, CHEN S Y, et al. Efficient utilization of various water sources in farmlands in the low plain nearby Bohai Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(8): 995−1004
|
| [4] |
李亚松, 费宇红, 钱永, 等. 沧州地区深层地下水位降落漏斗演变特征与形成机理探讨[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2013, 27(1): 181−184LI Y S, FEI Y H, QIAN Y, et al. Discussion on evolution characteristics and formation mechanism of deep groundwater depression cone in Cangzhou region[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2013, 27(1): 181−184
|
| [5] |
曹彩云, 郑春莲, 李科江, 等. 不同矿化度咸水灌溉对小麦产量和生理特性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(3): 347−355CAO C Y, ZHENG C L, LI K J, et al. Impact of saline water irrigation with different salinities on yield and physiological indices of wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(3): 347−355
|
| [6] |
苏寒, 王金涛, 董心亮, 等. 不同质量浓度咸水灌溉对冬小麦产量和生理生化特性的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(8): 1−9SU H, WANG J T, DONG X L, et al. Effects of different saline water irrigation on yield, physiological and biochemical traits of winter wheat[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(8): 1−9
|
| [7] |
吴忠东, 王全九. 微咸水连续灌溉对冬小麦产量和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2010, 41(9): 36−43WU Z D, WANG Q J. Effect of saline water continuous irrigation on winter wheat yield and soil physicochemical property[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(9): 36−43
|
| [8] |
杨莉琳, 杨友山, 李铃蔓, 等. 直灌咸水与施氮磷对重盐碱柽柳地的改良效应[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(8): 1372−1380YANG L L, YANG Y S, LI L M, et al. Effects of direct saline irrigation and application of nitrogen and phosphorus on coastal saline-alkali soil planted Tamarix chinensi[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(8): 1372−1380
|
| [9] |
张刘东, 王庆明. 咸水非充分灌溉对土壤盐分分布的影响及SWAP模型模拟[J]. 节水灌溉, 2015(7): 32−35,39ZHANG L D, WANG Q. Effect of non-sufficient irrigation with saline water on the distribution of water and salinity in soil and SWAP model simulation[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2015(7): 32−35,39
|
| [10] |
WEI C C, LI F H, YANG P L, et al. Effects of irrigation water salinity on soil properties, N2O emission and yield of spring maize under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Water, 2019, 11(8): 1548 doi: 10.3390/w11081548
|
| [11] |
刘兆昌, 李广贺, 朱琨. 供水水文地质[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011LIU Z C, LI G H, ZHU K. Hydrogeology of Water Supply[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2011
|
| [12] |
王全九, 徐益敏, 王金栋, 等. 咸水与微咸水在农业灌溉中的应用[J]. 灌溉排水, 2002(4): 73−77WANG Q J, XU Y M, WANG J D, et al. Application of saline and slight saline water for farmland irrigation[J]. Irrigation and Drainage, 2002(4): 73−77
|
| [13] |
FENG G X, ZHANG Z Y, WAN C Y, et al. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of summer maize (Zea mays L.) in subsurface drainage system[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2017, 193: 205−213 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2017.07.026
|
| [14] |
LI P, REN L. Evaluating the saline water irrigation schemes using a distributed agro-hydrological model[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 594: 125688 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125688
|
| [15] |
赵英, 王丽, 赵惠丽, 等. 滨海盐碱地改良研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(3): 67−74ZHAO Y, WANG L, ZHAO H L, et al. Research status and prospects of saline-alkali land amelioration in the coastal region of China[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(3): 67−74
|
| [16] |
谭莉梅, 刘金铜, 刘慧涛, 等. 河北省近滨海区暗管排水排盐技术适宜性及潜在效果研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(12): 1673−1679TAN L M, LIU J T, LIU H T, et al. Study on the adaptability and potential application effects of subsurface pipe drainage system in the coastal areas of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(12): 1673−1679
|
| [17] |
谭攀, 王士超, 付同刚, 等. 我国暗管排水技术发展历史、现状与展望[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(4): 633−639TAN P, WANG S C, FU T G, et al. Development history, present situation, and the prospect of subsurface drainage technology in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(4): 633−639
|
| [18] |
刘慧涛, 谭莉梅, 于淑会, 等. 河北滨海盐碱区暗管埋设下土壤水盐变化响应研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(12): 1693−1699LIU H T, TAN L M, YU S H, et al. Response of water and salt movement to subsurface pipe drainage system in saline-alkali coastal areas of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(12): 1693−1699
|
| [19] |
于淑会, 韩立朴, 高会, 等. 高水位区暗管埋设下土壤盐分适时立体调控的生态效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(4): 1061−1068YU S H, HAN L P, GAO H, et al. Ecological effects of soil salinity regulation through saline water irrigation and subsurface drainage in high water table level area[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(4): 1061−1068
|
| [20] |
郜洪强, 费宇红, 雒国忠, 等. 河北平原地下咸水资源利用的效应分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2010, 8(2): 53−56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2010.02.015GAO H Q, FEI Y H, LUO G Z, et al. Effect analysis of saline groundwater utilization in Hebei plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2010, 8(2): 53−56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2010.02.015
|
| [21] |
丁蓓蓓, 张雪靓, 赵振庭, 等. 华北平原限水灌溉条件下冬小麦产量及水分利用效率变化的Meta分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(12): 7−17 doi: 10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2021377DING B B, ZHANG X L, ZHAO Z T, et al. Change in winter wheat yield and its water use efficiency as affected by limited irrigation in North China plain: a meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(12): 7−17 doi: 10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2021377
|
| [22] |
苟淇书, 党红凯, 马俊永, 等. 灌溉水矿化度对土壤盐分及冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2022, 40(8): 850−856GOU Q S, DANG H K, MA Y J, et al. Effect of irrigation water salinity on soil salinity and winter wheat yield[J]. Journal of drainage and irrigation machinery engineering, 2022, 40(8): 850−856
|
| [23] |
马凤娇, 谭莉梅, 刘慧涛, 等. 河北滨海盐碱区暗管改碱技术的降雨有效性评价[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(2): 409−414 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00409MA F J, TAN L M, LIU H T, et al. Evaluation of the rainfall effectiveness for reclaim of saline soil by subsurface pipe drainage system in coastal saline regions of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(2): 409−414 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00409
|
| [24] |
陈文, 郑自宽, 谢军健, 等. 我国非常规水源苦咸水资源及其分布特征研究[J]. 水文, 2021, 41(5): 1−6 doi: 10.19797/j.cnki.1000-0852.20200160CHEN W, ZHENG Z K, XIE J J, et al. Study on the unconventional water sources: bitter-salty water resources and its distribution characteristics in China[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2021, 41(5): 1−6 doi: 10.19797/j.cnki.1000-0852.20200160
|
| [25] |
陈素英, 张喜英, 邵立威, 等. 微咸水非充分灌溉对冬小麦生长发育及夏玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(3): 579−585 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00579CHEN S Y, ZHANG X Y, SHAO L W, et al. Effect of deficit irrigation with brackish water on growth and yield of winter wheat and summer maize[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(3): 579−585 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00579
|
| [26] |
王海霞, 徐征和, 庞桂斌, 等. 微咸水灌溉对土壤水盐分布及冬小麦生长的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(3): 291−297WANG H X, XU Z H, PANG G B, et al. Effects of brackish water irrigation on water-salt distribution and winter wheat growth[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(3): 291−297
|
| [27] |
YUAN C F, FENG S Y, HUO Z L, ET A L. Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on soil water-salt distribution and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019: 424–432
|





 下载:
下载: